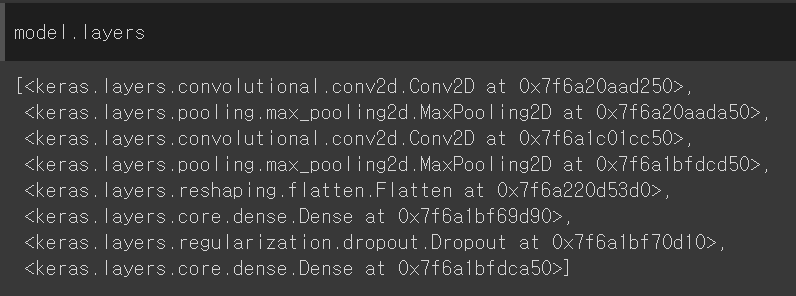
- 모델 layers
8개의 객체를 리스트로 가짐
- conv 층의 가중치 크기 확인
weights[0] = 가중치, weights[1] = 절편
conv = model.layers[0]
print(conv.weights[0].shape, conv.weights[1].shape)(3, 3, 1, 32) (32,)
-> 3x3x1 필터 32개
📌 층의 가중치 시각화
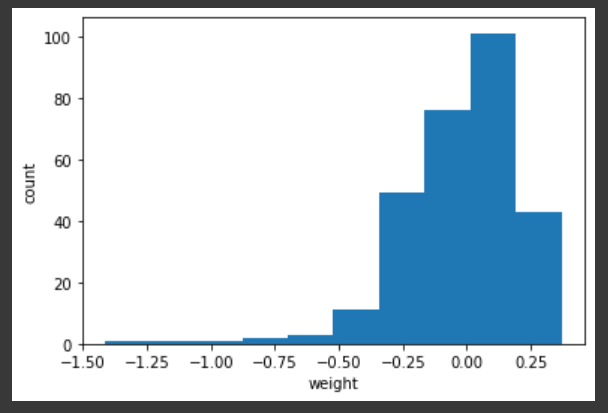
📍 1. 히스토그램
- 가중치 값의 분포 (3x3x1x32 개)
conv_weights = conv.weights[0].numpy()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.hist(conv_weights.reshape(-1, 1))
plt.xlabel('weight')
plt.ylabel('count')
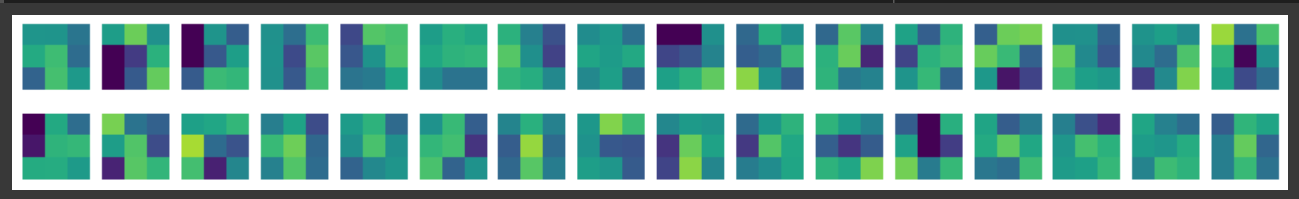
plt.show()📍 2. 3x3 이미지
- vmin보다 작은 값은 vmin으로, vmax보다 큰 값은 vmax로
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 16, figsize=(15,2))
for i in range(2):
for j in range(16):
axs[i, j].imshow(conv_weights[:,:,0,i*16 + j], vmin=-0.5, vmax=0.5)
axs[i, j].axis('off')
plt.show()📌 Functional API
-
합성곱 층의 활성화 출력 시각화
-
add를 사용하지 않고 함수처럼 호출하여 모델의 층을 자유롭게 조합 가능
-
Input() : InputLayer 객체 생성하여 첫 번째 층(dense1)에 입력 필요
-
DATA SET
(train_input, train_target), (test_input, test_target) = keras.datasets.fashion_mnist.load_data()
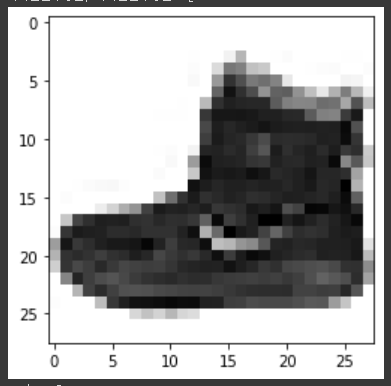
