2.1 systems of Linear Equations
다항식을 벡터로 표현하기
2.2 Matrices
matrix 는 m개의 row와 n개의 column을 가지고 있다.
2.2.1 matrix addition and multiplication
def) Identity Matirx
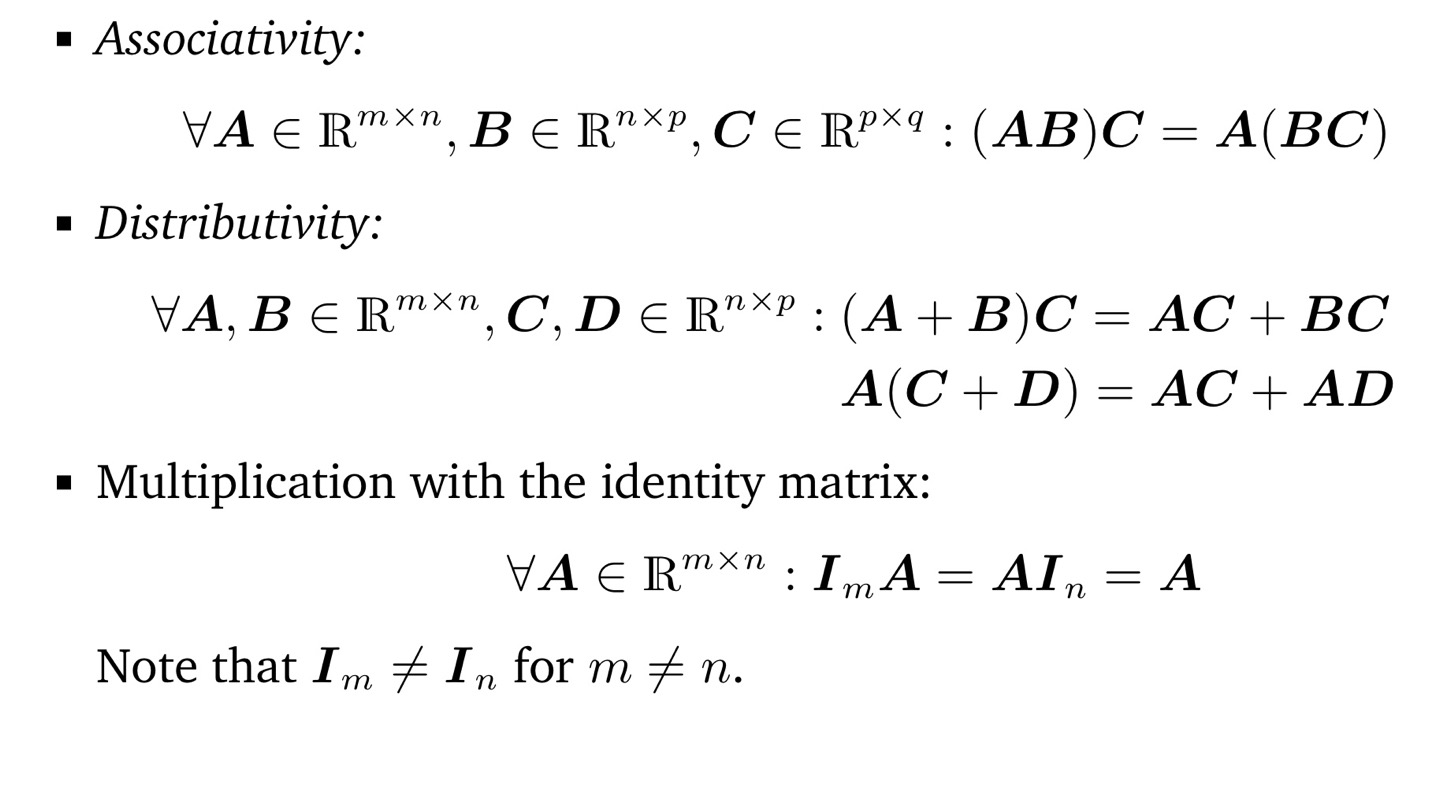
2.2.2 Inverse and Transpose
inverse)
일때, =이고,
를 의 inverse matrix라고 한다.
-
inverser matrix가 존재한다면, 는 regular, invertible, nonsingular 하다고 한다.
-
은 unique하다.
역행렬은 → 의 과정으로 구할 수 있다.
