An operating system is
- a software that manages a computer ‘s hardware
- It also provides a basis for application programs and
- acts as an intermediary between
- the computer user and the computer hardware → 유저와 하드웨어의 매개 역할
Computer system can be divided roughly into four components
- Hardware
- Operating System
- Application Programs
- User
Defining Operating Systems
- 통상적으로 정의되지 않았음.
- More common definition is that
- “the one program running at all times on the computer”
- usually called the kernel
→ Along with the kernel, there are two other types of programs - system programs
- application programs
What is bootstrap(부팅)?
- RAM은 휘발성이므로 ROM에 O/S 프로그램 존재
- the first program to run on computer power-on,
- loads the O/S
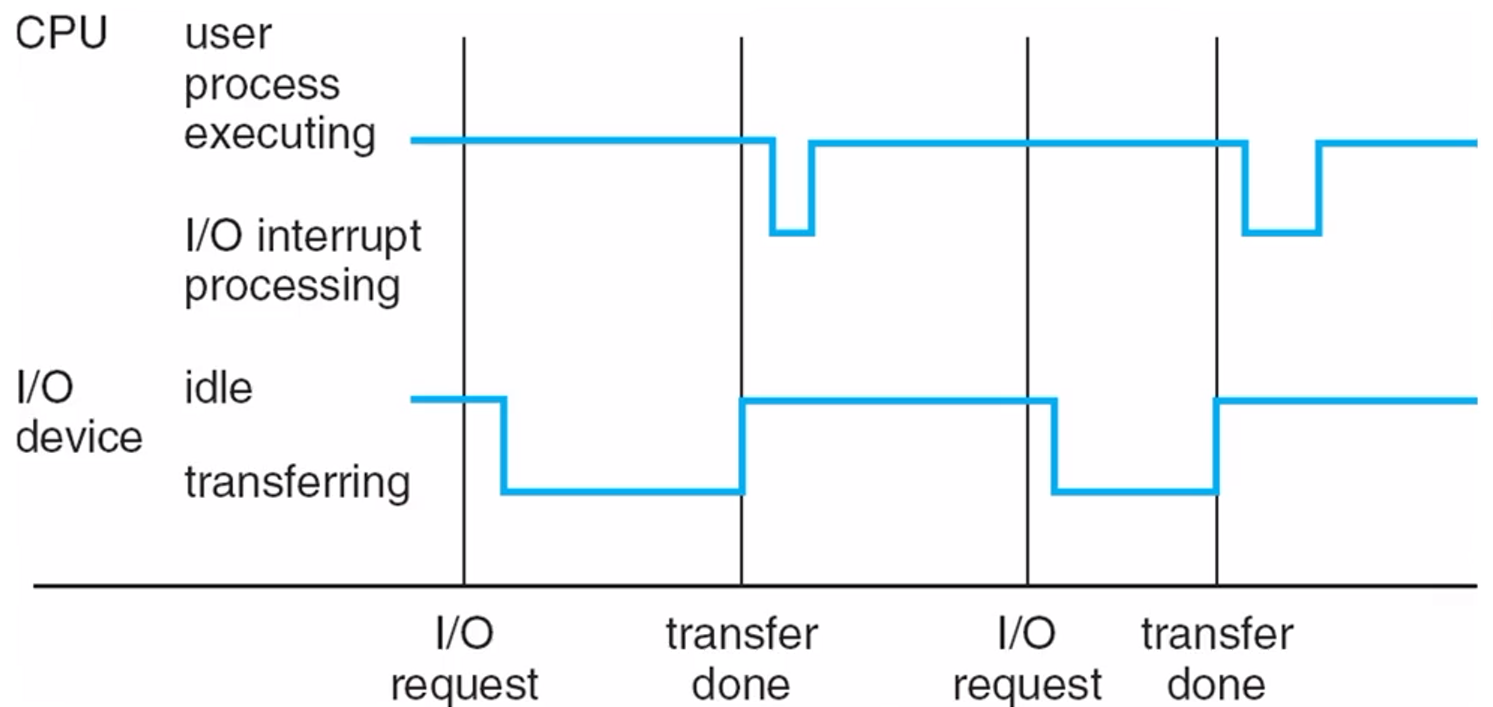
Interrupts
- Hardware may trigger an interrupt at any time → by sending a signal to the CPU, usually by way of the system bus
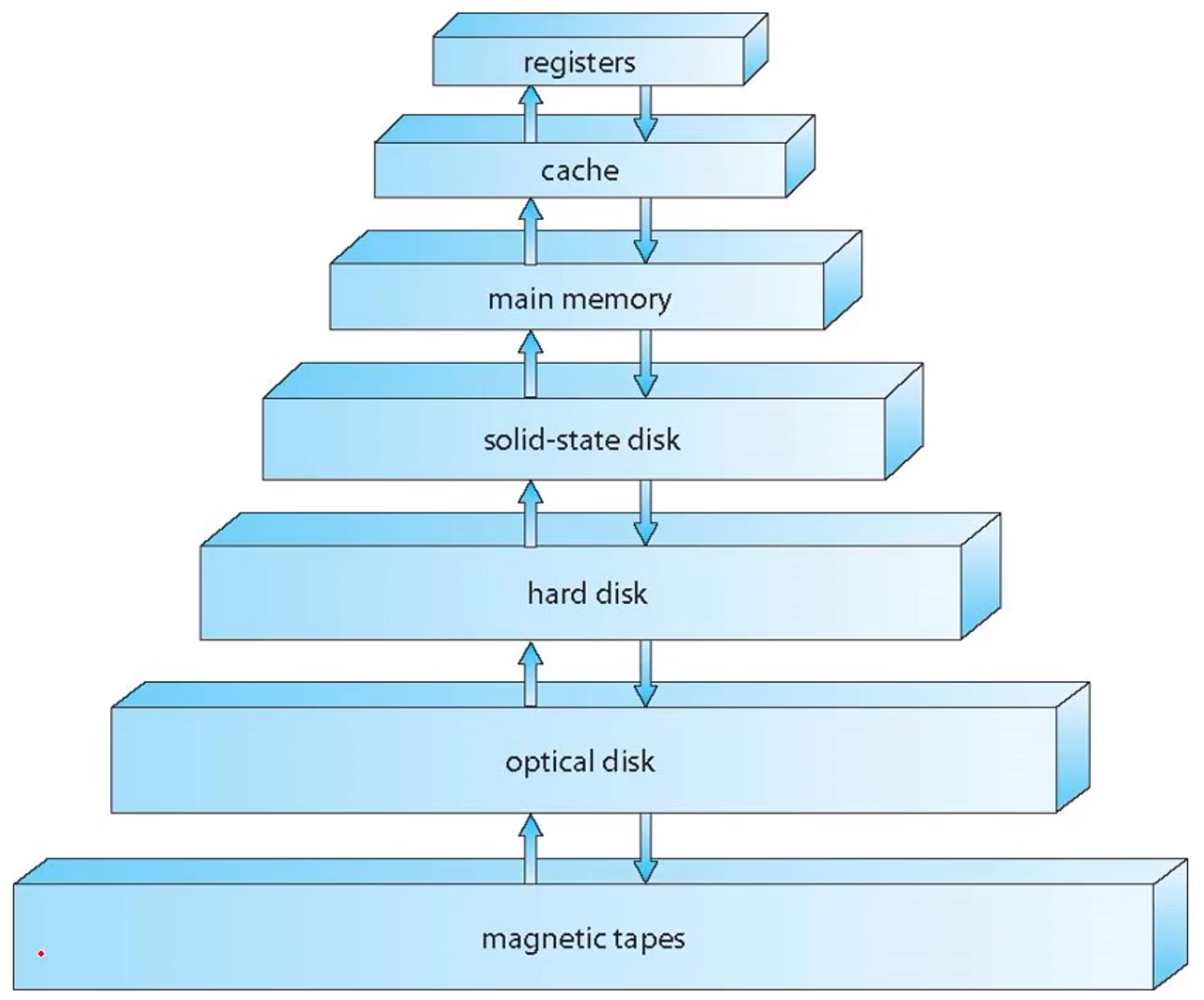
Storage systems
- Storage systems can be organized in a hierarchy according to: → storage capacity, and access time : 그림의 위쪽이 속도가 빠르고, 블록의 크기는 용량에 비례한다.
