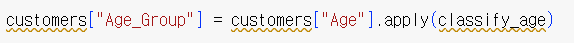데이터 세트 확인
- pd.read_csv("", index_col): 파일 읽어오기
- head(): 상위 5개만 읽기
- info(): 데이터 프레임 정보(결측치, 데이터, 메모리...)
- describe().round(): 집계 통계 기술
- describe(exclude=["int", "float"]): 숫자 아닌 정보 확인
apply
나이 계산 및 컬럼 추가

- apply(func)
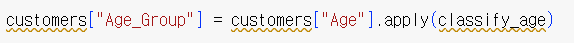
열 정리

map
mapping 하기
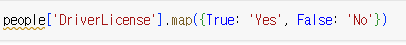
- 매핑이 안된다면 NaN으로
- value_counts 별로 집계
applymap
def uppercase(str):
return data.upper()
people['Name'].str.len()
people.applymap(str).applymap(uppercase): 모든 문자열 한번에 적용
customers['Kidhome'] = customers['Kidhome'].map({0: '자녀없음', 1: '자녀있음'})
customers.head()
astype
customer['Income'].astype('int64')
replace
customer['Marital_Status'].replace(['Alone','Absurd','YOLO'], 'Single').value_counts()
where
multiple_child_mask = customer['Kidhome'] >= 2
customer[multiple_child_mask].head()
customer.where(customer['Kidhome'] >= 2)
customer.where(customer['Kidhome'] >= 2).fillna()
customer.where(customer['Kidhome'] >= 2).dropna()
customer.where(customer['Kidhome'] >= 2, ohter = '000')
agg
- aggregate (집계)
- 지정된 axis를 기준으로 하나 이상의 연산을 사용하여 데이터 집계
customers.agg({'Income': 'max', 'Kidhome':'mean'})
customers.agg('max')
customers.agg(['max', 'mean'])
customers_numeric = customers.select_dtypes(include='number')
customers_numeric.agg(['max', 'mean'])
copy
id(cusotmers), id(customers.copy)
customers.equals(customers_copy)
multiIndex
pd.read_csv('', sep='\t', index = ['ID', 'Martial_Status'])
customers.set_index = ['ID', 'Martial_Status'], inplace = True)
customers.swapleve()
customers.sort_index()
customers.loc[['Single', 'Alone']]
customers.loc[['Single', 'Alone'], :]
customers.loc[(['Single', 'Alone'], [5524,2114]), :]
customers.loc[(slice(None), 2214), 'Income']
customers.loc[pd.indexSlice[:, 2214]]