출처:
Big-O notation
수학표기이지만 컴공에서는 알고리즘의 복잡도(시간 복잡도)를 단순화할때 사용
를 만족하는 충분히 큰 모든 에 대하여 가 성립하도록 하는 양의 실수 과 실수 가 존재하면 이다.
ex)
이라면 에 대해서
으로
사실 Big-O가 정확히 무엇을 뜻하는지는 모르겠고
여기서는 알고리즘의 시간 복잡도가 해당 차수 또는 그 이하의 차수라는 의미 (최악의 경우를 표현)
예를 들어 내가 가로가 n, 세로가 3n+5인 밭의 1x1 영역마다 씨앗을 하나씩 심는다면
번의 작업을 해야하는데 이를 Big-O로 표기하면
으로 표현할 수 있다. 밭의 가로 길이 n이 늘어나면 작업은 에 비례하는구나.
정렬
오름차순 정렬로 작성함
10000개의 무작위 정수 리스트로 작동 시간 측정
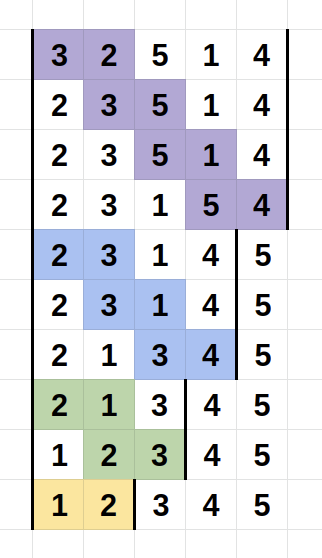
삽입 정렬
i번째 원소를 이미 정렬된 (i-1)개의 원소들 사이의 적절한 위치에 삽입하는 알고리즘
def insertion_sort(nums):
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
val = nums[i]
j = i
while j >= 1 and nums[j-1] > val:
# 원소를 삽입할 위치를 찾을때까지 원소들을 한칸씩 뒤로 밀기
nums[j] = nums[j-1]
j -= 1
nums[j] = val
return nums- 특징
- 안정 정렬
동일한 값의 원소들간의 순서는 바뀌지 않는다. 정렬에 이용되는 키값 외의 다른 값이 있는 경우에는 중요하다. - 구현이 간단 / 데이터가 정렬되어있을수록 효율적
- 적은 데이터에 효율적: 더 빠른 정렬 방식을 사용하되 데이터가 적을때 삽입정렬을 적용하기도 한다.
- 원소간 위치 변화가 잦음 - 데이터가 많을수록 비효율적
- 안정 정렬
- O
- best:
이미 정렬되어있다면 2번째~n번째 원소를 바로 앞의 원소들과 비교하여 총 (n-1)번 비교 - worst:
역순으로 정렬되어있다면 바깥 루프의 i번째 반복때 내부 루프에서 i번 비교 & 원소 위치 교환
- best:
- 3.45 s ± 36.5 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 3 runs, 3 loops each)
- 리팩토링 - 2.76 s ± 88.3 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 3 runs, 3 loops each)
j=i를j=i-1로 변경하며 while 루프의 조건에서j-1연산을 제거- while 루프 조건에서
j>=0보다nums[j]를 앞에 위치시킴- and 연산시에 선행하는 조건이 False라면 뒤의 조건은 연산없이 False 결과를 낸다.
def insertion_sort(nums):
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
val = nums[i]
j = i-1
while nums[j] > val and j >= 0:
# 원소를 삽입할 위치를 찾을때까지 원소들을 한칸씩 뒤로 밀기
nums[j+1] = nums[j]
j -= 1
nums[j+1] = val
return nums선택 정렬
i번째 원소와 (i+1)~n번째 원소 중 최솟값인 원소와 교환. 나머지 원소들에 반복한다.
def selection_sort(nums):
for i in range(len(nums)-1):
min_idx = i
for j in range(i+1, len(nums)):
if nums[min_idx] > nums[j]:
min_idx = j
nums[i], nums[min_idx] = nums[min_idx], nums[i]
return nums- 특징
- 구현이 간단 / 메모리가 제한적일때 효과적
- O
- best, worst:
데이터의 정렬 상태에 관계없이 바깥 루프가 (n-1)번 반복하며 내부 루프에서 (n-1), (n-2), ..., 1번 반복
- best, worst:
- 2.03 s ± 25.8 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 3 runs, 3 loops each)
❓ 삽입이 일반적으로 더 빠르다던데...? 파이썬에서 원소 위치 교환이 느려서 그런가??
