What is Process?
- A process is a program in execution - 실행중인 프로그램
- Shell, 혹은 GUI에서 프로그램을 실행시키면, 저장장치에서 memory로 프로그램이 올라가게 된다. 이를 실행중인 프로그램 즉, 프로세스라고 한다.
- Unit of work in an operating system
- Process will
need certain resourcesto accomplish its task
- CPU time, memory, files, I/O devices
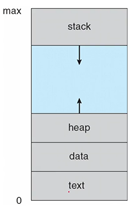
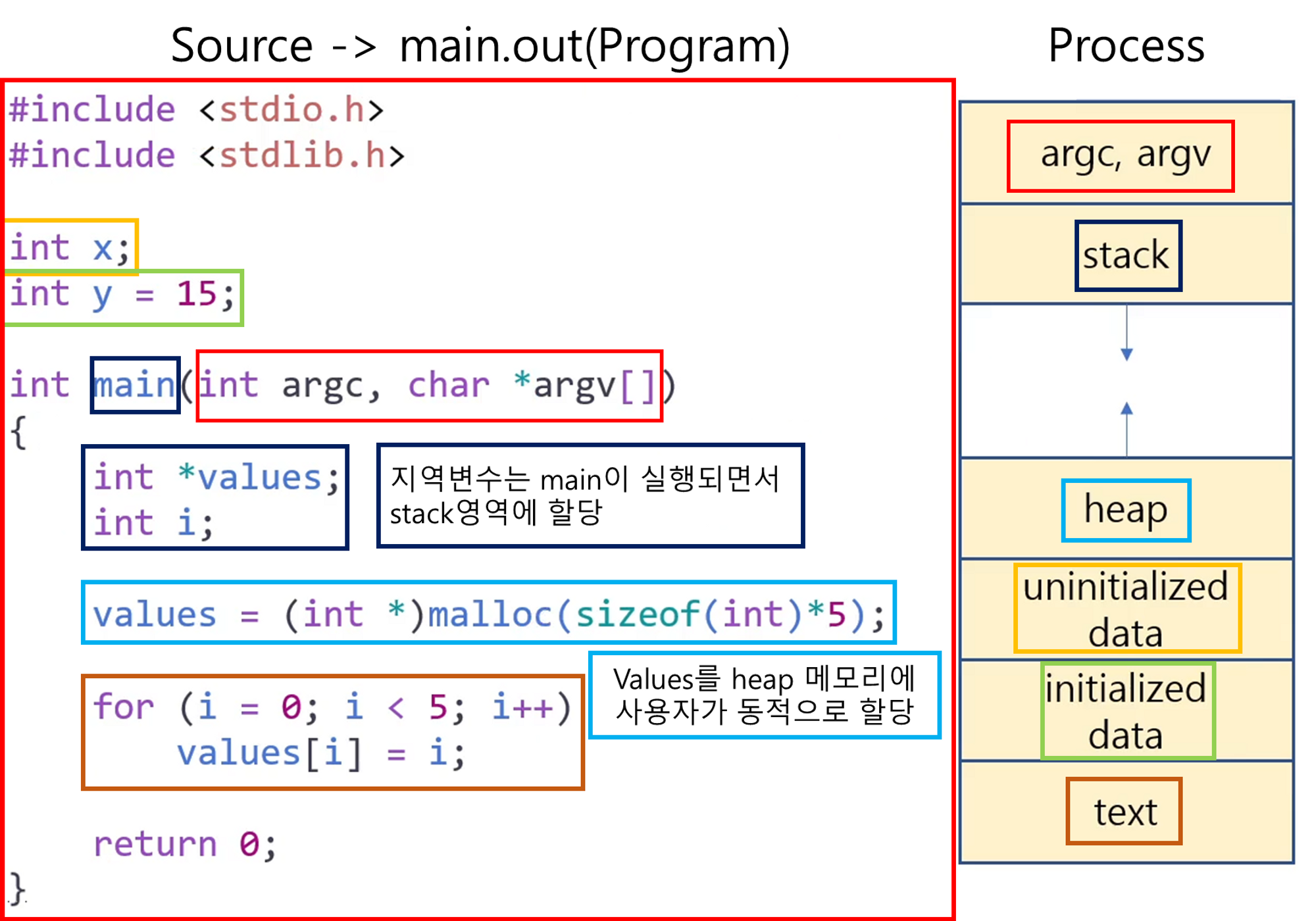
The memory layout of a process is divided into multiple sections
-
Text section: the executable code -
Data section: global variables -
Heap section: memory that is dynamically allocated during program run time(프로그램이 실행되는 동안 동적으로 할당된 메모리)
-
Stack section-
temporary data storage when invoking functions
(함수 호출 시 임시 데이터 저장공간)
-
such as function parameters, return addresses, and local variables
-
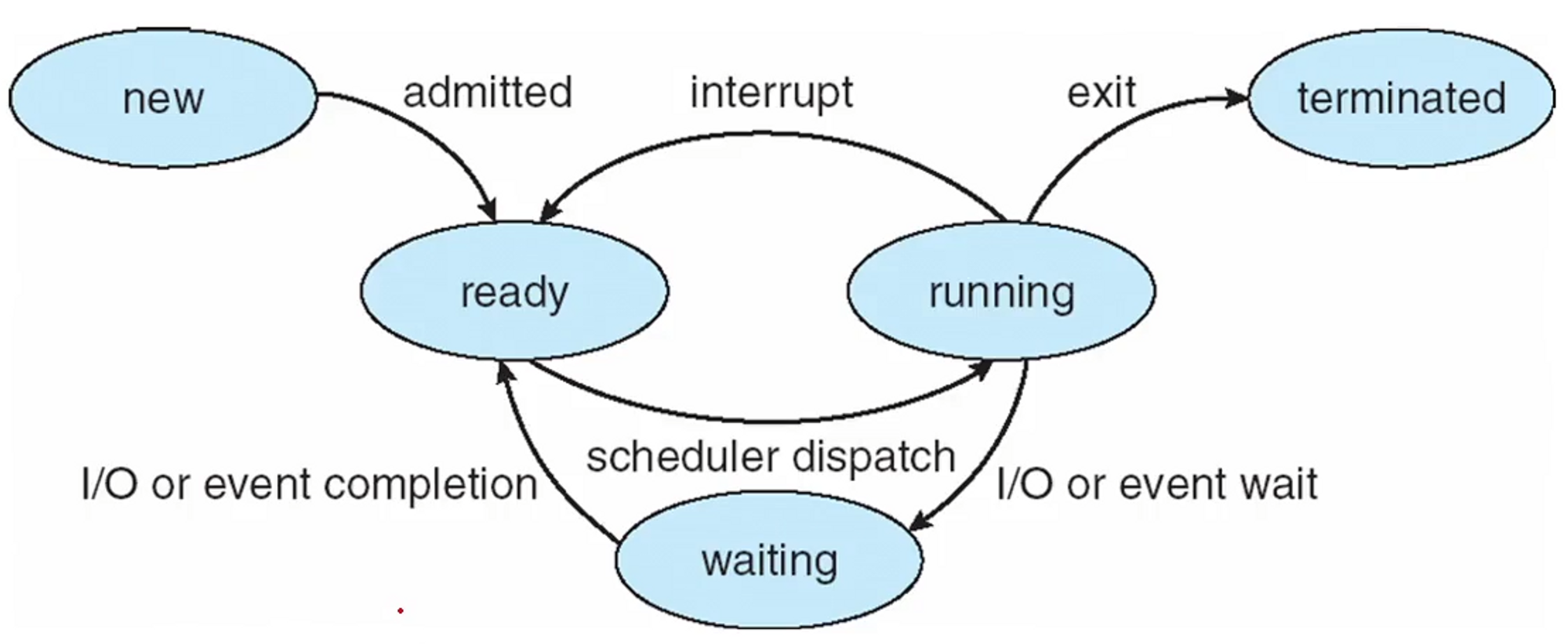
As a process executes, it changes its “state”
New: the process is being createdRunning: Instructions are being executed ****(프로그램을 실행시켜 CPU가 명령어를 실행할 준비가 된 상태)
Waiting: the process is waiting for some event to occur- such as an I/O completion or reception of a signal (다른 프로세스를 실행중인 경우 waiting)
Ready: the process is waiting to be assigned to a processor (프로세스가 프로세서에 할당되기를 기다리는 상태. 다른 프로세스를 종료해도 바로 프로세서를 점유 하지 못함.)
erminated: the process has finished execution
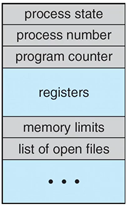
PCB (Process Control Block) or TCB (Task Control Block)
여러 프로세스 한 곳에 모아둔 자료구조
- Each process is represented in the operating system by the PCB
- PCB contains a lot of information associated with a specific process
- Process state (new, ready, running, waiting, terminated)
- Program Counter
- CPU registers (Instruction Register, Data Register…)
- CPU - scheduling information
- Memory - management information
- Accounting information
- I/O status information
A process is …!
