- Define of neuromorphic computing : referred to mixed analogue–digital implementations of brain-inspired computing;
DARPA Synapse project, (Systems of Neuromorphic Adaptive Plastic Scalable Electronics)
- 인간의 뇌 구조와 유사한 형태를 지닌 데이터 처리 칩셋인 뉴로모픽칩 개발에 착수.
Diff. between computers and neurmorphic computer
- Von Neumann computers are composed of separate CPUs and memory units, where data and instructions are stored in the latter.
- In a neuromorphic computer, on the other hand, both processing and memory are governed by the neurons and the synapses.
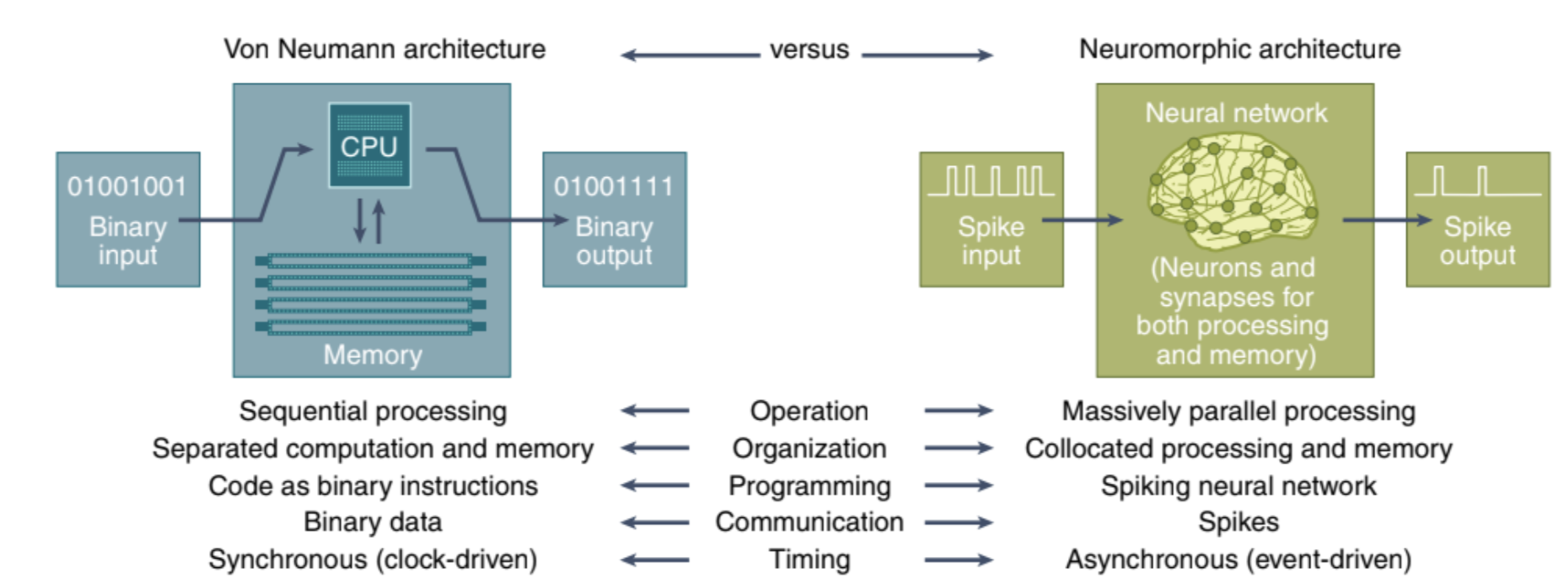
The collocation of processing and memory strength
- helps mitigate the von Neumann bottleneck regarding the processor/memory separation, which causes a ** slowdown in the maximum throughput that can be achieved.
- helps avoid data accesses from main memory, as in conventional computing systems, which consume a considerable amount of energy compared with the compute energy.
Large networks
- possible to take multiple physical neuromorphic chips and treat them as a single large neuromorphic implementation to run larger and larger networks . This has been successfully accomplished across a variety of large-scale neuromorphic hardware systems, including SpiNNaker and Loihi.
Stochasticity
- neuromorphic computers can include a notion of randomness, such as in the fring of neurons, to allow for noise.
Attractive features of neuromorphic computers for computation
1) extremely low power operation
- operate on orders of magnitude less power than traditional computing systems.
