Abstract
Background
Image 형성 process를 denoising autoencoder의 sequential application으로 분해(decompose)하여, diffusion model은 이미지 데이터 및 그 이상에 대해 sota 합성 결과를 달성하였다. 게다가 그들의 공식화는 guiding mechanism이 retraining 없이 image generation process를 control할 수 있게 하였다.
하지만 이 모델들은 일반적으로 pixel space에서 직접 작동하기 때문에, optimization은 종종 수백 일의 GPU를 소모하고, inference도 sequential evaluation 때문에 비용이 많이 든다.
Main Idea
1. 그들의 quality와 flexibility를 유지하면서 제한된 컴퓨팅 리소스에서도 DM training이 가능하게 하기 위해 이 논문은 DM을 powerful pretrained autoencoder의 latent space에 적용한다.
➡️ 이런 representation에 대해 diffusion model을 훈련하는 것은 처음으로 complexity 감소와 detail preservation 사이의 거의 optimal한 지점에 도달할 수 있도록 하여 visual fidelity를 크게 높인다.
- Model architecture에 cross-attention layer를 도입함으로써, diffusion model을 text 또는 bounding boxes와 같은 general conditioning inputs를 위한 powerful and flexible generator로 전환하고 고해상도 합성이 convolutional 방식으로 가능해진다.
Result
이 논문의 latent diffusion model은 pixel-based DMs에 비해 computational requirements를 크게 줄이면서 image inpainting, class-conditional image synthesis task에서 새로운 SOTA score를 달성하였고, text-to-image synthesis, unconditional image generation, super-resolution을 포함한 다양한 task에서 매우 경쟁력 있는 성능을 달성하였다.
3. Method
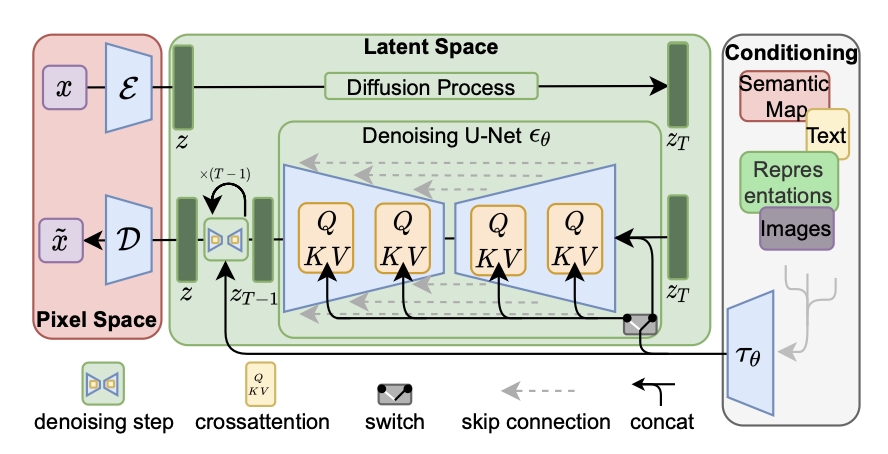
고해상도 image synthesis를 위한 diffusion model traning의 computational demands를 감소하기 위해 이 논문은,
비록 diffusion model이 undersampling the corresponding loss terms를 함으로써 perceptually irrelevant details를 무시하더라도, 그들은 여전히 costly function evaluations in pixel space를 요구하여 computation time과 energy resources에 엄청난 수요를 야기한다는 것을 관찰했다.
이 논문이 이 단점을 우회하기 위해 generative learning phase에서 compressive의 명확한 분리를 도입한다.
이를 달성하기 위해 image space와 perceptually equivalent한 space를 배우지만 computational complexity의 상당한 감소를 제공하는 autoencoding model을 이용한다.
이러한 접근은 여러 장점을 제공한다.
1. 고차원 이미지 공간을 벗어나면 저차원 공간에서 샘플링이 수행되기 때문에 계산적으로 훨씬 효율적인 DM을 얻을 수 있다.
2. U-Net architecture에서 유례된 DMs의 inductive bias를 이용한다. 이를 통해 spatial structure의 data에 특히 효율적이고, 그래서 이전의 접근 방식에서 요구되는 aggressive, quality-reducing compression levels의 필요성을 덜게 된다(완화시킨다).
3. 마지막으로, latent space가 다양한 generative models를 훈련하는데 쓰일 수 있고, single-image CLIP-guided synthesis와 같은 다른 downstream applications에서 사용될 수 있는 general-purpose compression models를 얻을 수 있다.
3.1 Perceptual Image Compression
Perceputal compression model은 perceptual loss와 patch-based adversarial objective의 조합으로 train된 autoencoder로 구성되어있다. 이를 통해 reconstruction은 local realism을 시행하여 image manifold로 제한되고 L2 또는 L1 objectives와 같은 pixel-space losses에만 의존하여 발생하는 흐림을 방지한다.
- Encoder ε
- z = ε(x)
- Encoder는 image를 factor f = H/h = W/w 만큼 downsample한다.