머지/합병 정렬
분할-정복 알고리즘으로 작동
데이터를 계속 반으로 나누며 길이 1인 배열들로 분할한다.
두개의 길이 1인 배열들의 원소를 비교하고 정렬하여 병합한다.
정렬된 두개의 길이 2인 배열들의 원소를 비교하고 정렬하여 병합한다.
... 반복
def merge_sort(nums):
# 길이가 1인 경우 바로 반환
if len(nums) <= 1:
return nums
n = len(nums)
# 반으로 분할
part_0, part_1 = nums[:n//2], nums[n//2:]
# 재귀로 분할된 파트를 정렬
part_0_sorted, part_1_sorted = merge_sort(part_0), merge_sort(part_1)
merged = []
# 정렬된 파트들의 원소들을 비교하고 정렬하여 하나로 병합함
while part_0_sorted and part_1_sorted:
if part_0_sorted[0] < part_1_sorted[0]:
merged.append(part_0_sorted.pop(0))
else:
merged.append(part_1_sorted.pop(0))
# 한 파트가 먼저 비워진다면 다른 파트 원소들을 순서를 유지한채로 병합 리스트에 추가
merged.extend(part_0_sorted+part_1_sorted)
return merged- 특징
- 병합을 위해 별도의 리스트가 필요 (입력 데이터만큼의 메모리 필요)
- 안정 정렬
- O
- best, worst:
길이 n의 배열을 반으로 계속 쪼개며 길이 1로 만들려면 번 쪼개야한다. (길이 16-8-4-2-1, 4번 쪼개기)
쪼갠 배열들을 다시 병합할때 번의 각 단계마다 병합을 위한 빈 리스트에 총 개의 데이터를 비교, 삽입
- best, worst:
- 34.6 ms ± 1.62 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 3 runs, 3 loops each)
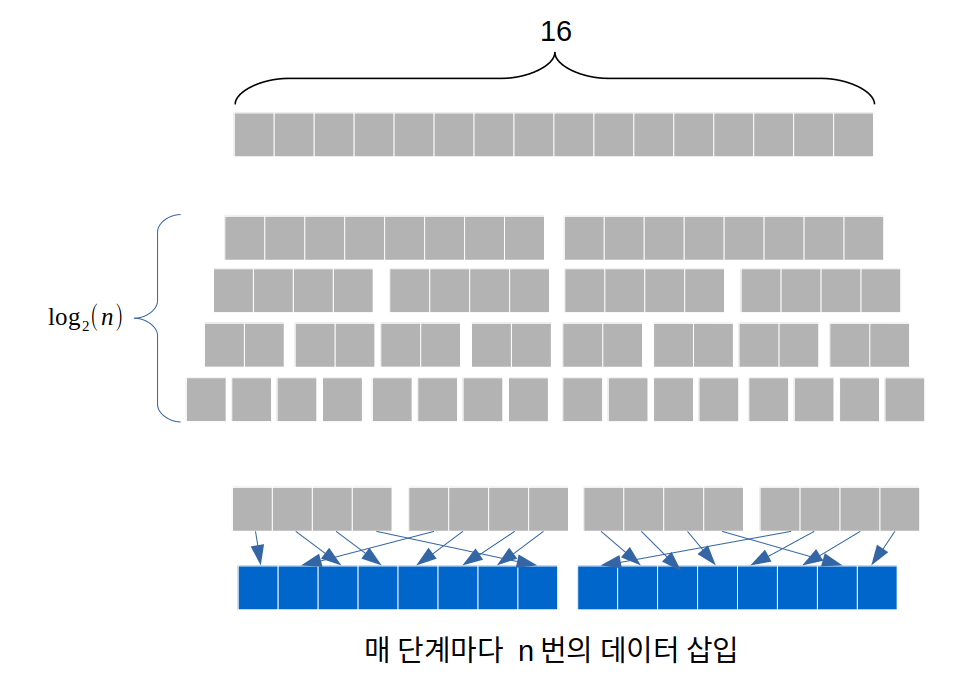
버블 정렬
배열의 처음부터 끝까지 나아가며 인접한 두 원소를 비교, 위치 교환을 반복하며 가장 큰 원소를 배열 끝으로 밀어올리는 작업을 반복한다.