Transpose)
일때, 이면,
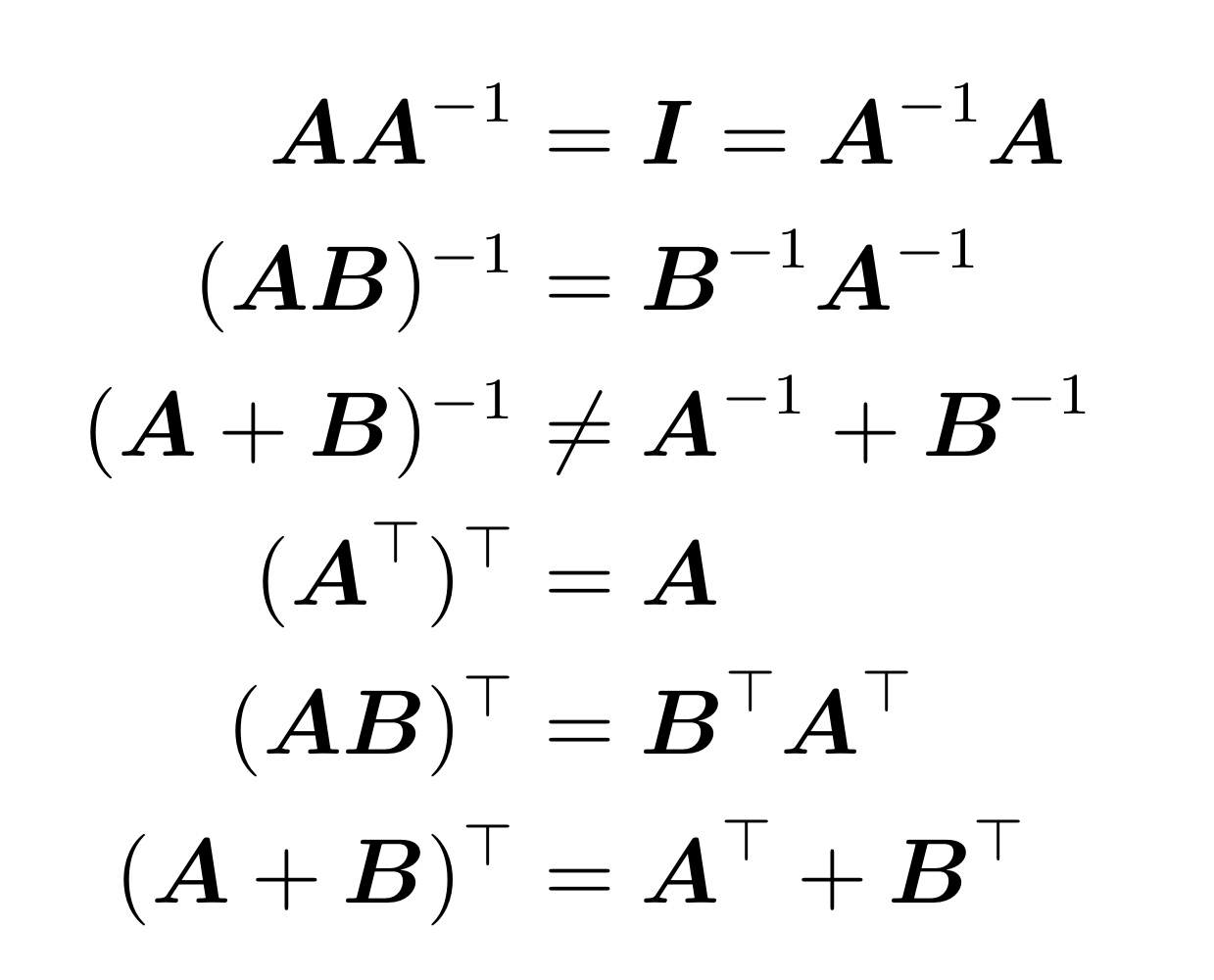
Symmetric Matirx)
인 행렬
- 가 invertible하면 도 invertible하다.
