GPU 컴퓨팅 수업을 수강하며 기본적인 GPU의 구조에 대한 이해와 GPU에 특화된 프로그래밍 언어인 CUDA를 어떻게 작성하는지, 이는 어떤 식으로 GPU 연산에 최적화되어 있는지 등을 배웠다.
GPU의 구조
복잡한 연산을 빠르게 수행하기 위한 연산 유닛 구조를 가지고 있는 CPU와는 다르게, GPU는 단순하지만 방대한 양의 연산을 병렬적으로 수행하기 위한 구조를 가지고 있다. GPU는 물리적으로 수백에서 수천 개의 processor를 가지고 있으며, 각 processor 내에는 서로 다른 목적의 연산을 수행할 수 있는 FPU, ALU, LSU가 포함되어 있다. 따라서 각 processor는 동시다발적으로 연관성 없는 병렬적인 연산을 수행할 수 있는데, 이것이 GPU가 가지고 있는 가장 큰 특징이다. 논리적으로 앞서 언급한 SP(Streaming Processor)가 8개 모이면 SM(Streaming Multiprocessor)을 이룬다. 각 SM은 이루고 있는 SP가 공유할 수 있는 데이터 영역인 Shared Memory를 포함하고 있으며, 특수한 연산을 수행하기 위한 SFU가 2개 포함되어 있다. 물론 시간이 흐르면서 GPU 성능을 개선하고, 새로운 표준을 정립하려는 노력의 영향으로 현재는 이러한 구조 이외에도 다양한 GPU 구조를 찾아볼 수 있다.
GPU연산
GPU의 multi threading 기본 단위는 SM이다. 각각의 SM은 스케쥴링에 따라서 작업을 수행하는데, CUDA에서는 처리영역을 분할하기 위해 연산 체계에서 grid, block, thread 단위를 사용하고 있다. 이러한 체계는 어떤 작업을 어떤 SM에서 수행하게 될지 예측하며 코딩할 수 없기 때문에, SM에 할당하는 작업의 인덱스를 불러올 수 있도록 하여 다양한 메모리 자료구조(특히 이미지)에 이를 적용할 수 있도록 한다.
GPU 연산의 최소단위는 thread이다. cuda에서 kernel함수를 호출할 때, 할당된 모든 thread에서 kernel 함수를 호출한다. 함수를 호출한 thread의 스케쥴링을 위해 이를 32개 단위로 묶어 warp라고 칭하는데, warp는 같은 명령어로 동시에 동작 가능한 thread의 집합을 의미하며, 이러한 동작을 lock-step이라고 칭한다. 즉, warp로 묶여 있는 thread는 모두 같은 연산을 수행하고 있어야 하는데, 이러한 작동 방식을 SIMT라고 부른다. 또한 SM 작업의 스케쥴링 단위가 warp이기 때문에 warp 내에서 수행할 thread가 할당되지 않는 processor는 같은 warp 내의 다른 processor들의 작업이 모두 완료될 때까지 대기상태에 있을 수 있다. 이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해 SM에서는 포함하고 있는 SP가 쉬지 않고 thread를 수행하도록 스케쥴링하는 warp scheduler를 포함하고 있다.
코드 레벨에서는 최소 연산 단위인 thread의 묶음을 block으로 표현하는데, 이러한 block을 한 번 더 묶어서 grid로 표현하게 된다. 연산을 위해 필요한 thread의 개수를 선언하고, 이를 block으로 묶은 뒤, 각 block과 thread의 index 정보를 포함한 채로 SM에 전달된다. 이런 전달 과정에는 grid가 thread block scheduler에 전달되어 SM에 스케쥴링되고, 뿌려지는 과정도 포함되어 있다. 각 SM에서는 할당된 block을 warp scheduler를 통해 스케쥴링하고, thread를 각 processor에 전달하여 작업을 수행하는 방식으로 연산을 수행한다. 이런 복잡한 물리적 / 논리적 구조가 맞물려 있는 GPU의 연산에서, 효율적인 자원의 사용을 위해서는 물리적 구조와 논리적 구조를 모두 고려하여 GPU연산 코드를 작성하여야 할 것이다.