def bubble_sort(nums):
for i in range(len(nums)-1):
for j in range(len(nums)-1-i):
if nums[j] > nums[j+1]:
nums[j], nums[j+1] = nums[j+1], nums[j]
return nums- 특징
- 매우 간단
- 선택 정렬처럼 무조건 매 반복마다 주어진 범위 끝까지 탐색해야하고, 삽입 정렬처럼 위치 교환이 잦다. 느리다.
- O
- best, worst:
외부 루프 (n-1)번 반복하며 매 반복마다 내부 루프에서 (n-1), (n-2), ..., 2, 1번 반복
- best, worst:
- 6.36 s ± 32.3 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 3 runs, 3 loops each)
퀵 정렬
배열의 한 원소를 피벗으로 삼고 원소간 위치 교환을 통해 피벗보다 작은 값은 피벗 좌측에, 피벗보다 큰 값은 피벗 우측에 위치시킨다. 이 작업을 피벗 좌측, 피벗 우측에 반복한다. 분할-점령 방식.
배열의 가장 마지막 원소를 피벗으로 설정한 경우
left는 피벗보다 크거나 같은 값을 선택하고, right는 피벗보다 작은 값을 선택하여 위치를 교환한다.
right가 피벗까지 도달하면 한 사이클 완료. 피벗을 제외한 피벗 좌우의 부분배열에 대해 작업을 반복.
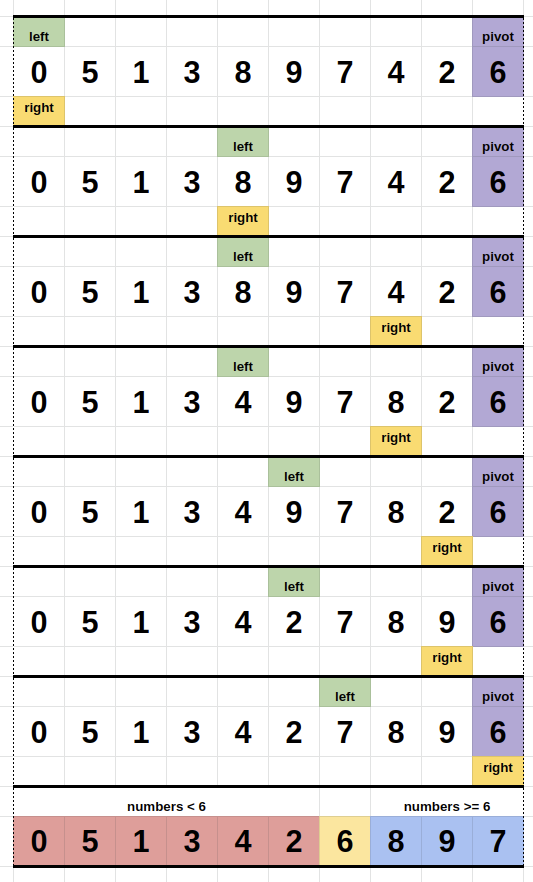
def quick_sort(nums, l_bound=None, r_bound=None):
l_bound = 0 if l_bound is None else l_bound
r_bound = len(nums)-1 if r_bound is None else r_bound
l = r = l_bound
pivot = nums[r_bound]
while True:
while nums[l] < pivot and r < r_bound:
l += 1
r += 1
while nums[r] >= pivot and r < r_bound:
r += 1
if l != r:
nums[l], nums[r] = nums[r], nums[l]
if r == r_bound:
break
if (l-1) - l_bound >= 1:
quick_sort(nums, l_bound, l-1)
if r_bound - (l+1) >= 1:
quick_sort(nums, l+1, r_bound)
nums_ = nums.copy()
quick_sort(nums_)- 특징
- 이름대로 빠르다.
- 이미 정렬된 데이터에 대해서는 느리다.
- 피벗을 선택하는 방식이 중요하다.
