지난 학기 학교 알고리즘 수업을 수강하며, 정리 해 놓았던 마크다운 문서입니다. 문제시 삭제하겠습니다
7. Graphs and Graph Traversals
-
Airline routes 그래프를 이용해 표현가능
(vertex와 edge이용) -
Binary relation
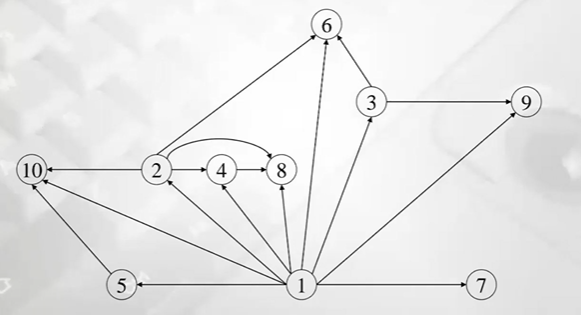
x는 y의 진 인수이다 (proper factor), S={1,2,... ,10}
y가 12라면 x!=y이고 x/y의 나머지가 0이면 x는 y의 proper factor
Directed Graph (유향 그래프)
- digraph라도 부르기도함, G=(V,E) (vertex, edge의 집합)
- V는 vertices의 집합
- E는 양끝의 V로 정의 가능 (순서중요, (v,w) != (w,v) )
- E는 edges, directed edges, arcs로 불림
- (v,w) = v -> w
- 간단하게 vw도 가능
Undirected Graph (무향 그래프)
- G=(V,E)
- V는 vertices의 집합
- E는 두개의 unordered V (ex.(v,w)=(w,v))
- 자기 자신으로 가는 edge 정의 안됨 (v,v)->x
- incident (인접한) vs adjacent (인접한)
- incident - 간선과 정점의 관계
- adjacent - 정점과 정점의 관계
Weighted Graph (가중 그래프)
- (V,E,W)의 집합
- W는 하나의 함수, edge 집합의 원소의값 실수로 mapping
- 어떤 edge e에 대해, W(e)는 e의 가중치
Graph Representations
G=(V,E), vertex의 원소의 수=n, edge의 원소의 수=m로 정의
- input size : n+m
- Adjacency matrix representation (인접 행렬 표현)
- Array of adjacency lists representaion (인접 리스트 표현)
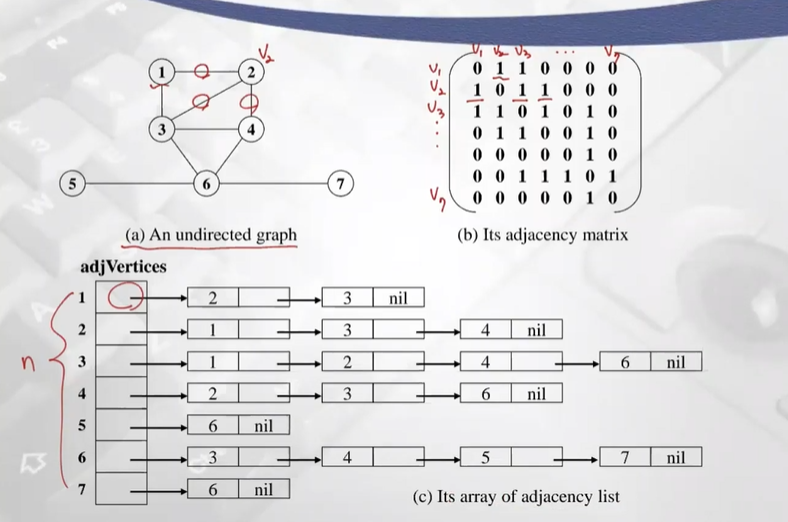
- 인접리스트 표현의 각각의 정점은 array, edge의 연결 유무에 대해 linked list로 구현
- array는 n, list는 2m -> O(n+m) space 사용
- 인접 행렬 표현 O(n^2) space 사용
v.incidentEdges() vs v.isAdjacentTo(w)
- v.incidentEdges()
- matrix : O(n) time
- list : 리스트 한번 스캔해주기 = list의 사이즈 = O(deg(v)) time
- v.isAdjacentTo(w)
- matrix : O(1) time (해당 인덱스 한번만 접근해주면됨)
- list : 두 정점중에 list 사이즈 작은것 선택->O(min(deg(v), deg(w))) time
- weighted digraph의 예
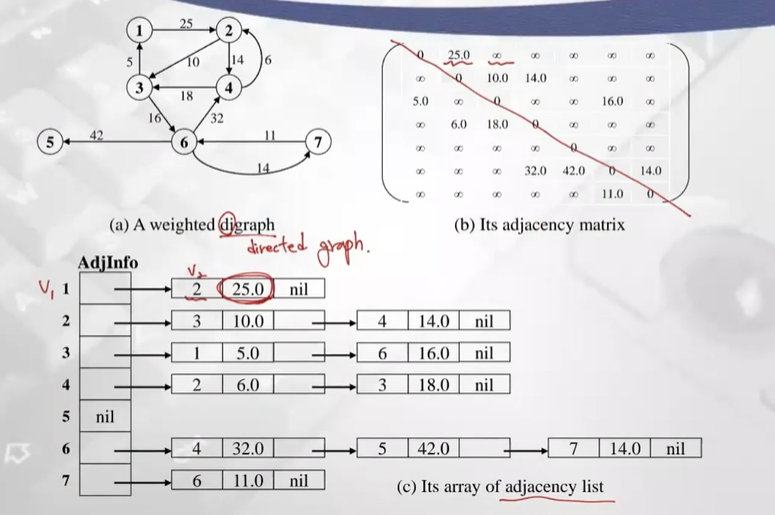
More Definitions
-
Subgraph: 어떤 G=(V,E)에 대해 G'=(V',E') of G : V' -> V and E' -> E
-
complete graph: 모든 정점쌍이 간선으로 연결되어있는 그래프