Canny Edge Detection
또한 Canny Edge Detection algorithm을 CUDA로 구현하는 예제를 수행하였다. Canny Edge Detection은 Image의 Edge를 크게 4단계에 걸쳐 검출하는 다단계 알고리즘이며, 대표적인 이미지 전처리 알고리즘이다. 예제 제안 폴더 내에 작성되어 있는 CPU 위에서 구동하는 C언어 기반 프로그램을 GPU 위에서 구동하는 CUDA 기반 프로그램으로 작성하는 것이 예제의 최종 목표이다. 본 프로젝트의 학술적 목표는 GPU 기반의 병렬 프로그래밍 작성 요령의 습득과, 하드웨어 아키텍처에 적합한 구동 방식을 고민해보며 시도하는 반복적인 리팩토링을 통한 GPU 코드의 성능개선 경험 정도로 선정할 수 있을 것이다.
Colab 환경
Google Colab 11.2 version 기준, GPU 런타임으로 제공되는 GPU는 Tesla T4이다. Tesla T4의 하드웨어 정보는 다음과 같다.
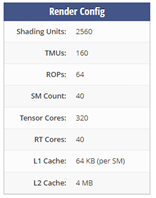
Device 0: "Tesla T4“
(40) Multiprocessors, ( 64) CUDA Cores/MP: 2560 CUDA Cores
Warp size: 32 threads per warp
Maximum number of threads per multiprocessor: 1024
Maximum number of threads per block: 1024
Max dimension size of a thread block (x,y,z): (1024, 1024, 64)
Max dimension size of a grid size (x,y,z): (2147483647, 65535, 65535)
single SM can manage/schedule 32 warps concurrently
32 warps per SM
32 blocks per SM
800 * 1000 pixel의 24bit 비트맵 파일을 병렬 연산하는데 절대로 부족함이 없는 GPU인 것 같다. 총 800,000 pixel의 연산을 수행해야 한다. 초기에는 tile size를 (8x8=64)로 설정하여 총 12,500개의 block을 생성하였다. 이후에 계산을 통해 총 block당 625(800,000 / 1,280)개의 thread를 선언하였을 때 최소 사이클로 작업이 수행될 것이라 예상하였고, 블록의 너비를 32, 높이를 20으로 설정하였을 때 예상했던 대로 연산 속도가 빨라지는 것을 확인할 수 있었다.
Canny Edge Detection
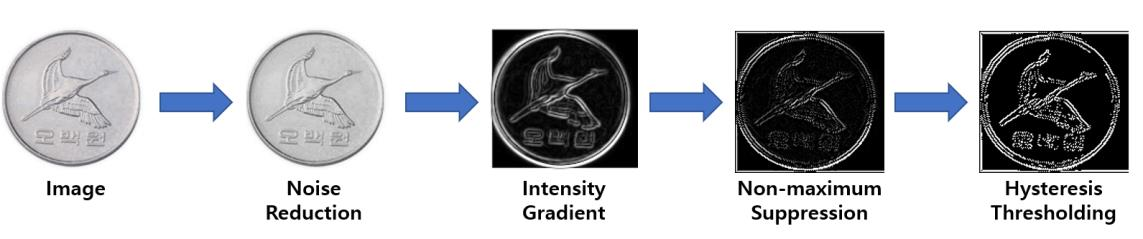 Canny Edge Detection은 Image의 Edge를 검출하는 대중적인 알고리즘으로 Noise Reduction, Intensity Gradient, Non-maximum Suppression, Hysteresis Thresholding 과정을 거쳐 Image의 Edge를 검출한다.
Canny Edge Detection은 Image의 Edge를 검출하는 대중적인 알고리즘으로 Noise Reduction, Intensity Gradient, Non-maximum Suppression, Hysteresis Thresholding 과정을 거쳐 Image의 Edge를 검출한다.
