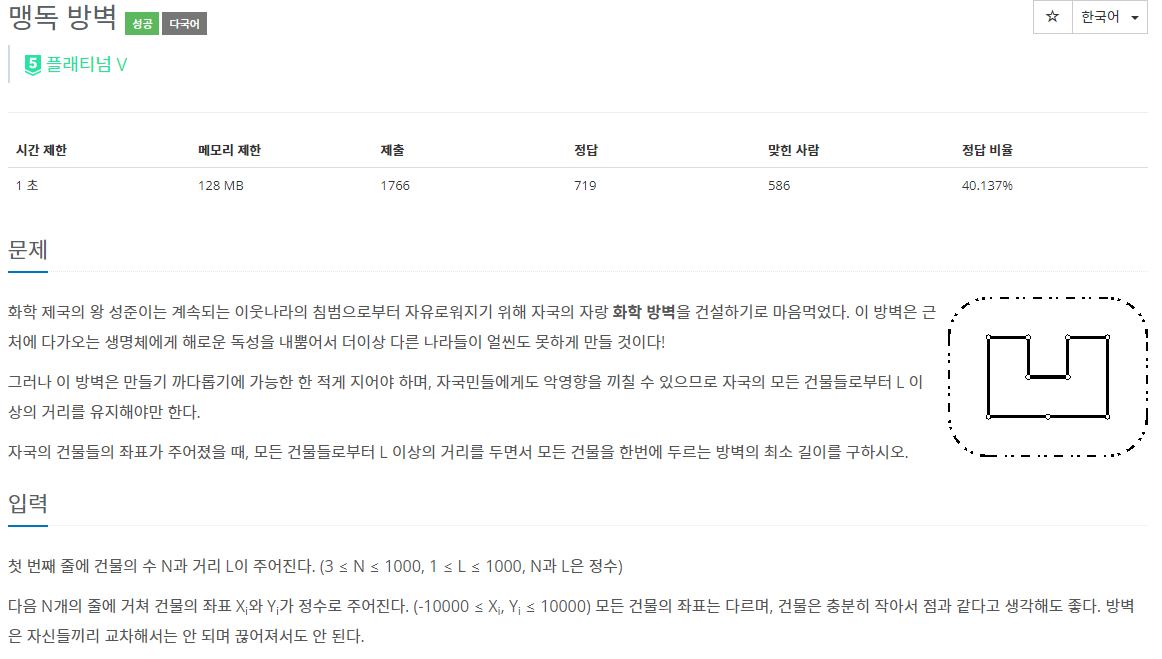
문제를 처음 보고 처음에 직관적으로 아 이거 그냥 볼록 껍질 구하고 원 하나 더하면 되는거 아닌가 생각을 했었는데 정작 문제를 읽다가 오히려 이해가 더 안돼서 좀 돌아갔던 문제였다.
볼록 껍질의 둘레를 구해서 반지름이 L인 원의 둘레와 더해주면 된다.
왜 그런가는 사실 너무 당연하기 때문에 그냥 그림을 그려보면 알 수 있다.
코드
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#ifdef LOCAL
constexpr bool local = true;
#else
constexpr bool local = false;
#endif
#define ll long long
#define FASTIO ios_base::sync_with_stdio;cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
#define debug if constexpr (local) std::cout
#define endl '\n'
ll fx, fy;
vector<pair<ll, ll>> dot;
vector<pair<ll, ll>> edges;
bool cmp(pair<ll, ll> a, pair<ll, ll> b){
if (a.second != b.second) return a.second < b.second;
return a.first < b.first;
}
bool _cmp(pair<ll, ll> a, pair<ll, ll> b){
ll l = (b.first - fx) * (a.second - fy);
ll r = (a.first - fx) * (b.second - fy);
if (l != r) return l < r;
if (a.second != b.second) return a.second < b.second;
return a.first < b.first;
}
ll ccw(pair<ll, ll> a, pair<ll, ll> b, pair<ll, ll> c){
return (b.first-a.first)*(c.second-b.second)-(c.first-b.first)*(b.second-a.second);
}
void solve(){
int N, L; cin >> N >> L;
dot.clear();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++){
ll x, y; cin >> x >> y;
dot.push_back({x, y});
}
sort(dot.begin(), dot.end(), cmp);
fx = dot[0].first; fy = dot[0].second;
sort(dot.begin()+1, dot.end(), _cmp);
//for (auto &i : dot) debug << i.first << ' ' << i.second << endl;
stack<int> task;
task.push(0);
task.push(1);
int next = 2;
while (next < N){
while (task.size() >= 2){
ll A, B;
B = task.top(); task.pop();
A = task.top();
// if ccw(A, B, next) > 0 => B is edge
if (ccw(dot[A], dot[B], dot[next]) > 0){
task.push(B);
break;
}
}
task.push(next);
next++;
}
debug << task.size() << endl;
edges.clear();
while (!task.empty()){
int t = task.top(); task.pop();
edges.push_back({dot[t].first, dot[t].second});
}
double len = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < edges.size(); i++){
int cur = i;
int next = (i+1)%edges.size();
ll x = (edges[cur].first - edges[next].first);
ll y = (edges[cur].second - edges[next].second);
double dist = sqrt(x*x+y*y);
len += dist;
}
len += 3.141592 * L * 2;
cout.precision(8);
cout << round(len);
}
int main(){
FASTIO;
solve();
}