지난 학기 학교 알고리즘 수업을 수강하며, 정리 해 놓았던 마크다운 문서입니다. 문제시 삭제하겠습니다
8. Graph optimization problems and Greedy Algorithms
optimization problems
최적의 해를 찾는 문제
비용의 측면: 비용 최소화 하기
이득의 측면: 이득 최대화 하기
가장 best한 결과 찾아내자, 어떤 일련의 선택들 optimal 되도록 하자
Greedy algorithms
선택할때 제일 이익이 되도록 선택
짧은 시간내에 best 찾기, 번복 불가
- minimum spaning tree 찾기
- single source shortest path 찾기
minimum spaning tree
input: connected, undirected graph 주어짐
spanning tree = G'=(V', E')라 하면
V`=V and E'->E and connected, acyclic해야함
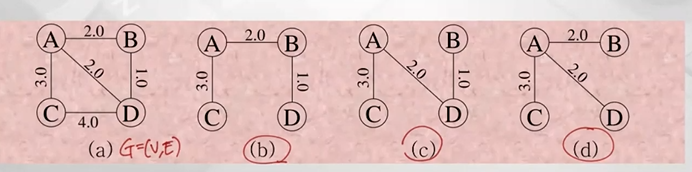
minimum weight 가지는 spanning tree찾기 -> b와 c만 만족 (최소 weight 6)
Prim's algorithm
- 임의의 starting 정점 선택 (minimum spanning tree의 루트)
- 각 iteration 마다 edge 추가
- 최소 weight 가진 edge를 tree에 추가
- 연관된 정점 또한 tree에 더함
세개의 disjoint 상태로 나눔
- Tree vertices : minimum spanning 트리에 포함할 정점
- Fringe vertices : 트리는 아니지만 tree에 포함될 후보들 (tree에 인접)
- Unseen vertices : 아직 볼 수 없는 정점
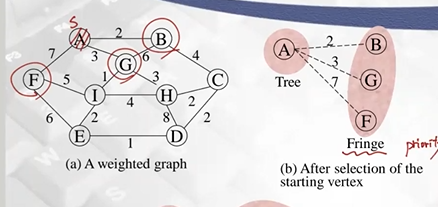
- Tree T1
- 시작 정점 A
- 인접한 정점 B,G,F를 Fringe 정점으로 업데이트
(Fringe 정점 관리하는데 우선순위 큐 좋음, O(N)번 삽입, 삭제)
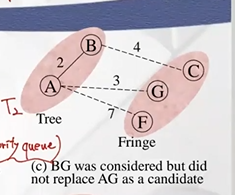
- Fringe 정점에서 가장 작은 weight가진 B를 tree로 넣기
- B에 인접한 unseen 상태의 C 를 Fringe에 추가
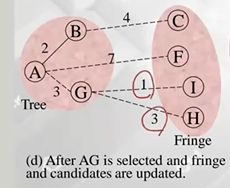
- Fringe 에서 가장 작은 weight 가진 G를 트리에 추가
- G에 인접한 unseen 상태의 I, H를 Fringe에 추가
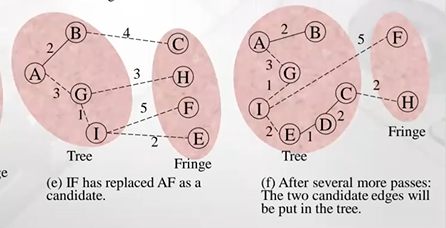
-
I 정점 tree에 추가
-
I에 인접한 F, E, H 정점 확인
-
F는 기존에 7로 갈수 있었는데 I 통하면 5 에 갈 수있음, 5로 업데이트 (decrease key), H로 가는 경우는 4인데, 기존에 3이 더작음->pass
-
Fringe 정점 존재하지 않을 때 까지 이런 과정 수행
PrimMST(G,n) // OUTLINE (m=n-1)
Initialize all vertices as unseen. // O(N) time
Select an arbitrary vertex s to start the tree; reclassify it as tree.