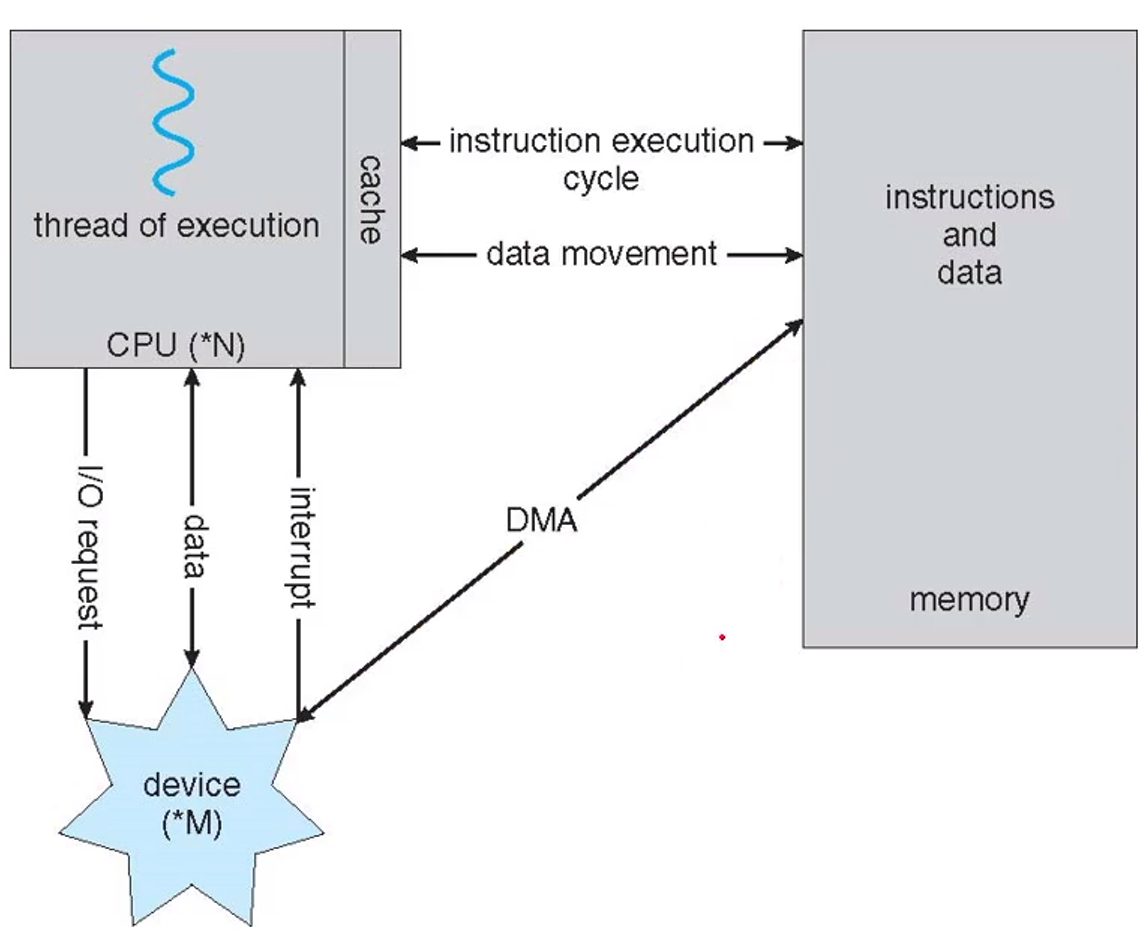
I/O Structure
- DMA(Directed Memory Access) : CPU의 개입 없이 I/O 장치와 Memory 사이의 데이터를 전송하는 접근방식
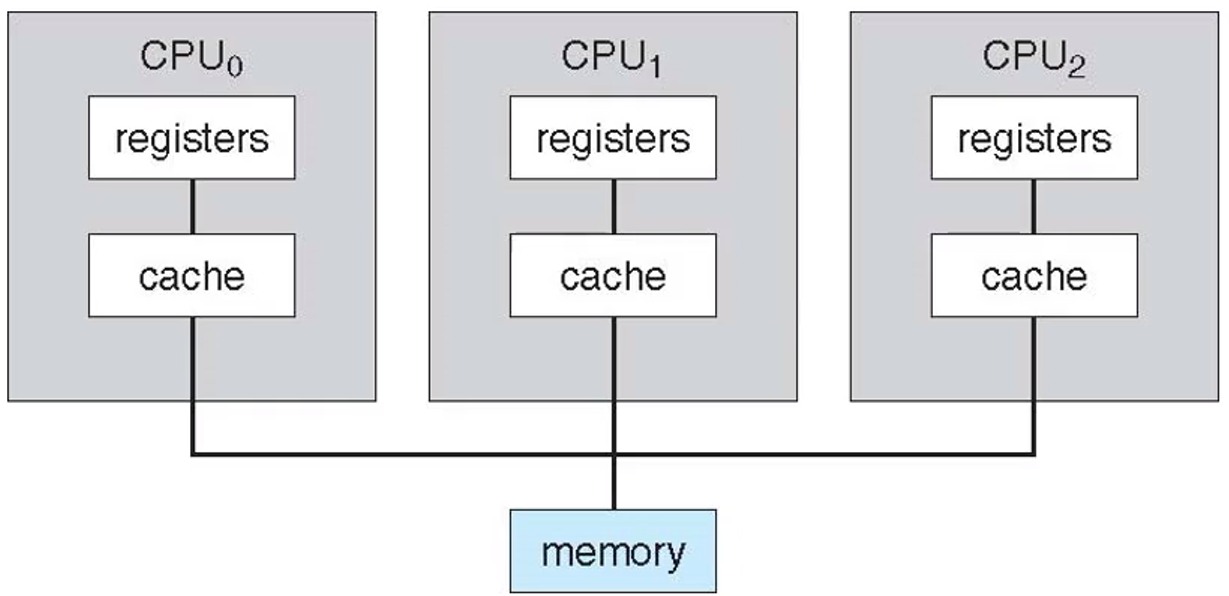
Symmetric multiprocessing(SMP)
- The most common multiprocessor systems
- in which each peer CPU processor performs all tasks.
