복습하자 복습!
여유로운 상황은 아니지만 과제 마무리를 조금 빨리 끝내서 오늘은 변수부터 처음부터 차근차근 복습을 해보았다
복습은 드림코딩 엘리님꺼 영상을 보고 노트에 작성하는 형식으로 복습을 해보았다.
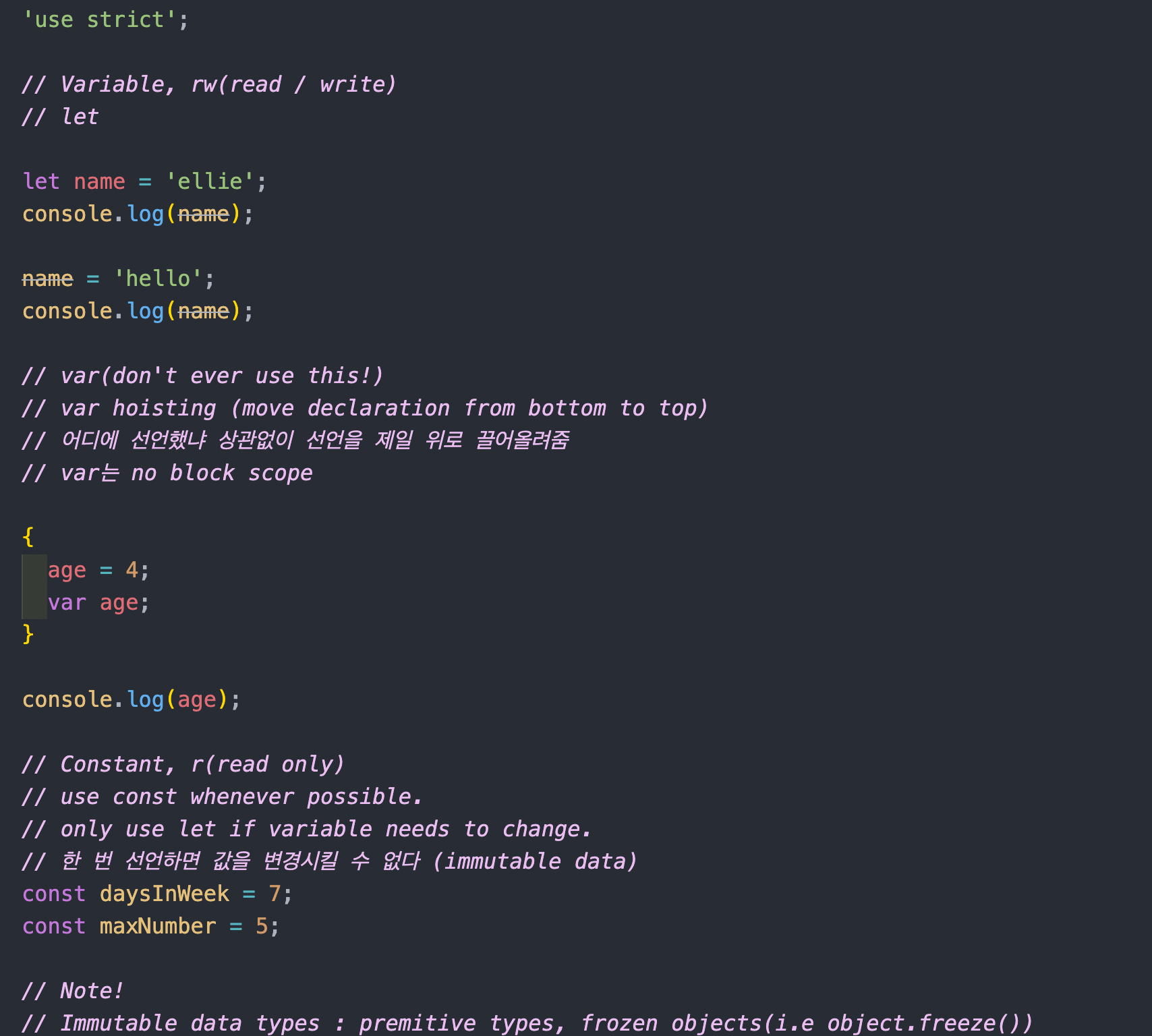
1. Variable, rw(read / write)
let(added in ES6)
let name = 'ellie';
console.log(name);
name = 'hello';
console.log(name);먼저 기본적인 변수 정의하는 것으로 시작
아래의 var는 let이 도입되기 전에 변수를 정의 할 때 쓰였다.
- var(don't ever use this!)
