참조
- Node.js 공식문서
https://expressjs.com/ko/
Express란
- 웹 및 모바일 앱을 위한 간결하고 유연한 Node.js 웹 애플리케이션 프레임워크다.
Express 실행방법
mkdir 폴더이름 cd 폴더이름 // 폴더로 들어감 npm init //package.json 파일 생성 npm install express --save npm install express
Express 기본 형태
const express = require('express') //express 불러옴 const app = express() //express를 실행한 객체를 app에 할당 const port = 3000 //3000번 포트 설정 app.get('/', (req, res) => { //app에 get + 엔드포인트가 '/'인 요청이 올 때 'Hello World'를 리턴한다. res.send('Hello World!') }) app.listen(port, () => { //app에 3000번 포트를 연결 console.log(`Example app listening at http://localhost:${port}`) })
기본 라우팅
- 라우팅은 URI(경로) 및 특정한 HTTP 요청 메소드를 통한 요청에 대한 응답을 결정하는 것이다.
기본 구조
app.METHOD(PATH, HANDLER) //app : express의 인스턴스 //method : HTTP 요청 메소드 //path : 서버에서의 경로 //handler : 라우트가 일치할 때 실행되는 함수ex)
app.get('/', function (req, res) { res.send('Hello World!'); }); app.post('/', function (req, res) { res.send('Got a POST request'); }); app.put('/user', function (req, res) { res.send('Got a PUT request at /user'); }); app.delete('/user', function (req, res) { res.send('Got a DELETE request at /user'); });
라우팅
라우팅 기본 예시
var express = require('express'); var app = express(); // respond with "hello world" when a GET request is made to the homepage app.get('/', function(req, res) { res.send('hello world'); });라우트 경로
- 라우트 경로는 요청 메소드와의 조합을 통해, 요청이 이뤄질 수 있는 엔드포인트를 정의한다.
ex)
app.get('/', function (req, res) {
res.send('root');
});
app.get('/about',function(req,res){
res.send('about')
})
app.get('/random.text',function(req,res){
res.send('random.text')
})라우트 핸들러
- 곧 배우게 될 미들웨어와 비슷하게 작동하는 여러 콜백함수를 제공하여 요청을 처리한다. 유일한 차이점은 이러한 콜백은 next('route')를 호출하여 나머지 라우트 콜백을 우회할 수 있다는 점이다.
ex) 2개의 콜백함수가 하나의 라우트를 처리
app.get('/example/b', function (req, res, next) { console.log('the response will be sent by the next function ...'); next(); //다음 콜백함수를 연결 }, function (req, res) { res.send('Hello from B!'); });ex) 하나의 콜백함수 배열은 하나의 라우트를 처리
var cb0 = function (req, res, next) { console.log('CB0'); next(); } var cb1 = function (req, res, next) { console.log('CB1'); next(); } var cb2 = function (req, res) { res.send('Hello from C!'); } app.get('/example/c', [cb0, cb1, cb2]);ex) 독립적인 함수와 배열의 조합은 하나의 라우트를 처리
var cb0 = function(req,res,next){ console.log('CB0') next(); } var cb1 = function(req,res,next){ console.log('CB1') next(); } app.get('/example/d',[cb0,cb1],function(req,res,next){ console.log('the response will be sent by the next function...') next() },function(req,res){ res.send('Hello from D!') })
응답 메소드
- 응답 object에 대한 메소드(res)는 응답을 클라이언트로 전송하고 요청-응답 주기를 종료할 수 있다.
메소드 설명 res.end() 응답 프로세스 종료 res.json() JSON 응답을 전송 res.send() 다양한 유형의 응답을 전송 res.sendFile() 파일을 옥텟 스트림의 형태로 전송 res.status(0 파일의 상태코드를 작성
app.route()
- 라우트 경로에 대해 체인 가능한 라우트 핸들러를 작성 할 수 있다.
app.route('/book') .get(function(req, res) { res.send('Get a random book'); }) .post(function(req, res) { res.send('Add a book'); }) .put(function(req, res) { res.send('Update the book'); });
express.Router
- 다른 경로의 라우터 모듈을 실행시키는 함수
//bird.js에 작성 var express = require('express'); var router = express.Router(); // middleware that is specific to this router router.use(function timeLog(req, res, next) { console.log('Time: ', Date.now()); next(); }); // define the home page route router.get('/', function(req, res) { res.send('Birds home page'); }); // define the about route router.get('/about', function(req, res) { res.send('About birds'); }); module.exports = router; //기본 라우터 설정
var bird = require('./birds') app.use('/birds',birds) // /birds로 끝나는 엔드포인트를 입력할 경우 birds.js로 이동
Express 앱에서 사용하기 위한 미들웨어 작성
- 미들웨어 함수란 req,res,그리고 앱의 요청-응답 주기 중 그 다음의 미들웨어 함수에 대한 엑세스 권한을 갖는 함수다.
일반적으로 next라는 이름으로 변수를 만든다.
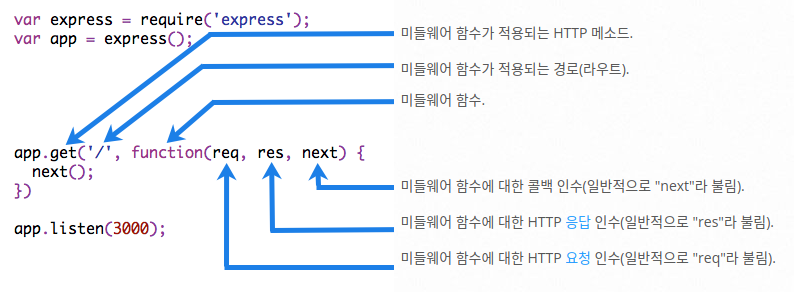
var express = require('express'); var app = express(); //미들함수 생성 var requestTime = function (req, res, next) { req.requestTime = Date.now(); next(); //다음 미들함수를 호출 }; app.use(requestTime); //미들함수를 지정하여 호출하는 함수 //미들웨어의 로드 순서는 중요하며, 먼저 로드되는 미들웨어 함수가 먼저 실행된다. //루트 경로에 대한 라우팅 이후에 myLogger가 로드되면, 루트 경로의 라우트 핸들러가 요청-응답 주기를 종료하므로 요청은 절대로 myLogger에 도달하지 못하며 앱은 “LOGGED”를 인쇄하지 않된다.. app.get('/', function (req, res) { var responseText = 'Hello World!'; responseText += 'Requested at: ' + req.requestTime + ''; res.send(responseText); }); app.listen(3000);