__global__ void GrayscaleKernel(uint8_t* buf, uint8_t* gray, int width, int height){
int x = threadIdx.x + (blockIdx.x * blockDim.x);
int y = threadIdx.y + (blockIdx.y * blockDim.y);
int e = (x + (y * width)) * 3;
int tmp = (buf[e] * 0.114 + buf[e+1] * 0.587 + buf[e+2]*0.299);
gray[e] = tmp;
gray[e+1] = tmp;
gray[e+2] = tmp;
}
void GPU_Grayscale(uint8_t* buf, uint8_t* gray, uint8_t start_add, int len) {
int imgWidth = 0;
int imgHeight = 0;
for (int i = 18; i < 22; i++) imgWidth += buf[i] * pow(256, i-18);
for (int i = 22; i < 26; i++) imgHeight += buf[i] * pow(256, i-22);
const int TILE_WIDTH = 8;
const int TILE_HEIGHT = 8;
uint8_t* dev_buf;
uint8_t* dev_gray;
cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_buf, (len - start_add) * sizeof(uint8_t));
cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_gray, (len - start_add) * sizeof(uint8_t));
cudaMemcpy(dev_buf,buf + (start_add * sizeof(uint8_t)), (len - start_add) * sizeof(uint8_t),cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
dim3 dimGrid((int)(imgWidth/TILE_WIDTH), (int)(imgHeight/TILE_HEIGHT), 1);
dim3 dimBlock(TILE_WIDTH, TILE_HEIGHT, 1);
GrayscaleKernel <<< dimGrid, dimBlock >>> (dev_buf, dev_gray, imgWidth, imgHeight);
cudaMemcpy(gray + (start_add * sizeof(uint8_t)), dev_gray, (len - start_add) * sizeof(uint8_t),cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
gray[len - 1] = buf[len - 1] * 0.114 + buf[len] * 0.587 + buf[len + 1] * 0.299; //handling padding of bmp
cudaFree(dev_buf);
cudaFree(dev_gray);
}
__global__ void NoiseReductionKernel(float* filter, uint8_t* pixel, uint8_t* gaussian, int width, int height){
int x = threadIdx.x + (blockIdx.x * blockDim.x);
int y = threadIdx.y + (blockIdx.y * blockDim.y);
float tmp = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < 5; j++){
tmp += pixel[(y + i) * (width + 4) + x + j] * filter[i * 5 + j];
}
}
int e = (x + (y * width)) * 3;
gaussian[e] = (int)tmp;
gaussian[e+1] = (int)tmp;
gaussian[e+2] = (int)tmp;
}
void GPU_Noise_Reduction(int width, int height, uint8_t *gray, uint8_t *gaussian) {
float filter[25] = {0};
float sigma = 1.0;
for (int i = -2; i <= 2; i++) {
for (int j = -2; j <= 2; j++) {
filter[(i + 2) * 5 + j + 2]
= (1 / (2 * 3.14* sigma * sigma)) * exp(-(i * i + j * j) / (2 * sigma * sigma));
}
}
uint8_t* tmp = (uint8_t*)malloc((width+4) * (height+4));
memset(tmp, (uint8_t)0, (width + 4) * (height + 4));
for (int i = 2; i < height+2; i++) {
for (int j = 2; j < width+2; j++) {
tmp[i * (width + 4) + j] = gray[((i - 2) * width + (j - 2)) * 3];
}
}
float* dev_filter;
uint8_t* dev_tmp;
uint8_t* dev_conv;
uint8_t* dev_gaussian;
cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_filter, 5 * 5 * sizeof(float));
cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_tmp, (width + 4) * (height + 4) * sizeof(uint8_t));
cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_conv, width * height * sizeof(uint8_t));
cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_gaussian, width * height * 3 * sizeof(uint8_t));
cudaMemcpy(dev_filter, filter, 5 * 5 * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMemcpy(dev_tmp, tmp, (width + 4) * (height + 4) * sizeof(uint8_t), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
