Natural language processing
Low-level parsing
토큰화, stemming(어간 추출)
의미 단위의 low level task
Word and phrase level (단어, 구)
part-of-speech(POS) tagging
Named entity recognition(NER)
- e.g., New York Times를 3개의 단어로 쪼개지 않고 하나 자체로 인식
Sentence level
Sentiment analysis(감정 분석)
machine translation(기계 번역)
Multi-sentence and paragraph
Question Answering (질의응답)
dialog systems (대화)
summarization (요약)
Entailment prediction
- 두 문장 사이의 논리적 관계를 파악
Related Discipline
Text mining
social science와 매우 밀접한 관계
Document clustering
- e.g., topic modeling
Information retrieval
정보 검색
추천 시스템으로 발전
Trends of NLP
Word Embedding
RNN 계열 모델
- LSTM, GRU
Transformer models
- Self-Attention
Self-supervised training
- 자가지도학습
- 대규모 text 데이터를 통해 별도의 label이 필요없는 학습
- 문장에서 단어 일부를 가리고 맞히게 하는 형식
Bag-of-Words
1. Unique words를 포함하는 Vocabulary 구축
- Sentences : “John really really loves this movie“, “Jane really likes this song”
- Vocabulary: {“John“, “really“, “loves“, “this“, “movie“, “Jane“, “likes“, “song”}