- typically only a small portion of the entire system is active at any given time while the rest is idle.
2) inherently implement neural network-style computation
- perform a wide variety of different types of computation.
Neurons and synapses have been a convenient level of abstraction for neuromorphic computers, but whether they are the most appropriate level of abstraction is still an open question.
One of the neuromorphic platforms targeting more general computations for wider classes of applications is the Tianjic chip , a platform that supports both neuromorphic spiking neural networks and the traditional artificial neural networks for different categories of problems.
- (SNN optimization proved)
The usefulness of neuromorphic hardware such as BrainScales-2 has been demonstrated in carrying out optimizations for learning to learn scenarios (meaning, where an optimization process is used to define how learning occurs) for spiking neural networks, running at a much accelerated timescales compared to biological time-scales.
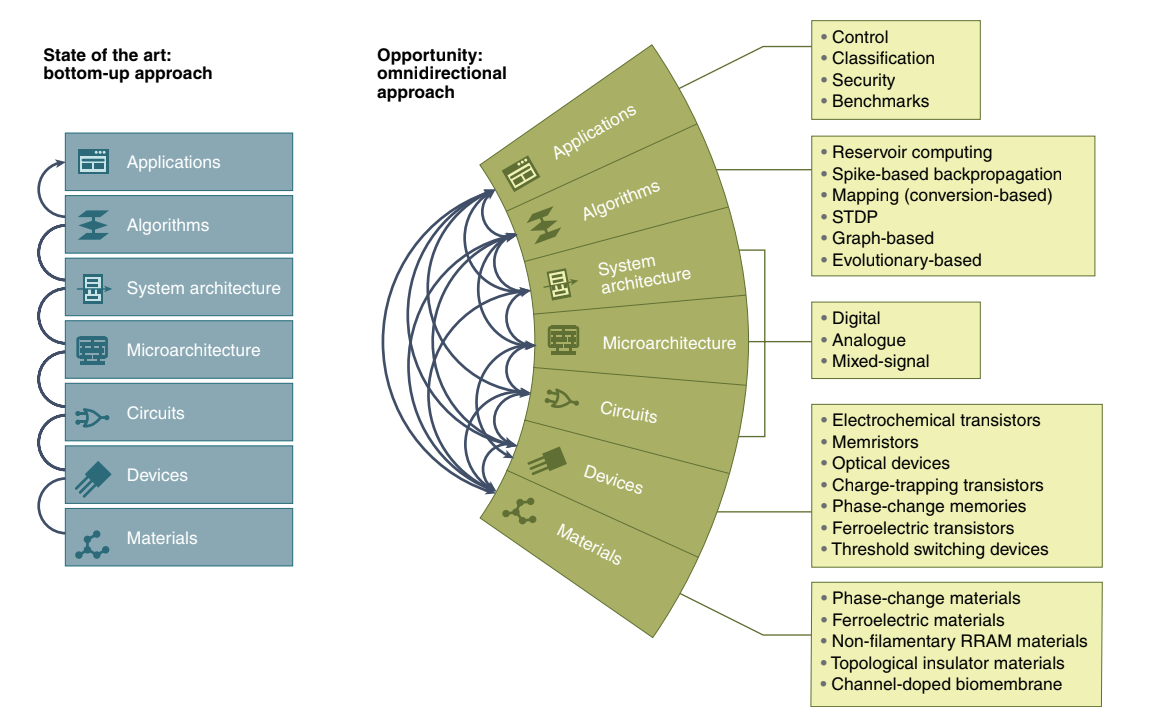
Each device and material used to implement neuromorphic com-
puters has unique operating characteristics, such as how fast they
operate, their energy consumption and the level of resemblance to
biology. The diversity of devices and materials used to implement
neuromorphic hardware today offers the opportunity to customize
the properties required for a given application.
Neuromorphic algorithms and applications
- Spiking neurons might leak charge over time based on a particular time constant, and neurons and/or synapses in SNNs might have an associated time delay.
2 wide categories for wide variety of algorithmic approaches for neuromorphic computing systems
1) algorithms for training or learning an SNN to be deployed to a neuromorphic computer
2) non-machine learning algorithms in which SNNs are hand-constructed to solve a particular task
- training and learning algorithms refer to the mechanism of optimizing the parameters of an SNN (typically the synaptic weights) for a particular problem.
