문제 풀이
1. 백준 1012 - 유기농 배추
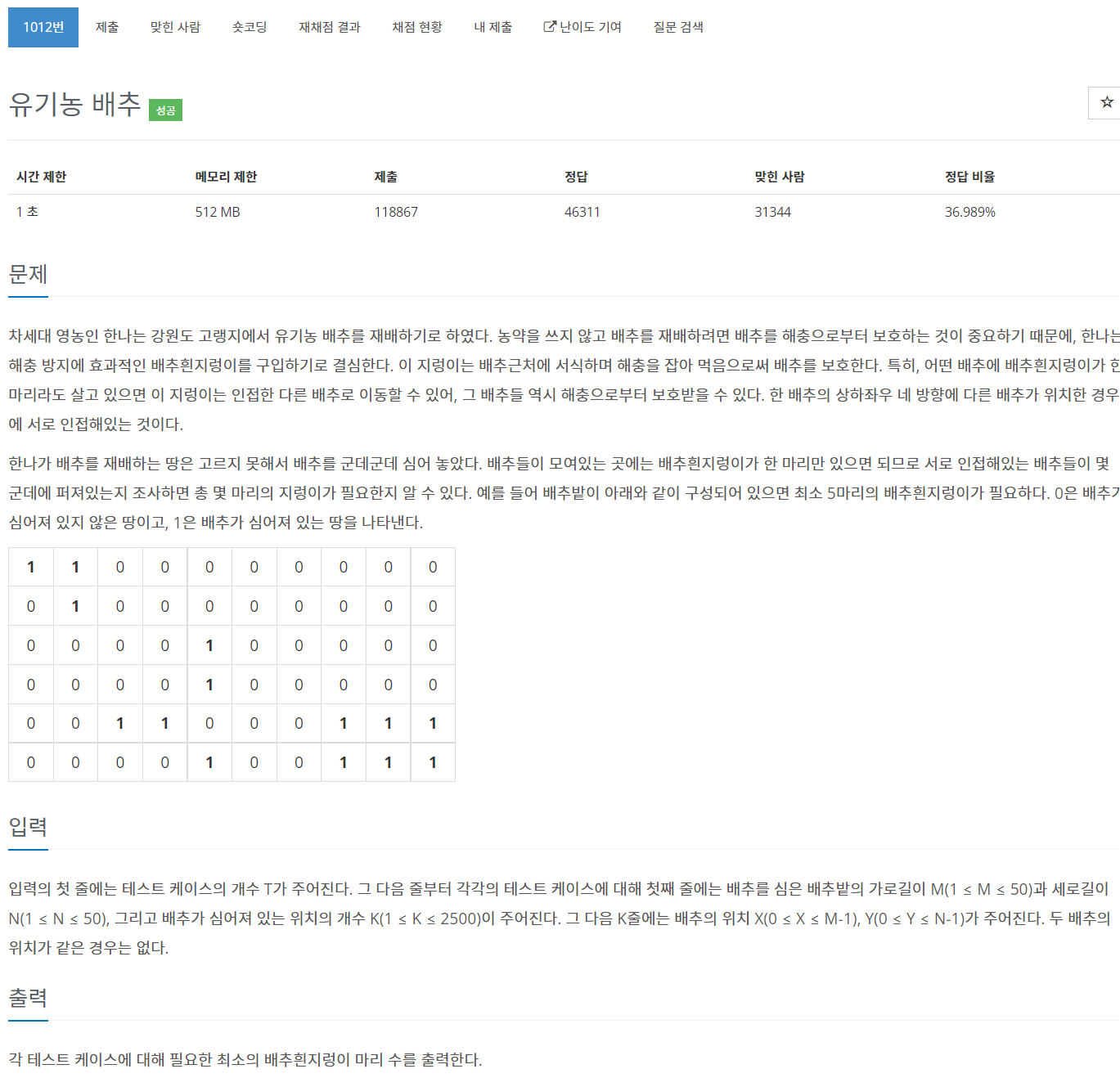
이전 포스팅의 그림 문제와 거의 같은 문제였다. 2차원 배열을 모두 탐색하며 1을 발견하면, BFS 탐색 후 카운트해주면 됐다.
package BFS;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class BOJ1012 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int testCase = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int[][] board;
boolean[][] visited;
for (int i = 0; i < testCase; i++) {
String[] a = br.readLine().split(" ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(a[1]); //행
int m = Integer.parseInt(a[0]); //열
int k = Integer.parseInt(a[2]);
board = new int[n][m];
visited = new boolean[n][m];
Queue<Pair> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int[] dx = {1, 0, -1, 0};
int[] dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {
String[] b = br.readLine().split(" ");
board[Integer.parseInt(b[1])][Integer.parseInt(b[0])] = 1;
}
int cnt = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (int l = 0; l < m; l++) {
if (board[j][l] == 0 || visited[j][l]) continue;
queue.offer(new Pair(j, l));
visited[j][l] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Pair tmp = queue.poll();
for (int o = 0; o < 4; o++) {
int nx = tmp.getX() + dx[o];
int ny = tmp.getY() + dy[o];
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx > n - 1 || ny > m - 1) continue;
if (visited[nx][ny] || board[nx][ny] == 0) continue;
queue.offer(new Pair(nx, ny));
visited[nx][ny] = true;
}
}
cnt++;
}
}
System.out.println(cnt);
}
}
}2. 백준 10026 - 적록색약
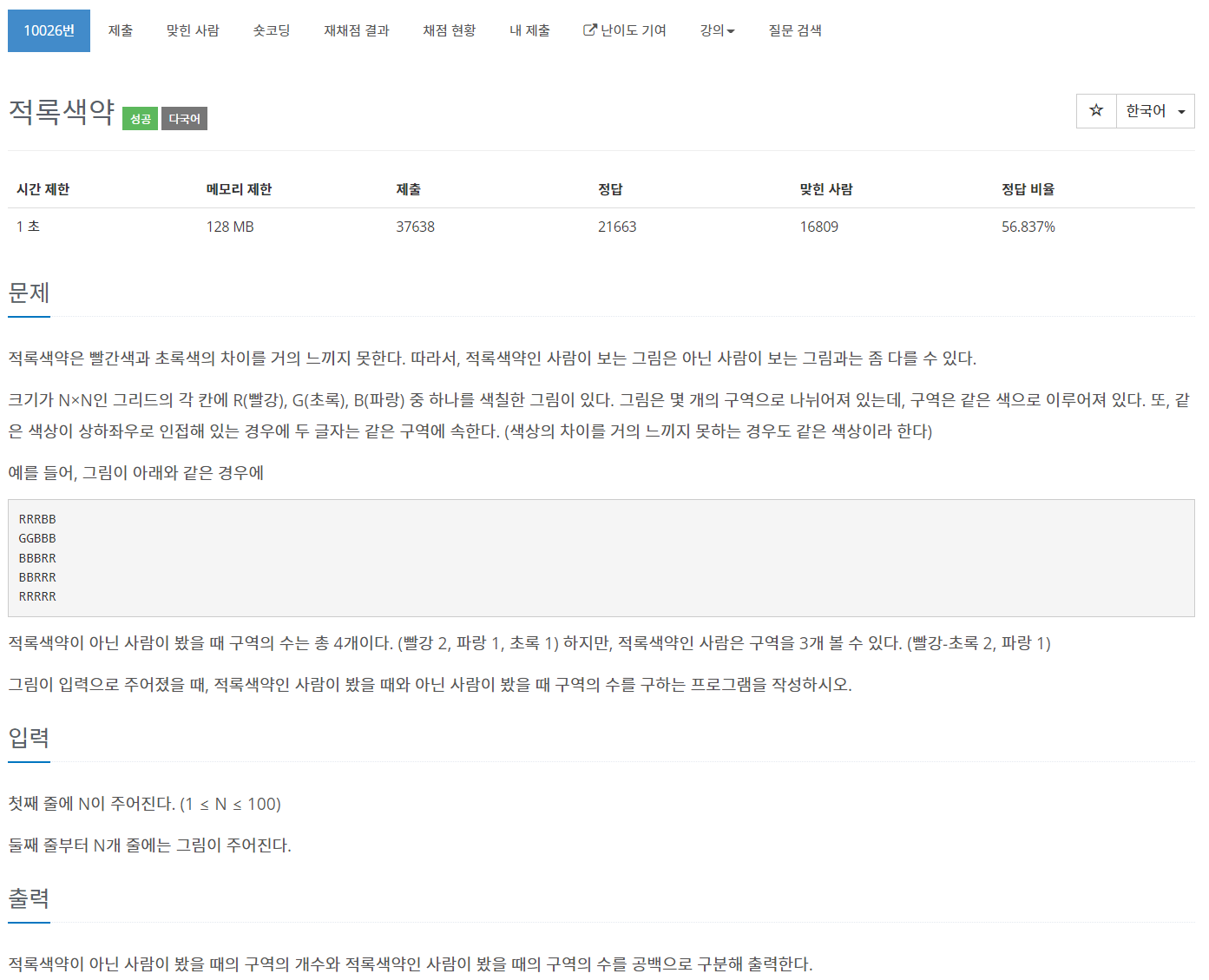
똑같이 영역의 개수를 탐색하는 문제다. 다만 탐색을 두번 하고, 한 번의 탐색에는 R과 G를 구분하지 않아야한다.