- 중복 제거
2. Unique words → one-hot vectors

어떤 두 단어를 선택하든, distance는
어떤 두 단어를 선택하든, cosine similarity는 0
- 단어의 의미에 상관없이 동일한 관계
3. sentence / documents를 one-hot vectors로 표현 가능
- bag-of-words 벡터라고 칭함

NaiveBayes Classifier
⇒ bag-of-words 벡터로 나타낸 document를 정해진 category 또는 class 중 하나로 분류
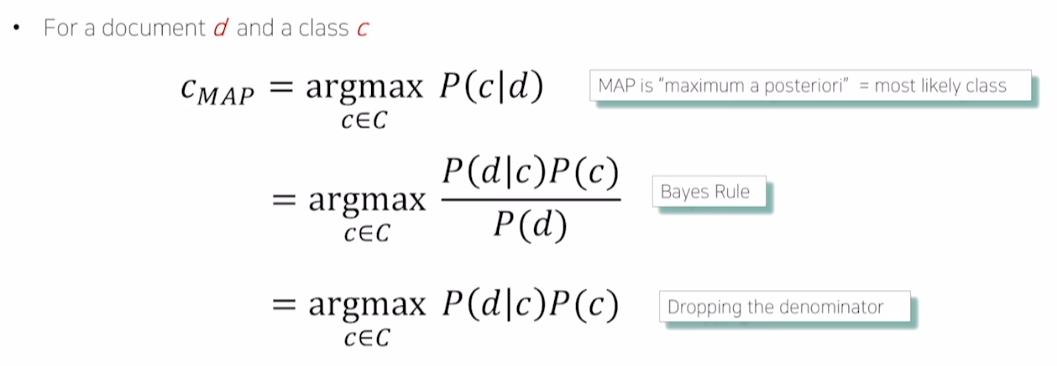
- d는 document, c는 class
- 문서가 주어졌을 때 가장 높은 확률로 분류될 class를 계산
- 베이지안 정리에 의해 아래와 같은 식으로 정리 가능
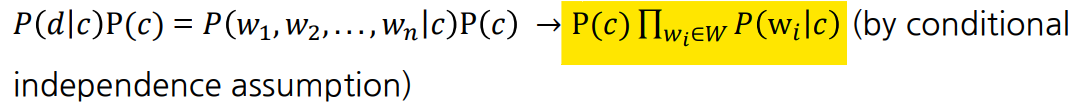
- w는 document에 속하는 words
- class를 고정시키고 해당 class에서 각 단어가 나타날 확률을 계산
- 각 단어가 독립이라면, 곱으로 나타낼 수 있음
Example
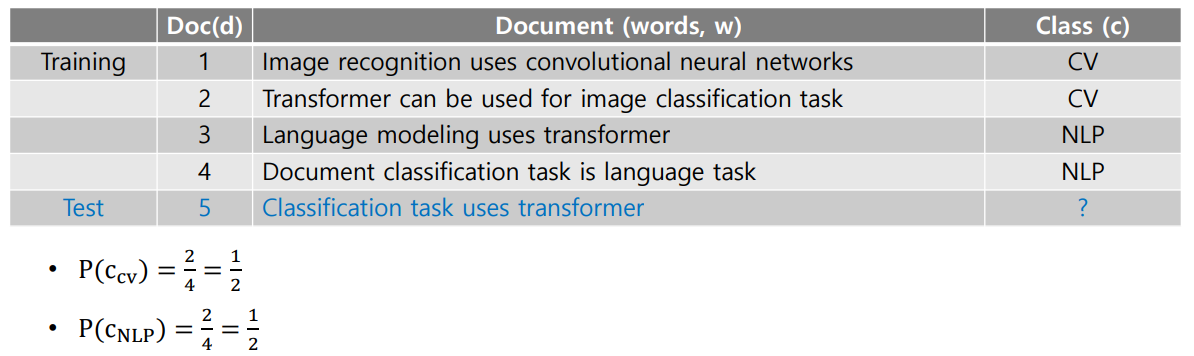
- class는 CV, NLP 2개이며 각 class가 나타날 확률은 1/2
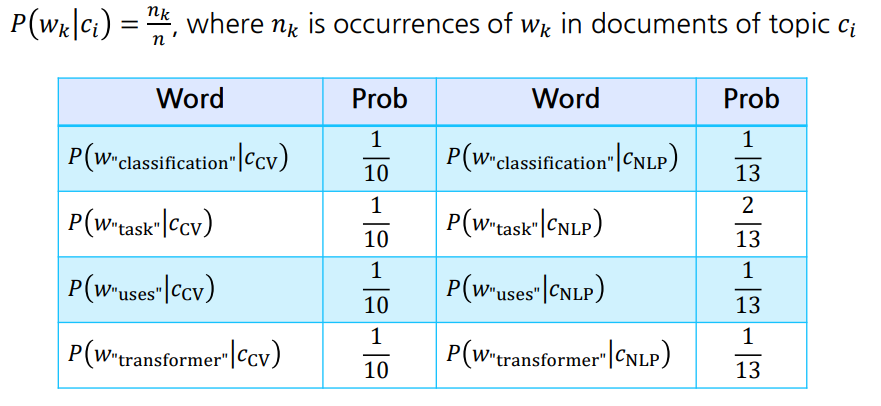
- 왼쪽은 class를 CV로 고정하고, CV 내 모든 document에서 각 단어가 나올 확률을 계산
- e.g., ‘task’는 CV class인 doc1, doc2에서 한 번 등장한다.
- ‘task’는 NLP class인 doc3, doc4에선 두 번 등장한다.
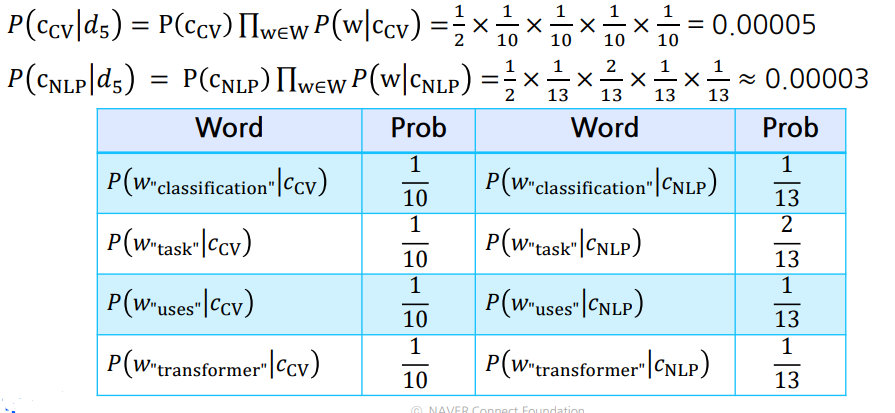
- 확률을 모두 곱해 더 높은 class인 CV로 분류
※ 모든 이미지 및 코드 출처는 네이버 커넥트재단 부스트캠프 AI Tech 5기입니다. ※