Quine-McCluskey Algorithm(QM)
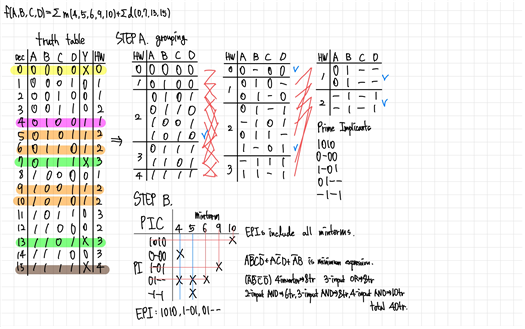
QM 알고리즘은 Boolean function의 SOP표현을 간략화하는 데 사용되는 방법 중 하나이다. SOP 표현을 간략화하는 데 사용되는 대표적인 방법은 카르노 맵(Karnaugh map)을 활용하는 것인데, 이는 SOP를 구성하는 product들을 map 형태로 도식화하고, 최소 횟수의 rectangle drawing으로 식을 표현하는 데 필요한 모든 minterm을 포함하도록 하여 식을 간략화하는 방법이다. QM 알고리즘은 이와 다르게 chart를 활용하여 SOP를 도식화한 뒤, 이를 활용한다. 카르노 맵의 경우 맵을 도식화하는 데에 있어서 variable의 수가 많아질 경우 이를 도식화하는 데 무리가 생길 수 있다. 물론 손으로 직접 알고리즘을 수행할 경우 QM 알고리즘도 차트를 그리는 데 무리가 생길 수 있지만, 그림이 아닌 차트를 그린다는 부분에서 컴퓨터 프로그램으로 구현하는 데 카르노 맵보다 적합하기 때문에 variable의 수가 직접 수행하기에 버거울 정도로 많아지는 경우에는 컴퓨터 프로그램으로 구현된 QM 알고리즘을 사용하여 수식을 간략화할 수 있다. QM 알고리즘의 수행 과정은 다음과 같다.
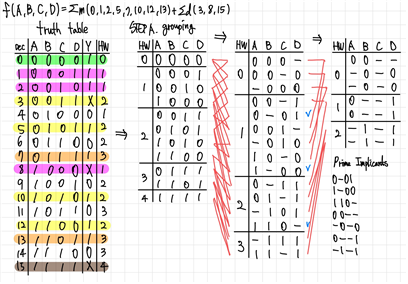
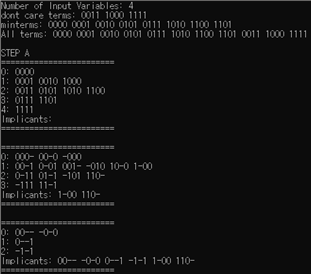
- 주어진 SOP를 구성하는 product들을 binary로 표현한다.(minterm과 don’t care term도 모두 포함)
- term의 binary 값에서 1이 포함된 개수로 term을 분류한다(grouping)
- 인접한 group의 term이 1비트만 다른 경우 결합하여 term의 개수를 줄이면서 새롭게 grouping한다.
- 더 이상 새로운 grouping이 발생하지 않을 때까지 3을 반복한다.
- 연속적인 grouping 과정 동안 다음 grouping에 포함되지 않은 term을 모두 모은다(여기서 모인 minterm을 PI(Prime Implicant)라 부른다.).
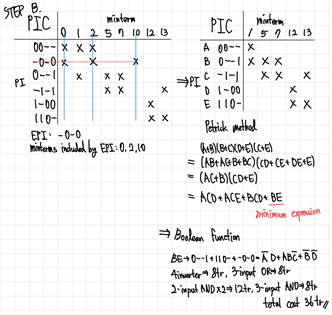
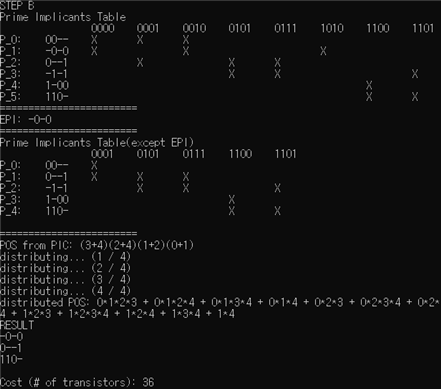
- 가로 범례를 minterm으로 하고, 세로 범례를 PI로 하는 PIC(Prime Implicants Chart)를 구성한다. 여기서 Chart의 세부적인 값은 PI를 구성하는 과정에서 사용된 term들을 나타낸다. 즉, PI로 표현할 수 있는 모든 term을 의미한다.(i.e.‘00-’의 경우 ‘000 = 0’과 ‘001 = 1’을 체크한다.)