package BFS;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class BOJ10026 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
char[][] board = new char[n][n];
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][n];
int[] dx = {1, 0, -1, 0};
int[] dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int nx = 0;
int ny = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
char[] a = br.readLine().toCharArray();
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
board[i][j] = a[j];
}
}
Queue<Pair> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int cnt = 0;
//정상인
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (visited[i][j]) continue;
queue.offer(new Pair(i, j));
visited[i][j] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Pair tmp = queue.poll();
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
nx = tmp.getX() + dx[k];
ny = tmp.getY() + dy[k];
if (nx < 0 || nx > n-1 || ny < 0 || ny > n-1) continue;
if (visited[nx][ny] || board[i][j] != board[nx][ny]) continue;
queue.offer(new Pair(nx, ny));
visited[nx][ny] = true;
}
}
cnt++;
}
}
System.out.println(cnt);
cnt=0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Arrays.fill(visited[i], false);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 'G') board[i][j] = 'R';
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (visited[i][j]) continue;
queue.offer(new Pair(i, j));
visited[i][j] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Pair tmp = queue.poll();
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
nx = tmp.getX() + dx[k];
ny = tmp.getY() + dy[k];
if (nx < 0 || nx > n-1 || ny < 0 || ny > n-1) continue;
if (visited[nx][ny] || board[i][j] != board[nx][ny]) continue;
queue.offer(new Pair(nx, ny));
visited[nx][ny] = true;
}
}
cnt++;
}
}
System.out.println(cnt);
}
