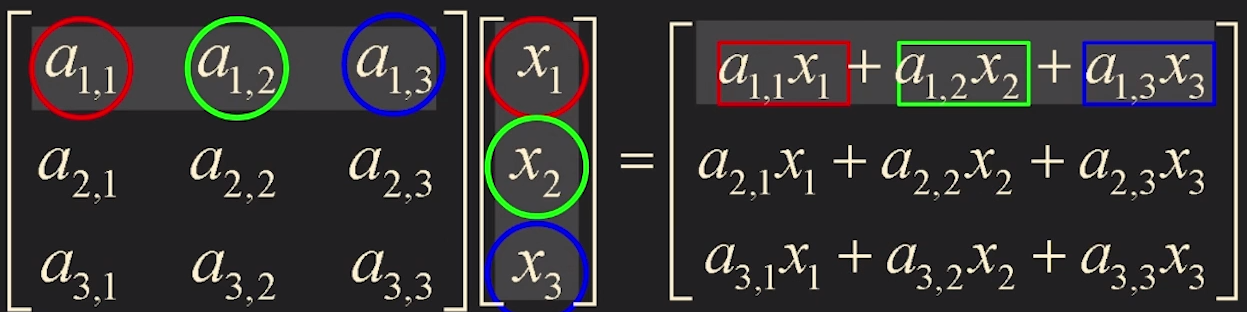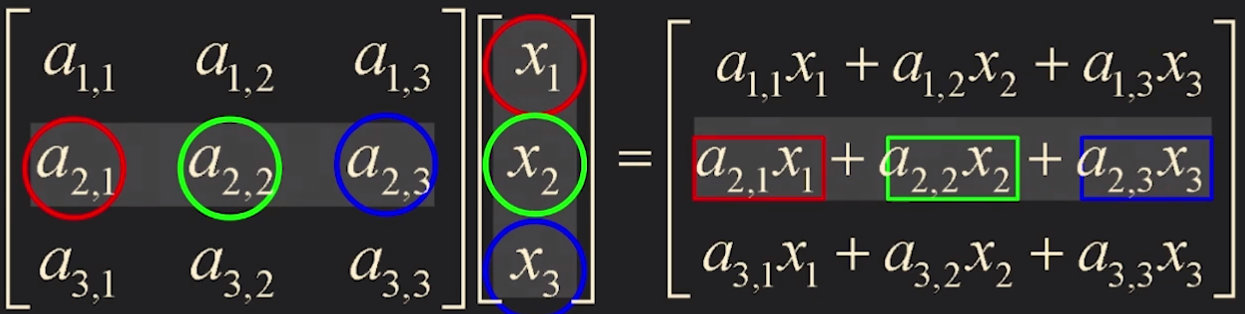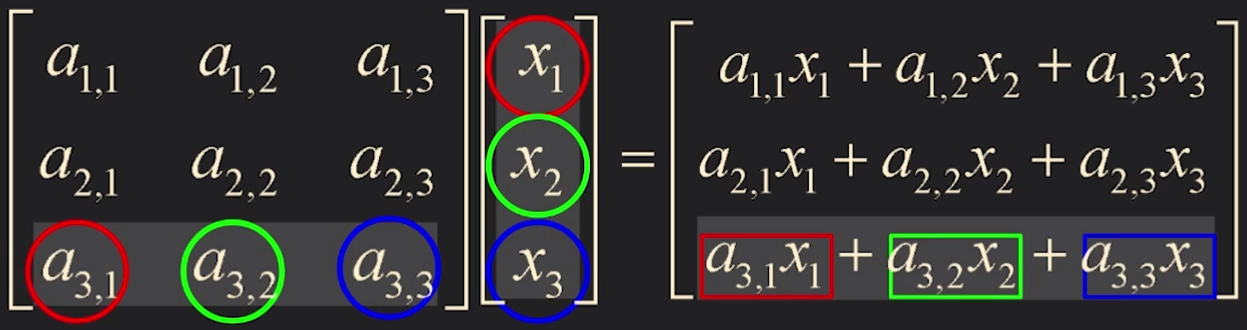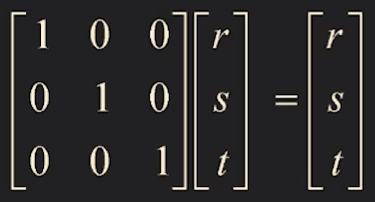조범희 선생님의 선형대수학개론 강의를 듣고 공부하며 정리한 내용입니다.