2.2.3 Multiplication by a scalar
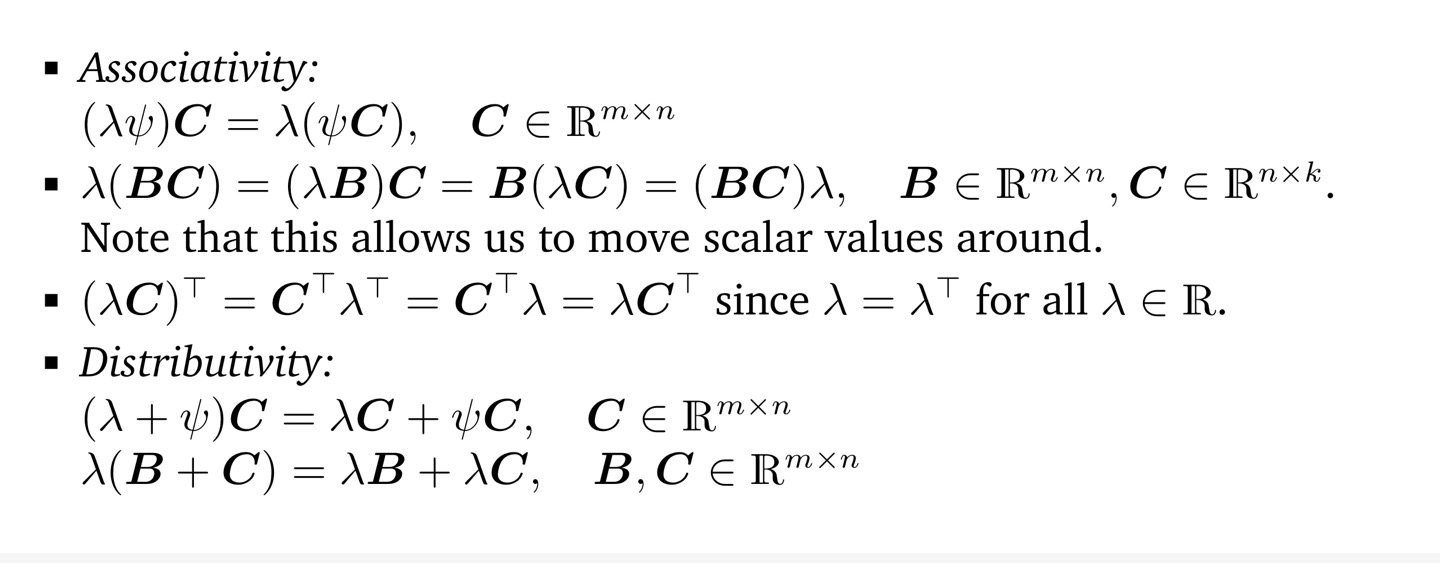
2.3 Solving Systems of Linear Equations
2.3.1 Particular and General Solution
particular solution은 해가 여려 개일 경우, 특정한 하나의 해를 뜻한다.
해가 여려개인 경우 General Soultion을 찾는 방법은 다음과 같다.
- particular solution 찾기
- particular solution 찾기
- 두 해를 합쳐서 표현 → General Solution
2.3.2 Elementary Tansfomations
- exchange two equations(rows)
- multiplicate an equation(rows) with constant λ
- add two equations(rows)
위의 세가지 변환으로 row-echelon form(REF)형태로 만들 수 있다.
pivot: REF의 row에서 0이 아닌 첫번째 값
reduced row echelon form: pivot은 모두 1이고, pivot외의 칼럼은 0인 REF
-> reduced row echelon form을 만듦으로 General Solution을 손쉽게 구할 수 있다.
2.3.3 The Minus-1 Trick
x 행렬에서 비어있는 행의 pivot만 -1인 행을 곱해 x 의 정방행렬로 만들어서 해를 더욱 쉽게 찾을 수 있다.
2.3.4 Algorithms to solve
but, 계산이 너무 복잡함.
Gaussian elimination을 통해 해결할 수 있으나, 변수가 많아지면 이것도 계산하기 힘들어짐.
-> Richardson method, Ja- cobi method, the Gauß-Seidel method, successive over-relaxation method, Krylov subspace methods, conjugate gradients, gener- alized minimal residual, biconjugate gradients등의 방법들은 아래의 식을 통해 간접적으로 해결가능
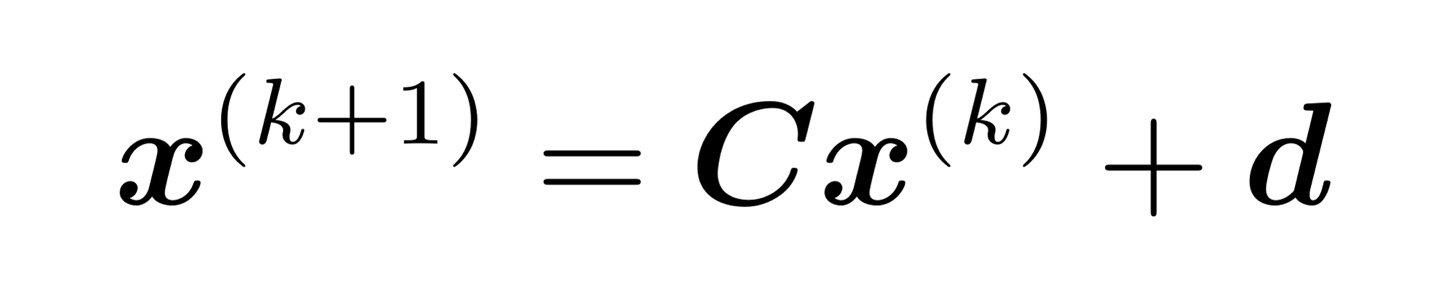
2.4 Vector Spaces
{} 가 정의되는 공간 정의
2.5 Linear Independence
Linear Combination: 벡터공간 에 속해있는 벡터 는 에 속해있는 다른 벡터 들의 상수(λ)배로 나타낼 수 있다.