- var hoisting (move declaration from bottom to top)
- 어디에 선언했냐 상관없이 선언을 제일 위로 끌어올려줌
- var는 no block scope
{
age = 4;
var age;
}
console.log(age);위에서 보듯이 var로 변수를 정의 했을 때 문제점을 바로 파악 할 수 있다.
블록안에서 변수를 정의 했으나 console.log(age);로 호출했을 때에도 변수의 값이 호출 되기 때문이다. 이렇게 코드를 작성하다 보면 중복되는 변수라던지 값을 불러오는 과정에서도 충돌이 될 가능성이 높아 보인다.
2. Constant, r(read only)
- use const whenever possible.
- only use let if variable needs to change.
- 한 번 선언하면 값을 변경시킬 수 없다 (immutable data)
const daysInWeek = 7;
const maxNumber = 5;const는 한 번 선언하면 값을 변경 시킬 수 없는 상수이다
3. Variable types (변수 타입들)
- primitive, single item: number, string, boolean, null, undefined
- object(객체), box container
- function(함수), first-class function
const count = 17; // integer(정수)
const size = 17.1; // decimal number(소수)
console.log(`value : ${count}, type : ${typeof count} `);
console.log(`value : ${size}, type : ${typeof size} `);
3-1. number - special numberic values: infinity, -infinity, NaN
- 무한수, 음의무한수, 숫자가 아니다
const infinity = 1 / 0;
const negativeInfinity = -1 / 0;
const nAn = 'not a number' / 2;
console.log(infinity);
console.log(negativeInfinity);
console.log(nAn);
3-2. bigInt (fairly new, don't use it yet) (엄청큰숫자)
- 지원하는 브라우저가 많이 없어서 아직은 사용하지 말라고 엘리님께서 말씀하셨다
const bigInt = 1234567890123456789012345678901234567890n;
console.log(`value : ${bigInt}, type : ${typeof bigInt}`);
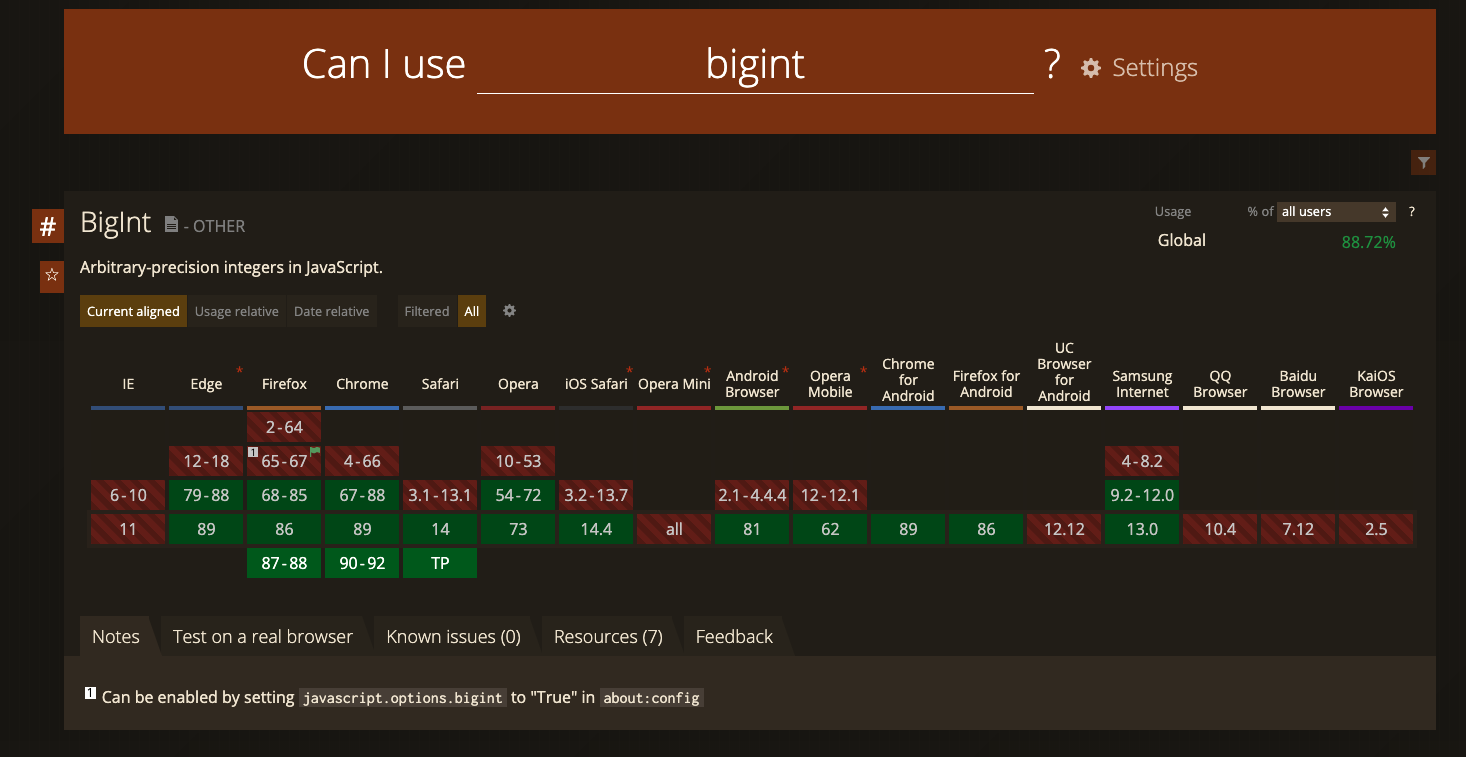
사용하고 싶으면 Can I use를 확인해보자!
