1. Question
You are given the head of a linked list. Delete the middle node, and return the head of the modified linked list.
The middle node of a linked list of size n is the ⌊n / 2⌋th node from the start using 0-based indexing, where ⌊x⌋ denotes the largest integer less than or equal to x.
For n = 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, the middle nodes are 0, 1, 1, 2, and 2, respectively.
Example 1:

Input: head = [1,3,4,7,1,2,6]
Output: [1,3,4,1,2,6]
Explanation:
The above figure represents the given linked list. The indices of the nodes are written below.
Since n = 7, node 3 with value 7 is the middle node, which is marked in red.
We return the new list after removing this node. Example 2:
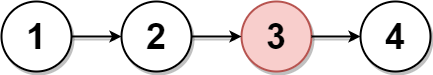
Input: head = [1,2,3,4]
Output: [1,2,4]
Explanation:
The above figure represents the given linked list.
For n = 4, node 2 with value 3 is the middle node, which is marked in red.Example 3:

Input: head = [2,1]
Output: [2]
Explanation:
The above figure represents the given linked list.
For n = 2, node 1 with value 1 is the middle node, which is marked in red.
Node 0 with value 2 is the only node remaining after removing node 1.2. Thoughts
3. Tips learned
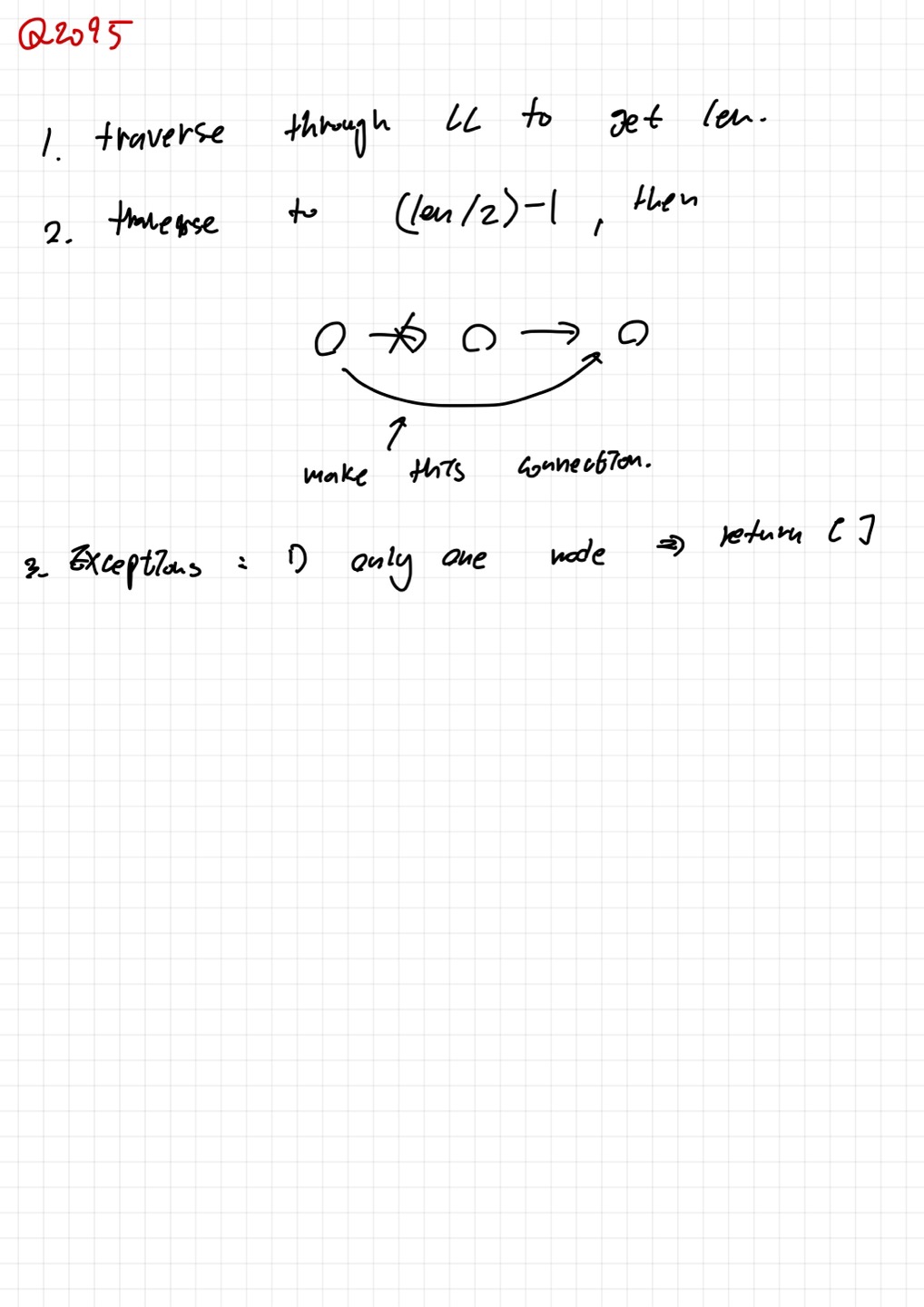
4. My solution
class Solution:
def deleteMiddle(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
length = 1
node = head
while node.next != None:
length += 1
node = node.next
if length == 1:
return ListNode(val="", next=None)
node = head
for i in range(int(length / 2) - 1):
node = node.next
node.next = node.next.next
return head70/70 cases passed (1305 ms)
Your runtime beats 33.94 % of python3 submissions
Your memory usage beats 14.6 % of python3 submissions (63 MB)5. AI Solution and Improvements
Here's how you can implement this solution:
- Initialize two pointers,
slowandfast, at the head of the list. - Move
fasttwo steps andslowone step at a time. - When
fastreaches the end,slowwill be at the node just before the middle. - Delete the next node of
slow.
This approach is more efficient as it requires only one traversal of the list. Here's the code for this solution:
class Solution:
def delete_middle(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
# Handle edge cases: empty list or single node list
if not head or not head.next:
return None
# Initialize two pointers
slow, fast = head, head.next.next
# Traverse the list with the two-pointer approach
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
# Delete the middle node
slow.next = slow.next.next
return headThis code effectively finds and removes the middle node in a single pass, making it more efficient than the original approach.
