Processes executing concurrently
- A process is
independent- does not share data
- A process is
cooperating
- can affect or be affected by the other process
- shares data with other processes
IPC(Inter-Process Communication)
Cooperating processesrequire IPC mechanism- that will allow them to exchange data
- send data and receive data from each other
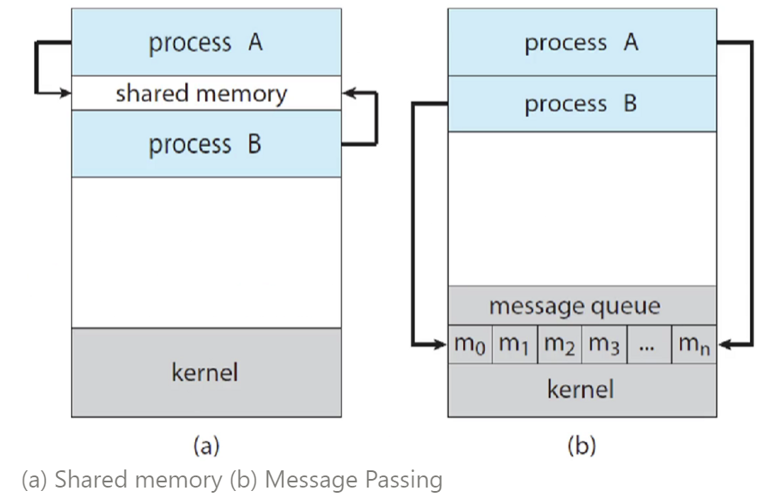
- Two fundamental models of IPC:
shared memory(공유 메모리)message passing(메시지 전달)
Producer-Consumer Problem
- A producer produces information that is consumed by as consumer. ex) web server produces an HTML file, and browser consumes it.
→ A solution using shared-memory(Producer, Consumer가 공유):
- to allow producer and consumer to run
concurrently - Let a
bufferof items be available (버퍼를 이용하자)- Producer : fill the buffer
- Consumer : empty the buffer
- 하지만, 공유 메모리에 접근하고 조작하기 위한 코드는 프로그래머에 의해 명시적으로 작성된다.
→ Message-Passing을 이용하자
- O/S는 메시지 전달을 통해 소통할 수 있는 수단을 제공한다. (프로그래머가 코드를 작성하지 않아도 된다.)
- Producer : send(message)
- Consumer : receive(message)
Communication Links(Message-Passing)
directorindirectcommunication
1. Direct
- each process that wants to communicate
- must explicitly name the recipient or sender of communication (수신자, 송신자의 이름 명확)
2. Indirect**send(P, message)** : P 에게 메시지를 보낸다. **receive(Q, message)** : Q에게 메시지를 받는다. → **Communication Link**가 **automatically**하게 생성 → **한 쌍의 프로세스**에 정확히 **하나의 링크** 존재
- messages are sent to and received from mailboxes or ports.
- A mailbox (ports)
- 추상적인 객체
- 메시지가 놓여지거나, 제거되는 장**send(A, message)** : mailbox A에 메시지를 보낸다. **receive(A, message)**: mailbox A에서 메시지를 받는다. → **Communication Link**가 **“2개 이상”의 프로세스가 mailbox를 이용해야** 생성된다 → **“2개 이상”의 프로세스**에 하나의 **공유 객체 mailbox** 존재 → **수 많은 링크** 존재 (여러 개의 mailbox 이용 가능) ※ **O/S provides a mechanism** that allows a process to do: 1. **Create new mailbox** 2. **Send and Receive messages** through the mailbox 3. **Delete a mailbox**- Different design options for implementation
- Blocking or Non-Blocking : Synchronous or Asynchronous
-
Blocking send : the sender is blocked until the message is received.
-
Blocking receive : the receiver blocks until a message is available.
→ mailbox의 용량 1MB / P가 1GB크기의 파일 send
: Q가 1GB의 파일을 다 받을 때 까지 P는 send, wait 반복
(파일을 다 보낸 후 요금 부과 가능 ⇒ 동기적)
-
Non-Blocking send : the sender sends the message and continue.
-
Non-Blocking receive : the receiver retrieves either a valid message or a null message.
→ mailbox의 용량 1MB / P가 1GB크기의 파일 send
: P ⇒ 파일 보내기, 다른 행동 반복
Q ⇒ 정상적인 메시지, null 메시지 수신 반복
(Q가 파일을 다 수신하기 전에 종료 할 수 있음. But 요금이 부과되면 안됨 ⇒ 비동기적)
-
- Blocking or Non-Blocking : Synchronous or Asynchronous
참고 :
Silberschatz et al. 『Operating System Concepts』. WILEY, 2020.