정말 좋은 강의힙니다. 강추합니다. 링크
Ax: product of A and x
A is m x n matrix, with columns a1,⋯,an
x is in Rn
Ax=[a1 a2 ⋯ an]⎣⎢⎢⎡x1⋮xn⎦⎥⎥⎤=x1a1+x2a2+⋯+xnan
A x is the linear combination of the columns of A using the corresponding entries in x as weights
Example 1. Matrix Equation
[102−5−13]⎣⎢⎡437⎦⎥⎤=4[10]+3[2−5]+7[−13]=[36]
⎣⎢⎡28−5−302⎦⎥⎤[47]=4⎣⎢⎡28−5⎦⎥⎤+7⎣⎢⎡−302⎦⎥⎤=⎣⎢⎡−1332−6⎦⎥⎤
Example 2. Vector equation to matrix equation
x1v1+x2v2+x3v3=[v1v2v3]⎣⎢⎡x1x2x3⎦⎥⎤
순서가 중요하다. x가 앞에 있으면 안된다. 절대로!
Example 3. System of linear equations to matrix equation
x1+2x2−x3=4−5x2+3x3=1
x1[10]+x2[2−5]x3[−13]=[41]
=[102−5−13]⎣⎢⎡x1x2x3⎦⎥⎤=[41]
Example 4. More efficient way to compute matrix equation
⎣⎢⎡a1,1a2,1a3,1a1,2a2,2a3,2a1,3a2,3a3,3⎦⎥⎤⎣⎢⎡x1x2x3⎦⎥⎤=⎣⎢⎡a1,1x1+a1,2x2+a1,3x3a2,1x1+a2,2x2+a2,3x3a3,1x1+a3,2x2+a3,3x3⎦⎥⎤
더 쉽게는 빨간 + 초록 + 파랑 을 자리에 맞게 넣어주면 된다
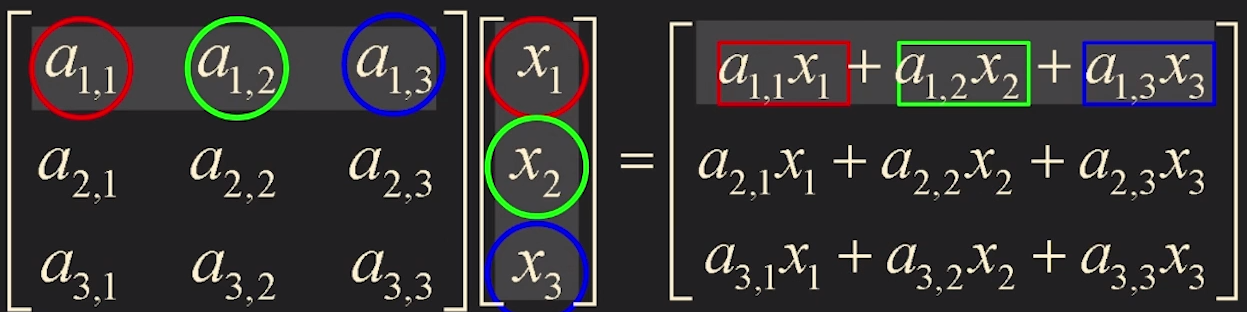
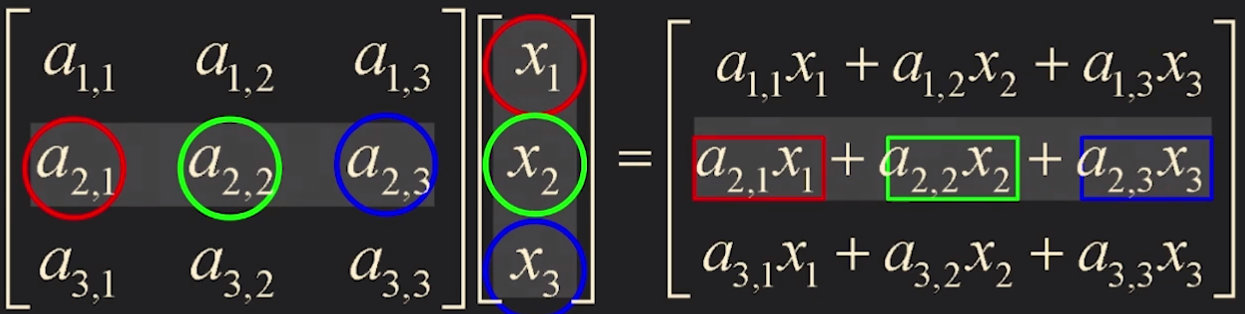
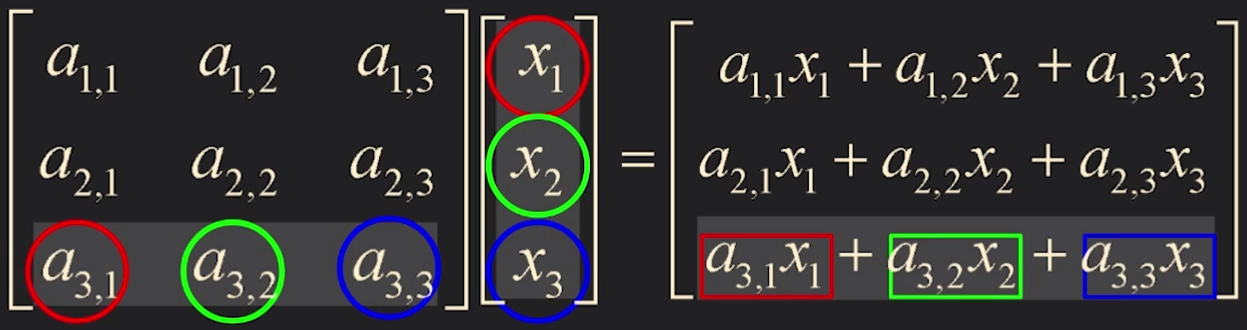
Identity Matrix I
∗⎣⎢⎡100010001⎦⎥⎤*
A x = b 꼴에서 matrix A가 Identity Matrix 이면 A x = x가 된다.
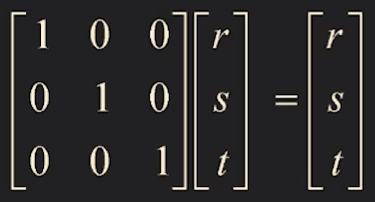
Theorem 3.
A is m x n matrix, with columns a1,⋯,an
x is in Rn
matrix equation : Ax=b
vector equation : x1a1+x2a2+⋯+xnan=b
augmented matrix : [a1 a2 ⋯ an b]
have the same solution set!
여기까지는 무리없이 이해가 가능하다.
Theorem 4.
A is m x n matrix, with columns a1,⋯,an
The followings are all true or all false;
a. For each b in Rn, A x = b has a solution
b. Each b in Rn is a linear combination of the columns of A
c. The columns of A span Rn
d. (Not augmented matrix) A has a pivot position in every row.
여기서는 c에 유의해서 이해해야 한다.
A가 Rn 을 span 한다는 것은, A의 column vector들을 a1, a2, ..., an이라 했을때,
Rn 내의 c1,c2,⋯,cn 에 의해 생긴 (c1,c2,⋯,cn 등은 실수라는 뜻)
c1a1+c2a2+...+cnan이 a1부터 an에 의해 span된 space라는 뜻이다.
즉 이는 a, b, d와 동치가 된다 (조범희 선생님 답변을 참고하여 이해하였다)
Theorem 5.
If A is an m x n matrix, u and v are vectors in Rn, and c is a scalar, then;
A(u+v)=Au+Av;A(cu)=c(Au)
너무나 당연한 것처럼 보이지만, c가 scalar일 때만 가능하다는 것을 명심하자. c가 vector라면 성립할 수도 있고 성립하지 않을 수도 있다