📕 참고: ROS2로 시작하는 로봇 프로그래밍
package
- 노드(Node) : 실행 가능한 최소한의 프로세서 단위
- 패키지(Package) : 하나 이상의 노드가 기능적 단위로 묶인 것

그림처럼 패키지에는 다양한 노드가 포함된다.
구성요소를 정리해보면 다음과 같다.
- 노드(Node): 특정 작업(로봇 제어, 센서 데이터 처리, 토픽 발행 등)을 수행하는 최소 단위
- 런치 파일(Launch file): 여러 노드를 관리하고 실행할 수 있도록 돕는 파일로 XML또는 Python으로 작성
- 설정 파일(Configuration file): 프로그램이나 시스템 통작을 제어하기 위해 필요한 설정값을 정의한 파일로 YAML로 작성
- 라이브러리(Library): 재사용 가능한 코드(매개변수, 토픽, 서비스 등)를 모듈화하여 다른 노드에서 사용할 수 있는 기능 제공
- 자원(Resource): 이미지, 파라미터 파일 등 노드나 시각화 도구에 사용
- 테스트(Test): 패키지 내 코드가 제대로 작동하는지 검증-Unit(단위)/Integration(통합)/End-to-End(종단 간) Test
- 문서(Documentaiotn) : README, 튜토리얼, API 등 패키지를 이해할 수 있도록 제공되는 문서
python으로 publisher와 subscriber 노드를 생성하고 실행해보려 한다.토픽상으로 talker/listener는 message를 전송/수신하는 역할을 한다.
1. 파이썬 패키지 생성/내부 구조
-
mkdir -p ros2_ws/src
작업을 수행할ros2_ws/src디렉토리를 생성한다. 패키지는 항상 src 폴더 안에 생성하면 된다. -
ros2 pkg create --build-type ament_python py_pubsub
python 타입의 패키지를 생성하였다.ls와tree를 통패 패키지 내부 구조를 확인할 수 있다.
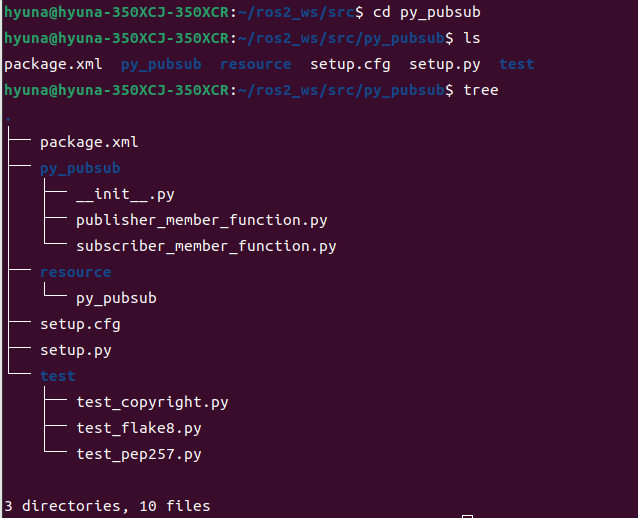
💡 __init__.py이 있어야 해당 디렉토리를 파이썬 패키지로 인식할 수 있다.
2. 파일 수정/의존성 관리
package.xml
- 모든 패키지에 필요한 파일
- 패키지에 대한 메타 정보(패키지 이름, 버전, 저작자, 라이센스 등)를 정의하는 파일 = 패키지의 신분증
- colcon build 수행 시 빌드할 패키지들 사이의 의존성을 해석하고 적절한 빌드 순서를 결정하기 위해 사용되는 파일
<package format="3"> #패키지 포맷 버전
<name>my_cpp_pkg</name> #패키지 이름
<version>0.1.0</version> #패키지 버전
<description>My C++ ROS2 package</description> #패키지에 대한 설명
<maintainer email="maintainer@example.com">Maintainer Name</maintainer> #패키지를 유지관리하는 사람의 정보
<license>Apache-2.0</license> #라이센스 정보
<buildtool_depend>ament_cmake</buildtool_depend> #빌드 도구에 대한 의존성
<build_depend>rclcpp</build_depend> #패키지 빌드에 필요한 의존성
<exec_depend>rclcpp</exec_depend>
</package> #페키지가 실행될 때 필요한 의존성
rosdep
- 의존성을 자동으로 설치해주는 명령어
💡 rosdep은 왜 쓰는걸까?