- minterm 중에서 PIC에 한 번만 포함된 minterm을 포함하는 PI를 EPI(Essential Prime Implicant)로 하여 EPI들을 모두 PIC에서 제거한다. EPI를 제거하면서 모든 EPI들이 포함하고 있는 minterm들도 PIC에서 함께 제거한다.
- EPI들이 제외된 PIC에서 최소한의 조합으로 모든 minterm을 포함시킬 수 있도록 PI를 조합한다.
- 8에서 조합된 PI와 EPI들을 합쳐서 SOP를 도출한다. 이 SOP는 최소한의 항으로 주어진 Boolean Function을 간략화한 형태가 된다.
본 프로젝트의 구현에서는 Prime Implicant를 Boolean Function에서 도출해내기 위해 반복적인 Grouping을 하는 1~4의 과정을 step A로 묶었고, PIC를 그린 뒤 EPI를 추출하고, minterm을 모두 포함하도록 하는 PI를 모아 최소한의 항으로 Boolean Function을 간략화하는 과정을 step B로 묶었다.
QM 알고리즘에서 가장 중요한 부분은 8번 과정이다. 위의 과정에서 8을 수행하는 데에 “최소한의 조합으로 모든 minterm을 포함시킬 수 있도록 PI를 조합”하는 것에는 다양한 방법이 있다. 손으로 직접 QM 알고리즘을 수행할 때는, 비교적 경우의 수가 적기 때문에 임의로 PI를 선택하여서 항들을 조합해서 최소항을 구성할 수 있다. 하지만 PI의 수가 많아질수록 임의의 PI 선택으로 최소항을 보장하기가 힘들어지기 때문에, 최소항을 보장하기 위한 방법들을 택해서 수행하여야 한다. 앞서 인간의 경험적 추론 등을 통해 PI의 조합을 도출하는 것은 heuristic하고 locally한 방법이기 때문에 전역적 최소항을 구하기에 적합하지 않다. 따라서 본 프로젝트는 항상 전역적 최소항을 보장받을 수 있는 Petrick method를 활용하여 최소항을 도출하였다.
Petrick Method
Petrick method란 QM 알고리즘의 PIC로부터 모든 minterm을 포함하기 위한 최소한의 PI 조합을 찾아내는 데에 적용할 수 있는 방법으로 Boolean Function을 단순화하고 최소화하는 기법 중 하나이다. PI를 기준으로 PIC를 보는 것이 아닌, minterm의 기준으로 PIC를 본다고 생각하면 적용이 쉬운데, minterm의 입장에서 본인이 선택되기 위해서 필요한 모든 PI들을 모아서, 그 PI들의 최소항 포함여부를 각각 따져 모두 Boolean Addition할 경우 무조건 1이 될 것이다. 따라서 EPI에 포함되지 않은 모든 minterm에 대해서 각 minterm을 포함하고 있는 PI들의 OR 연산값(sum)을 AND 연산으로 모두 엮어주면(product) 생기는 식은 POS의 형태를 띄게 된다. 이렇게 생긴 식의 값은 무조건 1이 되기 때문에, 이를 전개한 SOP 형태에서 단 하나의 product만 1이더라도 식의 값이 1임이 보장된다. 따라서 전개된 식에서 가장 적은 PI를 포함하고 있는 product를 찾아내면, 이것이 모든 minterm의 포함이 보장되는 최소항의 구성이 되는 것이다.