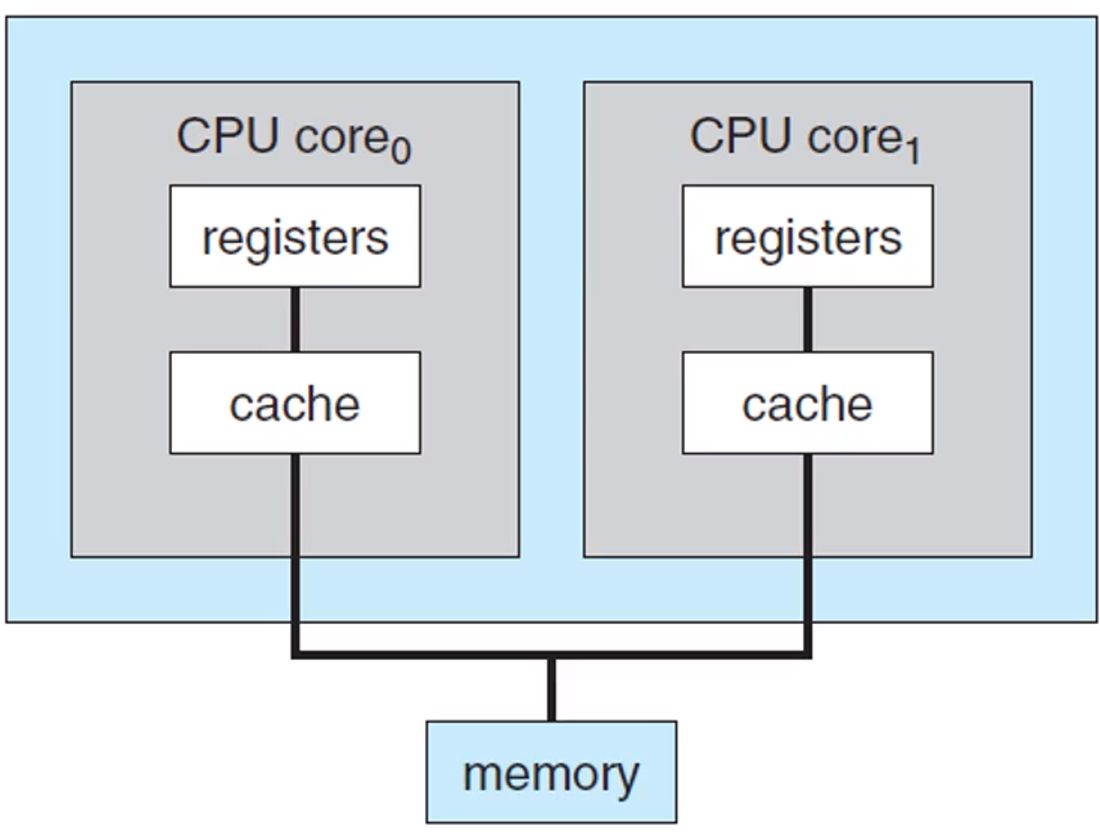
Multi-core design
- with several cores on the same processor chip
Multi programming
- runs more than one program at a time
- keeps several processes in memory simultaneously
- to increase CPU utilization
Multitasking(multiprocessing) [Concurrent]
logical extension of multi programming- in which CPU switches jobs so frequently that
- users can interact with each job while it is running
CPU scheduling
