조범희 선생님의 선형대수학개론 강의를 듣고 공부하며 정리한 내용입니다.
정말 좋은 강의힙니다. 강추합니다. 링크
Vectors in R2
R2 = real space (실수 2차원 공간)
u=u=[3−1] v=v=[0.30.1] w=w=[w1w2]
Vector Summation
u+v=[3−1]+[0.30.1]=[3.3−0.9]
Scalar multiplication
c=5, u=[3−1] c∗u=5[3−1]=[5∗35∗(−1)]=[15−5]
Geometric Description of R2
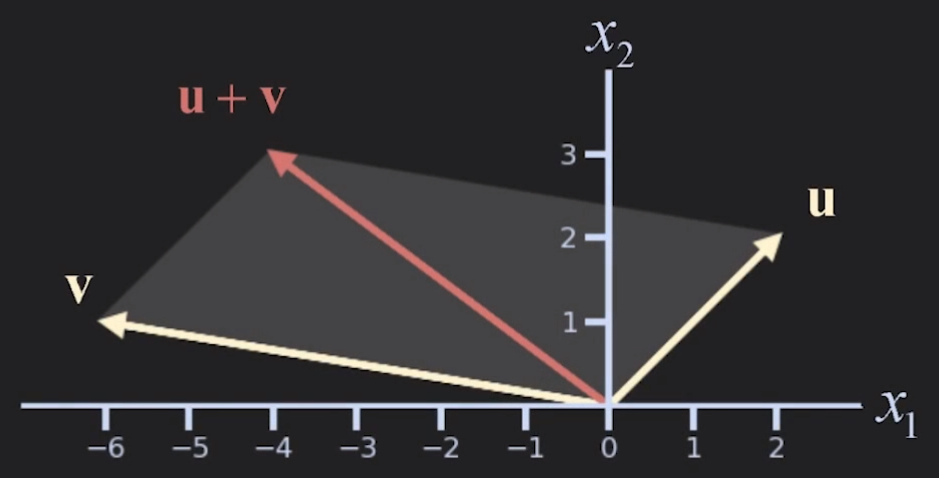
u=[22], v=[−61], u+v=[−43]
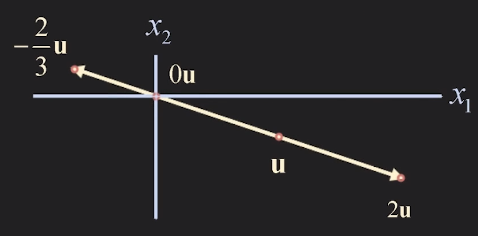
u=[3−1], 2u, −32u
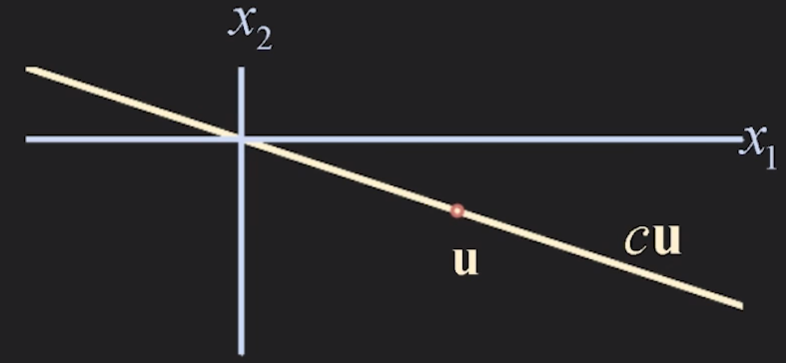
어떤 vector u 에 임의의 scalar 값을 곱하면, 그 vector cu 는 vector u 와 동일선상에 있게 된다.
따라서, 이때의 c를 실수 전체로 가정하면, vector cu 가 그리는 발자취는 직선과 같게 된다.
이를 set of all multiple of u 이라고 한다.
