What is it?

- Confidentiality: only the sender and the receiver can understand the message.
- Authentication: needs to authenticate the sender and the receiver.
- Message Integrity: any alteration can be detected easily (inviolable)
Confidentiality
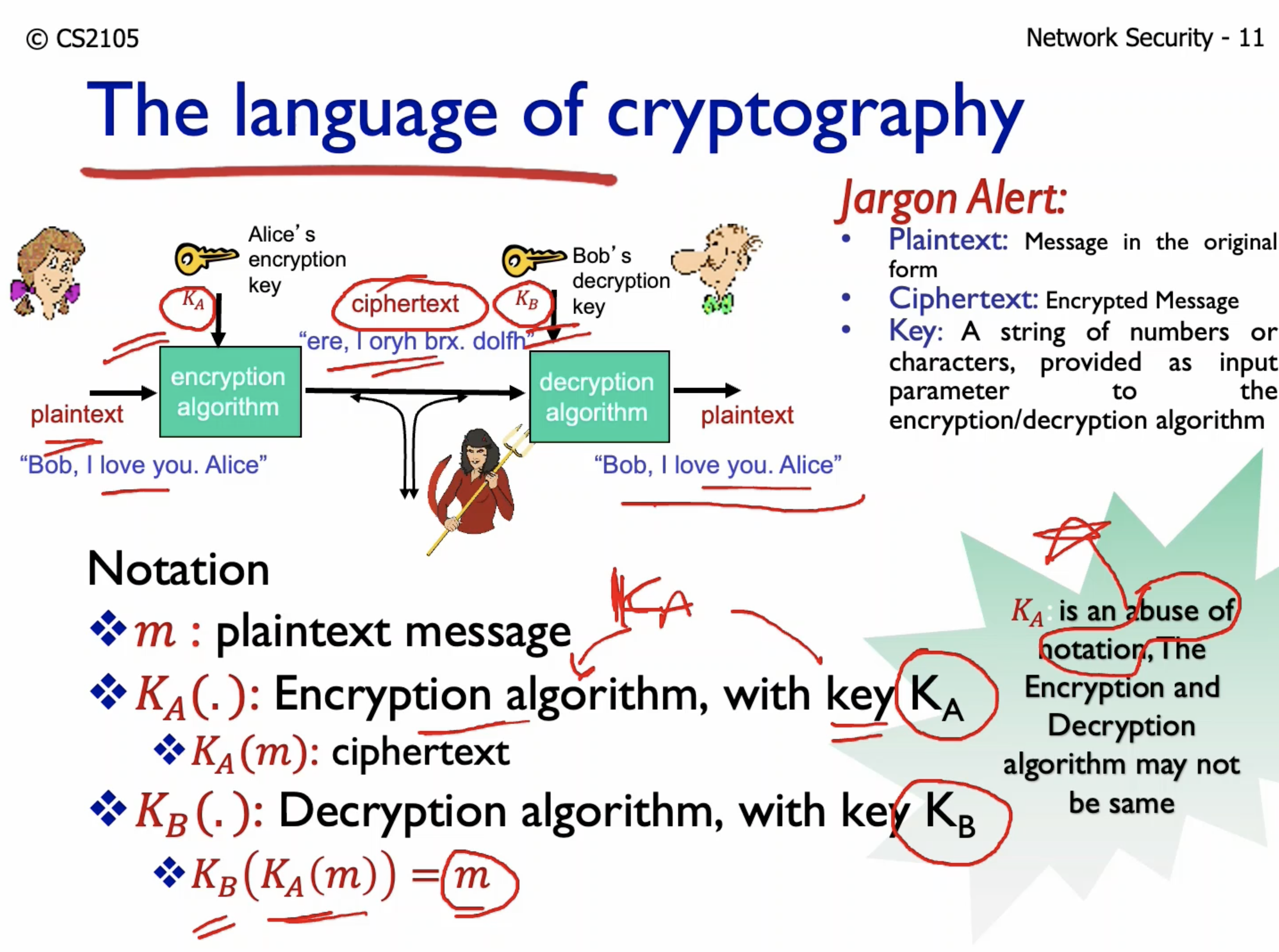
- m: plaintext message
- K_a: encryption key (string or number that is used in the encryption / decription algorithm)
- K_a(), K_a: encryption algorithm
- K_b: decryption key
- K_b(), K_b: decryption algorithm

- The two types of cryptography are: symmetric key cryptography and asymmetric key cryptography.
Symmetric Key Cryptography
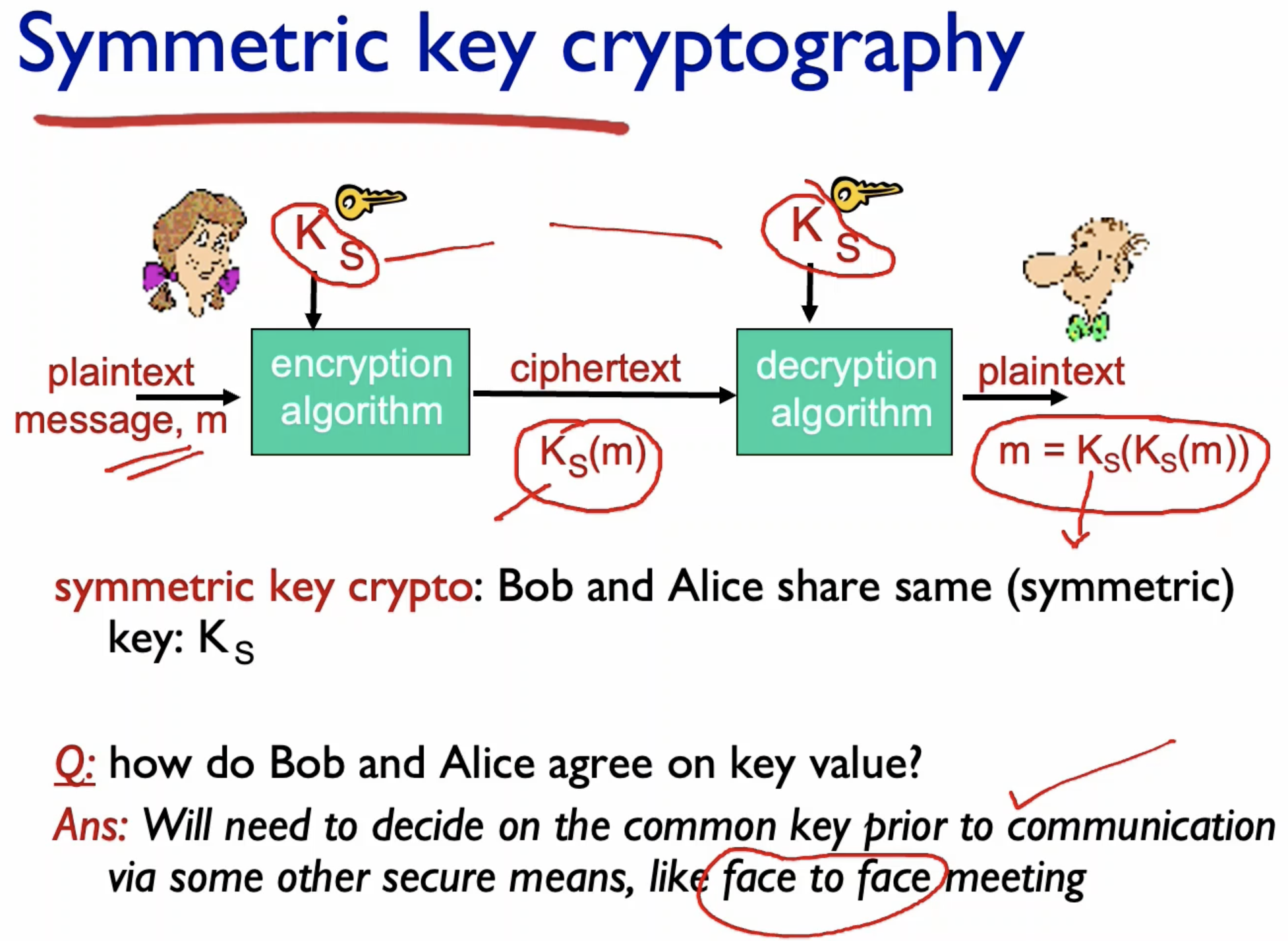
- It is important to know how the receiver and the sender decided on which key to use.
- TCP handshake? Then that should be secure as well!
- Need to think of a way to securely communicate the key to use.

- Only 25 possible values of shifting.
- The key in this case is number of shifting (ex: 3)

- The key here is the mapping of alphabet to the permutation (permutation string).
- 26! possible permutations

- Monoalphabetic cipher can be deciphered using statistical analysis.
- Some consonants appear more frequently than others.
- Knowing that "bob" or "alice" appears in the text already gives out some letters.