- If several processes are ready to run at the same time
- the system must choose which process will run next
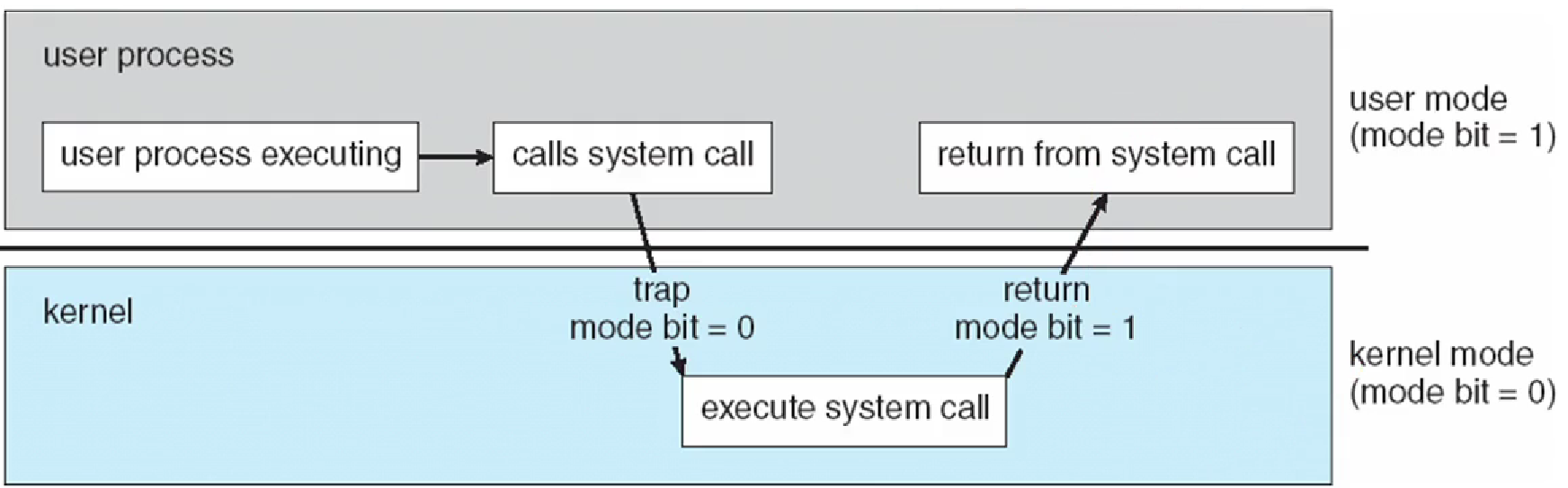
Two separate mode of operations
User modeandKernel mode- to ensure that an incorrect program
- cannot cause other programs to execute incorrectly
Virtualization(가상화)
- a technology that allow us
- to abstract the hardware of a single computer
- into several different execution environments
VMM(Vertual Machine Manager)→ 동시에 O/S를 여러개 실행 가능- VMware, XEN, WSL…