const int TILE_WIDTH = 8;
const int TILE_HEIGHT = 8;
dim3 dimGrid((int)ceil((width)/TILE_WIDTH), (int)ceil((height)/TILE_WIDTH), 1);
dim3 dimBlock(TILE_WIDTH, TILE_HEIGHT, 1);
NoiseReductionKernel<<<dimGrid, dimBlock>>>(dev_filter, dev_tmp, dev_gaussian, width, height);
cudaMemcpy(gaussian, dev_gaussian, width * height * 3 * sizeof(uint8_t), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaFree(dev_filter);
cudaFree(dev_tmp);
cudaFree(dev_gaussian);
free(tmp);
}
__global__ void IntensityGradientKernel(int width, int height, int* filter_x, int* filter_y, uint8_t* pixel, uint8_t* sobel, uint8_t* angle){
int x = threadIdx.x + (blockIdx.x * blockDim.x);
int y = threadIdx.y + (blockIdx.y * blockDim.y);
int gx = 0;
int gy = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++){
gx += (int)pixel[(y + i) * (width + 2) + x + j] * filter_x[i * 3 + j];
gy += (int)pixel[(y + i) * (width + 2) + x + j] * filter_y[i * 3 + j];
}
}
int t = __dsqrt_rn(gx * gx + gy * gy);
uint8_t v = 255;
if(t < 256) v = t;
int e = (x + (y * width));
sobel[e*3] = v;
sobel[e*3+1] = v;
sobel[e*3+2] = v;
float t_angle = 0;
if(gy != 0 || gx != 0)
t_angle= (float)atan2((float)gy, (float)gx) * 180.0 / 3.14;
if ((t_angle > -22.5 && t_angle <= 22.5) || (t_angle > 157.5 || t_angle <= -157.5)) angle[e] = 0;
else if ((t_angle > 22.5 && t_angle <= 67.5) || (t_angle > -157.5 && t_angle <= -112.5)) angle[e] = 45;
else if ((t_angle > 67.5 && t_angle <= 112.5) || (t_angle > -112.5 && t_angle <= -67.5)) angle[e] = 90;
else if ((t_angle > 112.5 && t_angle <= 157.5) || (t_angle > -67.5 && t_angle <= -22.5)) angle[e] = 135;
}
void GPU_Intensity_Gradient(int width, int height, uint8_t* gaussian, uint8_t* sobel, uint8_t* angle){
int filter_x[9] = {-1,0,1,-2,0,2,-1,0,1};
int filter_y[9] = {1,2,1,0,0,0,-1,-2,-1};
uint8_t* tmp = (uint8_t*)malloc((width + 2) * (height + 2));
memset(tmp, (uint8_t)0, (width + 2) * (height + 2));
for (int i = 1; i < height + 1; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < width + 1; j++) {
tmp[i * (width + 2) + j] = gaussian[((i - 1) * width + (j - 1)) * 3];
}
}
int* dev_filterX;
int* dev_filterY;
uint8_t* dev_tmp;
uint8_t* dev_sobel;
uint8_t* dev_angle;
cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_filterX, 9 * sizeof(int));
cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_filterY, 9 * sizeof(int));
cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_tmp, (width + 2) * (height + 2) * sizeof(uint8_t));
cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_sobel, width * height * 3 * sizeof(uint8_t));
cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_angle, width * height * sizeof(uint8_t));
cudaMemcpy(dev_filterX, filter_x, 9 * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMemcpy(dev_filterY, filter_y, 9 * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMemcpy(dev_tmp, tmp, (width + 2) * (height + 2) * sizeof(uint8_t), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
const int TILE_WIDTH = 8;
const int TILE_HEIGHT = 8;
dim3 dimGrid((int)ceil(width/TILE_WIDTH), (int)ceil(height/TILE_HEIGHT), 1);
dim3 dimBlock(TILE_WIDTH, TILE_HEIGHT, 1);
//kernel function