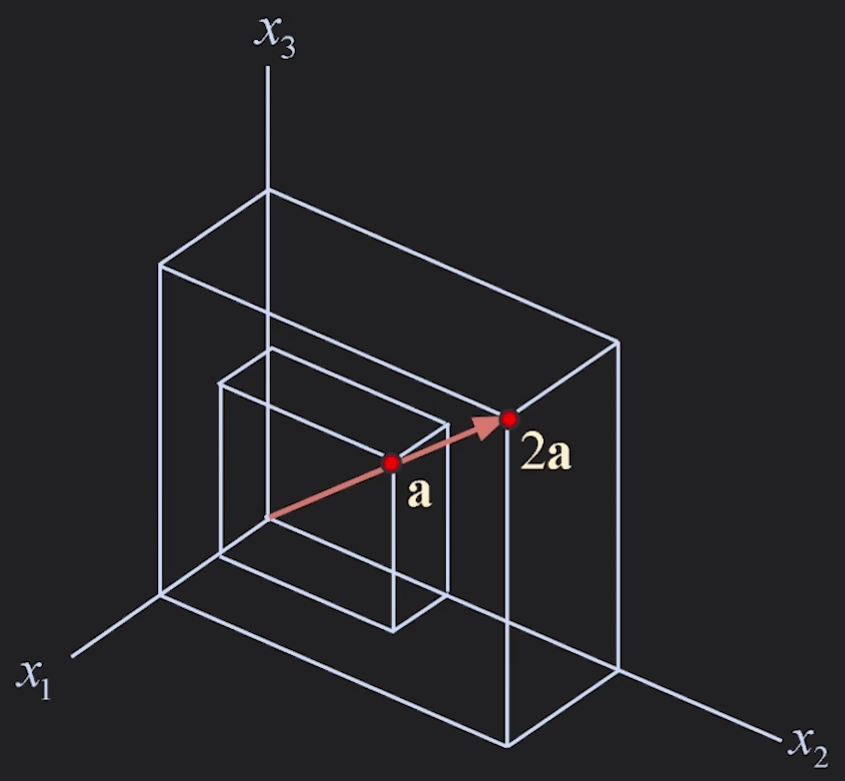
Vectors in R3
a=⎣⎢⎡154⎦⎥⎤
Vectors in Rn
u=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡u1u2⋮un⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤=(u1,u2,⋯,un)
Algebraic properties of Rn
uvwin Rn
cdis scalar
properties
i)u+v=v+u
ii)(u+v)+w=u+(v+w)
iii)u+0=0+u=u,(0=0)
iv)u+(−u)=−u+u=0,(0=0)
v)c(u+v)=cu+cv
vi)(c+d)u=cu+du
vii)c(du)=(cd)u
viii)1u=u
Linear Combinations
v1, v2, ⋯, vpin Rn
c1, c2, ⋯, cpis scalar
y=c1v1+c2v2+⋯+cpvp
y is linear combination of v1, v2, ⋯, vp with weights c1, c2, ⋯, cp
Example 1. can b be generated as a linear combination of a1 and a2 ?
a1=⎣⎢⎡1−2−5⎦⎥⎤
a2=⎣⎢⎡256⎦⎥⎤
b=⎣⎢⎡74−3⎦⎥⎤
Solution.
x1a1+x2a2=b
x1⎣⎢⎡1−2−5⎦⎥⎤+x2⎣⎢⎡256⎦⎥⎤=⎣⎢⎡x1+2x2−2x1+5x2−5x1+6x2⎦⎥⎤=⎣⎢⎡74−3⎦⎥⎤
⎣⎢⎡1−2−525674−3⎦⎥⎤∼⎣⎢⎡100291671832⎦⎥⎤∼⎣⎢⎡10021167232⎦⎥⎤∼⎣⎢⎡100210720⎦⎥⎤∼⎣⎢⎡100010320⎦⎥⎤
{x1=3x1=2
can b be generated as a linear combination of a1 and a2 ?
= Does the follwing augmented matrix have a solution?
[a1a2b]
so,
A vector equation
x1a1+x2a2+⋯+xnan=b
has the same solution set as the linear system whose augmented matrix is
[a1 a2 ⋯ an b]
Span {v1,⋯,vp}
is the collection of all vectors that can be written in the form
c1v1+c2v2+⋯+cpvp
Is a vector b in span {v1,⋯,vp} ?
= Does the follwing vector equation have a solution?
x1v1+x2v2+⋯+xnvp=b
= Does the follwing augmented matrix have a solution?
[v1⋯vpb]
따라서, 'Is a vector b in span {v1,⋯,vp} ?' 꼴로 질문이 많이 주어진다
Geometric descriptions of Span {v} and Span {u,v} in R3
(u랑 v는 scalar multiplication 으로 표현되지 않는 서로 다른 vector 이다)
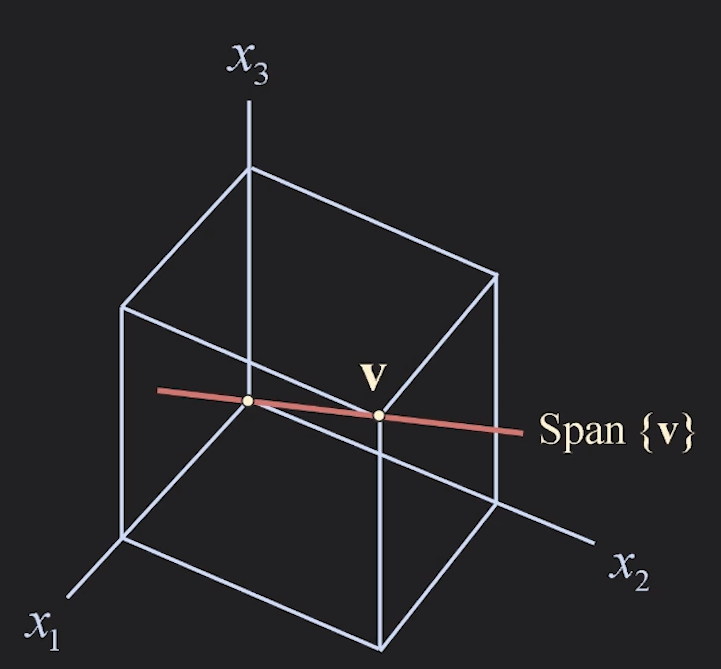
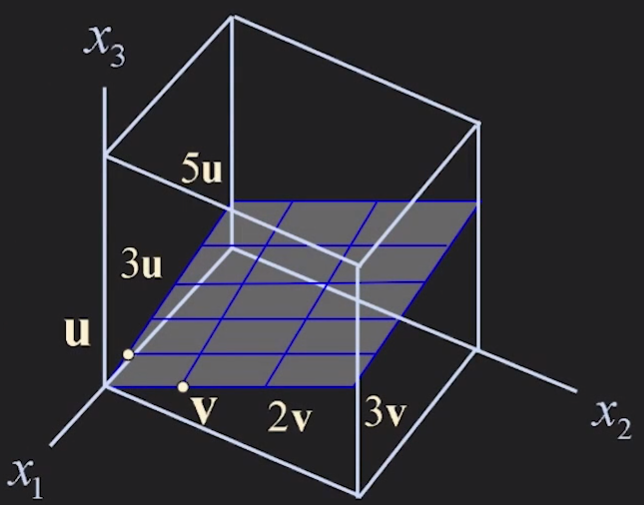
span을 이용해서 표현하면 공간에서의 직선과 평면을 간단하게 표현할 수 있다.
Example 2.
a1=⎣⎢⎡1−23⎦⎥⎤ a2=⎣⎢⎡5−133⎦⎥⎤ b=⎣⎢⎡−381⎦⎥⎤
Solution.
⎣⎢⎡1−235−133−381⎦⎥⎤∼⎣⎢⎡1005−3−18−3210⎦⎥⎤∼⎣⎢⎡1005−30−32−2⎦⎥⎤
by Theorem 2 (Existence and Uniqueness Theorem), this linear system has no solution (inconsistent)