SNN
- Neurons have an associated threshold value, and when the charge value on that neuron reaches the threshold value, it fres, sending communications along all of its outgoing synapses.
- Synapses form the connections between neurons, and each synapse has a pre-synaptic neuron and a post-synaptic neuron.Synapses have an associated weight value, which may be positive (excitatory) or negative (inhibitory). Synapses may have an associated delay value such that communications from the pre-synaptic neuron are delayed in reaching the post-synaptic neuron.
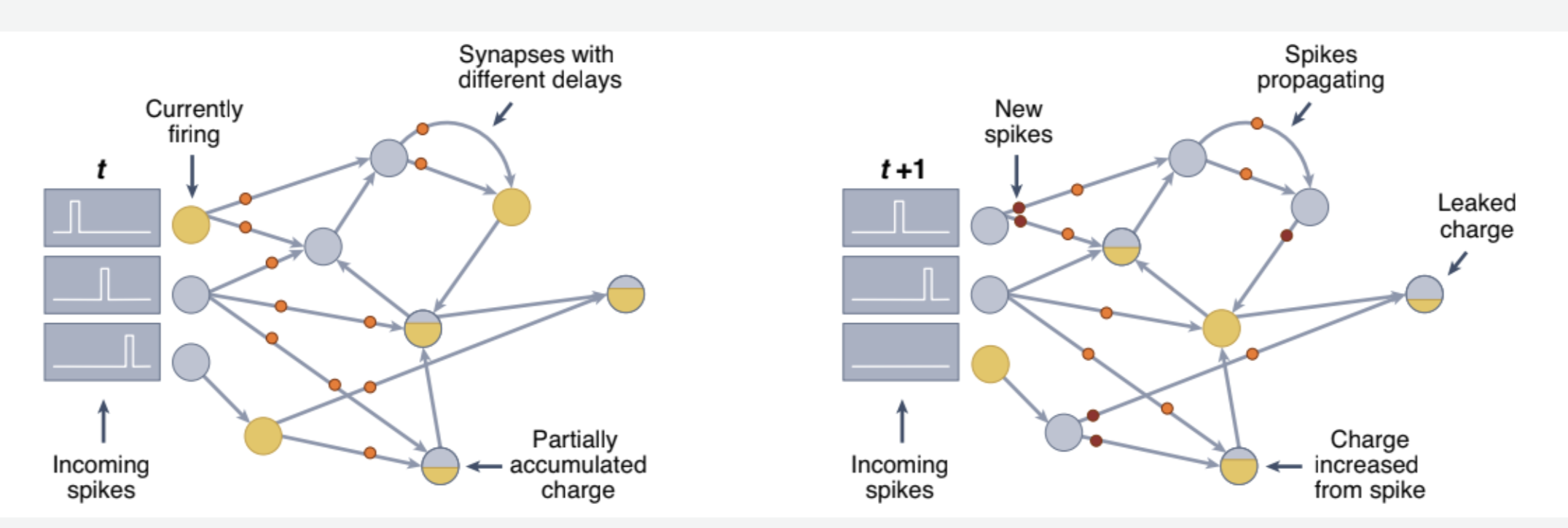
? 전기 charge의 총합이 t와 t+1에서 다르다. 기본 전제조건 원래 closed condition에서 하였다고 하였지만, 실제로는 바깥으로 방출되었을수도 있다. 그러면, 이것을 어느 방향성으로 컴퓨터에 학습시키는가?
Machine learning algorithms.