- Downsampling factors f =
- Decoder D
- = D(z) = D(ε(x))
Arbitrarily high-variance latent spaces를 피하기 위해 두 다른 종류의 regularizations를 실험했다.
- KL-regularization
- Imposes a slight KL-penalty to- wards a standard normal on the learned latent, similar to a VAE.
- VQ-regularization
- Uses a vector quantization layer within the decoder.
- This model can be interpreted as a VQGAN but with the quantization layer absorbed by the decoder.
Subsequent DM이 학습된 latent space z의 2D 구조에서 동작하도록 design되었기 때문에, 이 논문은 비교적 가벼운 compression rate를 사용할 수 있고 매우 좋은 recontruction을 달성할 수 있다.
따라서 이 논문의 compression model은 x의 detail을 더 잘 보존한다.
3.2 Latent Diffusion Models
ε와 D로 구성되어 있는 trained perceptual compression model을 사용하여, high frequency, imperceptible details가 추상화되는 efficient, low-dimensional latent space에 접근할 수 있다.
High-dimensional pixel space에 비해, 이 space는
1. 데이터의 중요한 bit에 초점을 맞추고
2. 낮은 차원의 computationally much more efficient한 space에서 훈련할 수 있기 때문에
likelihood-based generative models에 더 적합하다.
이전 연구가 highly compressed, discrete latent space의 autoregressive, attention-based transformer model들에 의존했던 것과 달리, 이 논문은 이 모델이 제공하는 image-specific inductive biases를 이용한다. 여기에는 주로 2D convolutional layers에서 기본 UNet을 구축하는 능력과, reweighted bound를 사용하여 perceptually most relevant한 bits에 objective를 더 집중하는 것이 포함된다.
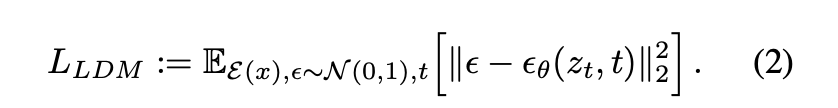
- (, t) : time-conditional UNet
- Forward process는 정해졌기 때문에 훈련하는 동안 는 encoder ε에 의해 효율적으로 얻을 수 있고, p(z)로부터 얻은 sample이 D를 single pas하면서 image space로 decode된다.
3.3 Conditioning Mechanisms
Image synthesis 맥락에서, DM의 generative power를 class layer또는 input image의 blurred variants를 넘어 다른 type들의 conditioning과 결합하는 것은 지금까지 충분히 탐구되지 않은 연구 분야이다.
Augmenting their underlying UNet backbone with the cross-attention mechanism을 통해, DMs를 more flexible conditional image generators로 바꾸었다. 이것은 various input modalities의 attention-based models를 학습하기에 효과적이다.
Various modalities의 y를 pre-process하기 위해 이 논문은 domain specific encoder 를 소개한다. 이 encoder는 y를 intermediate representation으로 project하고, 해당 representation은 cross-attention layer를 통해 UNet의 intermediate layers에 mapping된다.
Image-conditioning pairs를 통해, conditional LDM을 다음을 통해 학습할 수 있다.
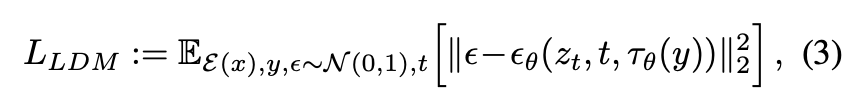
이는 와 를 jointly optimized한다.
이 conditioning mechanism은 가 domain-specific하게 parameterized될 수 있기 때문에 flexible하다.
Experiments
-
Training과 inference 둘 다에서 pixel-based diffusion models에 비해 이 모델이 갖는 이점을 분석하였다.
- 비록 VQ regularied first stage model이 continuous counterparts에 비해 reconstruction capability가 약간 뒤떨어지지만, 흥미롭게도 VQ regularized latent space에서 훈련된 LDMs가 가끔 더 좋은 sample quality를 달성하였다.
-
Visual comparison between the effects of first stage regularization schemes on LDM training and their generalization abilities to resolutions >
4.1 Perceptual Compression Tradeoffs
Behavior of LDMs with different downsampling factors f를 분석하였다.
- LDM-1(f=1)이면 pixel-based DMs
Result
1. Small downsampling factors for LDM-{1,2}는 slow training progress를 초래한다.
- 이 논문은 그 이유를 대부분의 perceptual compression을 diffusion model에 맡겼기 때문이라고 생각한다.
- Overly large values of f는 비교적 적은 training steps 후에 정체된 fidelity를 유발한다.
- 이 논문은 그 이유를 너무 강한 first stage compression이 information loss로 이어져 달성 가능한 quality를 제한하기 때문이라고 생각한다.
- LDM-{4-16}은 efficiency와 perceptually faithful results 사이의 균형을 잘 맞추고 있으며, 이는 2M step training 후 pixel-based diffusion(LDM-1)과 LDM-8 사이에 38의 상당한 FID gap으로 나타난다.