- Ciphertext only attack: Trudy has only the ciphertext she can analyze using statistical analysis.
- Known-plaintext attack: Trudy knows the mapping for "alice" and "bob" and the permutation string.
- Chosen-plaintext attack: Trudy forces Alice to send a string of message, from which the mapping can be figured out.
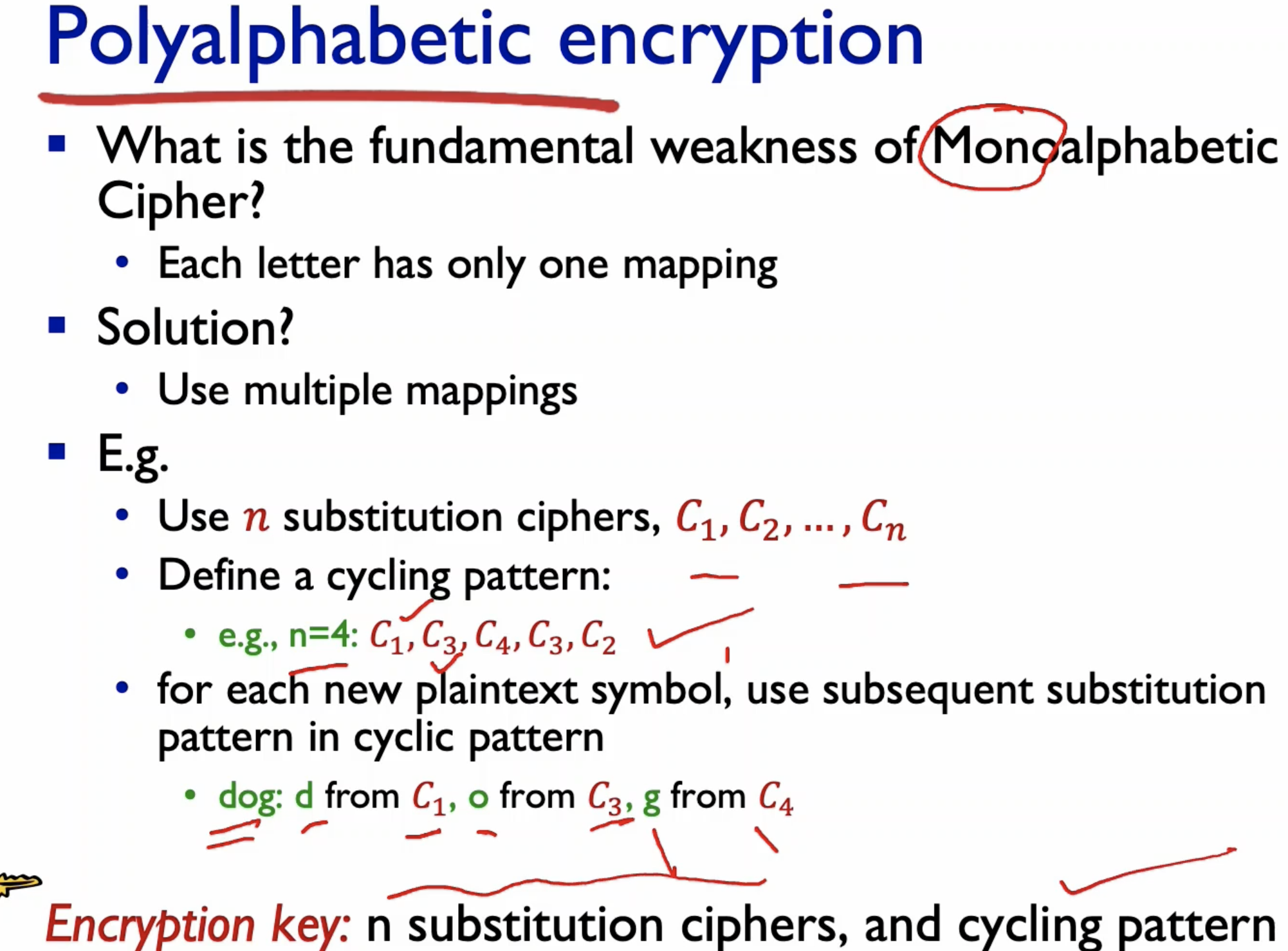
- Use several mappings in cycle.
- The encryption key here is the cycle pattern, and substitution ciphers.

- You can see for the same b, it is now mapped to different alphabets.
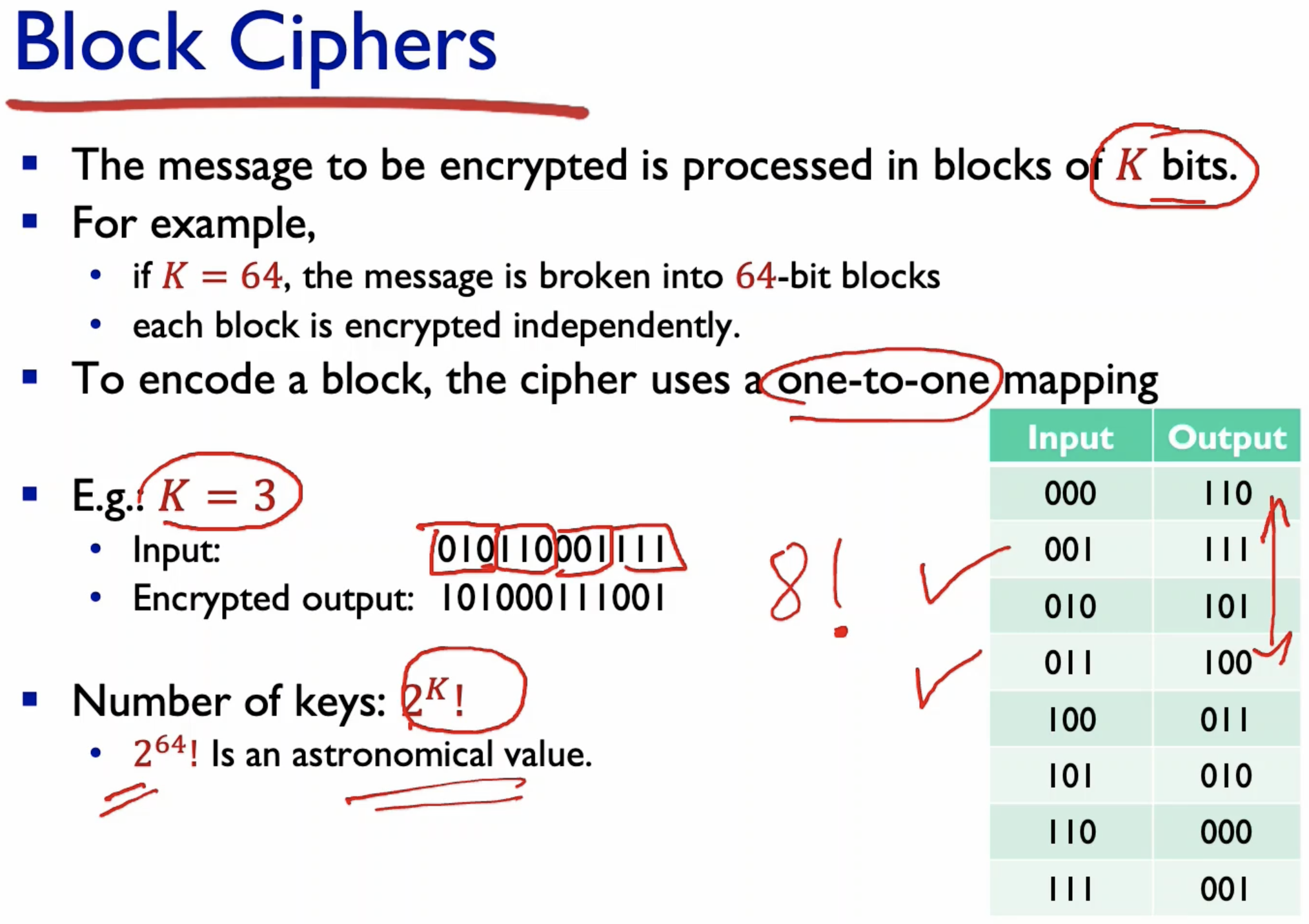
- Number of permutations of mappings: (2^(k))!
- where k is the number of bits in a block.

- DES and AES.
- AES > DES.
- DES can be solved easily now due to the technological advancement.

- The key issue with symmetric key cryptography is that both ends need to know the key.
- This is problematic when the two have never met.
- Thus, the motivation for asymmetric cryptography.
- The sender uses public key to encrypt,
- The receiver uses private key to decrypt.
Asymmetric Key Cryptography
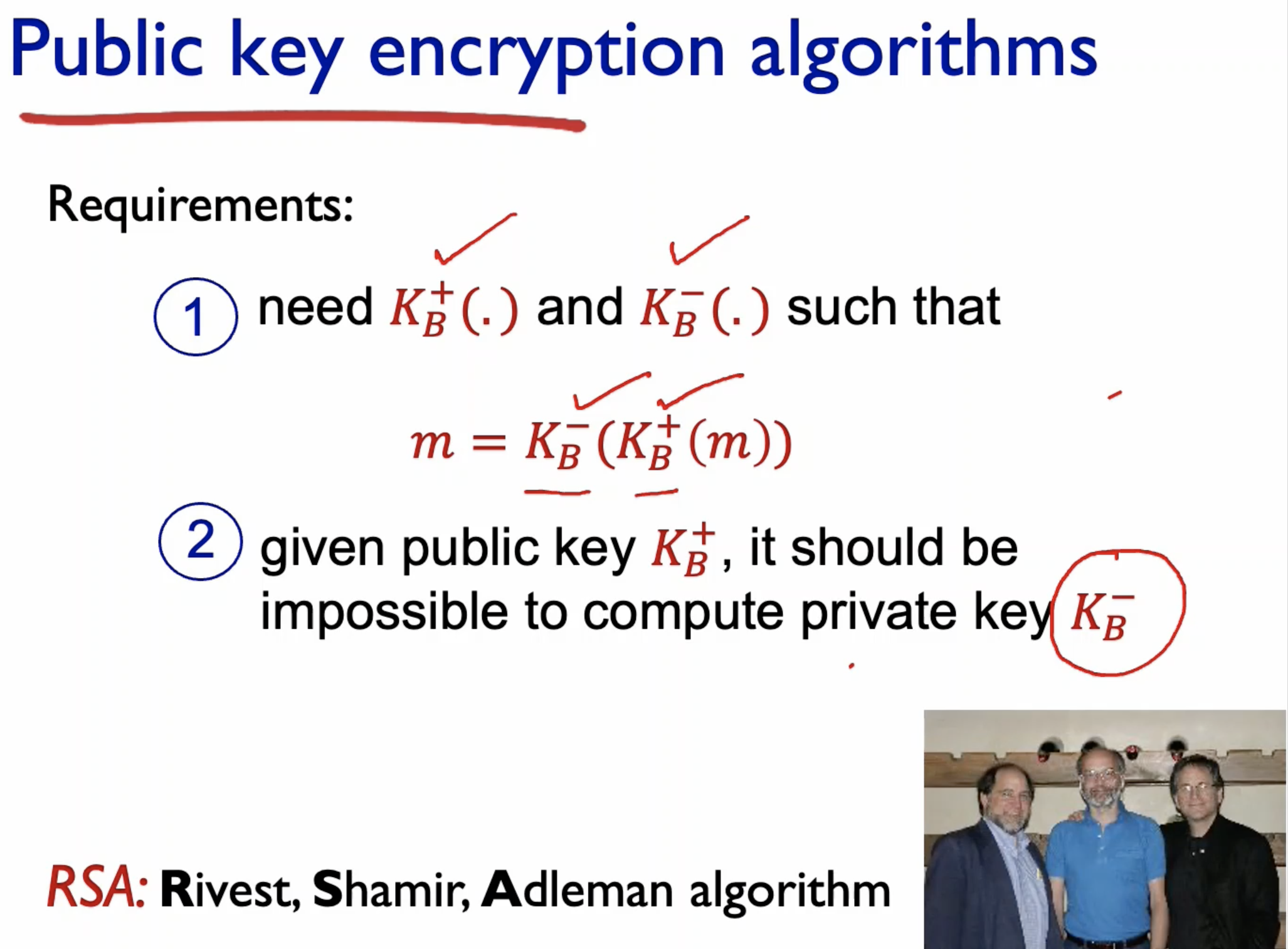
- Requirements:
- Need the encryption and decryption algorithms.
- Even if there is a coupling between the public and private keys, it should be impossible to even guess what the private key is from the public key.
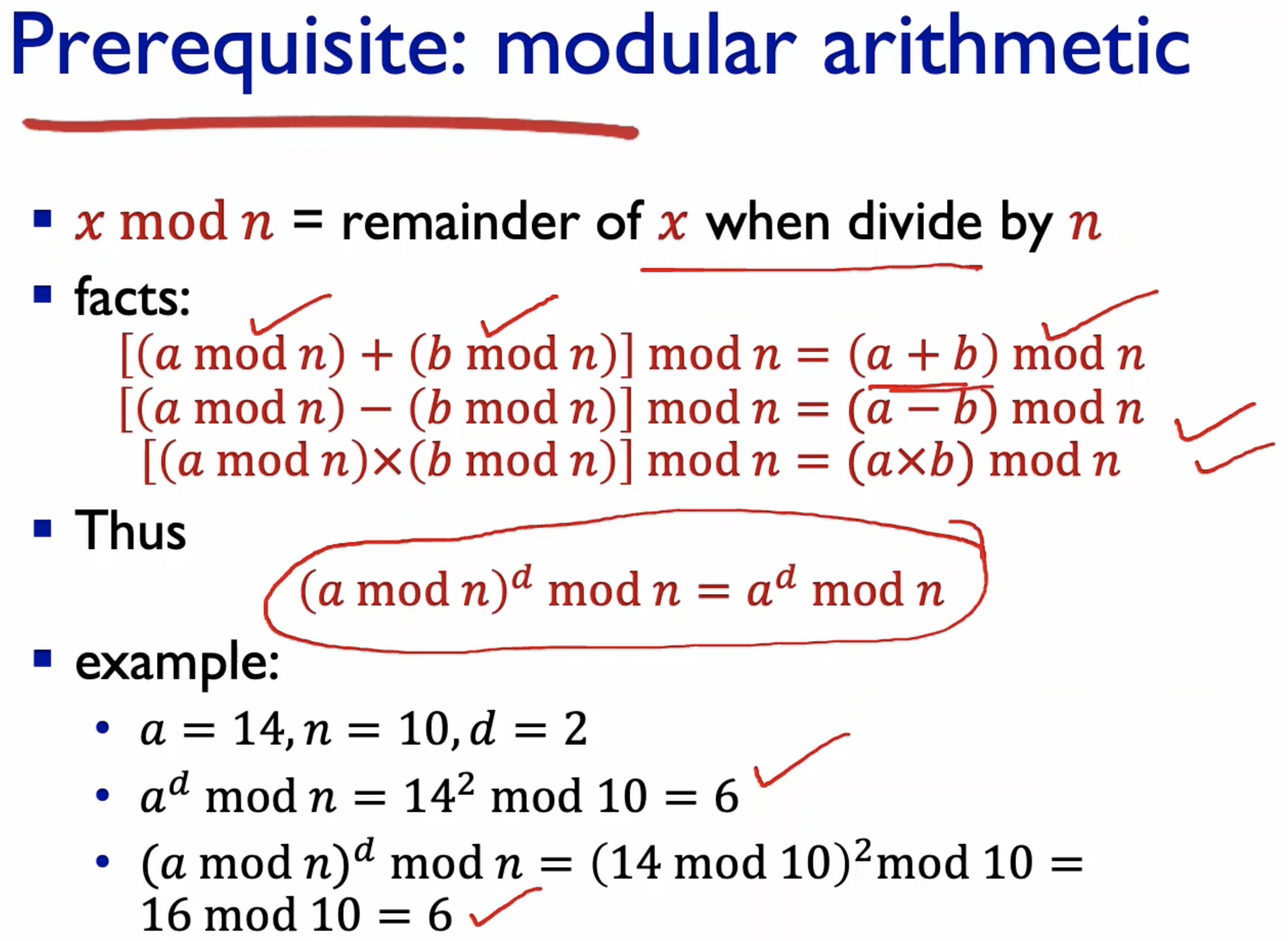