-
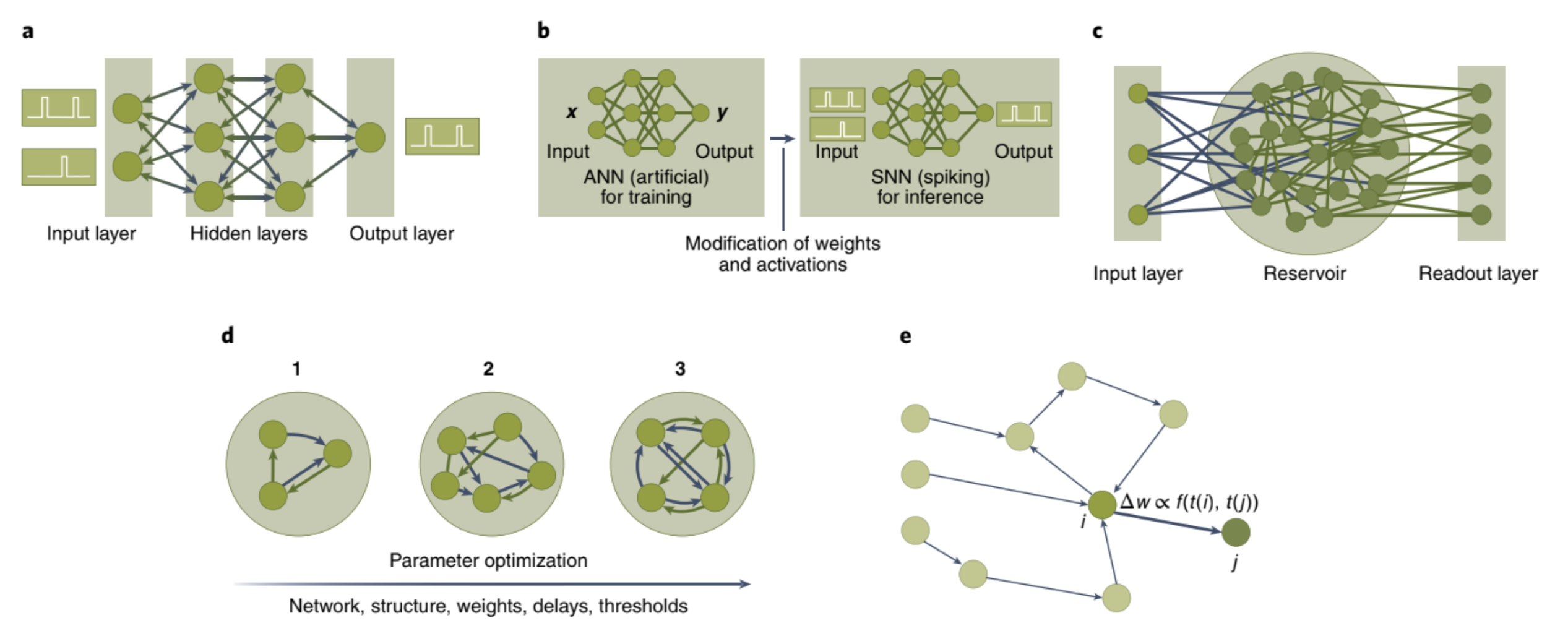
Spike-based quasi-backpropagation.
1) Propagation and gradient descents method do not apply towards SNN because there is no differentiable activation functions.
2) a problem begin by training a DNN and then performing a mapping process to convert it to an SNN for inference purposes(represented in b) -
Mapping a pre-trained deep neural network.
1) use of Few Spikes neuron model (FS-neuron), which can represent complex activation functions temporally with at most two spikes.
When creating a mapping technique, it is important to take into account how these characteristics might influence the inference performance of a mapped network.
- Reservoir computing.
1) common algorithm used in SNNs is reservoir computing or liquid state machines.
- 2 properties of liquid
-
input separability, which requires that different inputs result in different outputs
-
fading memory, which requires that signals do not continue to propagate infinitely through the reservoir and instead will eventually die out.
1)The key advantage of reservoir computing is that it does not require any training of the SNN component.
- Evolutionary approaches.
1) In an evolutionary algorithm, a random collection of potential solutions is created to form an initial population. Each member of the population is evaluated and assigned a score, which is then used to perform selection (preferentially selecting better performing individuals) and reproduction (creating new individuals through recombination of old individuals and mutations) to produce a new population.
-Plasticity.
1) Spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP)—which operates on the underlying principle of adjusting the weights on the basis of relative spike timings from pre- and post-synaptic neurons
2) approximate several machine learning approaches such as clustering and Bayesian inference.
ex) Combinations of spiking reservoirs and STDP have also been employed in an SNN approach called NeuCube
Non-machine learning algorithms.
- Graph Theory
In a random walk, a random node is selected as a starting point, and an agent moves along an edge departing from that node selected at random.
neuromorphic systems can achieve a similar performance in terms of time-to-solution and solution accuracy when compared with other conventional approaches, which use CPUs and GPUs to approximately solve NP-complete problems.