Numpy란?
요즘 1년간 거의 매일 진행해온 수학 공부가 결실을 맺고 있는 것 같아 기분이 좋다. 머신러닝 공부를 최근에 본격적으로 시작하면서 수학 때문에 막힌 적은 크게 없는 것 같다 (IQ가 몇 점 부족하여 발생하는 문제는 빈번하다).
아무튼, Numpy란 'multidimensional arrays'에 대한 연산을 용이하게 해주는 라이브러리다. 그냥 기본 리스트 혹은 딕셔너리를 사용하는 것보다 훨씬 빠르다. 특히 'gradient descent'를 생각한다면 for loop을 돌려 parameter를 업데이트 해주는 것보다 np.dot 혹은 np.matmul 등의 기능을 활용하면 훨씬 빠르게 행렬 연산을 진행할 수 있다. 이런 얘기는 추후 machine learning 관련 포스팅에서 더 자세히 하도록 하겠다.
Why Numpy?
'vectorization'은 머신러닝에 알고리즘에 매우 중요하다. 아래 코드를 살펴보자.
import numpy
import time
size = 1000000
list1 = range(size)
list2 = range(size)
array1 = numpy.arange(size)
array2 = numpy.arange(size)
initialTime = time.time()
resultantList = [(a * b) for a, b in zip(list1, list2)]
print("Time taken by Lists :",
(time.time() - initialTime),
"seconds")
initialTime = time.time()
resultantArray = array1 * array2
print("Time taken by NumPy Arrays :",
(time.time() - initialTime),
"seconds")> Time taken by Lists : 1.1984527111053467 seconds
Time taken by NumPy Arrays : 0.13434123992919922 seconds
리스트를 'vectorize'하여 행렬처럼 대하면 훨씬 빠르게 결과를 산출할 수 있다.
기본문법
- 행렬 생성
B = np.array([[0, 1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6, 7],
[8, 9, 10, 11]])- B 모양 확인
print(B.shape)> (3, 4)- 3 X 4 '0' 행렬 생성, 3 x 3 Identity 행렬 생성
print(np.zeroes((3,4)))
print(np.eye(3))[[0. 0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0. 0.]]
[[1. 0. 0.] [0. 1. 0.] [0. 0. 1.]]
Indexing and Slicing
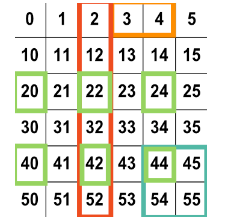
> Z= np.array([[0,1,2,3,4,5],
[10,11,12,13,14,15],
[20,21,22,23,24,25],
[30,31,32,33,34,35],
[40,41,42,43,44,45],
[50,51,52,53,54,55]])
# Construct `Z_green`, `Z_red`, `Z_orange`, and `Z_cyan`:
Z_green = Z[(2,4), ::2]
Z_red = Z[:, 2]
Z_orange = Z[0, 3:5]
Z_cyan = Z[(4,5), 4:6]크게 어려울 건 없다. 리스트 인덱싱과 비슷하다고 생각하면 된다.
메모리 공간을 고려했을때 Z_green 등은 그냥 'view'이다. Slicing을 하여 변수를 선언한다고 새로운 메모리 공간이 할당 되는 것은 아니다. 마찬가지로 새로운 객체를 생성하고 싶다면 Z[:, 2].copy() 를 선언하면 된다.
Indirect Addressing
'Boolean Mask' 또는 'Indices'로 구성된 array를 통해 indxing을 할 수도 있다.
from numpy.random import default_rng
rng = default_rng(12345)
x = rng.integers(0, 20, 15)
print(x)
> [13 4 15 6 4 15 12 13 19 7 16 6 11 11 4]
inds = np.array([3, 7, 7, 12])
print(x[inds])
> [6 13 19 11]
mask_mult_3 = (x > 0) & (x % 3 ==0)
print("x:", x)
print("mask_mult_3:", mask_mult_3)
print("==> x[mask_mult_3]:", x[mask_mult_3])
>x: [13 4 15 6 4 15 12 13 19 7 16 6 11 11 4]
>mask_mult_3: [False False True True False True True False False False False True
False False False]
>==> x[mask_mult_3]: [15 6 15 12 6]응용
20까지의 소수를 모두 찾는 알고리즘을 작성해보자. 에라토스테네스의 체를 numpy를 활용하여 작성할 수 있다. 사실 불필요하며 코딩테스트에서는 그냥 리스트를 활용할 것 같다.
from math import sqrt
def sieve(n):
is_prime = np.empty(n+1, dtype=bool) # the "sieve"
# Initial values
is_prime[0:2] = False # {0, 1} are _not_ considered prime
is_prime[2:] = True # All other values might be prime
m = int(sqrt(n)) + 1
for i in range(2, m):
if is_prime[i] == True:
for j in range(i+i, n+1, i):
is_prime[j] = False
return is_prime
# Prints your primes
print("==> Primes through 20:\n", np.nonzero(sieve(20))[0])
>==> Primes through 20:
[2 3 5 7 11 13 17 19]