Reclassify all vertices adjacent to s as fringe.
--------------------//초기화 단계 (T1 생성)
While there are fringe vertices; // O(N) 번 수행
Select an edge of minimum weight between
a tree vertex t and a fringe vertex v;
Reclassify v as tree; add edge tv to the tree;
Reclassify all unseen vertices adjacent to v as fringe. // deg(v)- min-우선순위 큐
| unsorted sequence | sorted sequence | heap | |
|---|---|---|---|
| insert | O(1) | O(n) | O(logn) |
| removeMin | O(n) | O(1) | O(logn) |
| decreaseKey | O(1) | O(n) | O(logn) |
- unsorted sequence 사용한 경우
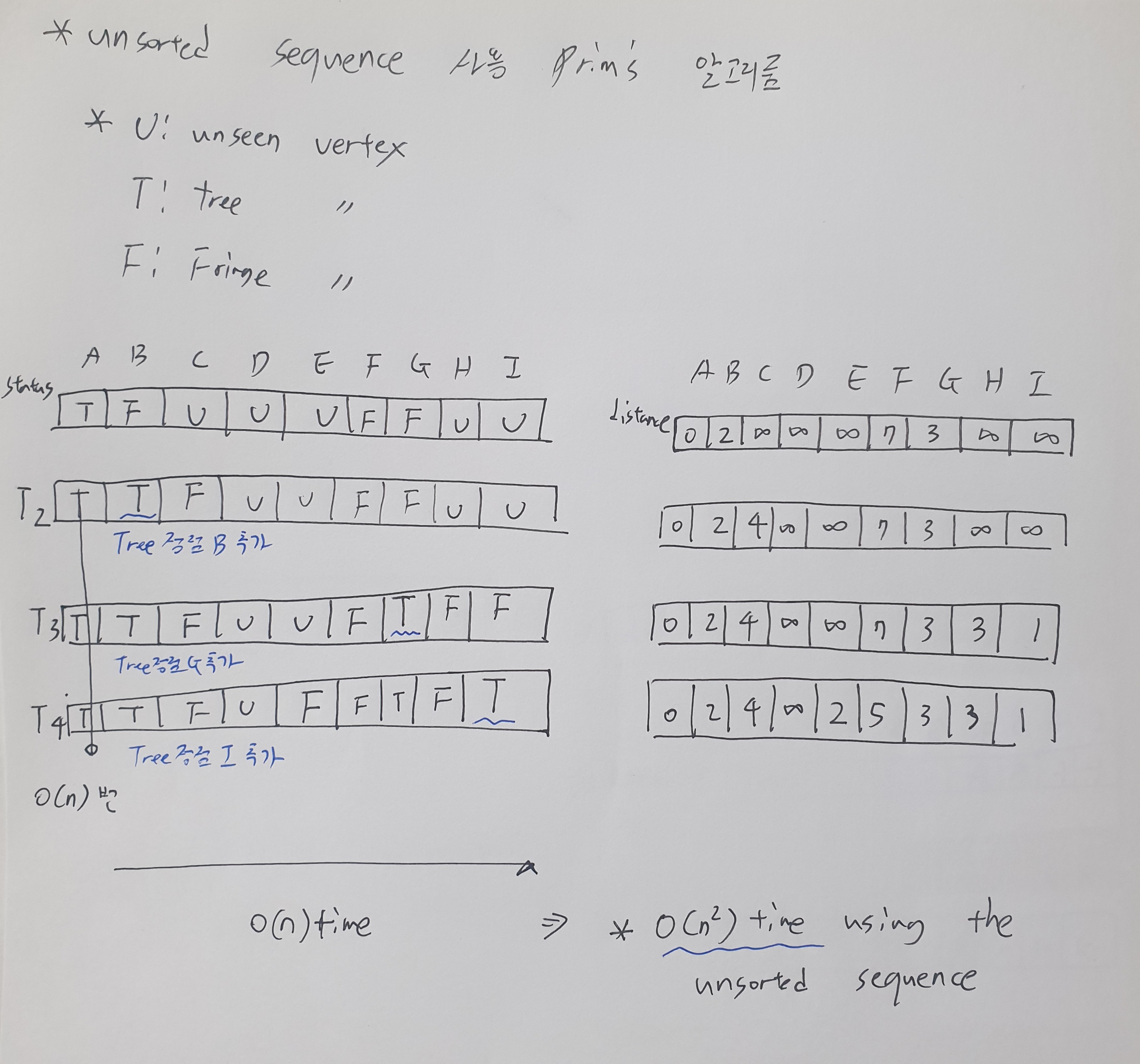
- heap 사용한 경우
- 초기화 하는데 O(N) time
- O(N)번 삽입, 삭제