IntensityGradientKernel<<<dimGrid, dimBlock>>>(width, height, dev_filterX, dev_filterY, dev_tmp, dev_sobel, dev_angle);
cudaMemcpy(sobel, dev_sobel, width * height * 3 * sizeof(uint8_t), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaMemcpy(angle, dev_angle, width * height * sizeof(uint8_t), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaFree(dev_filterX);
cudaFree(dev_filterY);
cudaFree(dev_tmp);
cudaFree(dev_sobel);
cudaFree(dev_angle);
free(tmp);
}
__global__ void NonMaximumSuppressionKernel(int width, int height, uint8_t *angle, uint8_t *sobel, uint8_t *suppression_pixel, uint8_t& min, uint8_t& max){
int x = threadIdx.x + (blockIdx.x * blockDim.x) + 1;
int y = threadIdx.y + (blockIdx.y * blockDim.y) + 1;
uint8_t p1 = 0;
uint8_t p2 = 0;
if( x > 0 && y > 00 && x < width - 1 && y < height - 1){
if(angle[y * width + x] == 0){
p1 = sobel[((y + 1) * width + x) * 3];
p2 = sobel[((y - 1) * width + x) * 3];
}
else if(angle[y * width + x] == 45){
p1 = sobel[((y + 1) * width + x - 1) * 3];
p2 = sobel[((y - 1) * width + x + 1) * 3];
}
else if(angle[y * width + x] == 90){
p1 = sobel[(y * width + x + 1) * 3];
p2 = sobel[(y * width + x - 1) * 3];
}
else{
p1 = sobel[((y + 1) * width + x + 1) * 3];
p2 = sobel[((y - 1) * width + x - 1) * 3];
}
int e = (x + (y * width)) * 3;
uint8_t v = sobel[e];
if(x < 10 && y < 10) printf("[%d, %d]: p1 = %d, v = %d, p2 = %d \n", y, x, p1, v, p2);
if(min > v) min = v;
if(max < v) max = v;
if((v >= p1) && (v >= p2)){
suppression_pixel[e] = v;
suppression_pixel[e + 1] = v;
suppression_pixel[e + 2] = v;
}else{
suppression_pixel[e] = 0;
suppression_pixel[e + 1] = 0;
suppression_pixel[e + 2] = 0;
}
}
}
void GPU_Non_maximum_Suppression(int width, int height, uint8_t *angle,uint8_t *sobel, uint8_t *suppression_pixel, uint8_t& min, uint8_t& max){
cudaError_t cudaStatus;
uint8_t* dev_angle;
uint8_t* dev_sobel;
uint8_t* dev_suppression_pixel;
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_angle, width * height * sizeof(uint8_t));
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_sobel, width * height * 3 * sizeof(uint8_t));
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_suppression_pixel, width * height * 3 * sizeof(uint8_t));
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(dev_angle, angle, width * height * sizeof(uint8_t), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
if(cudaSuccess != cudaStatus) printf("\ncudaMemcpy1 ERROR : %s\n", cudaGetErrorString(cudaStatus));
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(dev_sobel, sobel, width * height * 3 * sizeof(uint8_t), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
if(cudaSuccess != cudaStatus) printf("\ncudaMemcpy2 ERROR : %s\n", cudaGetErrorString(cudaStatus));
const int TILE_WIDTH = 8;
const int TILE_HEIGHT = 8;
dim3 dimGrid((int)ceil(width/TILE_WIDTH), (int)ceil(height/TILE_HEIGHT), 1);
dim3 dimBlock(TILE_WIDTH, TILE_HEIGHT, 1);
NonMaximumSuppressionKernel<<<dimGrid, dimBlock>>>(width, height, dev_angle, dev_sobel, dev_suppression_pixel, min, max);
//cudaMemset(dev_suppression_pixel,100,width * height * sizeof(uint8_t));
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(suppression_pixel, dev_suppression_pixel, width * height * 3 * sizeof(uint8_t), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