private static void showVisited(boolean[][] visited) {
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
for (int i = 0; i < visited.length; i++) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(visited[i]));
}
}
}
정상인에 대한 탐색 이후에 board 자체를적록색맹에 맞게 수정했다.
3. 백준 7562 - 나이트의 이동
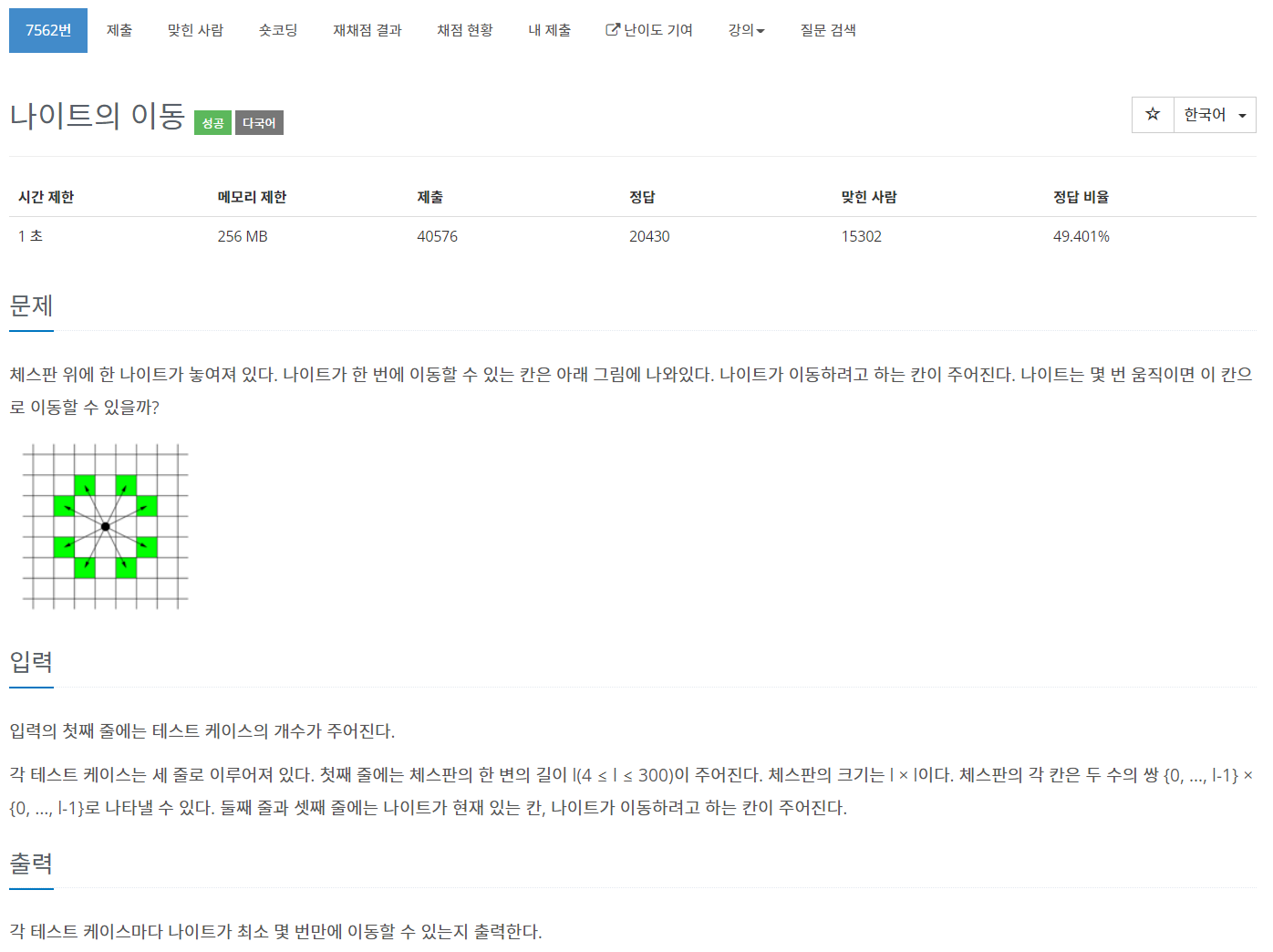
간단한 응용문제였다. 지금까지 상하좌우를 검사했던 것을 수정해주면 된다.
package BFS;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class BOJ7562 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int testCase = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
boolean[][] visited;
int[] dx = {-2, -1, 1, 2, 2, 1, -1, -2};
int[] dy = {1, 2, 2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1};
int ny = 0;
int nx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < testCase; i++) {
int cnt = 0;
Queue<Pair> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
visited = new boolean[n][n];
String[] begin = br.readLine().split(" ");
String[] a = br.readLine().split(" ");
Pair target = new Pair(Integer.parseInt(a[0]), Integer.parseInt(a[1]));
queue.offer(new Pair(Integer.parseInt(begin[0]), Integer.parseInt(begin[1])));
visited[Integer.parseInt(begin[0])][Integer.parseInt(begin[1])] = true;
a : while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int tmpSize = queue.size();
for (int k = 0; k < tmpSize; k++) {
Pair tmp = queue.poll();
if (tmp.equals(target)) {
System.out.println(cnt);
break a;
}
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
nx = tmp.getX() + dx[j];
ny = tmp.getY() + dy[j];
if (nx < 0 || nx > n - 1 || ny < 0 || ny > n - 1) continue;
if (visited[nx][ny]) continue;
queue.offer(new Pair(nx, ny));
visited[nx][ny] = true;
}
}
cnt++;
}
}
}
}dx와 dy 배열에 주목하자. 그 외에는 특별한 점 없다.
이번 문제들은 BFS 개념과 구현에 익숙해지기 위한 문제들이었고, 다음 포스팅에서는 본격적으로 BFS를 활용하는 난이도가 있는 문제들을 풀어볼 것이다.
연습문제 출처 : encrypted-def github