3-3. string (문자타입)
const char = 'c';
const brendan = 'brendan';
const greeting = 'hello' + brendan;
console.log(`value : ${greeting} type : ${typeof greeting}`);
const helloBob = `hi ${brendan}!`; // template literals (string)
console.log(`value : ${helloBob}, type : ${typeof helloBob}`);
console.log('value : ' + helloBob + ' type : ' + typeof helloBob);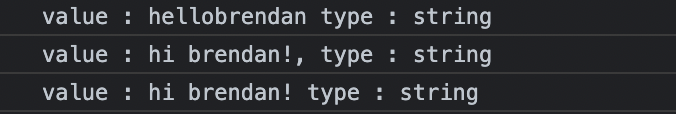
3-4. boolean (불린타입)
(거짓)false : 0, null, undefined, NaN, ''
(참)true : any other value
const canRead = true;
const test = 3 < 1; // false
console.log(`value : ${canRead}, type : ${typeof canRead}`);
console.log(`value : ${test}, type : ${typeof test}`);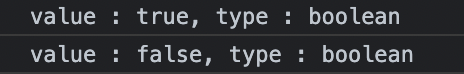
- null
let nothing = null;
console.log(`value : ${nothing}, type : ${typeof nothing}`);
- undefined
let x;
console.log(`value : ${x}, type : ${typeof x}`);
3-5 symbol, create unique indentifiers for objects
심볼은 사용해 본 적이 없어서 아직 정확히는 잘 모르겠다
const symbol1 = Symbol('id');
const symbol2 = Symbol('id');
console.log(symbol1 === symbol2);
const gSymbol1 = Symbol.for('id');
const gSymbol2 = Symbol.for('id');
console.log(gSymbol1 === gSymbol2);
console.log(`value : ${symbol1.description}, type : ${symbol1.description}`);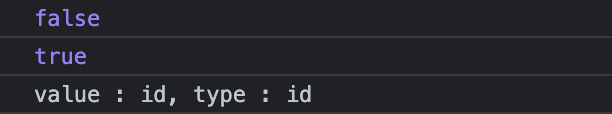
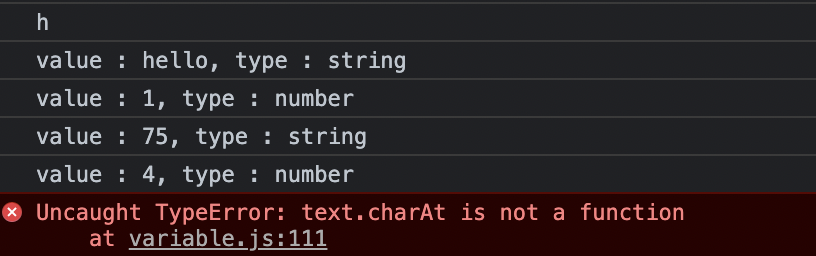
4. Dynamic typing : dynamically typed language
동적으로 타입을 정의하는 부분이 문제가 될 소지가 있다는 것을 알려주기 위한 예제
let text = 'hello';
console.log(text.charAt(0)); // h
console.log(`value : ${text}, type : ${typeof text}`)
text = 1;
console.log(`value : ${text}, type : ${typeof text}`)
text = '7' + 5;
console.log(`value : ${text}, type : ${typeof text}`)
text = '8' / '2';
console.log(`value : ${text}, type : ${typeof text}`)
console.log(text.charAt(0)); //위에 문자로 연산을 하였지만 JS가 숫자로 연산을 해주고 타입도 숫자로 바뀌었기 때문에 index를 호출 할 수 없다