- a program that performs a
single thread of execution - Single thread of control allows the process to perform
only one task at a time - Modern O/S have extended the process concept
- to allow a process to have
multiple threads of execution - and thus to perform more than one task at a time
- to allow a process to have
What is “Thread”?
- A thread is a
lightweight process. → Chapter4에서 자세하게 다룬다. / 여러개의 process를 사용하는 것 보다, 여러개의 thread를 사용하는 것이 장점이 많다.
Objective of “multi-programming”
- to have some process running at all times
- to
maximize CPU utilization
Objective of “time sharing”
- to
switch a CPU coreamong processes so frequently - that user can interact with each program while it is running (사용자 입장에서는 프로그램이 동시에 작동되고 있는 것 처럼 보이게 하자)
“Scheduling Queues” for time sharing
- As processes enter the system, they are put into a ready queue
- where they are ready and waiting to execute on a CPU’s core
- Processes that are waiting for a certain event to occur (ex. I/O request)
- are placed in a wait queue
- These queues are generally implemented in the linked lists of PCBs.
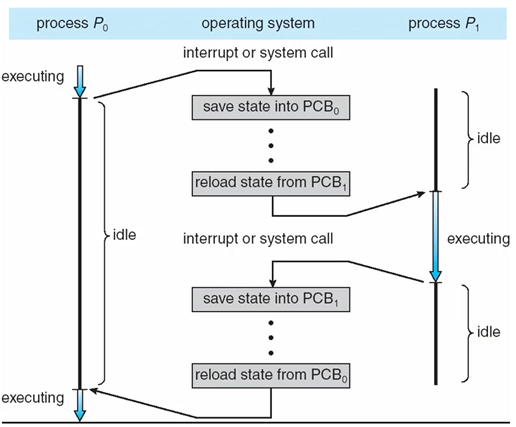
Context Switch (문맥 교환)
- The context of a process is represented in the PCB
- When an interrupt occurs
-
the system saves the current context of the running process
(어디까지 실행했는지 context 저장)
-
so that, later, it can restore that context when it should be resumed
(다시 CPU에서 running state를 획득했을 때, 저장된 context를 불러온다)→ The context switch is a task that
: switches the CPU core to another process -
performs a state save of current process
-
state restore of different process
-
A process may create several new processes
Parent process: the creating process (다른 프로세스를 생성)Child process: a newly created process (생성된 프로세스)
Two possibilities for “execution”
- The parent continues to execute concurrently with its children(부모, 자식이 동시에 실행)
- The parent waits until some or all of its children have terminated (자식이 종료될 때 까지 대기)
Two possibilities for “address-space”
-
The child process is a
duplicateof the parent process(parent, child process의 작업이 같다면 따로 메모리를 할당하지 않아도 된다)
-
The child process has a
new programloaded onto it
Terminates of a process
- When it finishes executing its final statement
- exit() system call : asks O/S to delete it
- OS deallocates and reclaims all the resources(
자원 할당 해제 및 회수)- allocated memories, open files, and I/O buffers…
Zombie and Orphan
zombie process: a process that has terminated, but whose parent has not yet called wait()
(자식 프로세스가 종료되었지만 부모 프로세스가 자식 프로세스의 종료 상태를 회수하지 않았을 경우에 자식 프로세스를 좀비 프로세스라고 한다)
orphan process: a process that has a parent process, who did not invoke wait() and instead terminated
(부모 프로세스가 자식 프로세스보다 먼저 종료되면 자식 프로세스는 고아프로세스가 된다)
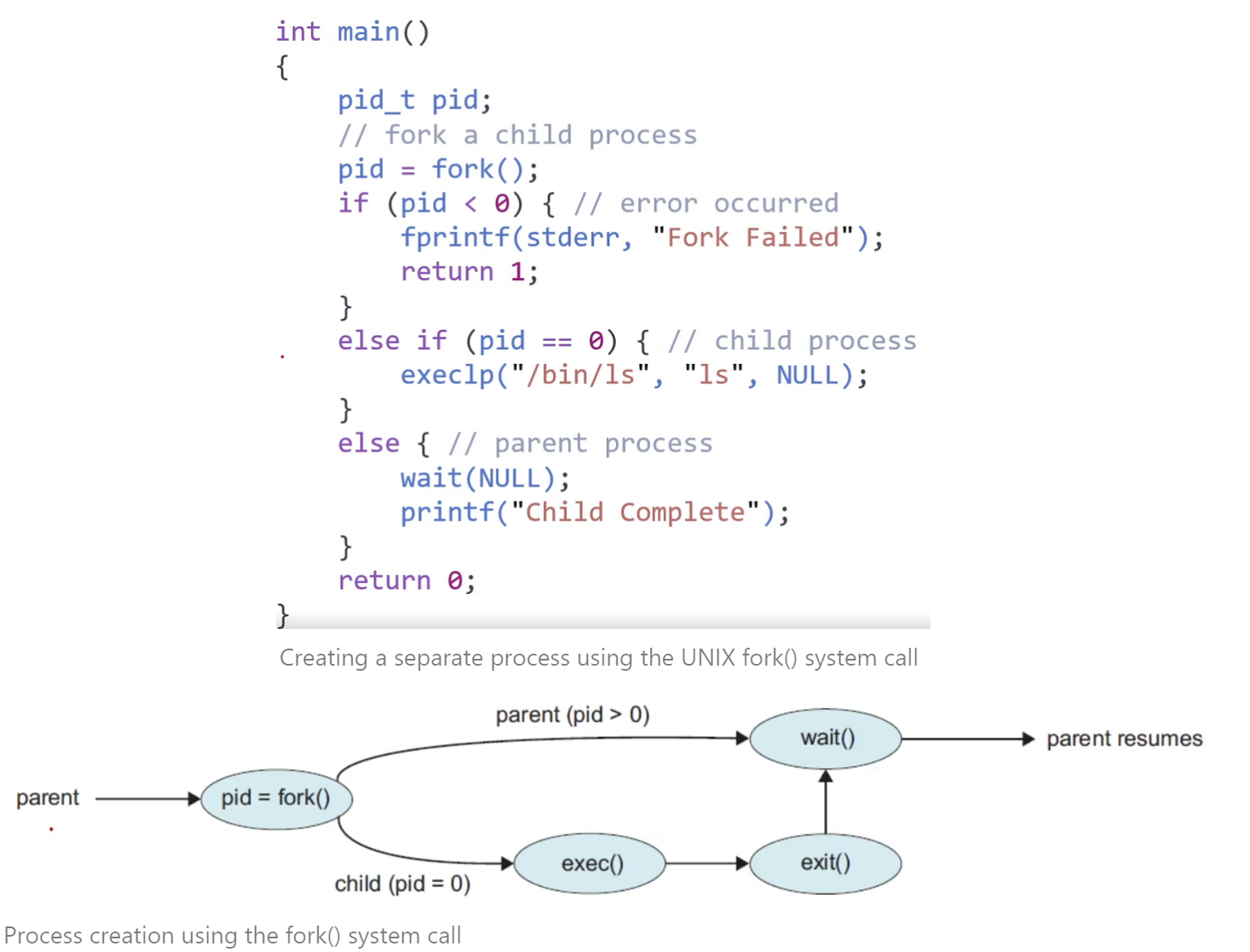
After a fork() system call
-
the child process consist of a “copy of the address space” of the parent process
- pid of child process : 0 | pid of parent process : number
-
the parent can continue its execution or,
if it has nothing else to do while the child runs;
- it can issue a “wait()” system call to move itself off the ready queue until the termination of the child (wait() 시스템 콜을 하면 부모는 ready queue 에서 빠져나와 wait queue로 이동한다. 이 후 자식 프로세스가 종료 된 후 interrupt를 걸어주면 ready queue로 다시 이동한다.)
- it can issue a “wait()” system call to move itself off the ready queue until the termination of the child (wait() 시스템 콜을 하면 부모는 ready queue 에서 빠져나와 wait queue로 이동한다. 이 후 자식 프로세스가 종료 된 후 interrupt를 걸어주면 ready queue로 다시 이동한다.)
Exercise 3.1 - What output will be at Line A?
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
pid = fork();
if (pid == 0) { // child process
value += 15;
return 0;
}
else if (pid > 0) { // parent process
wait(NULL);
printf("Parent: value = %d\n", value); // Line A
}
}Ans) 일반적인 흐름으로 코드를 따라가면 답이 20 이라고 생각할 수 있지만, 답은 “5”이다.
Sol) 먼저 parent process는 wait() 시스템 콜을 받았으므로 child process를 실행한다.
여기서 중요한 것은 “copy of the address space”이다. value가 child process에 그대로 복사가 된다.
따라서 5 + 15 = 20이 value 값이 되고, child process는 terminate 된다.
이제 parent process로 돌아오게 되는데, 이 때 parent process에 할당된 value 값은 5이다.
따라서 답으로 5를 출력한다.
Exercise 3.2 - How many processes are created?
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <wait.h>
/*
* How many processes are created?
*/
int main()
{
fork(); // fork a child process
fork(); // fork another child process
fork(); // and fork another
return 0;
} Ans) 8
Sol) 부모 프로세스를 P0이라 하자.
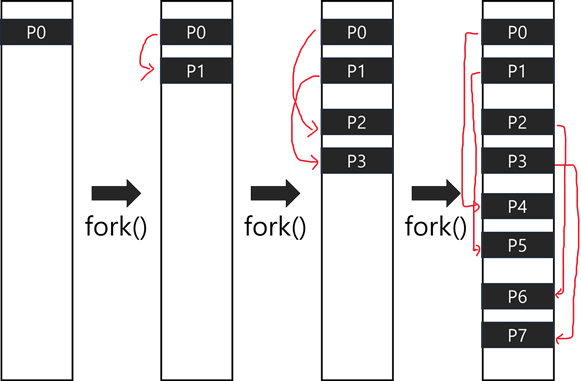
첫번째 fork()에 의해 P1 process가 생성된다..
두번째 fork()에 의해 P0의 child process인 P2 process, P1의 child process인 P3 process가 생성된다.
세번째 fork()에 의해 P0, P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P7 총 8개의 process가 생성된다.
Exercise 3.11 - How many processes are created?
int main()
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++
fork();
return 0;
} Ans) 16
Sol) fork()가 총 4번 호출되므로 1 → 2 → 4 → 8 → 16
Exercise 3.12 - When will LINE J be reached?
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
pid = fork();
if (pid == 0) { //child process
execlp("/bin/ls", "ls", NULL);
printf("LINE J\n");
}
else if (pid > 0) { //parent process
wait(NULL);
printf("Child Complete\n");
}
return 0;
}Ans) Can not reached
Sol) fork()를 통해 parent process가 복사된 child process가 생성된다.
이 때 execlp를 하게되면 ls가 process를 완전히 덮어버리기 때문에 이 후 존재하는 코드는 의미 X
Exercise 3.13 - What are the pid values?(부모 프로세스는 pid가 5156, 자식프로세스는 pid가 5157로 가정)
int main()
{
pid_t pid, pid1;
pid = fork();
if (pid == 0) { //child process
pid1 = getpid();
printf("child: pid = %d\n", pid); // A
printf("child: pid1 = %d\n", pid1); // B
}
else if (pid > 0) { // parent process
pid1 = getpid();
printf("parent: pid = %d\n", pid); // C
printf("parent: pid1 = %d\n", pid1); // D
wait(NULL);
}
return 0;
}Ans) C-D-A-B 순서로 출력되며, ex) 5157, 5156, 0, 5157
Sol) Parent process를 보면 코드 실행 후 wait(NULL)이 있다. 따라서 C-D-A-B 순서로 출력되고
[fork()를 하면 Parent process에게는 Child process의 주소를, Child process는 0을 할당한다.]
Parent process에서 pid1 = getpid(); 코드를 실행시켜 주었으므로
C : 5157, D : 5156이 된다. → C : fork()를 통해 할당받은 자식의 pid , D : getpid()를 통해 할당받은 본인의 pid
A : 0, B : 5157 → A : fork()를 통해 할당받은 0, B : getpid()를 통해 할당받은 본인의 pid
Exercise 3.16 - What output will be at Line X and Line Y?

Ans) Child : 0, 1, 4, 9, 16 | Parent : 0, 1, 2, 3, 4
참고 :
Silberschatz et al. 『Operating System Concepts』. WILEY, 2020.
