K-Means Clustering
- 비지도 학습(Unsupervised Learning) 기법
- 레이블(정답)이 없는 데이터를 비슷한 것끼리 그룹으로 묶는 알고리즘
- 목표는 각 데이터 x_i와 그것이 속한 클러스터의 중심 c_j 사이의 거리(보토 유클리드 거리)의 제곱합을 최소화하는 것
동작 원리
1. K개의 중심점(centroid)를 부여
2. 각 데이터를 보고 중심점과 가장 가까운 데이터를 기준으로 레이블링
3. 각 그룹에 속한 데이터들의 평균 위치를 찾아 새로운 중심점으로 지정
4. 2~3을 반복하며 중심점 변화가 거의 없는 지점에서 종료
장점
- 구현이 단순하고 빠름
단점
- 적절한 K값을 찾는 것이 필요하다.
- 구형에 가까운 군집만 잘 잡는다.
- 이상치에 민감하다.
적절한 K 선택방법
- 엘보우(Elbow) 방법: K를 바꿔가면서 군집 내 제곱오차합을 계산하고 감소폭이 급격히 꺾이는 지점을 적정 K로 선택
- 실루엣(Silhouette) 계수: 군집 간 분리도와 응집도를 평가해 최적의 K를 선정. 같은 군집 안에서는 서로 가깝고, 다른 군집과는 멀리 떨어져 있다.
Python 실습
from sklearn.preprocessing import scale
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
iris = load_iris()iris.feature_names
# feature에서 단위 텍스트 제거
cols = [i[:-5] for i in iris.feature_names]
cols
# 결과: ['sepal length', 'sepal width', 'petal length', 'petal width']iris_df = pd.DataFrame(data=iris.data, columns = cols)
iris_df.head()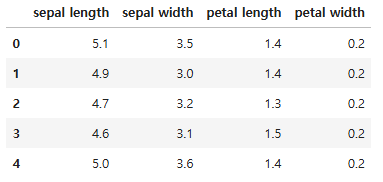
# 두 개의 특성만 사용
feature = iris_df[['petal length','petal width']]
feature.head()# 군집화
model = KMeans(n_clusters = 3)
model.fit(feature)- n_clusters: 군집개수
- init: 초기 군집 중심점의 좌표를 선정하는 방식 결정
- max_iter: 최대 반복횟수
model.labels_
해당 값들은 clustering 결과에 의한 라벨링으로 실제 라벨과 다르다.
# 중심점
model.cluster_centers_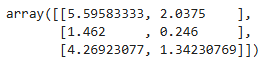
predict= pd.DataFrame(model.predict(feature), columns = ['cluster'])
feature = pd.concat([feature, predict], axis = 1)
feature.head(10)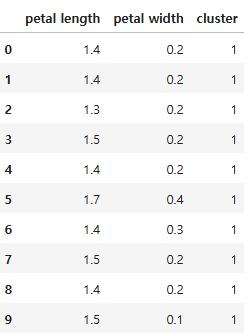
centers = pd.DataFrame(model.cluster_centers_, columns=['petal length', 'petal width'])
center_x = centers['petal length']
center_y = centers['petal width']
plt.figure(figsize=(10,6))
plt.scatter(feature['petal length'], feature['petal width'],
c=feature['cluster'], alpha = 0.5
)
plt.scatter(center_x, center_y, s = 50, marker = 'D', c = 'r')
plt.show()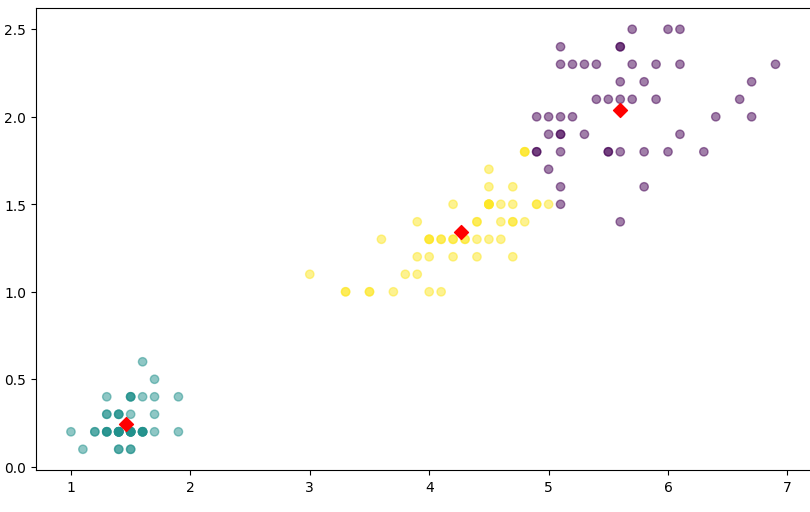
실루엣 계수를 사용한 군집 평가
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
iris = load_iris()
feature_names = ['sepal length', 'sepal width',' petal length','petal width']
iris_df = pd.DataFrame(data = iris.data, columns = feature_names)
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters = 3, init = 'k-means++', max_iter = 300, random_state = 23).fit(iris_df)iris_df['cluster'] = kmeans.labels_