undirected graph: m=n(n-1)/2를 넘을수 x
digraph: m=n(n-1)을 넘을수 x -
Adjacency relation: 두 정점이 하나의 엣지로 연결 되는가?
-
Path
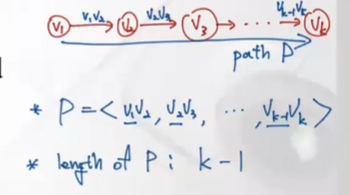
-
simple path: path상의 모든 정점들 distinct한 경우
-
reachable: 정점 v,w 가는 길존재하면->reachable
-
Connected: 그래프 모든 vertex쌍이 서로 reachable하면 connected graph (undirected graph의 경우)
-
Strongly Connected: 위와 같음 (digraph의 경우)
-
Cycle: 시작 정점과 끝 정점이 동일한 non-empty path (길이 가장 짧은 cycle: 자기자신 가리키는 cycle: self loop)
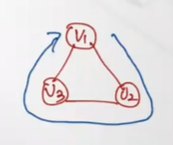 undirected graph에서 cycle 가장 작은경우 (적어도 3보단 커야한다)
undirected graph에서 cycle 가장 작은경우 (적어도 3보단 커야한다) -
simple cycle: 시작 정점과 끝 정점은 동일 나머지 정점은 path 상에 한번 나타나는 경우(distinct)
-
acyclic: 싸이클이 존재하지 않음 (ex. DAG : Directed Acyclic Graph)
-
free tree (undirected tree): 세가지 조건 만족 grpah
- connected
- acyclic
- undirected
-
undirected forest
1. acyclic
2. undirected
(connected 해도되고 안해도 됨) -
rooted tree: root가 존재하는 free tree
-
Connected component: maximal connected subgraph를 의미 (undirected graph에서)
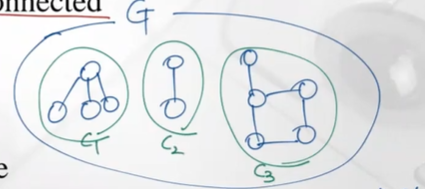 ex. 3개의 connected component
ex. 3개의 connected component
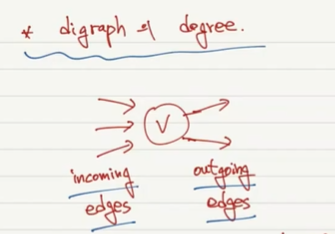
in-deg(v)=3
out-deg(v)=2
 digraph의 경우 모든 정점에 대해 in-degree의 sum은 edge의 개수 m이 된다 (outgoing edge도 반드시 어떤 정점에서는 incoming edge가 되기 때문에), out-degree도 마찬가지
digraph의 경우 모든 정점에 대해 in-degree의 sum은 edge의 개수 m이 된다 (outgoing edge도 반드시 어떤 정점에서는 incoming edge가 되기 때문에), out-degree도 마찬가지
-> 모든 정점에 대한 그냥 degree의 sum은 2m
- If an undirected graph G is connected, then m>=n-1
- If an undirected graph G is a tree, then m=n-1
- If an undirected graph G is a forest, then m<=n-1
- m이 O(n^2)에 가까우면, dense graph
- m이 O(n)에 가까우면, sparse graph