- O(M)번 decrease key
- (삽입삭제: nlogn time) + (deg time : mlogn) = nlogn + mlogn (m이 n보다 큼) -> O(mlogn) time
m=o(n) (sparse graph) 이면 heap 사용이 유리, m=O(n^2) (dense graph) 이면 unsorted sequence사용이 유리
Kruskal's algorithm
minimum spanning tree 찾는 또 다른 알고리즘
sorting, min-heap이용가능 -> 두방법 모두 O(mlogm) time
KruskalMST(G,n)
R = E // R is remaining edges
F = {} // F is forest edges
while (R is not empty)
Remove the lightest (shortest) edge, vw, from R;
if (vw does not make a cycle in F) // 싸이클 발생 하지 않을때만 minimum spanning tree에 추가 (union-find ADT 사용 = disjoint set)
Add vw to F;
return F ;
// 먼저 모든 정점이 minimum spanning tree에 포함 되있다고 보는 것이고 싸이클이 발생하지 않으면 edge 를 minumum spanning tree에 추가find(u): 어떤 정점 u가 주어졌을때 u를 포함하는 set이 무엇인지 알 수 있게해줌(set id(leader) 반환)
union(u,v): u, v 가 다른 집합이면 하나의 집합으로 merge해줌
Example
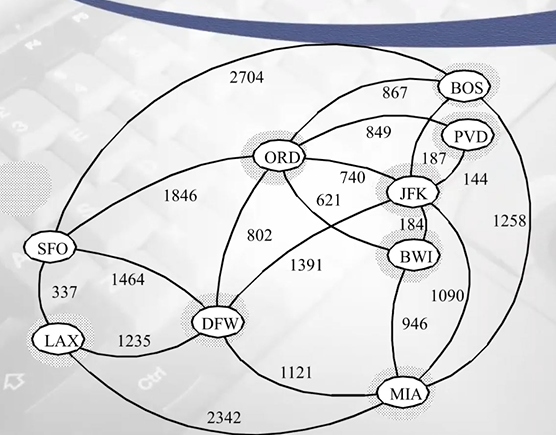
- edge에 대한 weight sorting 했다고 가정
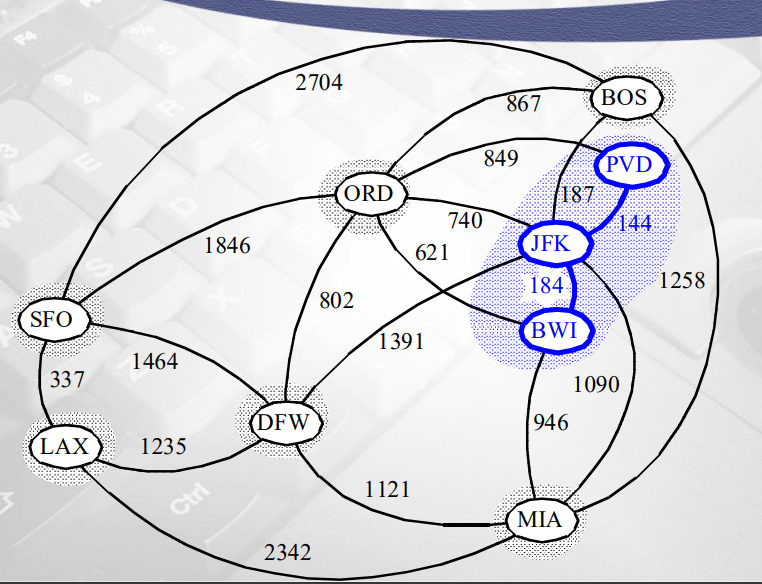
- 가장 작은 키값 144, 양끝의 정점 체크 (JKF, PVD)->서로 다른 집합이면 union
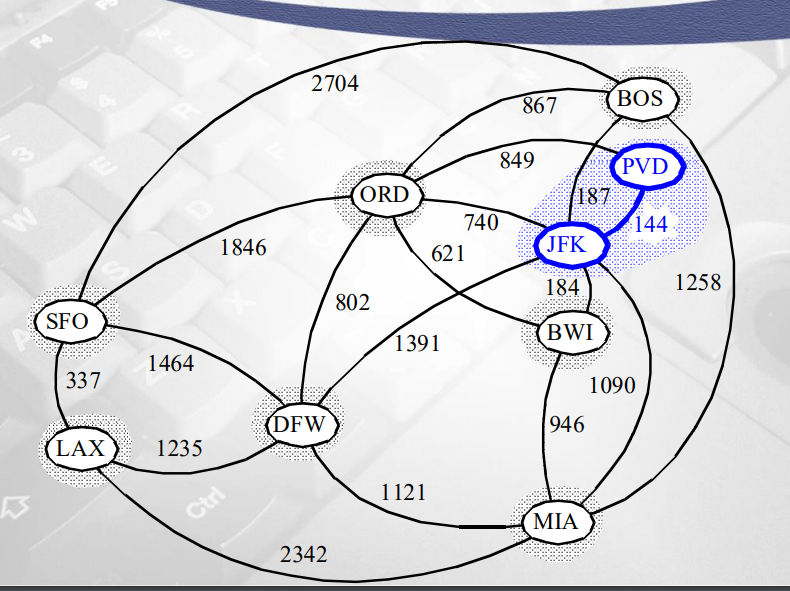
- 그다음 weight 작은 edge 184
- 양끝 정점 (JKF, BWI) 다른 집합이므로 union
-
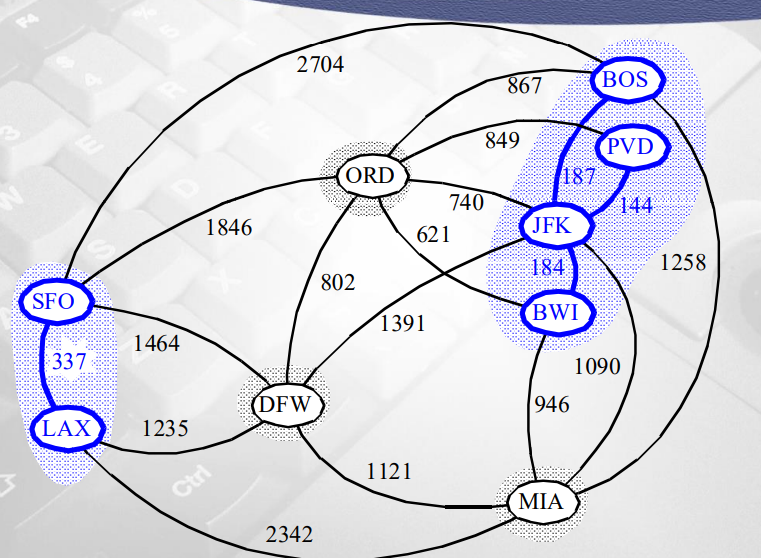
그다음 weight 작은 187
-
양끝 정점 (JFK, BOS) 서로 다른 집합-> union
-
그다음 작은 weight 337
-
양끝 정점 (SFO, LAX) 서로 다른 집합-> union
-
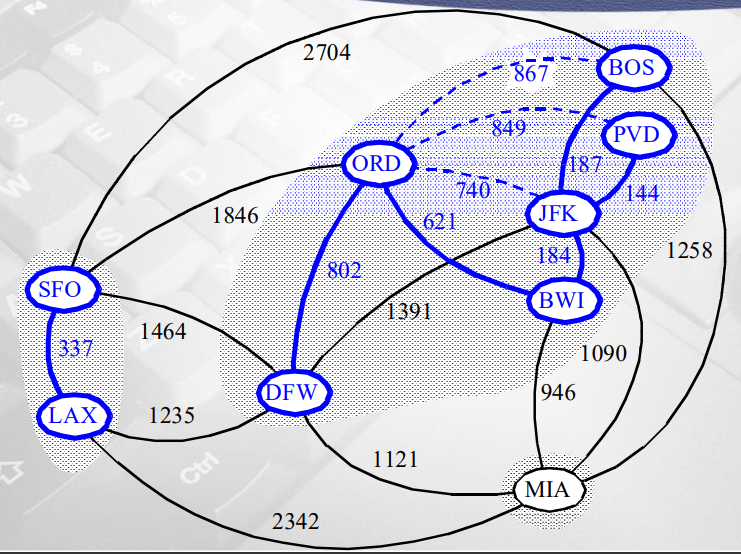
그다음 weight 작은 621
-