- Message is just a bit pattern, and bit pattern can be translate to a number.
- RSA encrypts a number to produce another number.
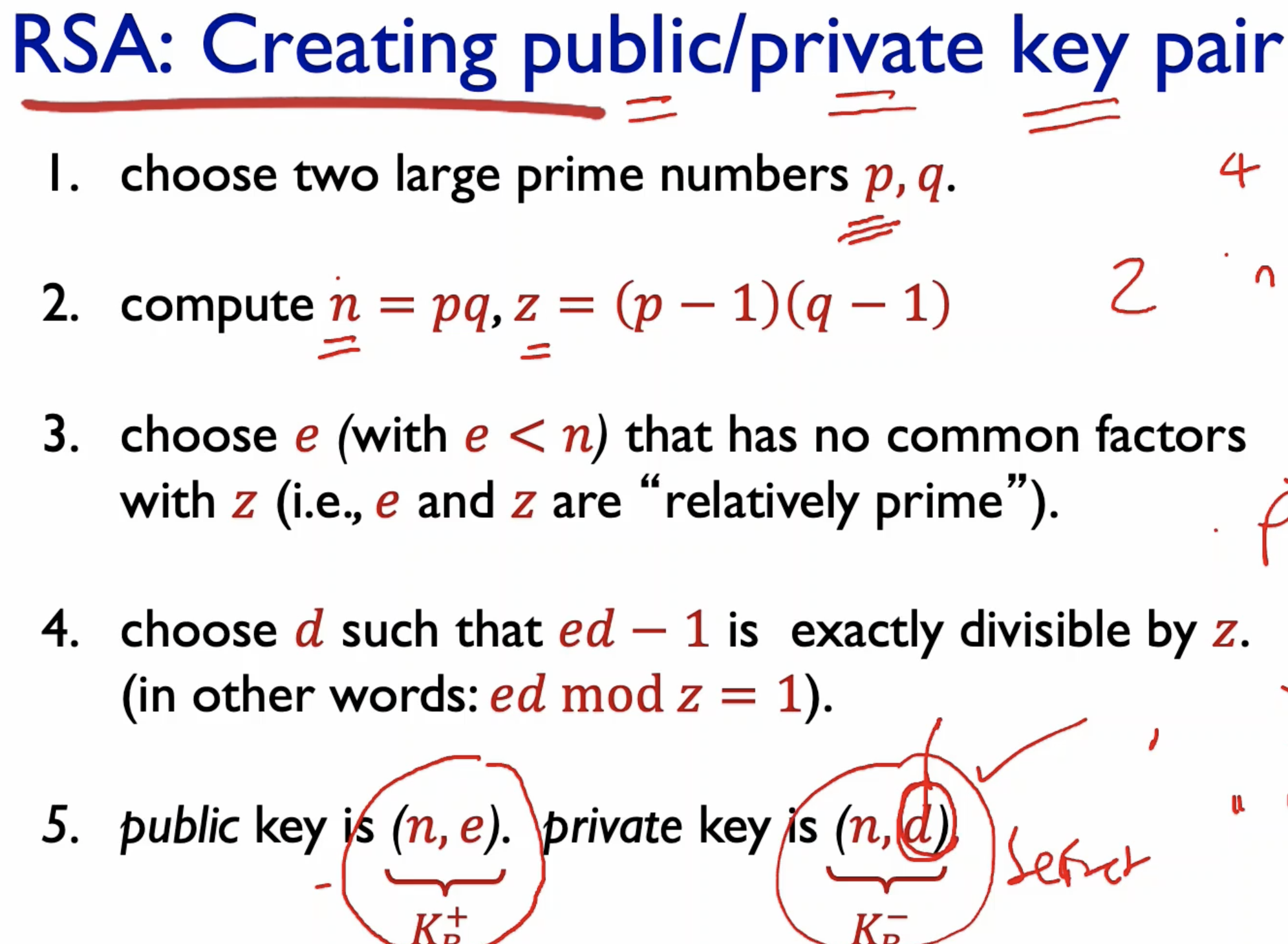
- Choose 4 numbers to encrypt:
- p and q (very large different prime numbers)
- e (no common factor with z)
- d (ed - 1 is divisible by z)
- (n, e) become public, (n, d) become private key.
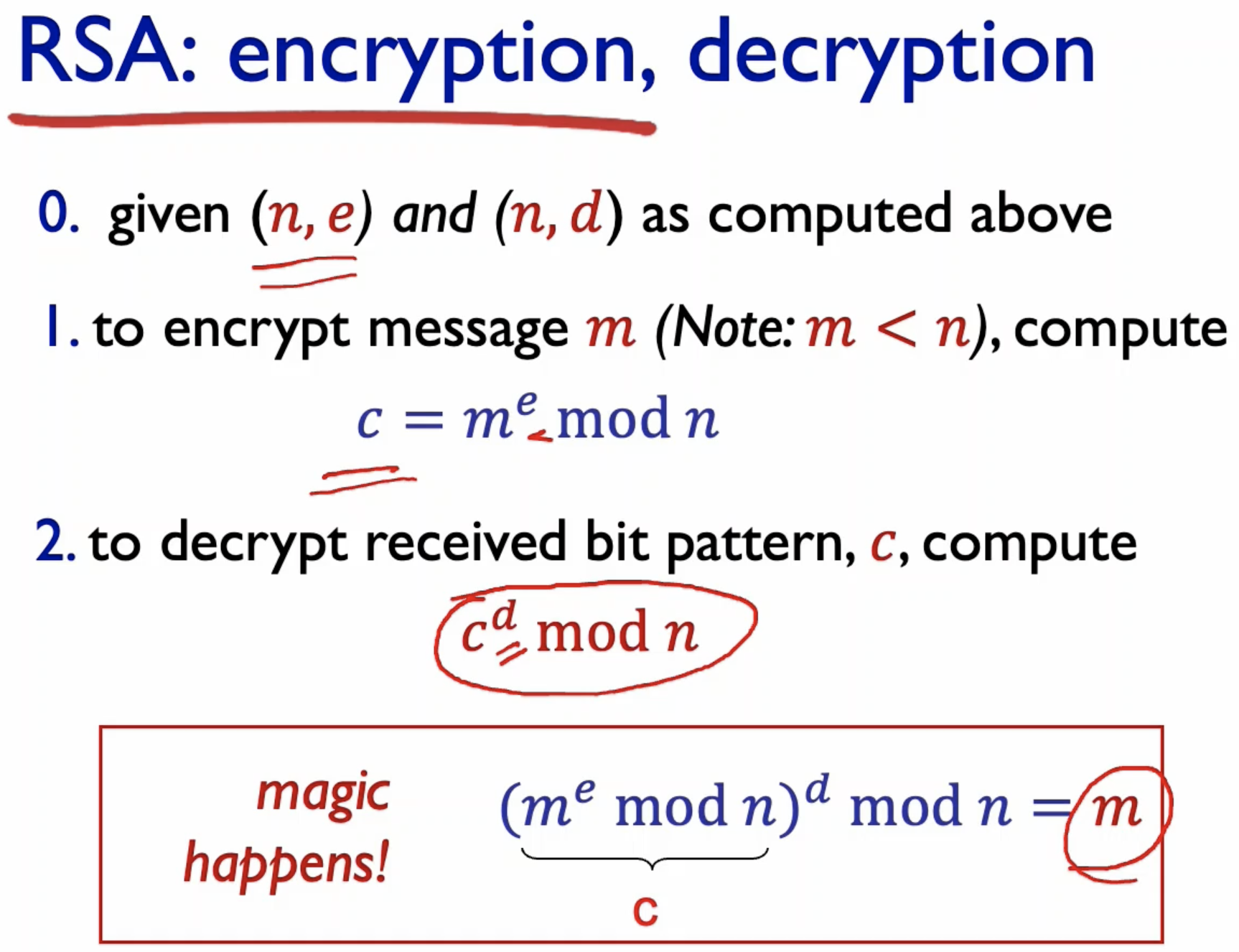
- What the heck?
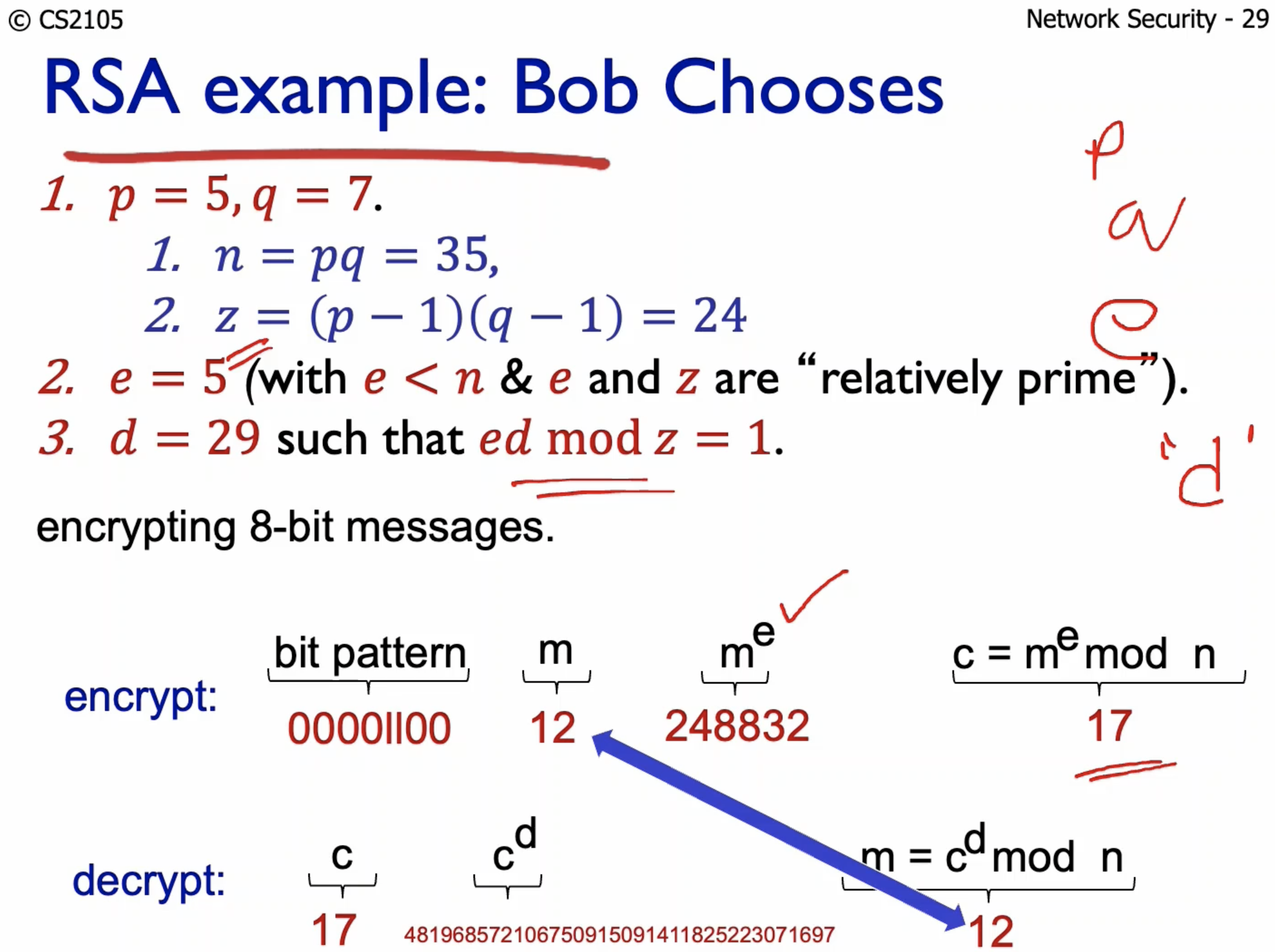
- What?
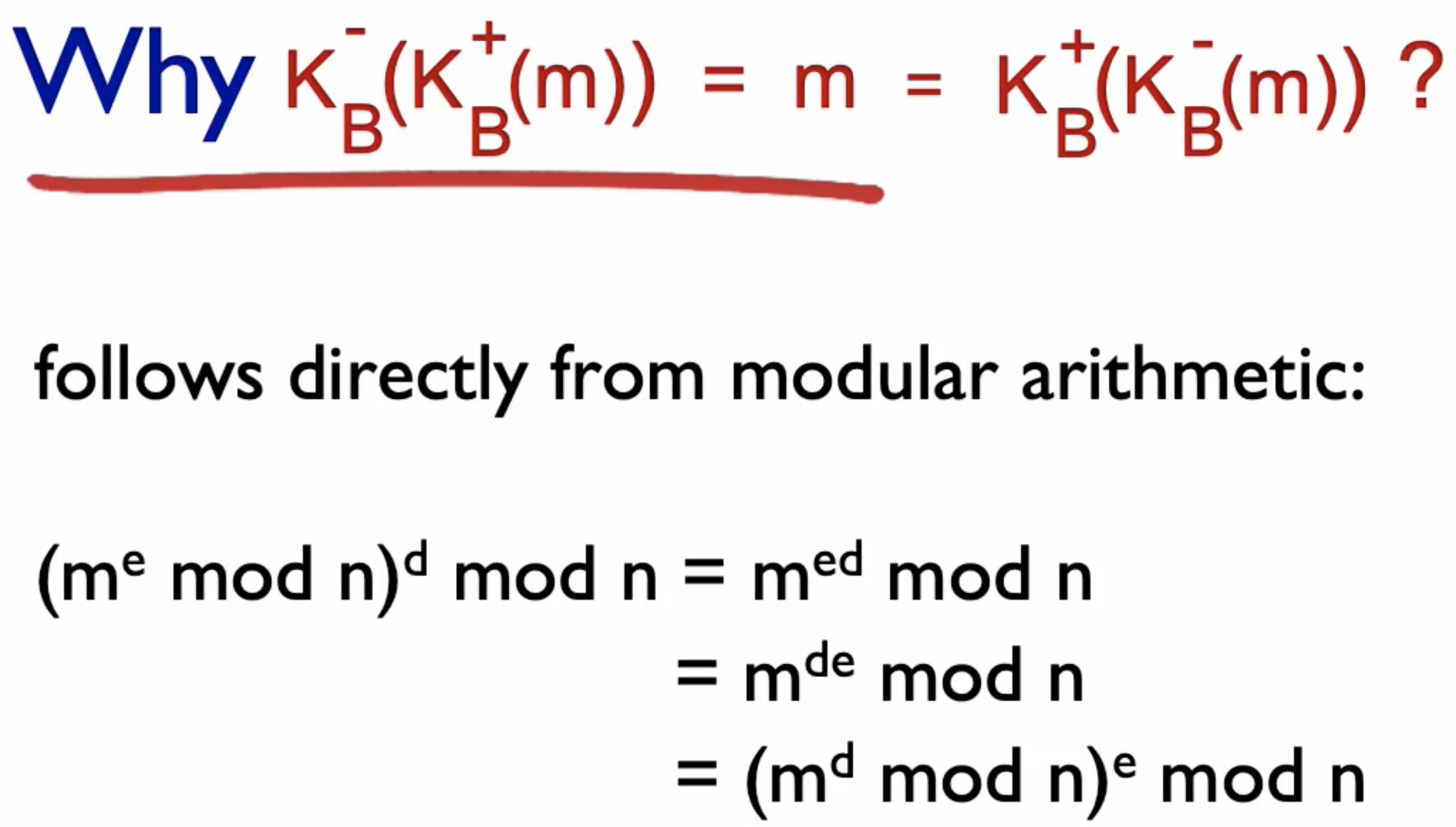
- swapping between public and private encryption algos still work.

- RSA on its own is too computationally-expensive.
- Use RSA on K_s. Decrypting the key to decrypt the DES.
Message Integrity
- We can use checksum, parity, and CRC.
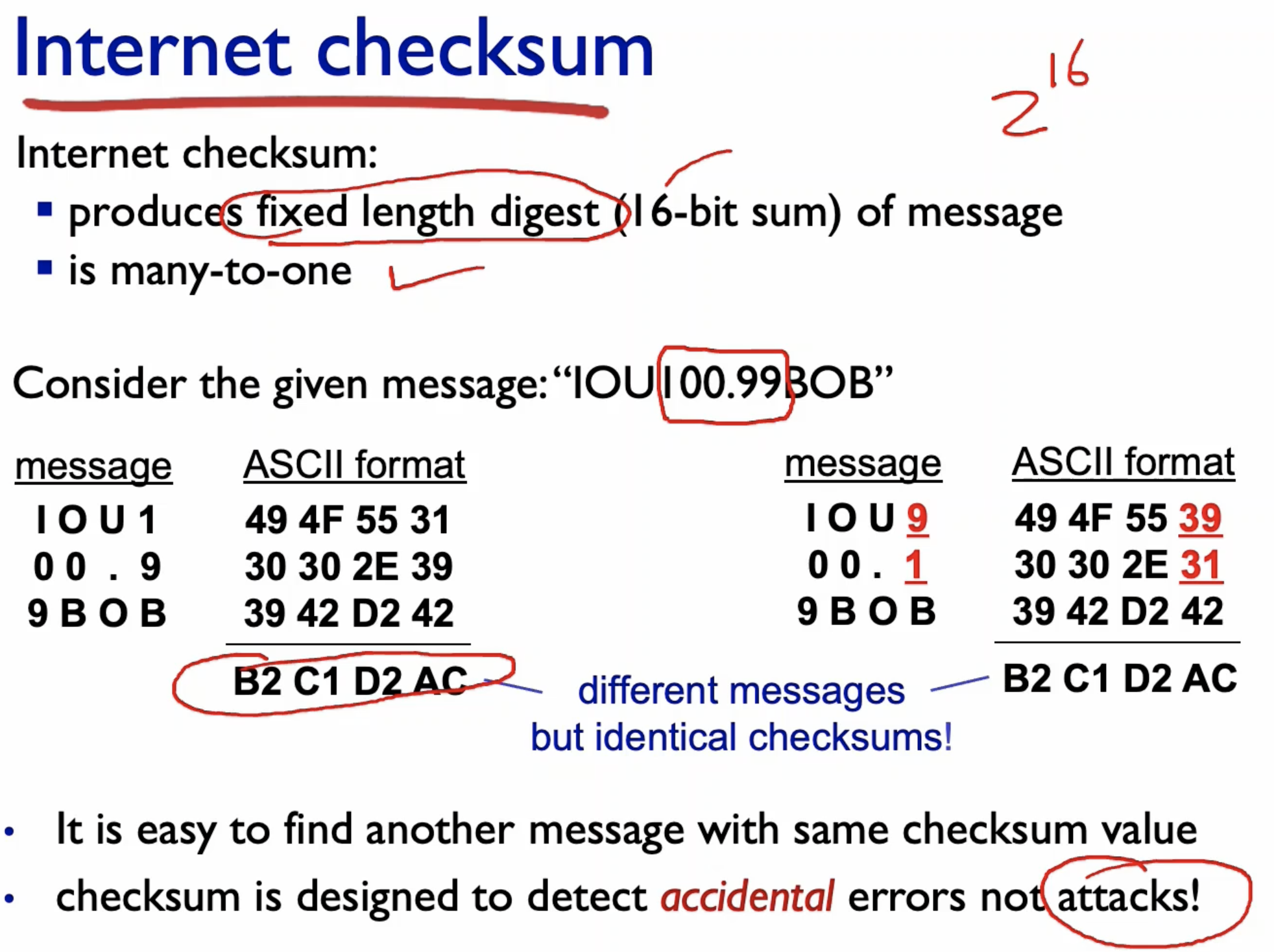
- Checksum is not good for preventing attacks.

- Two input strings can have the same CRC checksum.
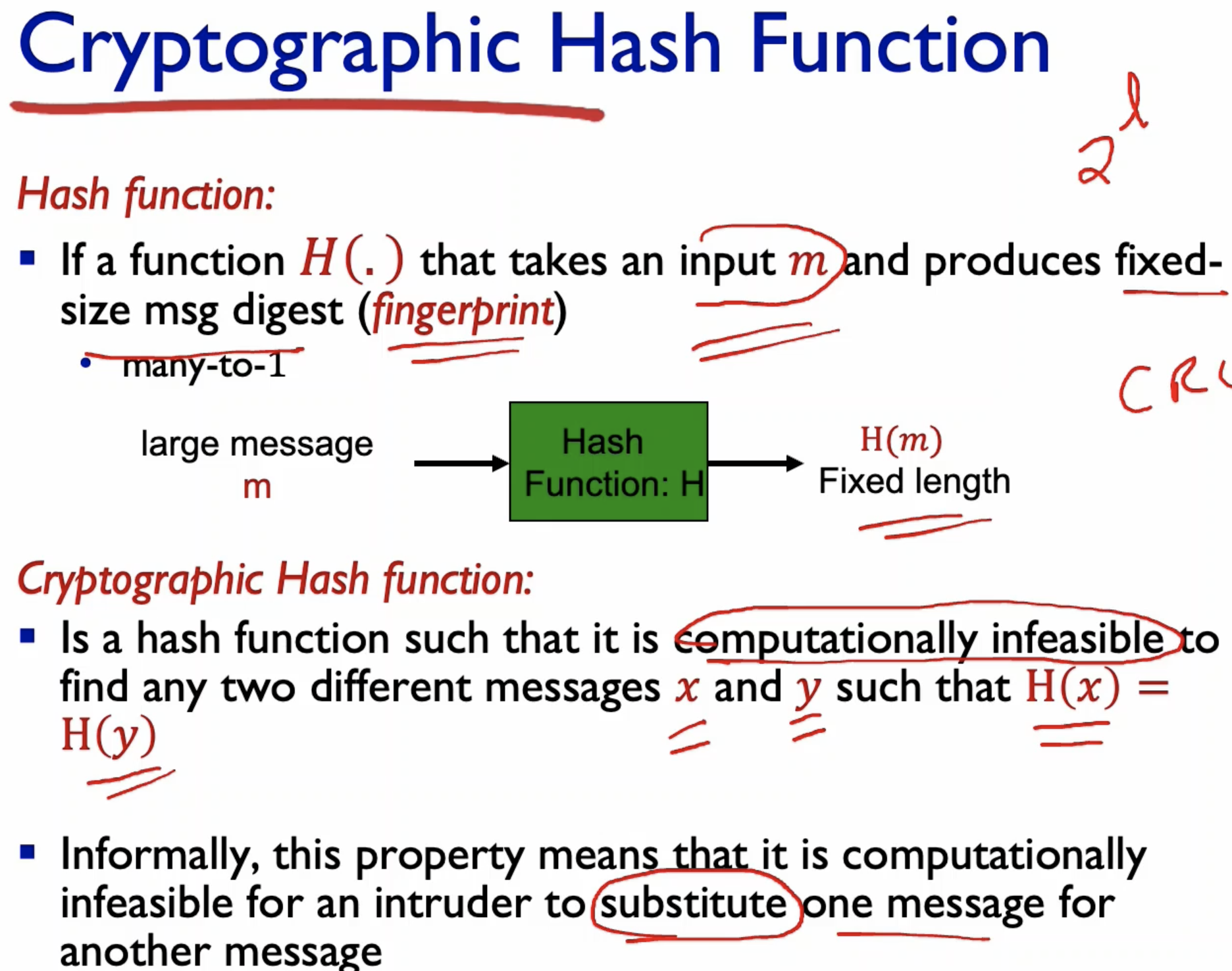
- The hash function should not have two input values that can generate the same hash outputs.
Hash Function: MD5
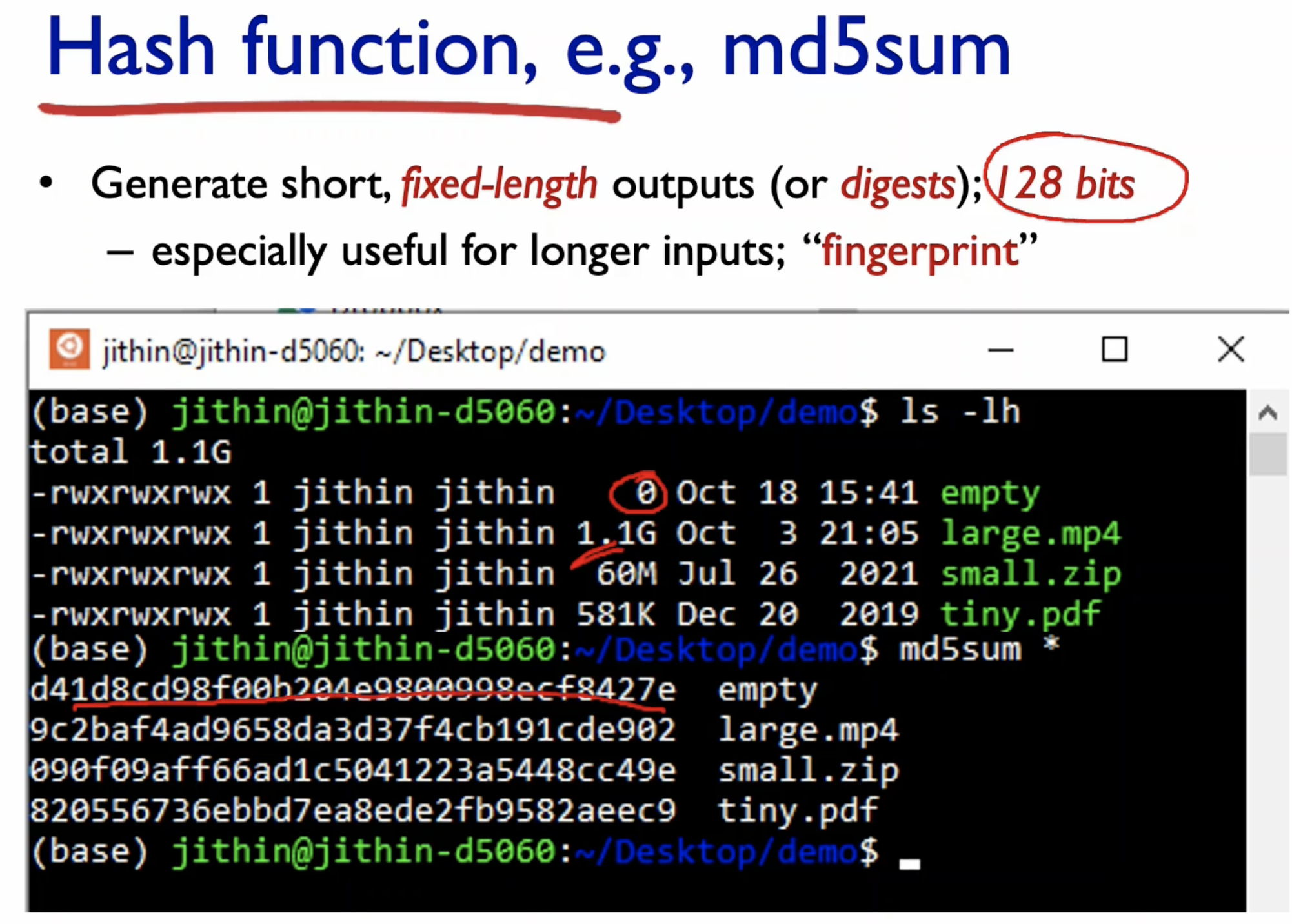
- Even though the file sizes are very different, they still produce 128 bits hash output.
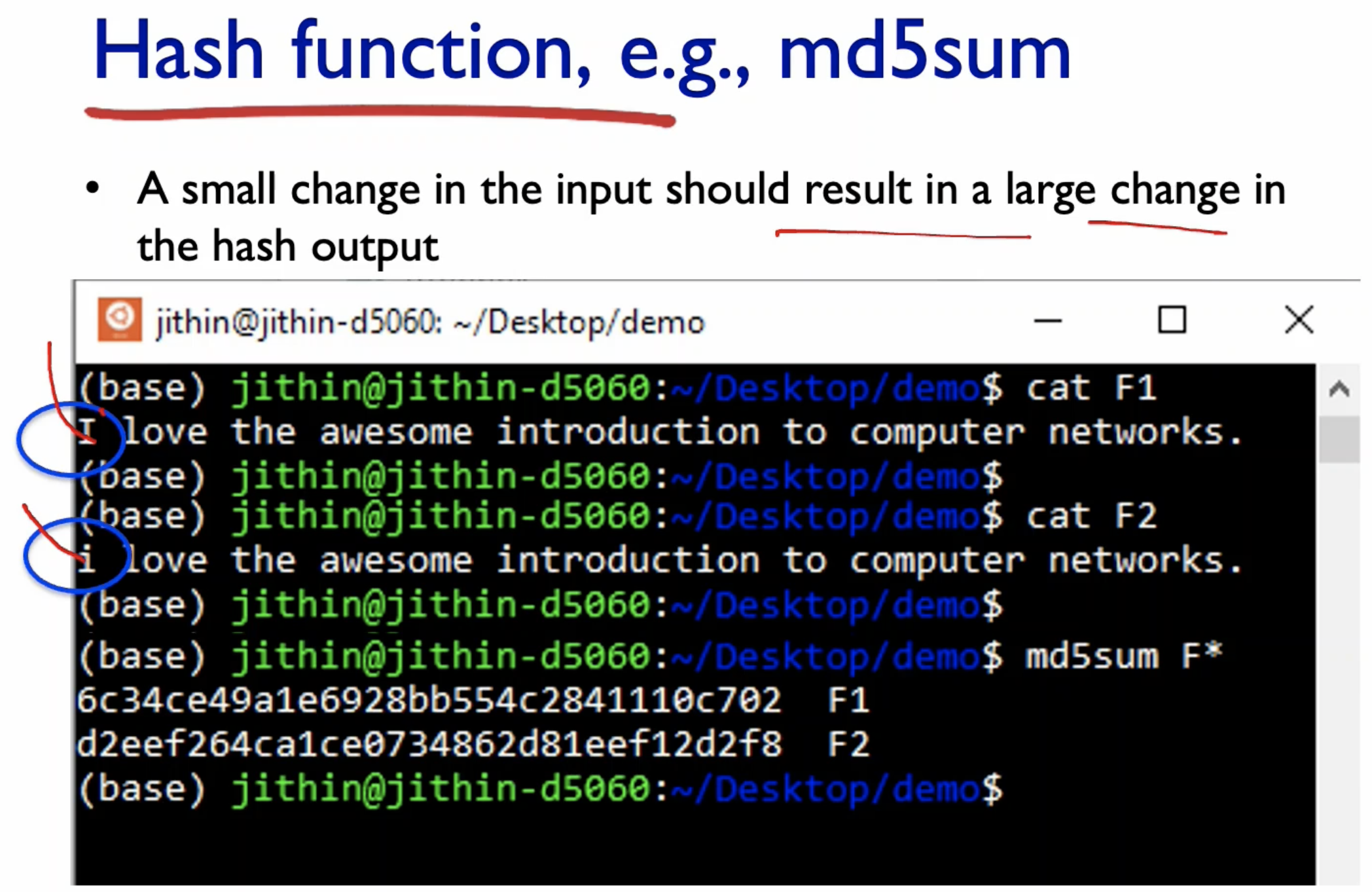
- A small change in the input shows great difference in output.

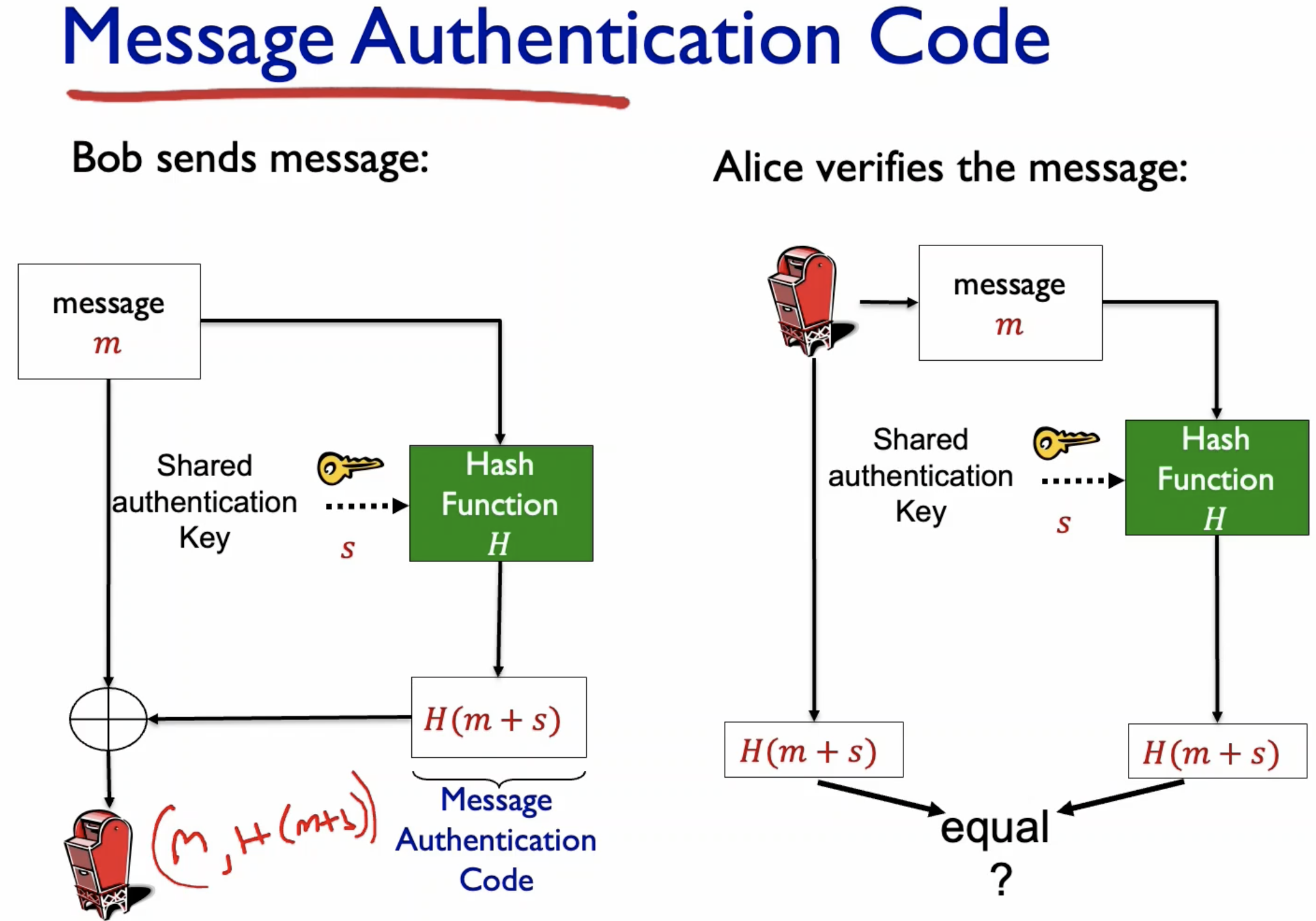
- The sender cannot send the pair (m, H(m)) because if both of them are replaced with something correct, there is no way to detect the replacement.

- Send the hash code of message + authentication key.
- Since the authentication key is only known between the sender and the receiver, there is no way an intruder can replace the H(m+s) since then it will be easily detected.
Authentication

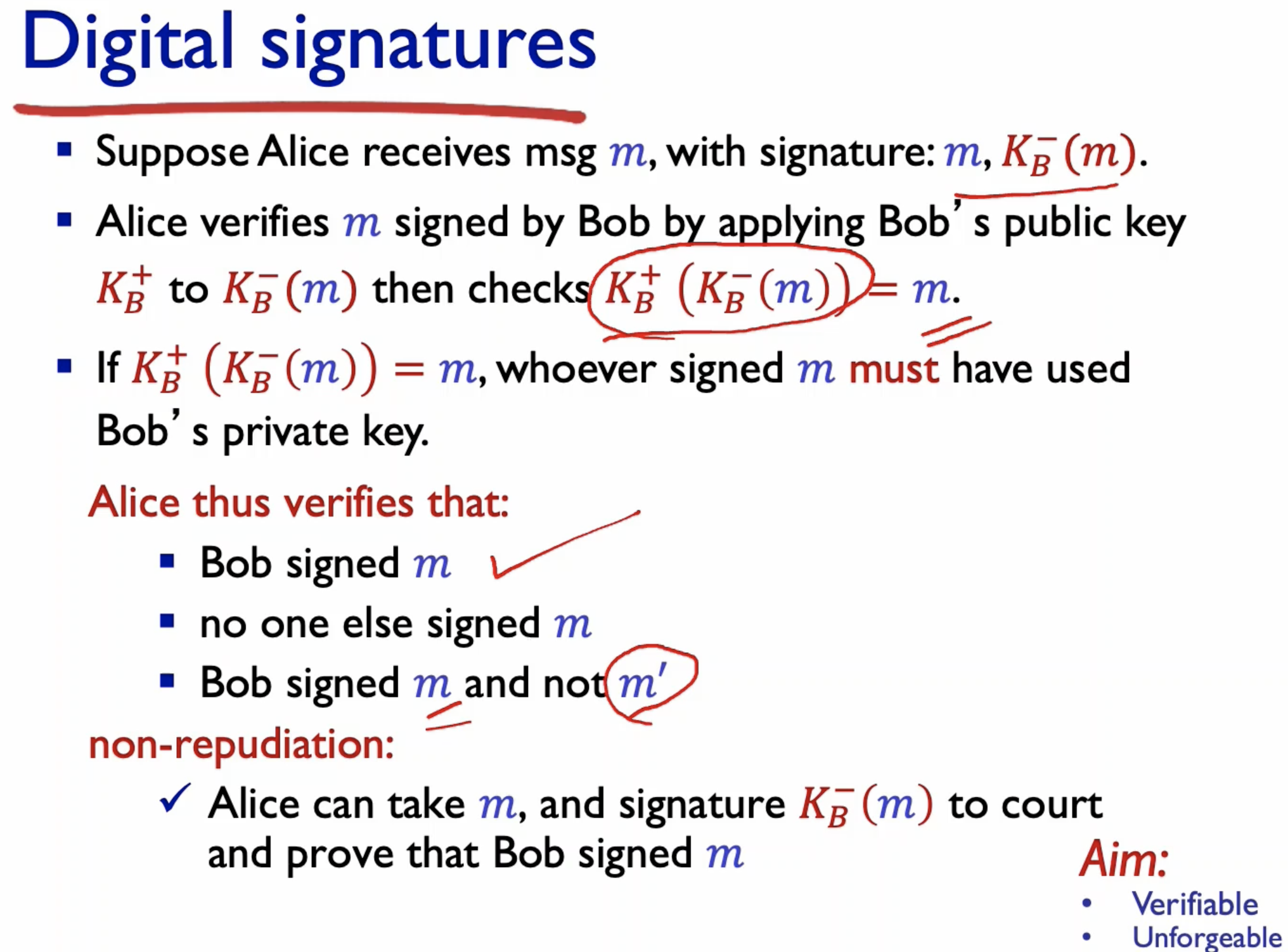
- Digital siganture: cryptographic technique used to authenticate the sender and the receiver.

- In digital signature, we use the private key to encrypt and public key to decrypt.
- This way, if the public key can decrypt the message, then we know that it is send by Bob, because it is using Bob's private key to encrypt.
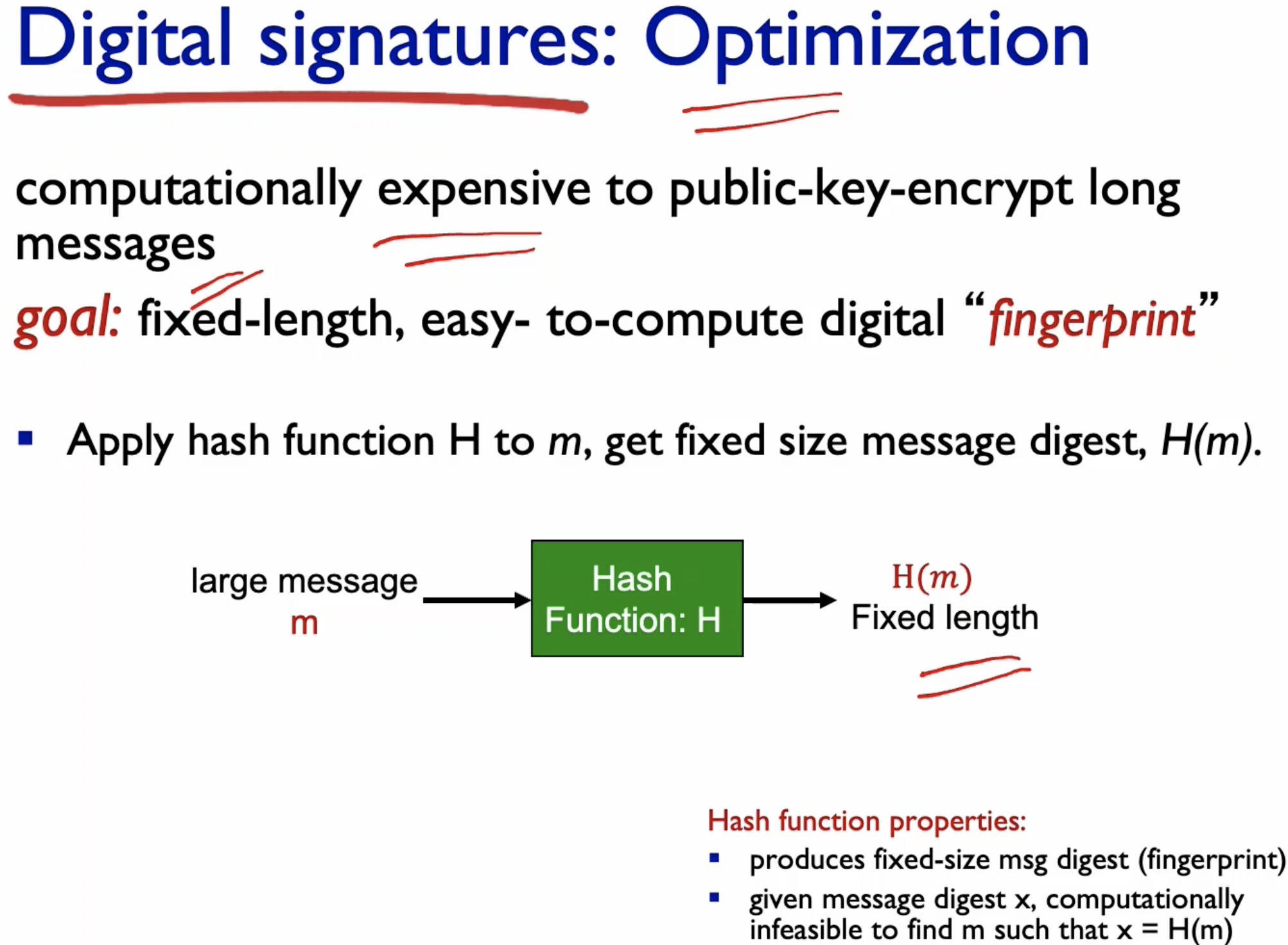
- It is quite expensive to encrypt the entire message, since the message can be long.
- The solution is to hash first so that a fixed size of hashed message can be encrypted.

- the message m is sent with the hased m.

- The issue right now is that there is no way to tell if the public key provided is by the intruder's or the sender's.

- We do not know if it is Bob's public key.
- Ask Certification Authority (CA) - which keeps the data base for public keys - if it is indeed Bob's public key.
- But what if Trudy intercepts the communication between CA?:
- CA signs the messages.
- Problem: We do not know CA's public key?
- Store them in hardware.
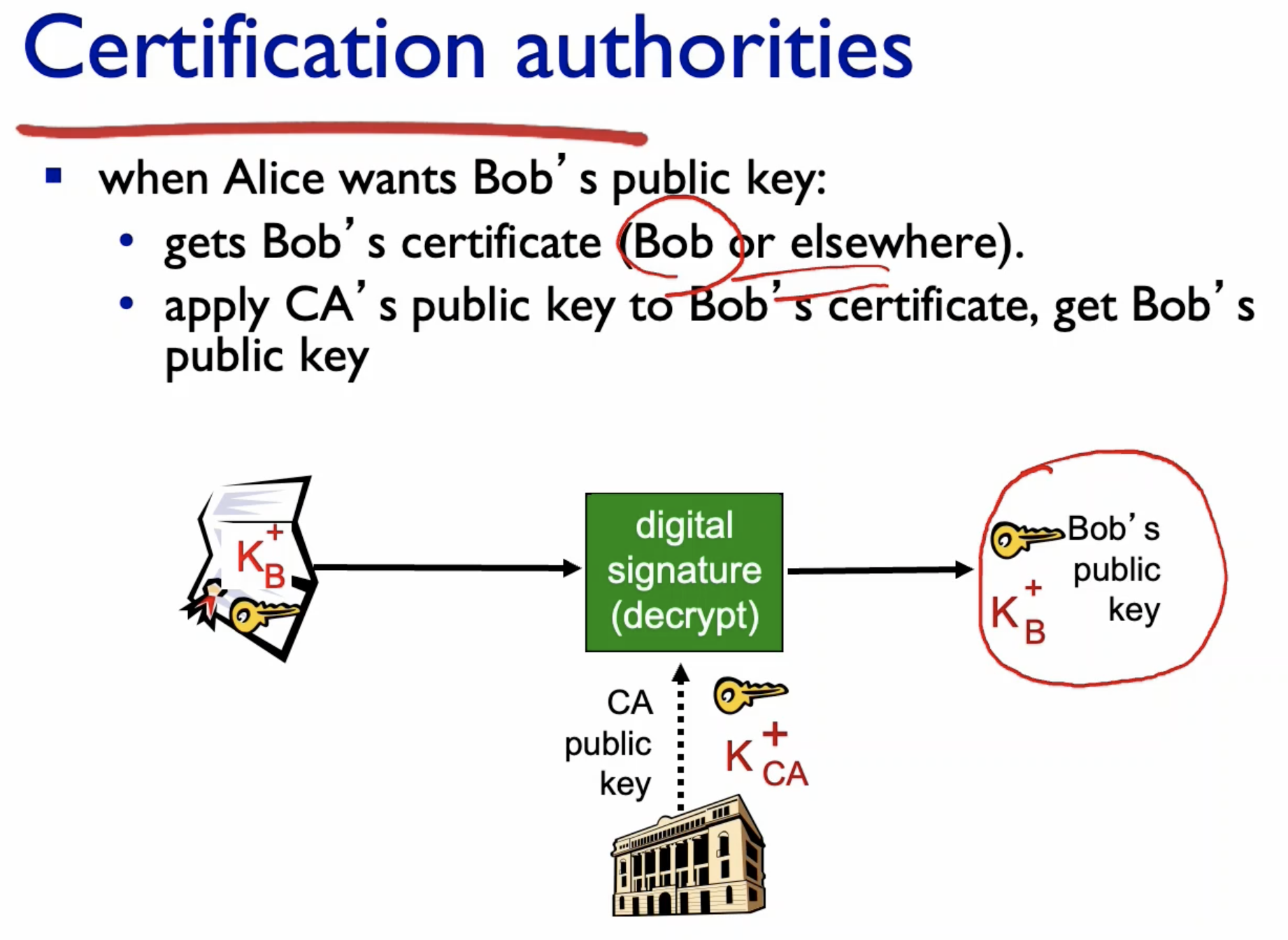
- Use CA key to verify that it is indeed bob's public key.
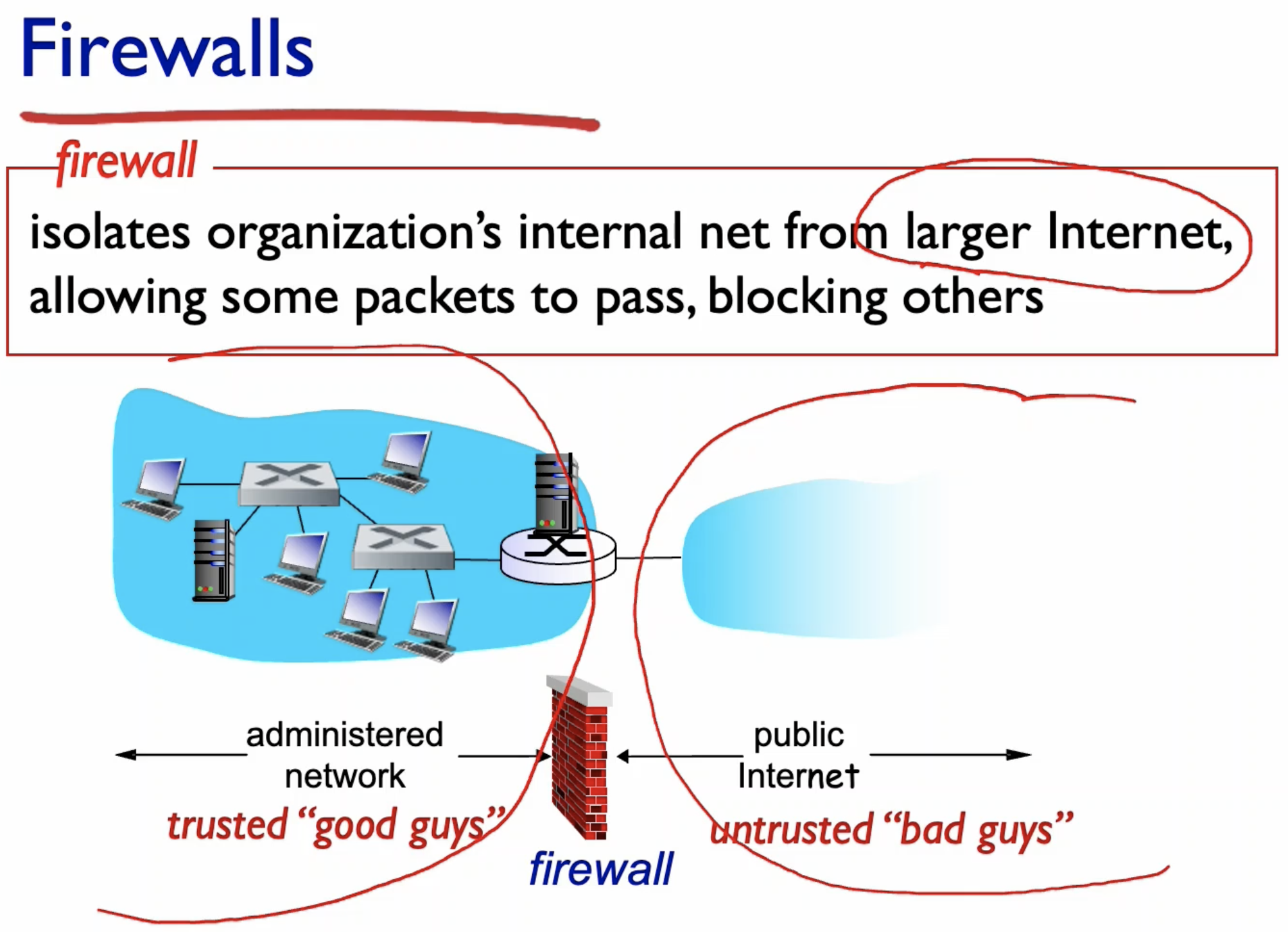
- Firewall is used to block the external people from accessing the internal network.