패키지 A는 패키지 B에 의존한다고 가정하자. 즉, 패키지 A를 실행시키려면 패키지B가 설치되어 있어야한다.
rosdep을 사용할 때
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
rosdep이 자동으로 패키지 A의 의존성을 분석하고, 패키지 B와 그에 필요한 모든 외부 라이브러리를 찾아 설치한다. 패키지 B가 numpy, rclpy에 의존하고 있다먄rosdep이 이를 자동으로 설치한다.
rosdep을 사용하지 않을 때
# 패키지 B 설치
sudo apt-get install ros-<distro>-package-b
# 외부 라이브러리 설치
pip install numpy
수동으로 패키지를 설치한다. 패키지 B에 대한 의존성을 제대로 설치하지 않는다면, 패키지A를 실행할 때 오류가 발생한다. 이를 해결하기 위해 여러 번의 수동 설치와 테스트가 필요하고 많은 시간이 소요될 수 있다.
CMakeList.txt
- C++ 및
ament_cmake를 사용하는 ROS 패키지에서 사용 - 패키지를 빌드하는 방법을 정의
- 패키지 내 소스 코드 빌드 및 의존성 연결과 설치 경로 제어
- 주로 C++에서 사용되지만 다른 언어도 지원하기 때문에 더 넓은 범위의 작업이 가능
| 항목 | CMakeLists.txt | package.xml |
|---|---|---|
| 역할 | 소스 코드를 컴파일하고 실행파일로 변환 | 패키지 메타데이터 정의하고 의존성 관리 |
| 언어 | CMake | XML |
| 의존성 관리 | 빌드 중 필요한 라이브러리 및 패키지 링크 | 빌드/실행 시 필요한 패키지 명시 |
| 사용 범위 | CMake 기반 프로젝트에서 사용(ament_cmake 등) | 모든 ROS2 패키지에서 필수 |
| 설정 대상 | 컴파일 과정, 빌드 타겟, 설치 경로 등 | 패키지 메타 정보, 의존 패키지, 빌드 도구 |
setup.py/setup.cfg
ament_python를 통해 생성된 파이썬 패키지 설치 및 빌드 설정을 정의
✔ setup.py
- 동적인 설정이 필요할 때 사용(의존성 추가, 특정 동작 설정 등)
setuptools.setup()함수를 사용해 python코드로 정의
from setuptools import find_packages, setup
# 패키지 이름 정의
package_name = 'py_pubsub'setup:setuptools에서 호출되어 패키지의 메타데이터 및 설정을 정의
setup(
name=package_name,
version='0.0.0',
packages=find_packages(exclude=['test']),
packagets=find_packages(): 패키지 내부 python파일을 자동으로 검색하고 설치
data_files: 패키지를 설치할 때 배포할 추가 파일 목록 정의, 튜플로 작성
data_files=[
('share/ament_index/resource_index/packages',
['resource/' + package_name]),
('share/' + package_name, ['package.xml']),
],
install_requires=['setuptools'],
zip_safe=True,
maintainer='hyuna',
maintainer_email='hyuna@todo.todo',
description='Examples of minimal publisher/subscriber using rclpy',
license='Apache License 2.0',
tests_require=['pytest'],maintainer,maintainer_email,description,license 는 package.xml파일과 동일하게 작성
entry_points: 패키지 빌드 후 명령줄에서 사용할 수 있는 스크립트 정의
entry_points={
'console_scripts': [
'talker = py_pubsub.publisher_member_function:main',
'listener = py_pubsub.subscriber_member_function:main',
],
},
)
터미널에 entry_points 에 정의된 이름으로 입력해야 노드를 실행시킬 수 있다!!!
현재는 talker와 listener 명령어를 통해 해당 모듈의 main함수를 실행시킬 수 있게 된다.
✔ setup.cfg
- 정적인 패키지 설정을 선언할 때 사용 (고정된 설정 정보 제공)
- 코드 실행 없이도 패키지 설정에 관한 내용을 읽을 수 있음
ros2 run을 실행할 때 path를 제대로 찾게 해주는 역할
[develop] #스크립트가 저장될 경로 지정
script_dir=$base/lib/py_pubsub
[install] # 정식 설치 때 스크립트가 설치될 경로 지정
install_scripts=$base/lib/py_pubsub
develop
publisher_member_function.py에서 직접 코드를 수정하고, 심볼릭 링크를 통해 변경사항 즉시 실행 가능 (소스 코드 설치 X)install
개발이 완료된 패키지를 정식 설치
💡 심볼릭 링크(symbolic link):
- 파일 시스템 내 다른 파일, 디렉토리 위치를 참조하여 링크를 통해 원본 파일에 접근하여 코드 수정 가능
- 직접적인 코드 수정은 해당 디렉토리에 가서 파일을 열고 수정하는 것
- 심볼릭 링크와 같은 간접적인 코드 수정은 원본 소스 코드 링크로 파일에 접근하여 코드를 수정하는 것
| 항목 | setup.py | setup.cfg |
|---|---|---|
| 형식 | python 코드 | INI형식 구성 파일 |
| 사용 방식 | setuptools.setup() 함수를 사용해 python 코드로 정의 | 설정을 텍스트 기반 형식으로 작성 |
| 유연성 | Python 코드이므로 논리적 처리가 가능 | 단순한 설정 정보만 담을 수 있음 |
| 유지보수 | 코드 기반으로 유연하지만, 설정만 포함할 때는 복잡해짐 | 설정 파일로 더 간단하고 유지보수가 용이함 |
| 사용 목적 | 복잡한 동작을 구현할 수 있는 패키지 설치 스크립트 | 주로 패키지의 메타데이터 및 단순 설정 관리 |
3. 노드 파일 작성
# Copyright 2016 Open Source Robotics Foundation, Inc.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.✔ publisher_member_function.py
import rclpy
from rclpy.node import Node
form std_msgs.msg import String
- Node 클래스를 상속받아 노드 정의-> 노드 이름:
minimal publisher
class MinimalPublisher(Node):
def __inint__(self):
super.__init__('minimal publisher') #부모 클래스인 Node의 생성자 호출
self.publisher_ = self.create_publisher(String, 'topic', 10)
timer_period = 0.5 #0.5초마다 한번씩 timer_callback 호출
self.timer = self.create_timer(timer_period, self.timer_callback)
self.i = 0
self.publisher_ = self.create_publisher(String, 'topic', 10) : 메시지가 topic이라는 이름으로 String으로 발행, 퍼블리셔 큐를 10으로 지정하여 메시지 수를 최대 10개 저장
timer_callback: 타이머의 의해 주기적으로 호출 ->msg_data에서 생성된 메시지 발행
def timer_callback(self):
msg = String()
msg.data = 'Hello World: %d % self.i
self.publisher_.publish(msg)
self.get_logger().info('Publishing: "%s" % msg.data)
self.i += 1
self.get_logger() : 저장된 노드의 상태, 메시지 등을 불러와서 모니터에 출력
- main 함수 (class 밖에 위치)
def main(args=None):
rclpy.init(args=args) #ROS2 초기화, 모든 노드가 실행되기 전 반드시 호출
minimal_publisher = MinimalPublisher() # 클래스 인스턴스화
rclpy.spin(minimal_publisher)
# Destroy the node explicitly
# (optional - otherwise it will be done automatically
# when the garbage collector destroys the node object)
minimal_publisher.destroy_node()
rclpy.shutdown()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
rclpy.spin()으로 노드 및 이벤트 루프를 시작한다.
destroy_node()/rclpy.shutdown() 을 호출하지 않으면 노드가 계속 실행되어 메모리에 남아 있게 된다. 이렇게 되면 일정 시간이 지난 후 메모리 누수(memory leak)가 발생할 수 있다.
💡 메모리 누수
프로그램이 더 이상 사용하지 않는 메모리가 계속 자리를 차지하고 있는 것으로, 메모리 누수가 지속되면 메모리 자원고갈과 이로 인한 성능저하, 프로그램 충돌이 발생할 수 있다.