- O
- best:
이상적인 경우 퀵소트 한 사이클 진행 후 피벗이 부분배열의 중간에 위치하면서 배열을 계속하여 반으로 나누는 경우 의 사이클이 수행되고, 각 사이클마다 원소 대부분을 피벗보다 작은지, 같거나 큰지 비교하므로 대충 번 비교. 따라서 . - worst:
이미 정렬된 데이터가 주어지면 피벗 위치가 변하지 않으며 배열을 길이 (n-1) 부분배열과 길이 0 부분배열로 나눔. (n-1) 길이의 부분배열에 대해서도 피벗과 (n-2)개 원소를 비교하고 (n-2) 부분배열과 길이 0 부분배열로 나눔, - worst 이지만 원소 교환 횟수도 적고 한 사이클이 지날때마다 피벗은 정렬 대상에서 제외되어 정렬 알고리즘 중에서 빠르다.
- best:
- 26.7 ms ± 388 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 3 runs, 3 loops each)
힙 정렬
힙heap 트리를 이용한 정렬. 힙 트리는 완전 이진 트리이면서 부모 노드가 자식 노드보다 항상 크거나(max heap) 작다(min heap).
힙 정렬은 힙 트리의 루트는 항상 최소값이거나 최대값임을 이용해 모든 데이터를 힙 트리에 넣고 루트부터 빼와 정렬된 배열을 만드는 방식이다.
- 힙트리의 동작 - 최소힙 기준
- 삽입: 완전 이진 트리를 유지하며 힙의 가장 마지막에 데이터 추가. 새로운 데이터보다 부모노드가 크다면 위치 교환. (부모노드 <= 자식노드) 조건을 만족할때까지 위치 교환 반복.
- 삭제: 루트 노드 삭제. 가장 마지막 노드를 루트에 삽입. (부모노드 <= 자식노드) 조건 만족할때까지 자식노드와 위치 교환. 두 자식노드 모두가 부모노드보다 작을 경우 더 작은 자식노드와 위치 교환.
데이터 배열 외에 새로운 힙을 생성하는 경우
- 72.1 ms ± 2.78 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 3 runs, 3 loops each)
- 힙 동작
def heap_insert(heap, elem):
if not heap:
heap.append(elem)
return
heap.append(elem)
idx = len(heap)-1
p_idx = (idx-1) // 2 # 부모노드 인덱스
while p_idx >= 0 and heap[p_idx] > heap[idx]:
# 부모노드각 자식노드보다 크면 위치 교환
heap[p_idx], heap[idx] = heap[idx], heap[p_idx]
idx = p_idx
p_idx = (idx-1) // 2
def heap_delete(heap):
if heap:
root_val = heap.pop(0)
else:
root_val = None
if heap:
heap.insert(0, heap.pop())
idx = 0
while True:
# 자식노드 인덱스
c_l_idx = 2 * idx + 1
c_r_idx = c_l_idx + 1
# 자식노드 중 유효하고, 더 작은 값을 가진 자식노드 인덱스 선택
if c_l_idx < len(heap) and c_r_idx < len(heap):
c_idx = c_l_idx if heap[c_l_idx] <= heap[c_r_idx] else c_r_idx
elif c_l_idx < len(heap) and c_r_idx >= len(heap):
c_idx = c_l_idx
else:
break
# 부모보다 자식이 더 작으면 위치 교환
if heap[idx] > heap[c_idx]:
heap[idx], heap[c_idx] = heap[c_idx], heap[idx]
idx = c_idx
else:
break
return root_val - 힙 정렬
heap = []
for n in nums:
heap_insert(heap, n)
sorted_heap = [heap_delete(heap) for _ in range(len(nums))]데이터 배열 자체에서 정렬하는 경우
- 35.4 ms ± 1.33 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 3 runs, 3 loops each)
- 정렬 방법:
- 최대 힙을 만들고 최대 힙의 루트와 가장 끝의 원소의 위치를 교환 - 최대값을 가장 뒤로 보냄.
- 루트로 올라온 원소를 최대 힙 규칙에 맞는 위치를 찾아주되 1번에서 교환된 가장 마지막 노드는 건드리지 않음.