pseudo code
def main():
input_file_open()
classify_minterm_dontcareterm(minterms, dontcares, input)
terms.insert(minterms)
terms.insert(dontcares)
#step A. find Prime Implicant (Grouping loop)
#step A-1. first grouping
for term in terms:
group[HammingWeight(term)].insert(term)
#step A-2. Grouping loop
while 1 :
for group in groups:
for termA in group:
for termB in next(group):
if(HammingDistance(termA,termB) == 1):
nextGroups[HammingWeight(termA)].insert(integrate(termA,termB))
PIs.insert(unUsed term in this loop)
if(nextGroups.empty()):
break
#step B. find minimum solution
#step B-1. init PIC
for PI in PIs:
for minterm in PI:
PIC[PI][minterm] = true
#step B-2. find EPI
for minterm in minterms:
for PI in PIs:
if(sum(PIC[PI][minterm]) = 1):
EPI.insert(PI)
#step B-3. erase EPI and minterms used by EPI from PIC
for PI in PIs:
if PI is in EPI:
PIExceptEPI.insert(PI)
for minterm in PI:
if minterm is in minterms:
mintermsExceptEPI.insert(minterm)
#step B-4. draw new PIC
for PI in PIExceptEPI:
for minterm in PI:
PICExceptEPI[PI][minterm] = true
#step B-5(petrick method). Convert the PIC into POS
for a in range(len(PICExceptEPI)):
for b in range(len(PICExceptEPI[a])):
if PICExceptEPI[a][b]:
sum.insert(b)
POS.insert(sum)
#step B-6(petrick method). distribute POS
for sum in POS:
if SOP.empty():
for var in sum:
product.insert(var)
SOP.insert(product)
else:
tmpPOS = []
for var in sum:
for product in SOP:
tmpSOP.insert(product + var)
SOP.swap(tmpSOP)
#step B-7(petrick method). convert each product of SOP into PI combination and merge EPIs
BoolFuncs = []
minTRANS = inf
for product in SOP:
BoolFunc = []
for PI in product:
BoolFunc.insert(PI)
BoolFunc.insert(EPIs)
minTRANS = min(minTRANS, getTRANScnt(BoolFunc))
BoolFuncs.insert(BoolFunc)
#step B-8. find minimum cost Boolean Function and print it
for BoolFunc for BoolFuncs:
if getTRANScnt(BoolFunc) == minTRANS:
printResult(BoolFunc)
return 0Verification strategy
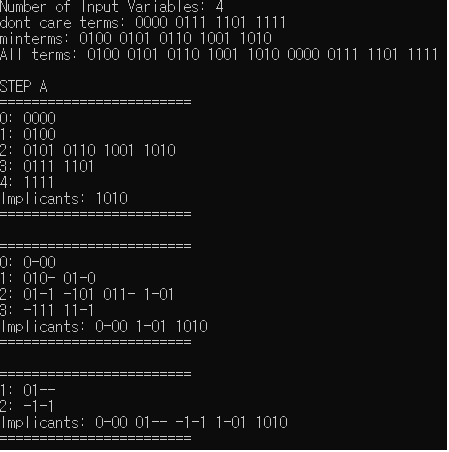
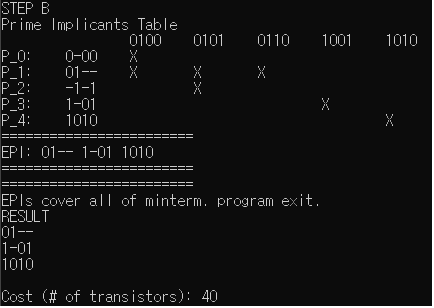
본 프로젝트의 구현 단계는 앞의 pseudo code와 flow chart에서의 프로그램의 각 step을 차례로 구현하면서 진행되었다. 따라서 각각의 step의 구현 단계마다 C++의 콘솔 출력을 활용하여 제대로 된 형식으로 데이터들의 가공 및 처리가 이루어지고 있는지 확인하였다.
프로그램 가동 과정에서 main 함수가 return하는 경우는 세 가지이다. 첫 번째는 file open error가 발생할 경우, 두 번째는 STEP B-3-2로, EPI를 추출했을 때 EPI가 모든 minterm을 포함하게 되어 더 이상의 PI 탐색이 필요치 않은 경우, 세 번째는 STEP B-8로 발생가능한 모든 PI 조합 중에서 항의 개수가 최소인 것들을 EPI와 합치고, 트랜지스터 cost를 계산하여 최소인 것을 발견한 경우이다. 두 번째와 세 번째 경우 프로그램의 flow가 달라지므로 이 두 가지 경우를 나타내는 일반적인 두 가지 예제를 통해 프로그램의 구현 과정의 검증을 수행했다.
- B-3-2로 main함수가 종료되는 경우
Verification_Example1의 STEP B. PIC로 EPI를 찾아내고, EPI로 모든 minterm이 포함됨을 확인하여서 이를 minimum expression으로 출력하고 프로그램 종료.
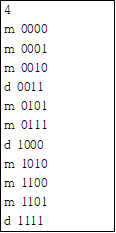
- B-8로 main함수가 종료되는 경우(Verification_Example2.txt)
source code
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <tuple>
using namespace std;
typedef tuple<vector<bool>, vector<bool>, set<int>> Term;
//Term is {Bit, Hyphen bit, Set of Combination}
string to_string(vector<bool> bits) {
string tmp = "";
for (int i = 0; i < bits.size(); i++) {
if (bits[i]) tmp += "1";
else tmp += "0";
}
return tmp;
}
//convert bits into string
string trim(string str) {
string tmp = str;
while (!tmp.empty() && tmp.front() == '\n') tmp.erase(0); //trim left
while (!tmp.empty() && tmp.front() == '\t') tmp.erase(0);
while (!tmp.empty() && tmp.front() == '\r') tmp.erase(0);
while (!tmp.empty() && tmp.front() == '\f') tmp.erase(0);
while (!tmp.empty() && tmp.front() == '\v') tmp.erase(0);
while (!tmp.empty() && tmp.back() == '\n') tmp.pop_back(); //trim right
while (!tmp.empty() && tmp.back() == '\t') tmp.pop_back();
while (!tmp.empty() && tmp.back() == '\r') tmp.pop_back();
while (!tmp.empty() && tmp.back() == '\f') tmp.pop_back();
while (!tmp.empty() && tmp.back() == '\v') tmp.pop_back();
return tmp;
}
//erase side blink of string
int getHammingWeight(vector<bool> n, int length) {
int HW = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
HW += n[i];
}
return HW;
} //Hamming Weight = Count of (N AND (N-1)) is non zero loop.
//return binary's Hamming Weight
Term isHammingDistanceOne(Term a, Term b, int length) {
if (get<1>(a) != get<1>(b)) return Term(vector<bool>(), vector<bool>(), {});
int cntDiff = 0;
int diffIndex = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (get<0>(a)[i] != get<0>(b)[i]) {
cntDiff++;
diffIndex = i;
}
} //get Hamming Distance of a and b
if (cntDiff == 1 && diffIndex != -1) {
vector<bool> tmpTerm(get<0>(a));
tmpTerm[diffIndex] = false;
vector<bool> tmpHyphen(get<1>(a));
tmpHyphen[diffIndex] = true;
set<int> tmpIndex(get<2>(a));
tmpIndex.insert(get<2>(b).begin(), get<2>(b).end());
return Term(tmpTerm, tmpHyphen, tmpIndex);
} //if Distance is 1, integrate a and b. return it.
return Term(vector<bool>(), vector<bool>(), {});
//if a's hyphen bits == b's hyphen bits and HammingWeight of XOR is 1,
//return tuple(term, hyphen bits, usedTerms) => if want to get real term, swap all 0 of term to hyphen where hypen bit positions
//ex. (1001,0110) => 1--1, (10000, 00100) = 10-00.
}
//calculate Hamming Distance = (a XOR b)'s Hamming Weight
string getPrint(Term a, int length) {
string tmp = "";
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (get<1>(a)[i]) tmp += "-";
else if (get<0>(a)[i]) tmp += "1";
else tmp += "0";
}
return tmp;
}
//return print string(minterm with hyphen)
int getTRANScnt(set<Term> Result, int length) {
int trans = 0;
vector<string> resultPrint;
for (auto minterm : Result) {
resultPrint.push_back(getPrint(minterm, length));
}
set<int> inverter; //using set Type to avoid redundancy of counting inverters
for (int i = 0; i < resultPrint.size(); i++) {
int nInputAND = length;
for (int j = 0; j < length; j++) {
char VAR = resultPrint[i][j];
if (VAR == '0') {
inverter.insert(j);
}
else if (VAR == '-') {
nInputAND--;
}
}
nInputAND = (nInputAND * 2) + 2;
trans += nInputAND;// add number of transistor of AND gates
}
trans += (Result.size() * 2) + 2; // add number of transistor of OR gates
trans += (inverter.size() * 2); // add number of transistor of inverters
return trans;
}
//return number of transistor to impliment SOP
void printResult(set<Term> Result, int length) {
ofstream output;
output.open("result.txt");
int TRANScnt = getTRANScnt(Result, length);
for (auto minterm : Result) {
string print = getPrint(minterm, length);
output << print << "\n";
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (print[i] != '-') break;
if (i == length - 1) TRANScnt = 0;
}
}
//TODO : calculate number of transistor and print it
output << "\nCost (# of transistors): " << TRANScnt << endl;
output.close();
return;
}
//print result of algorithm to output text file
int main() {
ifstream input;
//file open
input.open("input_minterm.txt");
if (!input) {
return 0;
}
int cntInput = 0;
string input_line = "";
//get Number of input variables(first line of input)
getline(input, input_line);
cntInput = stoi(trim(input_line));
vector <vector<bool>> minterms;
vector <vector<bool>> dontcares;
//get minterms and dont care terms
while (!input.eof()) {
getline(input, input_line);
stringstream checker(input_line);
string Type = "";
string Value = "";
getline(checker, Type, ' ');
getline(checker, Value, ' ');
vector<bool> tmp;
for (int i = 0; i < cntInput; i++) {
if (Value[i] == '1')tmp.push_back(true);
else if (Value[i] == '0')tmp.push_back(false);
}
if (Type == "d") { //classify input terms
dontcares.push_back(tmp);
}
else if (Type == "m") {
minterms.push_back(tmp);
}
}
input.close();
vector <vector<bool>> terms; //integrate terms
terms.insert(terms.end(), minterms.begin(), minterms.end());
terms.insert(terms.end(), dontcares.begin(), dontcares.end());
//step A. find all Prime Implicants
//step A-1. first Grouping
map<int, set<Term>> groups;
for (int i = 0; i < terms.size(); i++) {
auto term = terms[i];
int indexOfMinterm = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < minterms.size(); j++) {
if (minterms[j] == term) indexOfMinterm = j;
}
Term tmp(term, vector<bool>(cntInput, false), { indexOfMinterm });
groups[getHammingWeight(term, cntInput)].insert(tmp);
} //groups's index is HammingWeight of terms.
//groups[HammingWeight] = tuple(term, bits of '-', usedMinterms)
//step A-2. loop for grouping and collecting Implicants
set<Term> PrimeImplicants;
while (!groups.empty()) {
map<int, set<Term>> nextGroups;
set<Term> used;
for (auto group = groups.begin(); group != prev(groups.end()); group++) {
for (auto termA : group->second) {
for (auto termB : next(group)->second) {
Term tmp = isHammingDistanceOne(termA, termB, cntInput);
if (get<0>(tmp).size()) { //if Hamming distance of termA and termB is 1,
nextGroups[getHammingWeight(get<0>(tmp), cntInput)].insert(tmp);
used.insert(termA);
used.insert(termB);
}
}
}
}
for (auto group : groups) {
for (auto term : group.second) {
if (used.count(term) == 0) {
PrimeImplicants.insert(term);
}
}
}
if (nextGroups.empty())break;
groups.swap(nextGroups);
}
//step B. find minimum solution
//step B-1. init PIC(Prime Implicant Chart)
vector<vector<bool>> PIC(PrimeImplicants.size(), vector<bool>(minterms.size(), 0));
//PIC[essential variable(minterm)][prime implicant]
int i = 0;
for (auto implicant : PrimeImplicants) {
for (auto mintermIndex : get<2>(implicant)) {
if (mintermIndex != -1)PIC[i][mintermIndex] = true;
}
i++;
}
set<Term> EPIs;
//step B-2. find EPI(essential prime implicant)
for (i = 0; i < minterms.size(); i++) {
int cntTerm = 0;
int j = 0;
Term EPI;
for (auto PI : PrimeImplicants) {
if (PIC[j][i]) {
cntTerm++;
EPI = PI;
}
if (cntTerm > 1) break;
j++;
}
if (cntTerm == 1) EPIs.insert(EPI);
} //if 'i'th minterm included by only one PI, it's EPI.