1. prevents DoS attacks by an outsider.
- DoS attack sends countless TCP connection requests that any proper TCP request cannot be succeded.
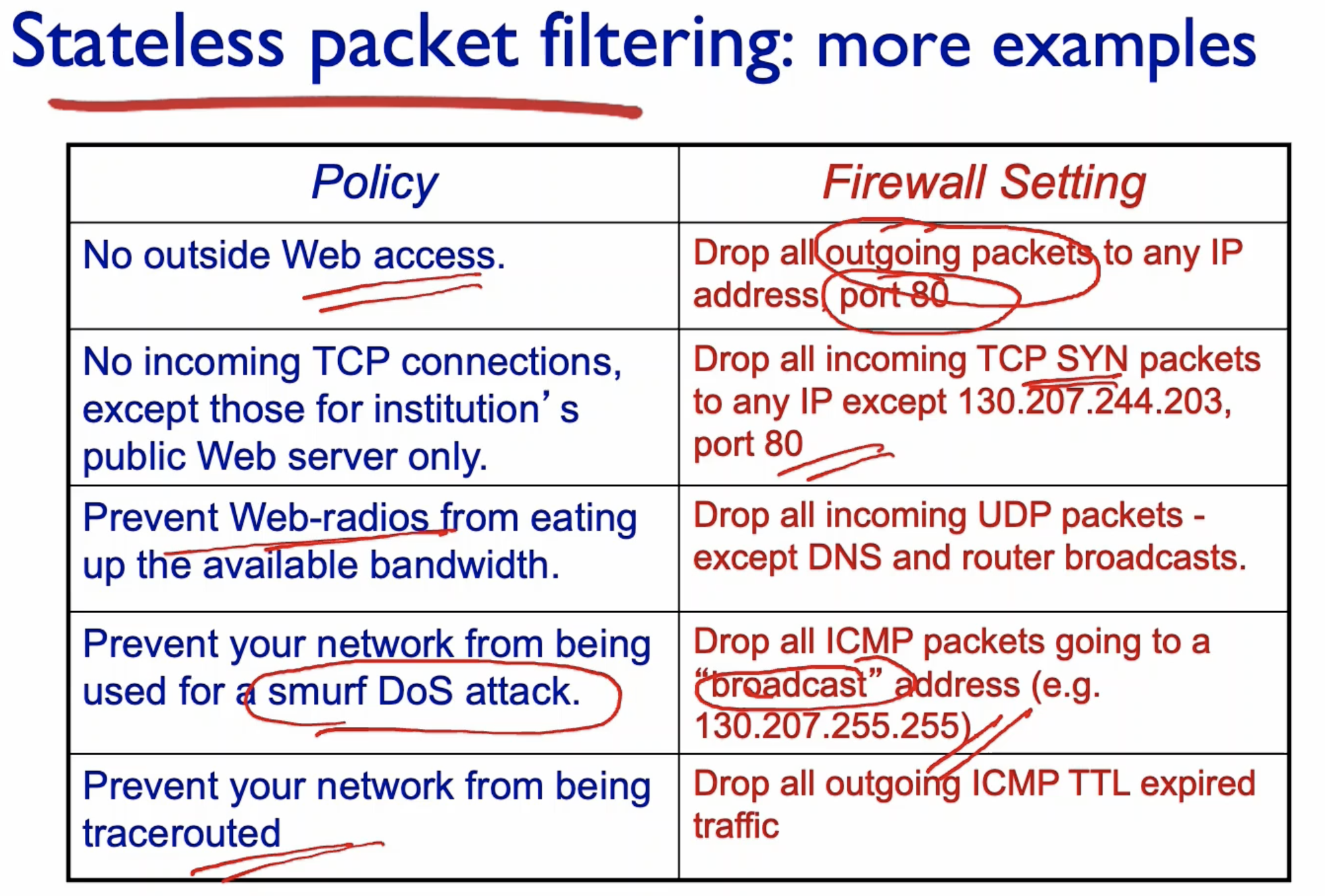
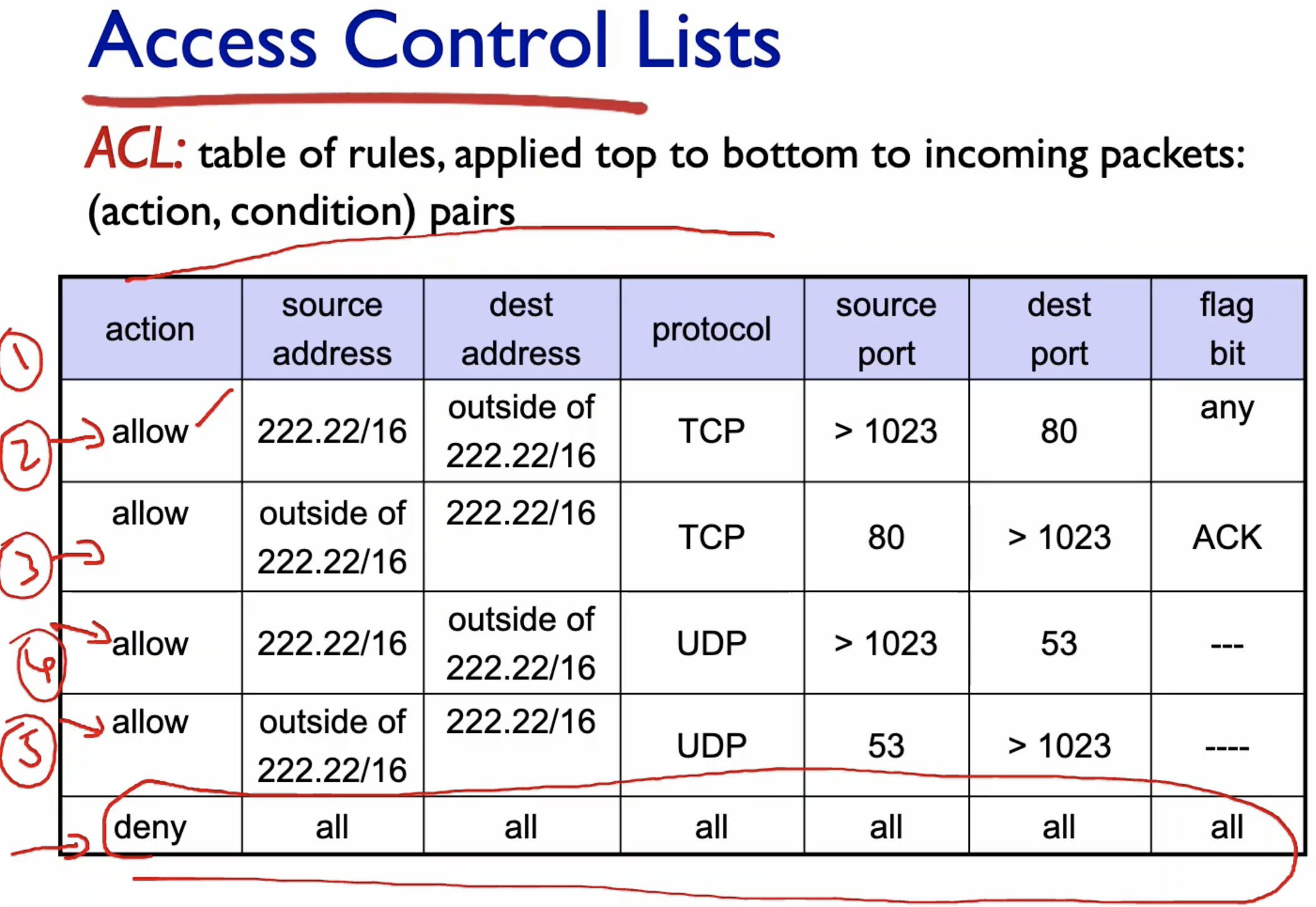
- The packets go through the list of rules known as Access Control Lists to be checked if they can be passed.

- IP spoofing: when packets fake the IP address, there is no way to tell it by the firewall.