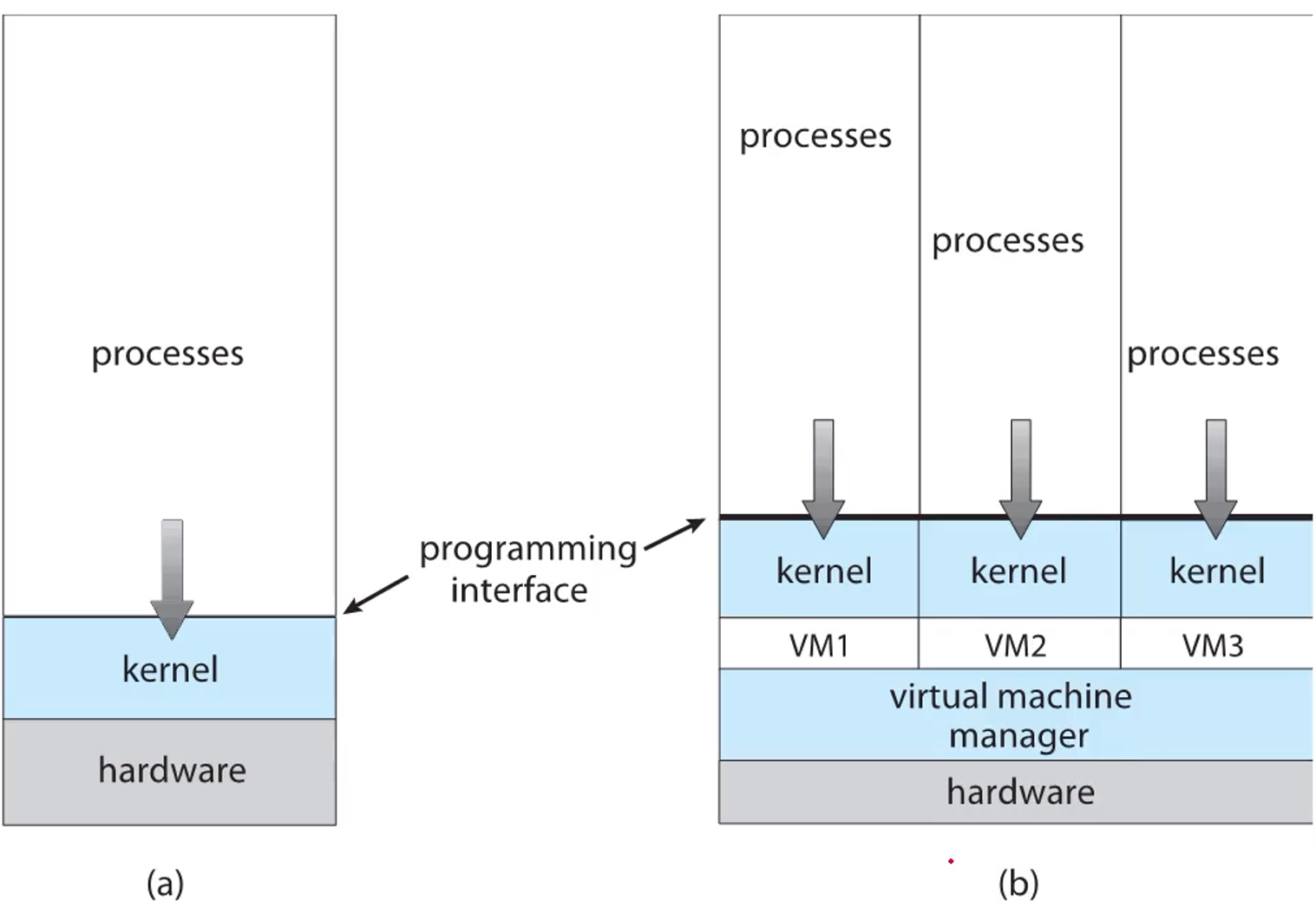 A computer running(a) a single O/S and (b) three virtual machines
A computer running(a) a single O/S and (b) three virtual machines
OS provides an environment for the execution of programs
- User interface
- Program execution
- I/O operation
- File-system manipulation(파일 조작)
- Communications
- Error detection
- Resource allocation(자원 할당)
- Logging
- Protection and security
가장 중요한 것은 Process, thread. → multiprocessing(CPU-scheduling) → synchronization → deadlock