- 1번, 2번 과정 반복, ex) 루트와 끝에서 2번째 원소 위치 교환, 최대힙 규칙 준수 (제일 끝의 원소는 정렬된 값이므로 건드리지 않음.) -> 루트와 끝에서 3번째 원소 위치 교환, 최대힙 규칙 준수 (제일 끝에서 첫번째, 두번째 원소는 정렬된 값이므로 건드리지 않음.)-> ...
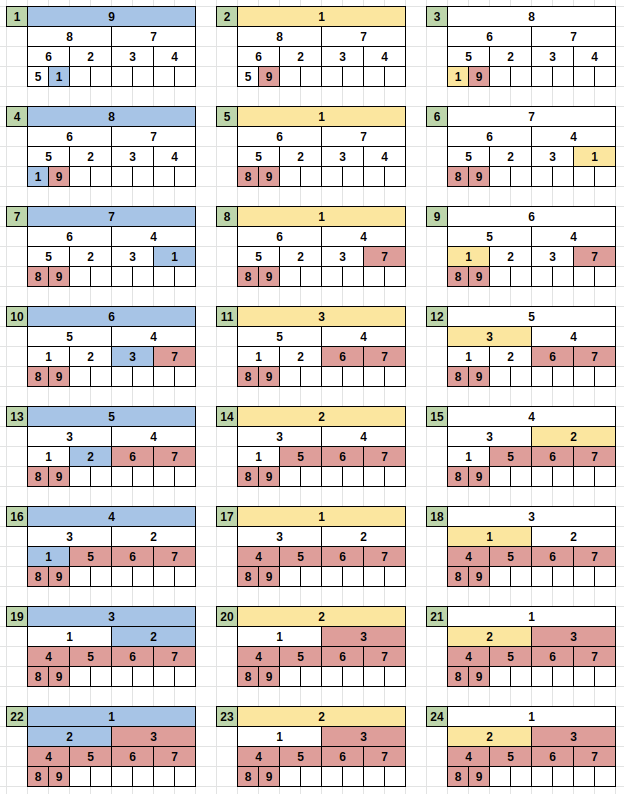
최대힙으로 변환하기
def convert_to_max_heap(nums):
n = len(nums) - 1
if n % 2 == 0:
n -= 1
for c_idx in range(n, 0, -2): # 가장 끝에서부터 자식 노드 중 왼쪽 노드만 순회
idx = c_idx // 2 # 부모노드 인덱스
# 부모노드가 루트인 부분 트리가 최대힙 규칙을 준수하도록 변환
while True:
c_l_idx = 2 * idx + 1
c_r_idx = c_l_idx + 1
if c_l_idx < len(nums) and c_r_idx < len(nums):
c_idx = c_l_idx if nums[c_l_idx] >= nums[c_r_idx] else c_r_idx
elif c_l_idx < len(nums) and c_r_idx >= len(nums):
c_idx = c_l_idx
else:
break
if nums[idx] < nums[c_idx]:
nums[idx], nums[c_idx] = nums[c_idx], nums[idx]
idx = c_idx
else:
break
def heap_sort(nums):
# 최대힙으로 변경 - 루트가 최댓값
convert_to_max_heap(nums)
n = len(nums)
for i in range(n-1, 0, -1):
# 루트(최댓값)을 가장 뒤의 원소와 교환
nums[0], nums[i] = nums[i], nums[0]
idx = 0
# 루트로 올라온 원소를 최대힙 규칙을 준수하는 위치로 옮긴다.
while True:
c_l_idx = 2 * idx + 1
c_r_idx = c_l_idx + 1
if c_l_idx < i and c_r_idx < i: # i번째와 그 뒤의 원소들은 이미 정렬된 상태
c_idx = c_l_idx if nums[c_l_idx] >= nums[c_r_idx] else c_r_idx
elif c_l_idx < i and c_r_idx >= i:
c_idx = c_l_idx
else:
break
if nums[idx] < nums[c_idx]:
nums[idx], nums[c_idx] = nums[c_idx], nums[idx]
idx = c_idx
else:
breaknums_ = nums.copy()
heap_sort(nums_)
print(sorted_nums == nums_)- 특징
- 힙을 이용해 가장 작은 원소를 찾아내는 방식
- 항상 으로 안정적인 성능
- O
- best, worst:
아직 이해 못함..
- best, worst:
