Breadth-First Search 0-1 Knapsack Problem
Breadth-First Search_너비 우선 탐색
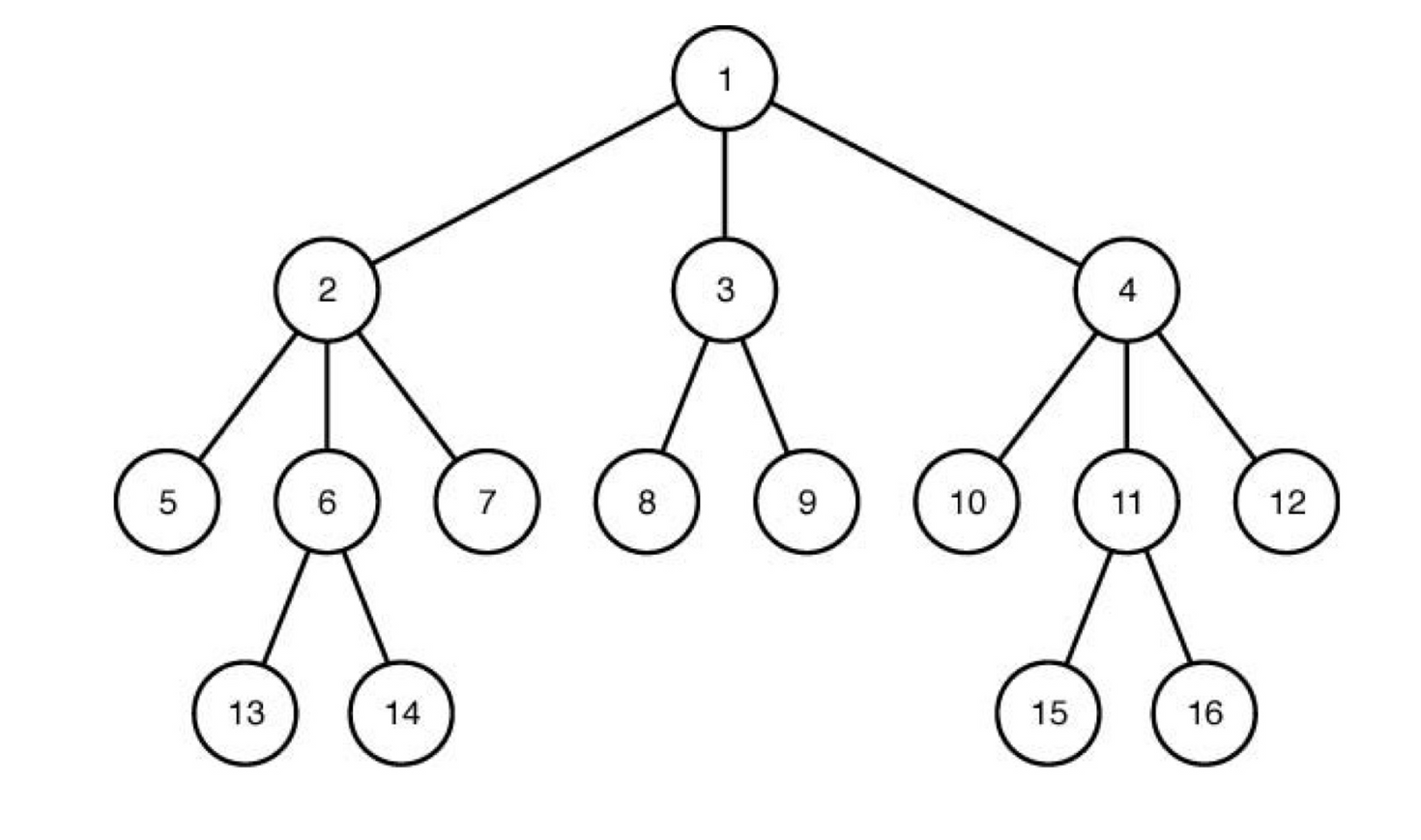
BFS를 사용하면 다음과 같은 순서로 노드를 방문한다.
BFS Pseudo Code
void breadth_first_search(tree T) {
queue_of_node Q;
node u, v;
initialize(Q); // Initialize Q to be emptyv = root of T;
visit v;
enqueue(Q,v);
while(!empty(Q)) {
dequeue(Q,v);
for(each child u of v) {
visit u;
enqueue(Q,u);
}
}
}Depth First는 재귀적인 방식으로 노드를 방문하지만, breadth First는 Queue(이하 Q)를 사용한다.
- Q를 초기화 하고 루트를 방문해 할 일을 한다.
- root 노드를 먼저 Q에 넣어준다.
- 반복문을 수행하면서 노드를 탐색한다.
- 노드를 차례로 하나 꺼낸다. ⇒ queue이므로 FIFO
- 그 노드에 자식이 있으면 자식을 방문하고, Q에 넣는다.
이걸 Branch and Bound에 어떻게 사용할 건데?
BFS는 ‘노드를 Queue에 넣으면, 자식을 방문한다.’ 는 패턴을 가지고 있다는 것을 알 수 있다.
따라서 Bound를 정하고, Bound에 따라 그 노드가 유망하지 않다고 판단되면
Branch하지 않도록 Queue에 넣지 않으면 된다.
void breadth_first_branch_and_bound(state_space_tree T, number &best) {
queue_of_node Q;
node u, v;
initialize(Q); // Initialize Q to be emptyv = root of T; // Visit root
enqueue(Q, v);
best = value(v);
while (!empty(Q)) {
dequeue(Q, v);
for (each child u of
v) { // Visit each childif(value(u) is better than best)
best = value(u);
if (bound(u) is better than best)
enqueue(Q, u);
}
}
}dfs에서는 root에도 bound가 있지만, bfs는 root에 bound가 없다.
bound가 best보다 좋아야 queue에 넣을 수 있다.
Breadth-FS 0-1 Knapsack Problem
문제 상황
앞서 Backtracking에서 나온0-1 Knapsack Problem과 같으므로 간단하게 사진만 첨부함
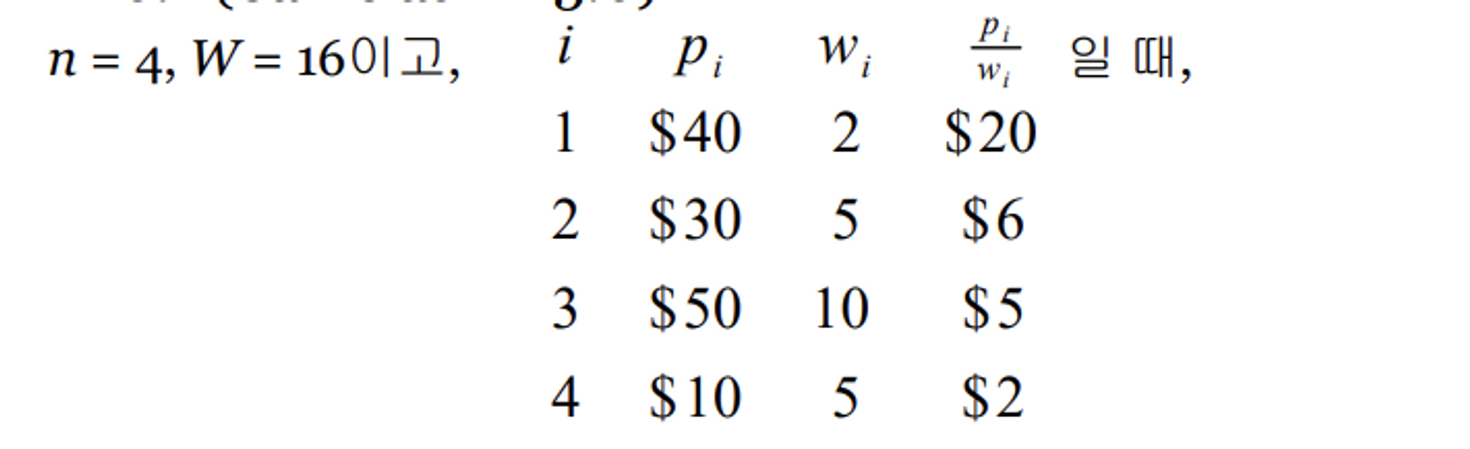
Pseudo Code
Struct node {
int level;
int profit;
int weight;
}
void knapsack2(int n, const int p[], cont int w[], int W, int &maxprofit) {
queue_of_node Q;
node u, v;
initialize(Q);
v.level = 0;
v.profit = 0;
v.weight = 0;
maxprofit = 0;
enqueue(Q, v);
while (!empty(Q)) {
dequeue(Q, v);
u.level = v.level + 1;
u.profit = v.profit + p[u.level];
u.weight = v.weight + w[u.level];
//maxprofit 갱신 여부를 나타냄
if (**(u.weight <= W) && (u.profit > maxprofit)**)
maxprofit = u.profit;
//Q에 넣을지 말지 결정함=> 유망한가?
if **(bound(u) > maxprofit**)
enqueue(Q, u);
u.weight = v.weight;
u.profit = v.profit;
if (bound(u) > maxprofit)
enqueue(Q, u);
}
}
float bound(node u) {
index j, k;
int totweight;
float result;
if (u.weight >= W)
return 0;
else {
result = u.profit;
j = u.level + 1;
totweight = u.weight;
while ((j <= n) && (totweight + w[j] <= W)) {
totweight = totweight + w[j];
result = result + p[j];
j++;
}
k = j;
if (k <= n)
result = result + (W - totweight) * p[k] / w[k];
return result;
}
}
여기서 구조체는 queue에 node를 넣는 용도 만으로 사용한다.
직접 left와 right를 가리키지 않는다.
dfs에서 bound는 promising함수 안에서 구해지고, promising의 여부만 판단해주었는데,
bfs에서는 bound를 구해 float으로 return 해주어야한다.
⇒만약, u노드까지 선택한 물건들의 무게의 합이 W보다 크거나 같으면(유망하지 않으면)
bound를 0으로 return하는데, 이렇게 되면 무조건 maxprofit보다 작으므로,
노드를 queue에 넣지 않는다.
예시로 보는 동작 원리
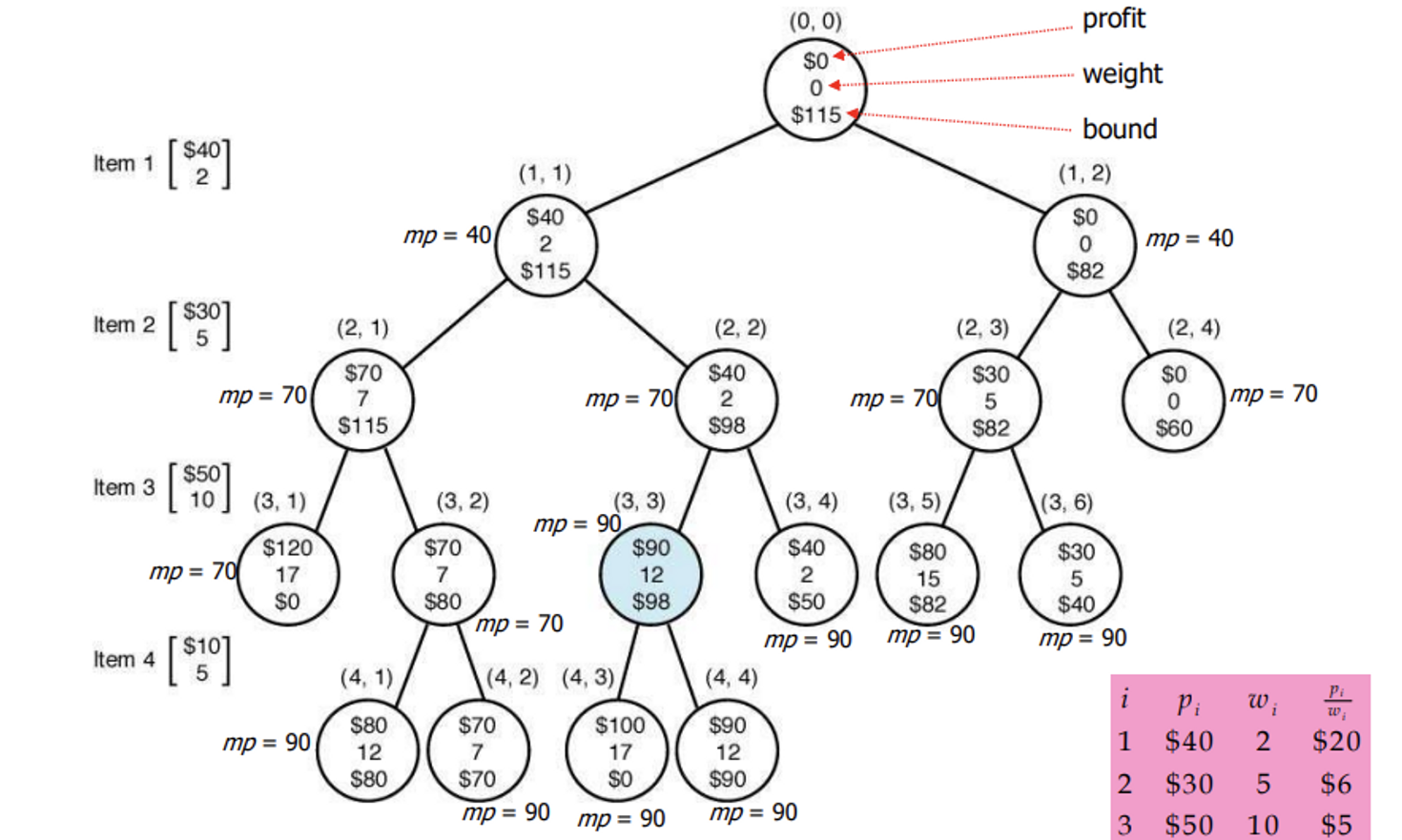
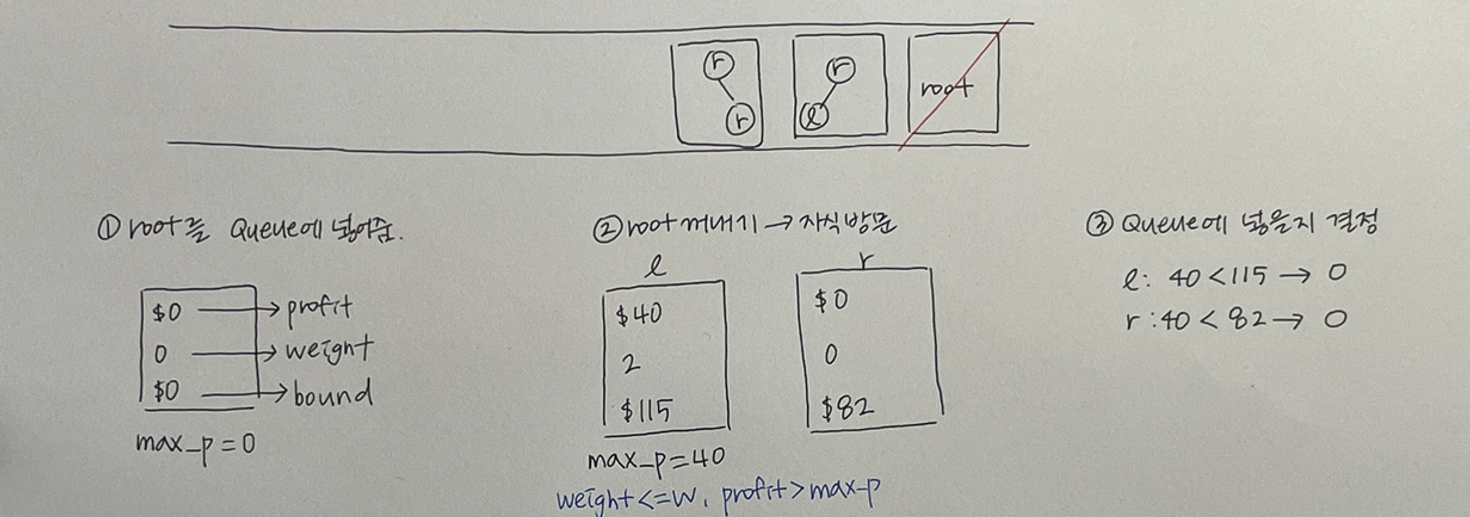
max_p는 노드마다 바뀔 수도 있고, 바뀌지 않을 수도 있음
⇒ 갱신 조건과 유망 조건 헷갈리지 말 것
DFS보다 더 많은 노드를 탐색한다→ 성능이 좋아지진 않는다
⇒ max_profit이 더 많이, 빨리 갱신 될 수록 탐색할 노드 수는 줄어들 것이다