DDIM sampler로 여러 다른 denoising step에서의 sampling speed에 대해 각각 Celeb-HQ와 ImageNet으로 훈련된 모델을 비교하였고, FID-scores에 대해 plot하였다.
Result
- Pixel-based LDM-1과 비교하여 LDM-{4,8}이 더 낮은 FID scores를 달성하였고 동시에 sample throughput도 크게 증가하였다.
- ImageNet과 같은 복잡한 dataset은 quality 감소를 피하기 위해 더 낮은 compression rate가 필요했다.
- 그래서 요약하면 LDM-4와 LDM-8이 높은 퀄리티의 합성 결과를 얻기에 가장 적합한 조건이다.
4.2 Image Generation with Latent Diffusion
이미지의 unconditional models를 각각 CelebA-HQ, FFHQ, LSUN-Churches, LSUN-Bedrooms에 훈련시키고 FID와 Precision-and-Recall을 사용하여
1. sample quality
2. their coverage of the data manifold
를 evaluate하였다.
4.3 Conditional Latent Diffusion
4.3.1 Transformer Encoders for LDMs
Text-to-Image
- Train a 1.45B parameter KL-regularized LDM conditioned on language prompts on LAION-400M.
- Employ BERT-tokenizer
- Implement as a transformer
- Classifier-free diffusion guidance를 적용하는 것이 parameter 개수는 상당히 감소시키면서 sample quality를 크게 증가시킨다.
Semantic layouts
- Train on OpenImages, and finetune on COCO
마지막으로, 이 논문의 best performing class-conditional ImageNet models를 evaluate한 결과, computational requirements와 parameter 개수를 크게 줄이면서 SOTA diffusion model ADM을 능가하였다.
- f = 4 or 8
4.3.2 Convolutional Sampling Beyond
Spatially aligned conditioning information을 의 input에 concatenate하여 LDMs가 efficient general purpose image-to-image translation models의 역할을 할 수 있다.
이를 semantic synthesis, super-resolution, inpainting에 사용하였따.
Semantic synthesis
-
Semantic maps와 짝을 이룬 풍경 image를 사용한다.
-
Semantic maps의 downsampled version을 f=4 model(VQ-reg)의 latent image representation과 concatenate한다.
-
input resolution(crops from )에서 train하였지만 더 큰 resolution으로 generalize될 수 있고 convolutional 방식으로 evaluated될때 최대 megapixel regime까지 이미지를 생성할 수 있다.
-
Signal-to-noise ratio(scale of the latent space에 의해 야기됨)가 결과에 크게 영향을 미친다.
- component-wise standard deviation에 의해 scale된 rescaled version과 그렇지 않은 버전에 대해 비교하였다.
- 후자는 classifier-free guidance와 결합했을 때 text-conditional LDM-KL-8-G에 대해 > images를 직접 합성하는 것 또한 가능하였다.
4.4 Super-Resolution with Latent Diffusion
LDMs는 concatenation을 통해 low-resolution images에 directly conditioning하여 super-resolution에 대해 효율적으로 훈련될 수 있다.
-
We follow SR3 and fix the image degradation to a bicubic interpolation with 4×-downsampling and train on ImageNet following SR3’s data processing pipeline.
- f=4 autoencoding model pretrained on OpenImages(VQ-reg)
- concatenate the low-resolution conditioning y and the inputs to the UNet(즉, 는 identity)
-
We conduct a user study comparing the pixel-baseline with LDM-SR
- We follow SR3 where human subjects were shown a low-res image in between two high-res images and asked for preference.
-
We train a generic model, LDM-BSR, by using more diverse degradation.
4.5 Inpainting with Latent Diffusion
- Analyze the effect of different design choices for the first stage.
- Compare the inpainting efficiency of LDM-1 with LDM-4, for both KL and VQ regularizations, as well as VQ-LDM-4 without any attention in the first stage.
Limitations & Societal Impact
Limitations
- LDMs가 pixel-based approaches에 비해 상당히 computational requirements를 감소시켰지만, sequential sampling process는 여전히 GANs보다 느리다.
- LDMs의 사용은 high precision이 요구될때는 적절할지 의문이다.
- 비록 f=4 autoencoding models에서는 image quality의 loss는 매우 적지만, reconstruction capability는 pixel space에서의 fine-grained accuracy가 필요한 task에 대해서는 bottleneck으로 작용할 수 있다.
- 이 논문은 superresolution model이 이미 이 점에서 다소 제한적이라고 가정한다.
Summary
What
- Quality 저하 없이 training과 inference(sampling)에서 denoising diffusion models에 비해 computational requirements를 크게 줄인다.
- Diffusion model을 general conditioning inputs를 위한 powerful and flexible generator로 전환하고 고해상도 합성이 convolutional 방식으로 가능해진다.
How
- DM을 powerful pretrained autoencoder의 latent space에 적용한다.
- Cross-attention conditioning mechanism, 즉 model architecture에 cross-attention layer를 도입한다.
