⚡ Spring AOP
📌 AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)
🔷 모듈화의 단위
OOP: 클래스AOP: Aspect(관점)
💡
Aspect
여러 타입과 객체에 거쳐서 사용되는 기능(Cross Cutting, 트랜잭션 관리 등)의 모듈화
💡
Cross Cutting: 공통 관심사항(핵심 관심사항을 관통하는 관점)
💡Core Concern: 핵심 관심사항(주 기능들)
🔷 Spring framework의 필수요소는 아니지만, AOP 프레임워크는 Spring IoC를 보완한다.
🔷 기존의 경우
🖥 Programmer
package com.Bzeromo.proxy;
import java.util.Random;
public class Programmer {
public void coding() {
System.out.println("컴퓨터를 켜용");
try {
System.out.println("코딩을 열심히 해용");
if(new Random().nextBoolean())
throw new DiseaseException();
System.out.println("Git에 Push 해용");
} catch (DiseaseException e) {
System.out.println("병원을 가용");
} finally {
System.out.println("이제 잠을 자용");
}
// System.out.println("컴퓨터를 켜용"); // 이전에 해야될 것
// System.out.println("코딩을 열심히 해용"); // 핵심 관심사항
// System.out.println("Git에 Push 해용"); // 이상 없이 마무리가 되었을 때
// System.out.println("이제 잠을 자용"); // 모든게 마무리가 되었을 때
}
}🖥 DiseaseException
package com.Bzeromo.proxy;
public class DiseaseException extends RuntimeException{
}🖥 Test
package com.Bzeromo.proxy;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Programmer p = new Programmer();
p.coding();
}
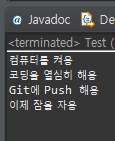
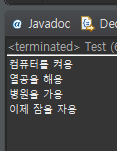
}예외 발생 시
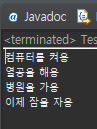
정상 실행 시
🔷 프록시 패턴 적용
🖥 interface Person
package com.Bzeromo.proxy2;
public interface Person {
public void coding();
}🖥 PersonProxy
package com.Bzeromo.proxy2;
import java.util.Random;
import com.Bzeromo.proxy.DiseaseException;
public class PersonProxy implements Person{
// Ssafy와 Programmer를 핵심 관심사항으로 넣을수 있다
private Person person;
public void setPerson(Person person) {
this.person = person;
}
@Override
public void coding() {
System.out.println("컴퓨터를 켜용");
try {
person.coding();
if(new Random().nextBoolean())
throw new DiseaseException();
System.out.println("Git에 Push 해용");
} catch (DiseaseException e) {
System.out.println("병원을 가용");
} finally {
System.out.println("이제 잠을 자용");
}
}
}🖥 Programmer
package com.Bzeromo.proxy2;
public class Programmer implements Person {
@Override
public void coding() {
System.out.println("코딩을 열심히 해용"); // 핵심 관심사항
}
}🖥 Ssafy
package com.Bzeromo.proxy2;
public class Ssafy implements Person {
@Override
public void coding() {
System.out.println("열공을 해용");
}
}🖥 Test
package com.Bzeromo.proxy2;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Programmer p = new Programmer();
Ssafy s = new Ssafy();
PersonProxy px = new PersonProxy();
px.setPerson(s);
px.coding();
}
}정상 실행 시
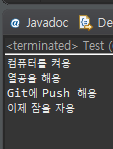
예외 발생 시
🤔 AOP 용어
-
Join Point: 메서드 실행이나 예외처리와 같은 프로그램 실행중의 특정 지점. (Spring에서는 메서드 실행) -
Pointcut: Join Point에 Aspect를 적용하기 위한 조건 서술. Aspect는 지정한 pointcut에 일치하는 모든 join point에서 실행된다. -
Advice: 특정 조인포인트(Join Point)에서 Aspect에 의해서 취해진 행동. Around, Before, After 등의 Advice 타입이 존재 -
Target 객체: 하나이상의 advice가 적용될 객체. Spring AOP는 Runtime Proxy를 사용하여 구현되므로 객체는 항상Proxy(대행자)객체가 된다. -
AOP Proxy: AOP를 구현하기 위해 AOP 프레임워크에 의해 생성된 객체, Spring Framework에서 AOP 프록시는 JDK dynamic proxy 또는 CGLIB proxy이다. -
Weaving: Aspect를 다른 객체와 연결하여 Advice 객체를 생성. 런타임 또는 로딩 시 수행할 수 있지만 Spring AOP는 런타임에 위빙을 수행
⭐ Spring AOP
🔷 Spring AOP Proxy
- 실제 기능이 구현된 Target 객체를 호출하면, target이 호출 되는 것이 아니라 advice가 적용된 Proxy 객체가 호출된다.
- Spring AOP는 기본값으로 표준 JDK dynamic proxy를 사용
- 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스가 아닌 경우 CGLIB 프록시를 사용
🔷 Spring AOP
@AspectJ: 일반 Java 클래스를 Aspect로 선언하는 스타일, AspectJ 프로젝트에 의해 소개되었다.- Spring AOP에서는 pointcut 구문 분석, 매핑을 위해서 AspectJ 라이브러리를 사용함
- 하지만 AOP runtime은 순수 Spring AOP이며, AspectJ에 대한 종속성은 없음
🔷 AOP 설정
🖥 pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>Spring_Day02_AOP_1_Proxy</groupId>
<artifactId>Spring_Day02_AOP_1_Proxy</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<spring-version>5.3.18</spring-version>
<aspectj-version>1.9.8</aspectj-version>
</properties>
<build>
<sourceDirectory>src</sourceDirectory>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.0</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-context -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.aspectj/aspectjweaver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>${aspectj-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.aspectj/aspectjrt -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId>
<version>${aspectj-version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>💡 properties 내에 설정된 프로퍼티의 버전을 바꾸면 dependency로 불러온 라이브러리의 버전이 함께 수정된다.
🔷 Aspect 선언 - xml 방식
- Aspect는 공통 관심사항!
- pointcut 선언
- 포인트 컷은 어떤 조인포인트를 사용할지 결정한다. Spring AOP는 메서드 실행만 지원한다.
- 포인트 컷 선언은 두 내용을 포함한다.
1) 조인포인트에 대한 표현식 ( "execution(접근제한자반환타입패키지클래스메서드)" )
2) 포인트 컷의 이름 (id)
🔷 Advice type에 따른 메서드 지정이 가능하다.
1) before - target 메서드 호출 이전
2) after - target 메서드 호출 이후, java exception 문장의 finally와 같이 동작
3) after returning - target 메서드 정상 동작 후
4) after throwing - target 메서드 에러 발생 후
5) around - target 메서드의 실행 시기, 방법, 실행 여부를 결정
🖥 applicationContext.xml(around X)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd">
<!-- AOP 관련 어노테이션들을 자동으로 인식하고 용도에 맞게 처리해주기 때문에 꼭 넣어야 한다 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
<bean class="com.Bzeromo.aop.Programmer" id="programmer"/>
<bean class="com.Bzeromo.aop.Ssafy" id="ssafy"/>
<bean class="com.Bzeromo.aop.MyAspect" id="myAspect"/>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(public void com.Bzeromo.aop.*.coding())" id="mypt"/>
<aop:aspect ref="myAspect">
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="mypt"/>
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturning" pointcut-ref="mypt"/>
<aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowing" pointcut-ref="mypt" throwing="th"/>
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="mypt"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
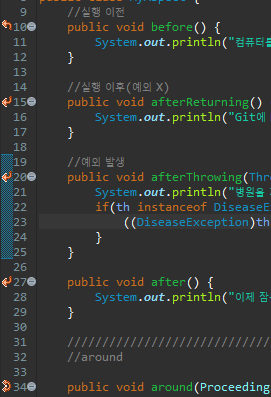
</beans>🖥 MyAspect(around X)
package com.Bzeromo.aop;
import java.util.Random;
//공콩 관심사항들을 작성할 클래스 생성
public class MyAspect {
//실행 이전
public void before() {
System.out.println("컴퓨터를 켜용");
}
//실행 이후(예외 X)
public void afterReturning() {
System.out.println("Git에 Push해용");
}
//예외 발생
public void afterThrowing(Throwable th) {
System.out.println("병원을 가용");
if(th instanceof DiseaseException) {
((DiseaseException)th).handleException();
}
}
public void after() {
System.out.println("이제 잠을 자용");
}
}
//행동 하나하나를 advice라고 한다.🖥 Programmer(around X)
package com.Bzeromo.aop;
import java.util.Random;
public class Programmer implements Person {
//join point
//프록시가 만들어지면 그것이 위빙
@Override
public void coding() {
System.out.println("코딩을 열심히 해용"); // 핵심 관심사항
if(new Random().nextBoolean()) {
throw new DiseaseException();
}
}
}🖥 DiseaseException
package com.Bzeromo.aop;
public class DiseaseException extends RuntimeException{
public void handleException() {
System.out.println("입원을 해용");
}
}🖥 Test
package com.Bzeromo.aop;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Person p = context.getBean("programmer", Person.class);
p.coding();
}
}정상 실행 시
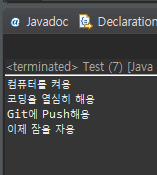
예외 발생 시
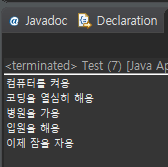
💡 around 사용 시에는 코드가 달라진다.
🖥 applicationContext.xml(around O)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd">
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
<bean class="com.Bzeromo.aop.Programmer" id="programmer"/>
<bean class="com.Bzeromo.aop.Ssafy" id="ssafy"/>
<bean class="com.Bzeromo.aop.MyAspect" id="myAspect"/>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(public void com.Bzeromo.aop.*.coding())" id="mypt"/>
<aop:aspect ref="myAspect">
<aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="mypt"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>🖥 MyAspect(around O)
package com.Bzeromo.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
//공콩 관심사항들을 작성할 클래스 생성
public class MyAspect {
//실행 이전
public void before() {
System.out.println("컴퓨터를 켜용");
}
//실행 이후(예외 X)
public void afterReturning() {
System.out.println("Git에 Push해용");
}
//예외 발생
public void afterThrowing(Throwable th) {
System.out.println("병원을 가용");
if(th instanceof DiseaseException) {
((DiseaseException)th).handleException();
}
}
public void after() {
System.out.println("이제 잠을 자용");
}
//////////////////////////////////////////
//around
//xml에서 메서드들을 따로따로 지정한 것이 아닌 만큼 코드로 지정을 구현해주어야 한다.
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjt) {
//before
this.before();
//afterThrowing
try {
pjt.proceed();
this.afterReturning();
} catch (Throwable e) {
this.afterThrowing(e);
} finally {
this.after();
}
}
}💡 Aspect와 메서드 지정이 되면 이클립스는 앞에 화살표로 이를 표시해준다. 실행 이전, 이후, around, 공통 관심사항을 호출하는 메서드인지에 따라 모양이 달라진다.
🔷 Aspect 선언 - Annotation 방식
- bean을 Annotation으로 등록한 것과 비슷한 방식이다.
🖥 applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd">
<!-- AOP 관련 어노테이션들을 자동으로 인식하고 용도에 맞게 처리해주기 때문에 꼭 넣어야 한다 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.Bzeromo.aop"></context:component-scan>
</beans>🖥 MyAspect
package com.Bzeromo.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//공콩 관심사항들을 작성할 클래스 생성
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.Bzeromo.aop.*.coding())")
public void mypt() {}
//실행 이전
@Before("mypt()")
public void before() {
System.out.println("컴퓨터를 켜용");
}
//실행 이후(예외 X)
@AfterReturning("mypt()")
public void afterReturning() {
System.out.println("Git에 Push해용");
}
//예외 발생
@AfterThrowing(value = "mypt()", throwing = "th")
public void afterThrowing(Throwable th) {
System.out.println("병원을 가용");
if(th instanceof DiseaseException) {
((DiseaseException)th).handleException();
}
}
@After("mypt()")
public void after() {
System.out.println("이제 잠을 자용");
}
//////////////////////////////////////////
//around
@Around("mypt()")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjt) {
//before
this.before();
//afterThrowing
try {
pjt.proceed();
this.afterReturning();
} catch (Throwable e) {
this.afterThrowing(e);
} finally {
this.after();
}
}
}애너테이션 실습에는 그냥 around도 한꺼번에 넣었다.
🖥 Programmer
package com.Bzeromo.aop;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Programmer implements Person {
@Override
public void coding() {
System.out.println("코딩을 열심히 해용"); // 핵심 관심사항
}
}🖥 Test
package com.Bzeromo.aop;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Person p = context.getBean("programmer", Person.class);
p.coding();
}
}테스트 결과는 xml 방식과 동일하다.
Spring은 설정이 반이라더니, 이제야 그 뜻을 알 것 같다.