⇒ memory management → virtual memory management …
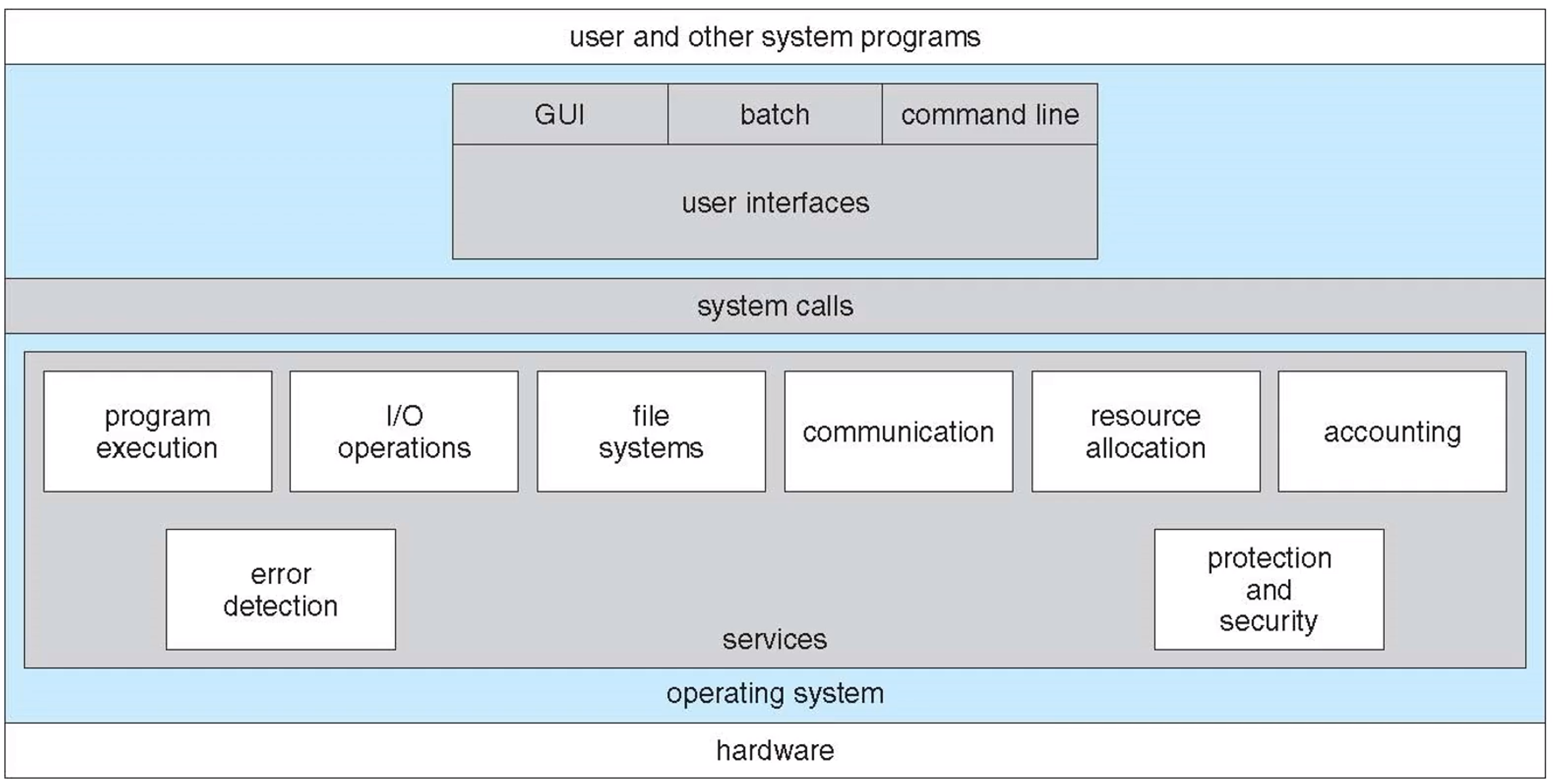 A view of O/S services
A view of O/S services
Three fundamental ways for “users” to interface with OS
CLI: command line interface, or command interpreter- known as shells : sh, bash, csh, tcsh, zsh…
GUI: graphical user interface(can use mouse)- Windows, Aqua for MacOS, KDE/GNOME for Linux…
Touch-Screen Interface- Android UI, iPhone UI…
