✅ What I did today
- Project BCA
📝 Things I Learned
🏷️ Unity :: Quaternion.Inverse()
Quaternion.Inverse() returns the inverse of a given quaternion. In practical terms, it gives you the rotation that exactly "undoes" the original rotation. When you multiply a quaternion by its inverse, you get the identity rotation (i.e., no rotation).
How to Use It in Unity
Here's a simple example:
// Suppose we have a quaternion representing a rotation:
Quaternion originalRotation = transform.rotation;
// Get the inverse of that rotation:
Quaternion inverseRotation = Quaternion.Inverse(originalRotation);
// Applying the inverse rotation will cancel out the original rotation:
transform.rotation = originalRotation * inverseRotation; // This results in no rotation (identity)Key Points to Remember
- Order Matters:
Quaternion multiplication is not commutative. When calculating relative rotations, the order of multiplication is important. - Normalization:
Ensure your quaternions are normalized (i.e., have a unit length) when performing inverse operations, as Unity quaternions typically are.
🎮 Project BCA
Moving pieces using robotic arm
Move Continously
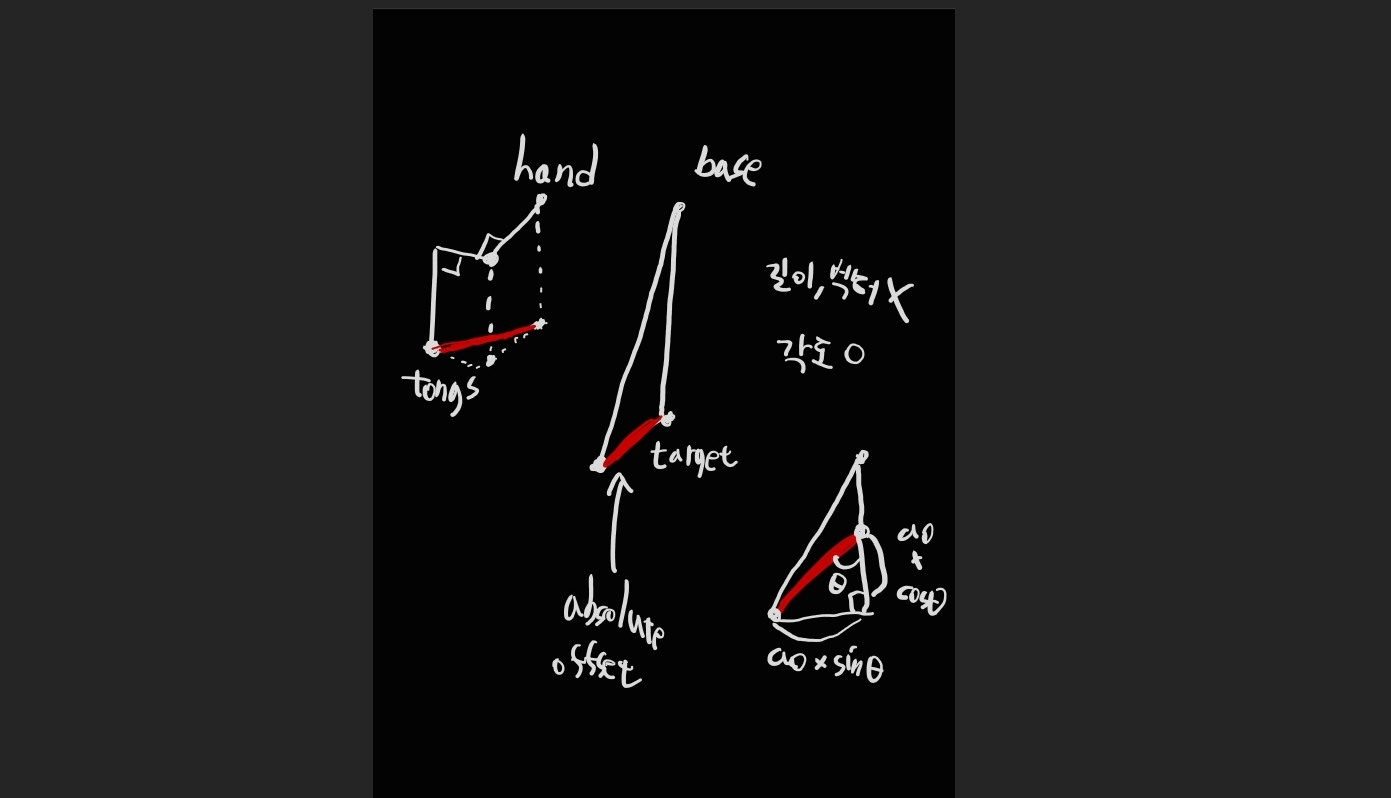
- y_axis의 각도가 이상하게 틀어졌던 건 rotation이 아니라 localRotation에 각도를 적용해서 그랬던 것. y_axis의 회전 각도는 월드 좌표계 기준으로 구해놔서 localRotatino에 넣으면 안됐다.