✔ subscriber_member_function.py
import rclpy
from rclpy.node import Node
from std_msgs.msg import Stringlistener_callback: 서브스크라이버가 메시지를 수신할 때 호출
class MinimalSubscriber(Node):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__('minimal_subscriber')
self.subscription = self.create_subscription(
String,
'topic',
self.listener_callback,
10)
self.subscription # prevent unused variable warning
def listener_callback(self, msg): # 퍼블리셔가 발행한 msg자동으로 호출
self.get_logger().info('I heard: "%s"' % msg.data)
서브스크라이버는 외부에서 발행된 메시지를 수신하는 역할을 하기 때문에 timer_callback은 필요하지 않다.
def main(args=None):
rclpy.init(args=args)
minimal_subscriber = MinimalSubscriber()
rclpy.spin(minimal_subscriber)
# Destroy the node explicitly
# (optional - otherwise it will be done automatically
# when the garbage collector destroys the node object)
minimal_subscriber.destroy_node()
rclpy.shutdown()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()4. 빌드
✔ 의존성 체크
rosdep install -i --from-path src --rosdistro humble -y
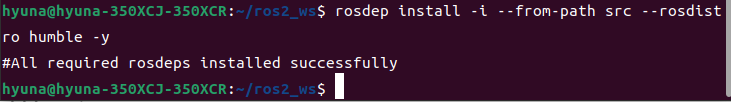
모든 의존성이 설치된 것을 확인하였다.
✔ colcon build
- 소스 코드를 실제 실행 가능한 프로그램, 라이브러리로 변환하기 위한 도구
colcon build또는colcon build --packages-select ros_study_msgs
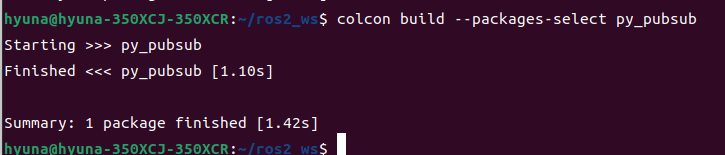
(아래 내용은 install 활성화 후 실행)
- 특정 패키지로 바로 이동하고 싶을 때
colcon_cd my_robot_package - 빌드 내용을 삭제하고싶을 때
rm -rf build/ install/ log또는colcon claen
5. 실행 결과
📌 ROS 기본 환경 설정
nano ~/.bashrc 후 source /opt/ros/humble/setup.bash를 추가하여 ROS 기본환경을 설정해놓는다. 설정이 되면 ROS 2 명령어(ros2 CLI), 메시지 타입, 서비스, 다양한 기본 패키지들을 사용할 수 있게 된다.
📌 워크스페이스 설정
빌드 후 반드시 source install/setup.bash를 실행시켜야 패키지가 ROS2 환경에 인식되도록 해야한다. 이렇게 하면 사용자가 작업 공간에서 빌드한 패키지들을 ROS2 환경에 추가할 수 있다.
src: 패키지의 소스 코드가 들어있는 디렉토리
build: 패키지들이 빌드 중 생간 중간 파일 저장
install: 빌드가 끝난 후 최종적으로 실행 가능한 파일들과 패키지가 설치된 디렉토리
log: 로그 파일(실행 결과)
이 명령어를 통해 ROS2가 빌드된 패키지를 인식하고 실행 파일, 메시지타입, 라이브러리 등을 제대로 사용할 수 있다.

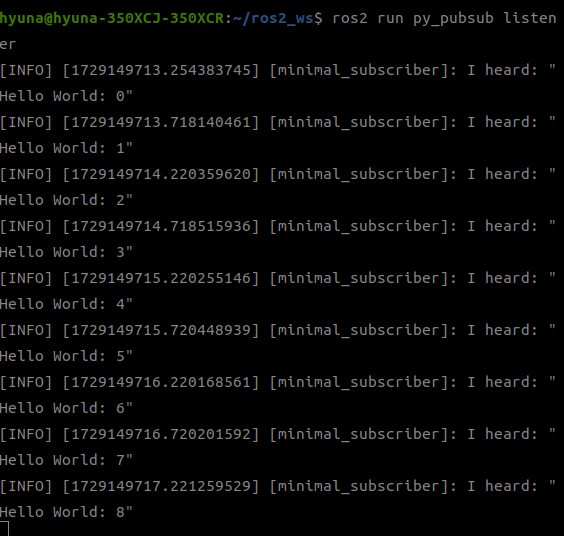
최종적으로 퍼블리셔가 보낸 Hello World 메시지를 서브스크라이버가 받아서 몇번째 메시지인지 수신하였다.