양끝 정점 (ORD, BWI) 서로 다른 집합 -> union
-
그 다음 weight 작은 740
-
양끝 정점 (ORD, JFK) 서로 같은 집합 -> union X
-
그 다음 802
-
양끝 정점 (ORD, DFW) 서로 다른 집합 -> union
-
그 다음 849, 867
-
둘다 같은 집합 -> union X
- 이런 방식으로 계속 진행함
- 추가되는 edge의 수가 n-1이 될때까지 진행
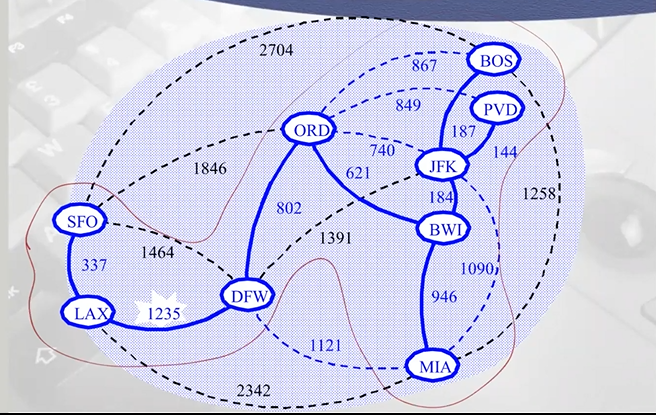
- 최종 결과 : 정점의 수 = n개, edge 수 : n-1개
분석
- sorting 이용 : O(mlogm) 에 수행
- min-heap 이용 : m개의 edges -> O(m) time에 heap 생성 (R에 대한 정보 저장)
R에서 edge 제거 -> O(logm) time
최악의 경우 while loop O(m)번 수행가능, 따라서 총 O(mlogm) time에 수행
(kruskal 알고리즘은 prim 알고리즘과 동일한 수행시간에 수행 가능함)
kruskal : O(mlogm)
prim : O(mlogn) (힙 이용)
-> m은 아무리 많아야 o(n^2), 로그의 성질에 의해
kruskal은 O(mlogn^2)이라고 볼수있고, O(2mlogn)으로 표현가능 따라서 O(mlogn)