- SetAngle()은 base와 target까지의 거리가 달라질 때마다 결과가 바뀐다. 그래서 Update()에 넣었을 때 한 번에 가는게 아니라 여러 번의 계산을 거쳐서 부동 소수점 한계까지 가고서야 연산을 멈췄던 것으로 추정됨. 실시간으로 변동되는 팔의 위치가 아니라 절대적인 계산 결과를 넣어야 함.
- 진짜 target에 닿기 위해 길이도 줄이고 각도도 덜 돌려야 하는데, 길이는 매직 넘버로 이미 줄여놨고, 각도만 생각하면 된다. 각도는 tongs와 hand의 상대적 위치 정보를 이용하면 구할 수 있다.
- Fold_Arm() 해놓기 전에 표준 자세 (Init_Arm()으로 초기화해두기) 기준으로 hand의 부모 part의 xz평면 방향 벡터와 hand -> tongs의 xz평면 방향 벡터를 Angle()에 넣어 각도를 구한다. Distance()로 길이도 구해놓는다.
- target과 tongs까지의 거리에 구해뒀던 offset의 길이와 각도를 이용하여 되돌려야 하는 각도 오프셋을 atan2()로 구한다.
- Atan2의 결과가 rad라는 사실을 인지하지 못하고 Quaternion.Euler에 결과값을 그대로 넣었다가 어디서 잘못됐는지 한참을 헤맴
void Start()
{
y_axis_part_rotation_goal = y_axis_part.rotation; // 이상한 초기값으로 가버리지 않도록 현재 회전으로 초기화
hand_y_offset = -tongs_part.localPosition.y * 110; // 원 교점 구할 때 쓰이는 손 길이
r1 = (hand_part.position - x_axis_part_2.position).magnitude;
r2 = (x_axis_part_2.position - x_axis_part.position).magnitude;
Init_Arm();
Set_Hand_Tongs_Offset();
Fold_Arm();
}
private void Init_Arm()
{
y_axis_part.localRotation = Quaternion.Euler(-90, 0, 0);
x_axis_part.localRotation = Quaternion.Euler(-90, 0, 0);
x_axis_part_2.localRotation = Quaternion.Euler(90, 0, 0);
hand_part.localRotation = Quaternion.Euler(90, 0, 0);
}
private void Set_Hand_Tongs_Offset()
{
Vector3 handPosXZ = hand_part.position;
Vector3 tongsPosXZ = tongs_part.position;
handPosXZ.y = 0;
tongsPosXZ.y = 0;
hand_tongs_distance = Vector3.Distance(handPosXZ, tongsPosXZ);
Vector3 handToXAxis = hand_part.position - x_axis_part.position;
Vector3 tongsToHand = tongs_part.position - hand_part.position;
handToXAxis.y = 0;
tongsToHand.y = 0;
hand_tongs_angle = Vector3.Angle(handToXAxis, tongsToHand);
bonus_h = hand_tongs_distance * Mathf.Cos(hand_tongs_angle * Mathf.Deg2Rad);
bonus_w = hand_tongs_distance * Mathf.Sin(hand_tongs_angle * Mathf.Deg2Rad);
}
private void Fold_Arm()
{
x_axis_part_rotation_goal = Quaternion.Euler(-90, 0, 0);
x_axis_part_2_rotation_goal = Quaternion.Euler(0, 0, 0);
hand_part_rotation_goal = Quaternion.Euler(180, 0, 0);
}
void Update()
{
if (target_to_reach == null) return;
Rotate_To_Goal_Continously();
}
private void Rotate_To_Goal_Continously()
{
y_axis_part.rotation = Quaternion.RotateTowards(y_axis_part.rotation, y_axis_part_rotation_goal, move_time); // local이 아니라 월드 좌표계 기준 회전 해야 함
x_axis_part.localRotation = Quaternion.RotateTowards(x_axis_part.localRotation, x_axis_part_rotation_goal, move_time);