plt.imshow(train_input[0], cmap='gray_r')
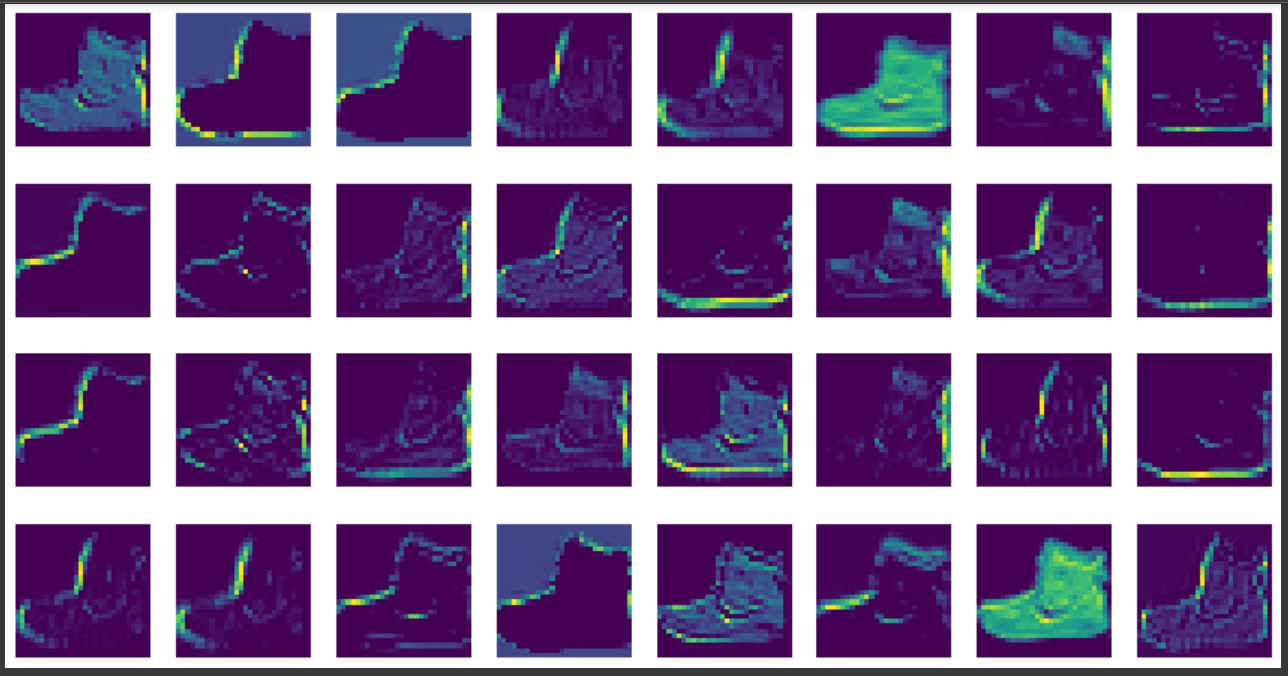
plt.show()📍 첫 번째 특성 맵 시각화
- conv_acti : Sequential Model 의 input과 첫번째 층 Conv2D 객체의 출력값으로 만든 Model
conv_acti = keras.Model(model.input, model.layers[0].output)
inputs = train_input[0:1].reshape(-1, 28, 28, 1)/255.0
feature_maps = conv_acti.predict(inputs)
print(feature_maps.shape)(1, 28, 28, 32)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(4, 8, figsize=(15,8))
for i in range(4):
for j in range(8):
axs[i, j].imshow(feature_maps[0,:,:,i*8 + j])
axs[i, j].axis('off')
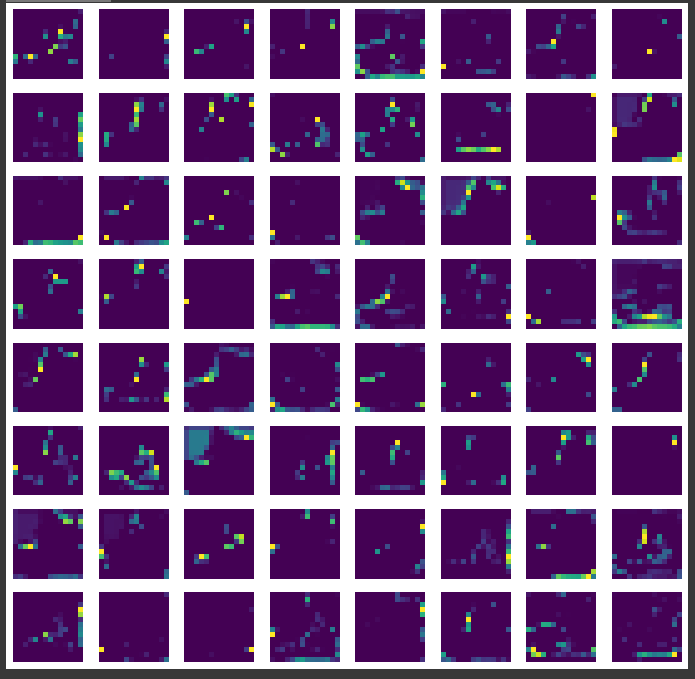
plt.show()📍 두 번째 특성 맵 시각화
- 두 번째 합성곱 층 : Conv2D -> Maxpooling -> Conv2D_1 이므로 layers[2]
- Maxpooling 으로 크기 1/2 감소
- 64개 (= 필터)
conv2_acti = keras.Model(model.input, model.layers[2].output)
feature_maps = conv2_acti.predict(inputs)
print(feature_maps.shape)(1, 14, 14, 64)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(8, 8, figsize=(12,12))
for i in range(8):
for j in range(8):
axs[i, j].imshow(feature_maps[0,:,:,i*8 + j])
axs[i, j].axis('off')
plt.show()-> 층이 깊어질 수록 고수준 추상적 학습