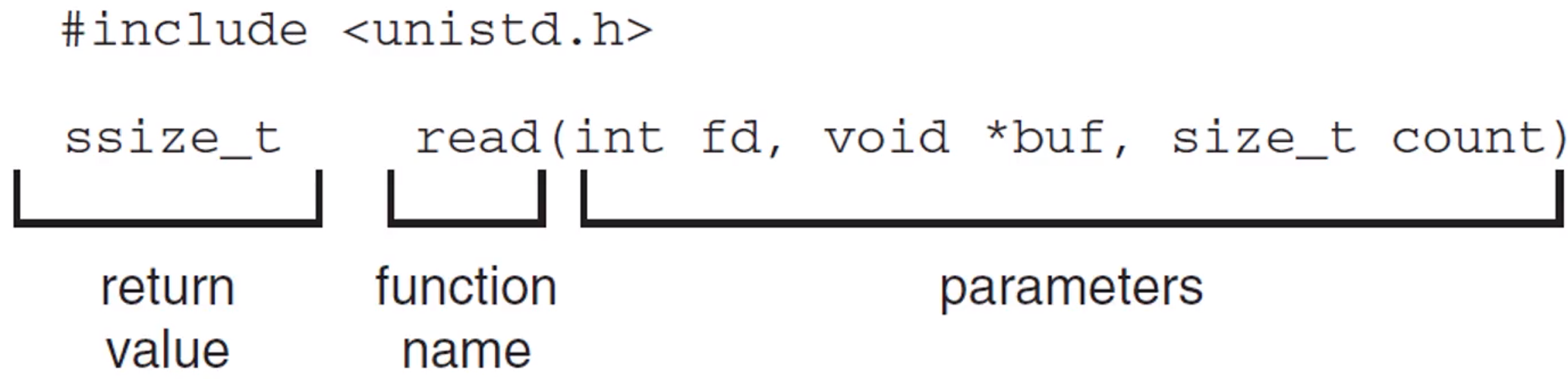
How can programs interface with OS? [System calls]
- provide an interface to the services made available by the OS
- API : Application Programming Interface
So, API of OS is “System call”
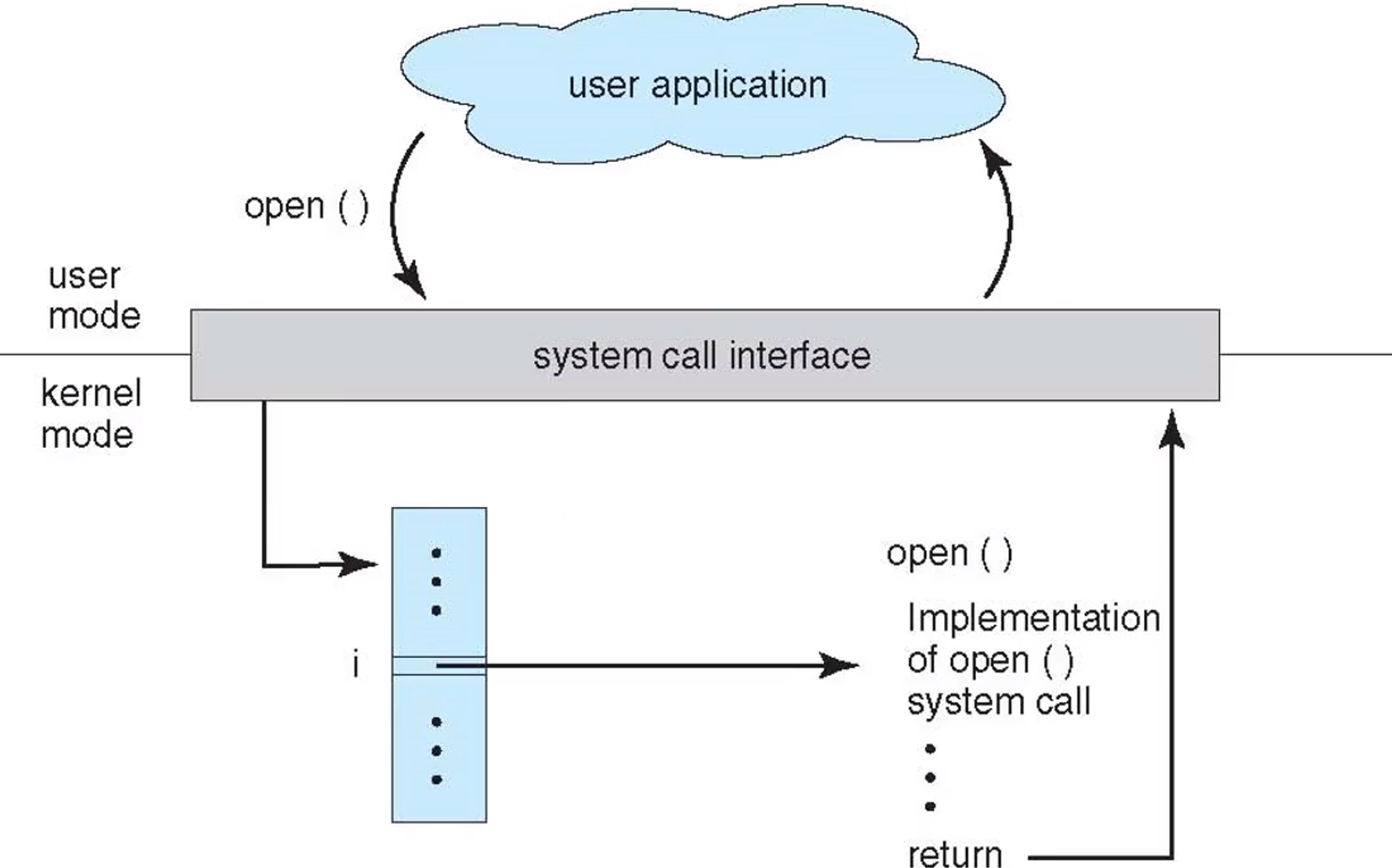 The handling of a user application invoking the open() system call
The handling of a user application invoking the open() system call
참고 :
Silberschatz et al. 『Operating System Concepts』. WILEY, 2020.