//setp B-3. erase EPIs and minterms used by EPI in PIC
set<int> usedMinterms;
vector<vector<bool>> mintermsExceptEPI;
set<Term> PIexceptEPI;
for (auto EPI : EPIs) {
for (auto minterm : get<2>(EPI)) {
usedMinterms.insert(minterm);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < minterms.size(); i++) {
bool finded = false;
for (auto usedMinterm : usedMinterms) {
if (i == usedMinterm) {
finded = true;
break;
}
}
if (!finded)mintermsExceptEPI.push_back(minterms[i]);
}
for (auto implicant : PrimeImplicants) {
if (EPIs.find(implicant) == EPIs.end()) PIexceptEPI.insert(implicant);
}
//step B-3-2. if EPIs cover all of minterm, program exit.
if (mintermsExceptEPI.empty()) {
printResult(EPIs, cntInput);
return 0;
}
//step B-4. draw new PIC
vector<vector<bool>> PICExceptEPI(PIexceptEPI.size(), vector<bool>(mintermsExceptEPI.size(), 0));
i = 0;
for (auto PI : PIexceptEPI) {
for (auto mintermIndex : get<2>(PI)) {
if (mintermIndex == -1) continue;
auto minterm = minterms[mintermIndex];
int indexOfMintermsExceptEPI = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < mintermsExceptEPI.size(); j++) {
if (mintermsExceptEPI[j] == minterm) {
indexOfMintermsExceptEPI = j;
break;
}
}
if (indexOfMintermsExceptEPI != -1)PICExceptEPI[i][indexOfMintermsExceptEPI] = true;
}
i++;
}
//step B-5. Convert the PIC into POS.
set<set<int>> POS;
for (i = 0; i < mintermsExceptEPI.size(); i++) {
set<int> sum;
for (int j = 0; j < PICExceptEPI.size(); j++) {
if (PICExceptEPI[j][i]) {
sum.insert(j);
}
}
POS.insert(sum);
}
//step B-6. distribute POS(convert POS into SOP)
set<set<int>> SOP;
i = 1;
for (auto sum : POS) {
if (SOP.empty()) { //first loop
for (auto variableA : sum) {
set<int> tmp;
tmp.insert(variableA);
SOP.insert(tmp);
}
}
else {
set<set<int>> tmpSOP;
for (auto variableA : sum) {
for (auto product : SOP) {
set<int> newP(product);
newP.insert(variableA);
tmpSOP.insert(newP);
}
}
SOP.swap(tmpSOP);
}
i++;
}
//step B-7. convert each product of SOP into PI combination and merge EPIs
//SOP = {{0,2},{0,3},{1,2},{1,3}} => PIexceptEPI 's index
set<pair<set<Term>, int>> minimumBF;
int minTRANS = 2147483646;
int minTermCnt = 2147483646;
for (auto product : SOP) {
set<Term> BoolFunc(EPIs); //merge EPI
for (auto PIindex : product) { //find SOP's PI's minterms's index of PIC(exceptEPI)
auto finding = PIexceptEPI.begin();
for (int j = 0; j < PIindex; j++) finding++;
BoolFunc.insert(*finding);
}
int TRANScnt = getTRANScnt(BoolFunc, cntInput); //calculate number of transistor
if (minTRANS > TRANScnt) minTRANS = TRANScnt;
if (minTermCnt > BoolFunc.size()) minTermCnt = BoolFunc.size();
minimumBF.insert(pair<set<Term>, int>(BoolFunc, TRANScnt));
}
//step B-8. find minimum cost Boolean Function and print it.
for (auto BoolFunc : minimumBF) {
if (minTermCnt == BoolFunc.first.size() && BoolFunc.second == minTRANS) {
printResult(BoolFunc.first, cntInput);
return 0;
}
}
return 0;
}