iris_df.head(100)
from sklearn.metrics import silhouette_samples, silhouette_score
avg_value = silhouette_score(iris.data, iris_df['cluster'])
score_values = silhouette_samples(iris.data, iris_df['cluster'])
print('avg_value', avg_value)
print('silhouette_samples() return 값의 shape', score_values.shape)
def visualize_silhouette(cluster_lists, X_features):
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from sklearn.metrics import silhouette_samples, silhouette_score
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.cm as cm
import math
n_cols = len(cluster_lists)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(figsize=(4*n_cols, 4), nrows=1, ncols=n_cols)
for ind, n_cluster in enumerate(cluster_lists):
clusterer = KMeans(n_clusters = n_cluster, max_iter=500, random_state=0)
cluster_labels = clusterer.fit_predict(X_features)
sil_avg = silhouette_score(X_features, cluster_labels)
sil_values = silhouette_samples(X_features, cluster_labels)
y_lower = 10
axs[ind].set_title('Number of Cluster : '+ str(n_cluster)+'\n' \
'Silhouette Score :' + str(round(sil_avg,3)) )
axs[ind].set_xlabel("The silhouette coefficient values")
axs[ind].set_ylabel("Cluster label")
axs[ind].set_xlim([-0.1, 1])
axs[ind].set_ylim([0, len(X_features) + (n_cluster + 1) * 10])
axs[ind].set_yticks([]) # Clear the yaxis labels / ticks
axs[ind].set_xticks([0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1])
for i in range(n_cluster):
ith_cluster_sil_values = sil_values[cluster_labels==i]
ith_cluster_sil_values.sort()
size_cluster_i = ith_cluster_sil_values.shape[0]
y_upper = y_lower + size_cluster_i
color = cm.nipy_spectral(float(i) / n_cluster)
axs[ind].fill_betweenx(np.arange(y_lower, y_upper), 0, ith_cluster_sil_values, \
facecolor=color, edgecolor=color, alpha=0.7)
axs[ind].text(-0.05, y_lower + 0.5 * size_cluster_i, str(i))
y_lower = y_upper + 10
axs[ind].axvline(x=sil_avg, color="red", linestyle="--")visualize_silhouette(cluster_lists = [2,3,4], X_features = iris.data)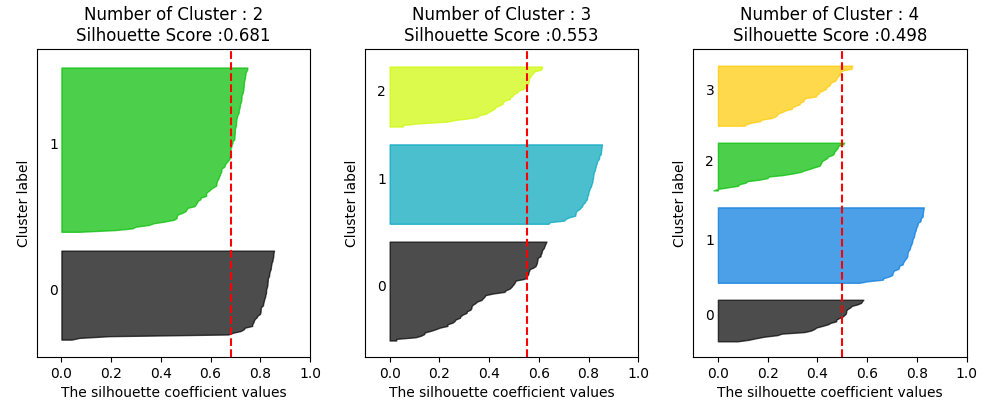
실루엣 계수 해석
- a(i): 같은 군집 안의 다른 점들과 평균 거리 (응집도, Cohesion)
- b(i): 가장 가까운 다른 군집의 평균 거리 (분리도, Seperation)
- 0.7 이상 → 아주 잘 나눠짐
- 0.5 ~ 0.7 → 꽤 괜찮음
- 0.25 ~ 0.5 → 애매, 군집 구조가 약함
- 0 이하 → 군집이 잘못됐을 가능성 높음