if(cudaSuccess != cudaStatus) printf("\ncudaMemcpy3 ERROR : %s\n", cudaGetErrorString(cudaStatus));
cudaFree(dev_angle);
cudaFree(dev_sobel);
cudaFree(dev_suppression_pixel);
}
__global__ void DoubleThresholdingKernel(int width, int height, uint8_t low_t, uint8_t high_t, uint8_t* suppression_pixel, uint8_t* hysteresis){
int x = threadIdx.x + (blockIdx.x * blockDim.x);
int y = threadIdx.y + (blockIdx.y * blockDim.y);
int e = (x + (y * width)) * 3;
uint8_t v = suppression_pixel[e];
if(v < low_t){
hysteresis[e] = 0;
hysteresis[e + 1] = 0;
hysteresis[e + 2] = 0;
}else if(v < high_t){
hysteresis[e] = 123;
hysteresis[e + 1] = 123;
hysteresis[e + 2] = 123;
}else{
hysteresis[e] = 255;
hysteresis[e + 1] = 255;
hysteresis[e + 2] = 255;
}
}
__global__ void HysteresisCheckKernel(int width, int height, uint8_t* hysteresis, uint8_t* tmp_hysteresis){
int x = threadIdx.x + (blockIdx.x * blockDim.x);
int y = threadIdx.y + (blockIdx.y * blockDim.y);
int e = (x + (y * width)) * 3;
if(tmp_hysteresis[e] == 123){
for(int i = y - 1; i < y + 2; i ++){
for(int j = x - 1; j < x + 2; j++){
if((i < height && j < width) && (i >= 0 && j >= 0)){
if(tmp_hysteresis[(i * width + j)*3] == 255){
hysteresis[e] = 255;
hysteresis[e + 1] = 255;
hysteresis[e + 2] = 255;
}
}
}
}
}
}
__global__ void HysteresisKernel(int width, uint8_t* hysteresis){
int x = threadIdx.x + (blockIdx.x * blockDim.x);
int y = threadIdx.y + (blockIdx.y * blockDim.y);
int e = (x + (y * width)) * 3;
if(hysteresis[e] != 255){
hysteresis[e] = 0;
hysteresis[e + 1] = 0;
hysteresis[e + 2] = 0;
}
}
void GPU_Hysteresis_Thresholding(int width, int height, uint8_t *suppression_pixel,uint8_t *hysteresis, uint8_t min, uint8_t max) {
uint8_t diff = max - min;
uint8_t low_t = min + diff * 0.01;
uint8_t high_t = min + diff * 0.2;
uint8_t* dev_suppression_pixel;
uint8_t* dev_hysteresis;
uint8_t* dev_tmp_hysteresis;
cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_suppression_pixel, width * height * 3 * sizeof(uint8_t));
cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_hysteresis, width * height * 3 * sizeof(uint8_t));
cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_tmp_hysteresis, width * height * 3 * sizeof(uint8_t));
cudaMemcpy(dev_suppression_pixel, suppression_pixel, width * height * 3 * sizeof(uint8_t), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
const int TILE_WIDTH = 8;
const int TILE_HEIGHT = 8;
dim3 dimGrid((int)ceil((width - 2)/TILE_WIDTH), (int)ceil((height - 2)/TILE_HEIGHT), 1);
dim3 dimBlock(TILE_WIDTH, TILE_HEIGHT, 1);
DoubleThresholdingKernel<<<dimGrid, dimBlock>>>(width, height, low_t, high_t, dev_suppression_pixel, dev_hysteresis);
cudaMemcpy(dev_tmp_hysteresis, dev_hysteresis, width * height * 3 * sizeof(uint8_t), cudaMemcpyDeviceToDevice);
HysteresisCheckKernel<<<dimGrid, dimBlock>>>(width, height, dev_hysteresis, dev_tmp_hysteresis);
HysteresisKernel<<<dimGrid, dimBlock>>>(width, dev_hysteresis);
cudaMemcpy(hysteresis, dev_hysteresis, width * height * 3 * sizeof(uint8_t), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaFree(dev_suppression_pixel);
cudaFree(dev_hysteresis);
cudaFree(dev_tmp_hysteresis);
}