1. Question
Given an n-ary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes' values.
Nary-Tree input serialization is represented in their level order traversal, each group of children is separated by the null value (See examples).
Example 1:
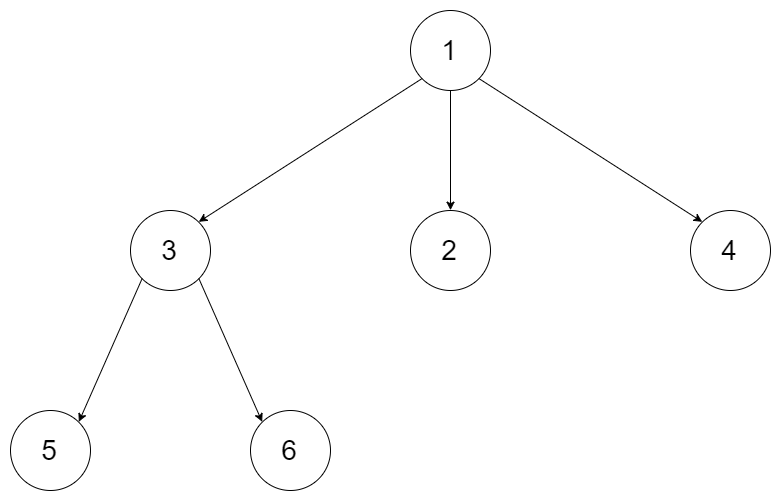
Input: root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
Output: [[1],[3,2,4],[5,6]]Example 2:
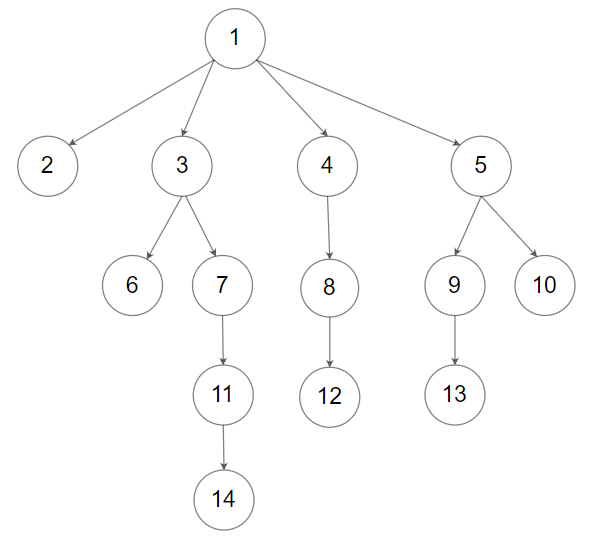
Input: root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
Output: [[1],[2,3,4,5],[6,7,8,9,10],[11,12,13],[14]]2. Thoughts
3. Tips learned
4. My solution
class Solution:
def levelOrder(self, root: "Node") -> List[List[int]]:
if not root:
return []
tree_queue = deque([root])
result = [[root.val]]
while len(tree_queue) != 0:
level_result = []
parent_num = len(tree_queue)
for _ in range(parent_num):
node = tree_queue.popleft()
for children in node.children:
if children:
level_result.append(children.val)
tree_queue.append(children)
if level_result:
result.append(level_result)
return result38/38 cases passed (49 ms)
Your runtime beats 52.43 % of python3 submissions
Your memory usage beats 94.51 % of python3 submissions (18.1 MB)5. AI Solution and Improvements
Your solution for performing a level order traversal on an n-ary tree is quite efficient and follows the standard Breadth-First Search (BFS) algorithm, which is the appropriate approach for this type of problem. You make use of a queue to keep track of nodes at each level and process them accordingly, which is exactly what's needed for level order traversal.
However, there are a few minor adjustments and improvements that can make your code cleaner or slightly more efficient:
- Direct Initialization of Queue: You can directly initialize the
dequewithroot, which you already did. This is just to emphasize that it's a good practice. - Code Readability: Your code is already quite readable, but ensuring that it's easy for others to understand is always beneficial. Adding comments or more descriptive variable names can sometimes help, though in this case, your variable names are quite descriptive.
- Optimization: In terms of algorithmic efficiency, your solution is already optimized for the problem given. BFS is the best approach for level order traversal, and your use of a queue is appropriate. The time complexity is O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the tree, since every node and edge is visited exactly once, and the space complexity is O(m), where m is the maximum number of nodes at any level, which is required for storing the queue. There's not much room for improvement without changing the problem constraints.
Given these points, here's a slightly refined version of your solution. The core logic remains the same, but with slight adjustments for readability:
from collections import deque
from typing import List
class Node:
def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):
self.val = val
self.children = children if children is not None else []
class Solution:
def levelOrder(self, root: "Node") -> List[List[int]]:
if not root:
return []
result = []
queue = deque([root])
while queue:
level_size = len(queue)
current_level = []
for _ in range(level_size):
node = queue.popleft()
current_level.append(node.val)
for child in node.children:
queue.append(child)
result.append(current_level)
return resultThis version maintains the structure of your original solution but aims for slightly improved readability. Note that algorithmic improvements beyond this are largely dependent on the specific constraints of the problem or the environment in which this code is executed. For the given problem statement, your approach is already optimal.