x_axis_part_2.localRotation = Quaternion.RotateTowards(x_axis_part_2.localRotation, x_axis_part_2_rotation_goal, move_time);
hand_part.localRotation = Quaternion.RotateTowards(hand_part.localRotation, hand_part_rotation_goal, move_time);
}
public void SetTarget(Transform target, float time)
{
target_to_reach = target;
move_time = time;
Set_Angle_Offset();
Set_Y_Rotation();
Set_X_Axis_Angles();
}
private void Set_Angle_Offset()
{
Vector3 a = target_to_reach.position - x_axis_part.position;
a.y = 0;
float h = a.magnitude;
angle_offset = Mathf.Atan2(bonus_w, h + bonus_h) * Mathf.Rad2Deg;
}
private void Set_Y_Rotation()
{
Vector3 direction = target_to_reach.position - y_axis_part.position;
direction.y = 0; // 불연속적 계산 방지
float angle = Vector3.SignedAngle(Vector3.forward, direction, Vector3.up);
y_axis_part_rotation_goal = Quaternion.Euler(-90, angle - angle_offset, 0);
}
private void Set_X_Axis_Angles()
{
(float angle2, float angle3) = Find_Angle_Set();
if (float.IsNaN(angle2) || float.IsNaN(angle3)) return;
x_axis_part_rotation_goal = Quaternion.Euler(angle2, 0, 0);
x_axis_part_2_rotation_goal = Quaternion.Euler(angle3, 0, 0);
float angle1 = 90 - angle2 - angle3;
hand_part_rotation_goal = Quaternion.Euler(angle1, 0, 0);
}
Arm basic animation
public void SetTarget(Vector3 point, float time)
{
move_time = time;
Sequence seq = DOTween.Sequence();
seq.AppendCallback(() => Set_Course_Dot(point + new Vector3(0, 0.5f, 0), move_time));
seq.AppendInterval(move_time + 0.2f);
seq.AppendCallback(() =>
{
Set_Course_Dot(point, move_time / 2);
});
}Transform을 이용하던 기존 코드를 Vector3로 변경하여 좀 더 유연하게 타겟 설정하게 바꿈.
DoTween의 Sequnece로 메서드 순차 진행 제어.
private void Fold_Arm()
{
x_axis_part.DOLocalRotate(new Vector3(-90, 0, 0), 1f);
x_axis_part_2.DOLocalRotate(Vector3.zero, 1f);
hand_part.DOLocalRotate(new Vector3(180, 0, 0), 1f);
}코드가 지저분해지고 시간도 정확하게 맞추기 힘든 RotateToward 대신 Dotween의 DOLocalRotate 사용.
이동할 거리가 달라지면 움직이는 속도도 달라져서 부자연스러워 보일수도 있지만, 로봇 팔이 느리게 움직여서 답답해지면 더 큰 문제.
Grip with tongs
- 집게들의 부모인 tongs_part의 피벗과 집게들의 피벗이 모두 같아서, 적절하게 회전을 하기가 불가능했음
- RotateAround()를 사용하자니 DoLocalRotate()로 팔이 움직이고 있어서 뭔가 오류가 나거나 컴퓨터에 따라 의도하지 않은 움직임이 나타날까 우려됨
- 블랜더에서 애니메이션 만드는 건 아직 숙련도가 부족하기도 하고, 속도나 집는 정도 등을 정확히 조절하기가 번거로울 것 같았음.
- 기존 계층 구조에 집게 별 부모를 하나씩 더 추가하고, 새 부모의 피벗이 각 집게의 매시 렌더러의 중심을 가리키도록 함.
- 이후 새 부모의 localRotation의 x축을 증가시키면 집게를 집는 애니메이션을 만듦.
- 게임 시작 때 동적으로 결정하기보다 에디터 코드를 통해 정적으로 결정해놓는게 나을 것 같아서 에디터 코드 사용.
- 까지도 필요 없고, lookat 후의 rotation을 ctrl+c 했다가 게임을 끈 뒤 ctrl+v하여 코드 없이 적용.
- GetChild()로 tongs_part의 자식들이자 각 집게의 부모들을 배열에 넣어놓았다. GetChild()는 손자 오브젝트는 가져오지 않음.
public void Open_Tongs()
{
foreach (Transform tongs in tongs_arr)
tongs.DOLocalRotate(tongs.transform.localRotation.eulerAngles - new Vector3(8, 0, 0), 1f);
}
public void Grip_Tongs()
{
foreach (Transform tongs in tongs_arr)
tongs.DOLocalRotate(tongs.transform.localRotation.eulerAngles + new Vector3(8, 0, 0), 1f);
}Move a piece to a specific position
- MoveTo()가 실행될 때 현재 AI의 턴이라면 roboticArm.MovePieceToPos(GameObject piece, Vector3 moveToPos, float time)를 호출.
- (해당 기물의 position + 메시 렌더러 꼭대기까지의 높이 + 0.3f)를 타겟으로 지정.
- 끝났다면 (해당 기물의 position + 메시 렌더러 꼭대기까지의 높이)를 다음 타겟으로 지정하며 Grip_Tongs() 호출.
- 끝났다면 기물을 tongs_part의 자식으로 설정함. 월드 좌표계 기준 rotation도 현재 어땠는지 저장해둠.
- (moveToPos + 0.3f)를 타겟으로 지정.
- 끝났다면 (moveToPos + 메시 렌더러 꼭대기까지의 높이)를 다음 타겟으로 지정..
- 끝났다면 현재 기물의 월드 좌표계 기준 rotation과 이전 rotation을 비교하여 그 차이만큼 hand_part를 회전함.
- 끝났다면 부모 관계를 끊고 씬에 놔둠. Open_Tongs()과 Fold_arm() 호출.
발견된 문제
- 매직 넘버로 빼주었던 길이가 팔이 뻗는 길이에 따라 동적으로 변해야 한다는 사실을 발견. 매직 넘버가 아닌 실제 논리적으로 맞는 값을 계산하여 넣어주어야 함. 일단 눈에 띄는 문제는 아니니 향후 문제가 되면 고치기.
- 기물의 각도 보정을 위해 손 부분을 분리하여 모델링해주니 이전보다 깊게 들어가는 문제 발생.
tongs_part.localPosition.y을 사용해서 그랬던 것. hand_part와 tongs_part의 y 좌표 차이를 계산하는 것으로 변경. - rotation.eulerAngles를 직접 뺐더니 각도 보정을 제대로 해주지 못함. euler는 짐벌락 뭐시기 문제가 일어난다고 함. y축에 대한 회전만 계산하는거라 너무 trivial해서 문제 안될 것 같았는데 문제가 된다니 일단 바꿈.
- 제일 치명적 문제는 사실 hand_part_2의 localRotation을 돌려놓고, 이를 반영하지도 않고 월드 좌표계 상 기물의 이전 각도, 이후 각도의 차이를 localRotate하려고 했던게 문제. hand_part_2의 localRotation를 더해줘서 해결.
/// <summary>
/// 로봇 팔을 이용해 기물을 특정 위치로 움직인다
/// </summary>
public void MovePieceToPos(GameObject piece, Vector3 moveToPos, float time)
{
Vector3 piecePos = piece.transform.position;
float pieceHeight = piece.transform.GetComponent<MeshRenderer>().bounds.size.y;
Quaternion pieceRotation = piece.transform.rotation;
Sequence seq = DOTween.Sequence();
seq.AppendCallback(() => Set_Course_Point(piecePos + new Vector3(0, pieceHeight + 0.5f, 0), time)); // 기물 머리 위까지 간다
seq.AppendInterval(time + 0.2f);
// 기물을 집는다
seq.AppendCallback(() =>
{
Set_Course_Point(piecePos + new Vector3(0, pieceHeight, 0), time / 2);
Grip_Tongs(time / 2);
});
seq.AppendInterval(time / 2 + 0.1f);
// 기물을 원하는 위치 위까지 옮긴다
seq.AppendCallback(() =>
{
piece.transform.SetParent(tongs_part.transform);
Set_Course_Point(moveToPos + new Vector3(0, pieceHeight + 0.5f, 0), time);
});
seq.AppendInterval(time + 0.2f);
// 기물을 내려놓는다
seq.AppendCallback(() =>
{
Set_Course_Point(moveToPos + new Vector3(0, pieceHeight, 0), time / 2);
hand_part_2.DOLocalRotate((hand_part_2.localRotation * pieceRotation * Quaternion.Inverse(piece.transform.rotation)).eulerAngles, time / 2);
});
seq.AppendInterval(time / 2 + 0.1f);
// 기물을 놓고 제자리로 돌아간다
seq.AppendCallback(() =>
{
piece.transform.SetParent(null);
Open_Tongs(time / 2);
Fold_Arm();
});
}