Linear dependence: 의합으로 0을 만들어 낼 수 없다면, 벡터 들은 서로 linarly independent 하다고 할 수 있다.
2.6 Basis and Rank
2.6.1 Basis
basis: 벡터공간 를 생성하는 선형독립의 최소단위의 벡터 집합
basis 의 집합을 라고 하자.
- 가 벡터공간 에 속할 때 에는 더이상의 선형독립 벡터는 존재하지 않는다.
- 인 벡터 들은 의 선형결합으로 나타낼 수 있다.
basis 결정하는법
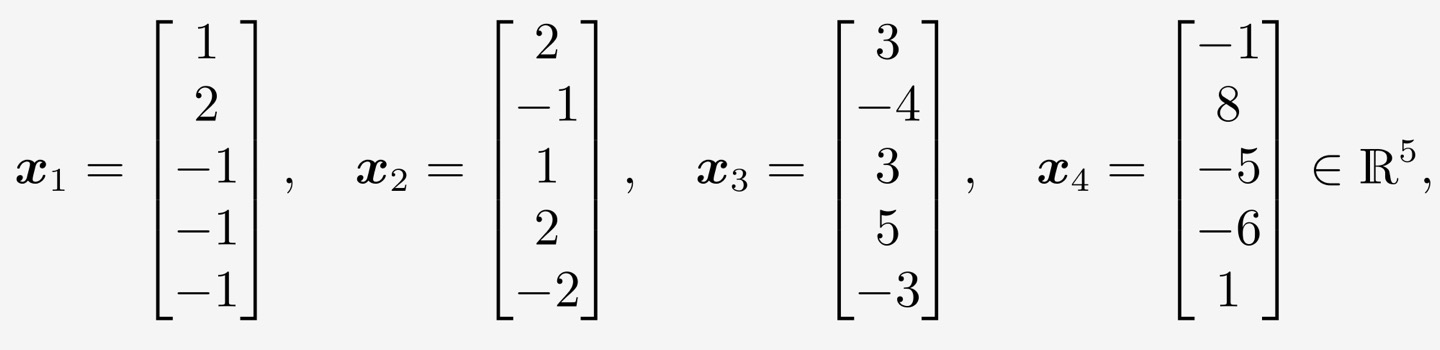
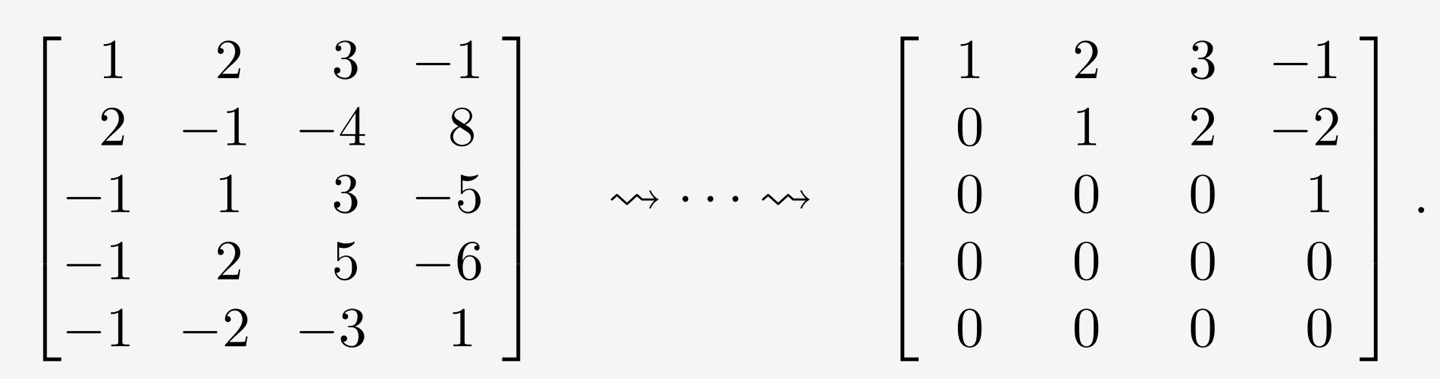
pivot 이 있는 열에 해당하는 벡터가 기저이다.
2.6.2 Rank
rank:
한 행렬에서 linear independent 한 column의 수
= 한 행렬에서 linear independent 한 row의 수
= rk()
