🖥️ R-DBMS
Database
- Organized collection of inter-related data that models some aspect of the real-world (A. Pavlo)
- Things related are laid together; c.f., files are not like this
Database system
: Informal definition
- Magnetic tapes (storage) : Sequential access ( search )
- SSD, HDD : Random access ( search )
- File System : Store a database as comma-separated value (CSV) files ➡️ low level
- Issue : data integrity ( 같은 Data, but 다른 내용 )
➡️ How to examine the validity(타당성) of the values? - Issue: implementation ( 여러 기능을 상황에 맞게 따로 구현? )
➡️ How to find a particular record? (search)
➡️ How to write a new application that uses the same data - Issue: durability ( 내구성, 연속성 )
➡️ What if the machine crashes while file writing?
- Issue : data integrity ( 같은 Data, but 다른 내용 )
- Database System, File system : Abstraction 역할
Database management system (DBMS)
- Software that allows applications to store and analyze information in a database
- Access data without worrying about the file I/O-level details
- A general-purpose DBMS is designed to allow the definition, creation, querying(search), update, and administration(관리) of databases
DBMS as a data storage
- Database abstraction to avoid low-level implementation and maintenance chores
- Store database in simple data structures
- Access data through high-level language
- Database abstraction does not include:
- How to implement the storage, relations, ...
DBMS as an interface
- Data definition language (DDL)
- Data manipulation language (DML)
➡️ Structured query language (SQL) includes both DDL and DML
🖥️ Relational Data Model
Data Model
: Underlying(기본) the structure of a database
: A notion for describing data or information
- Data model consists of three parts:
- Structure
- Operations
- Constraints
- Examples
- Relational data model: the most conventional ⬅️ focus
- NoSQL ( Hadoop, MongoDB(JSON) ... )
- Machine Learning ( Array, Matrix )
- Misc ( hierachical, network )
Network Data Moedel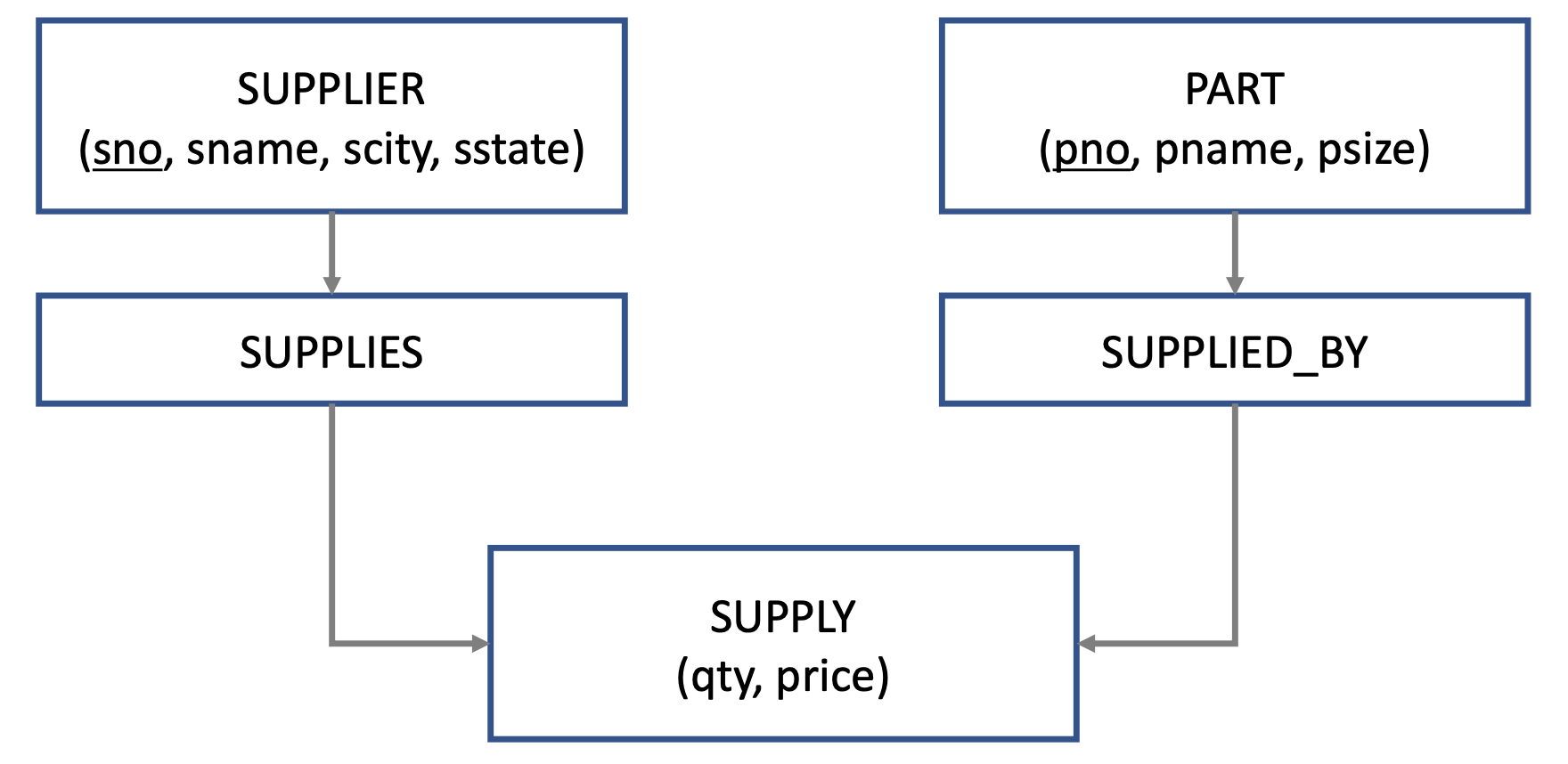
➡️ Integrated Data Storage
➡️ Linked list
➡️ Difficult to maintain
➡️ Writing queries is complex
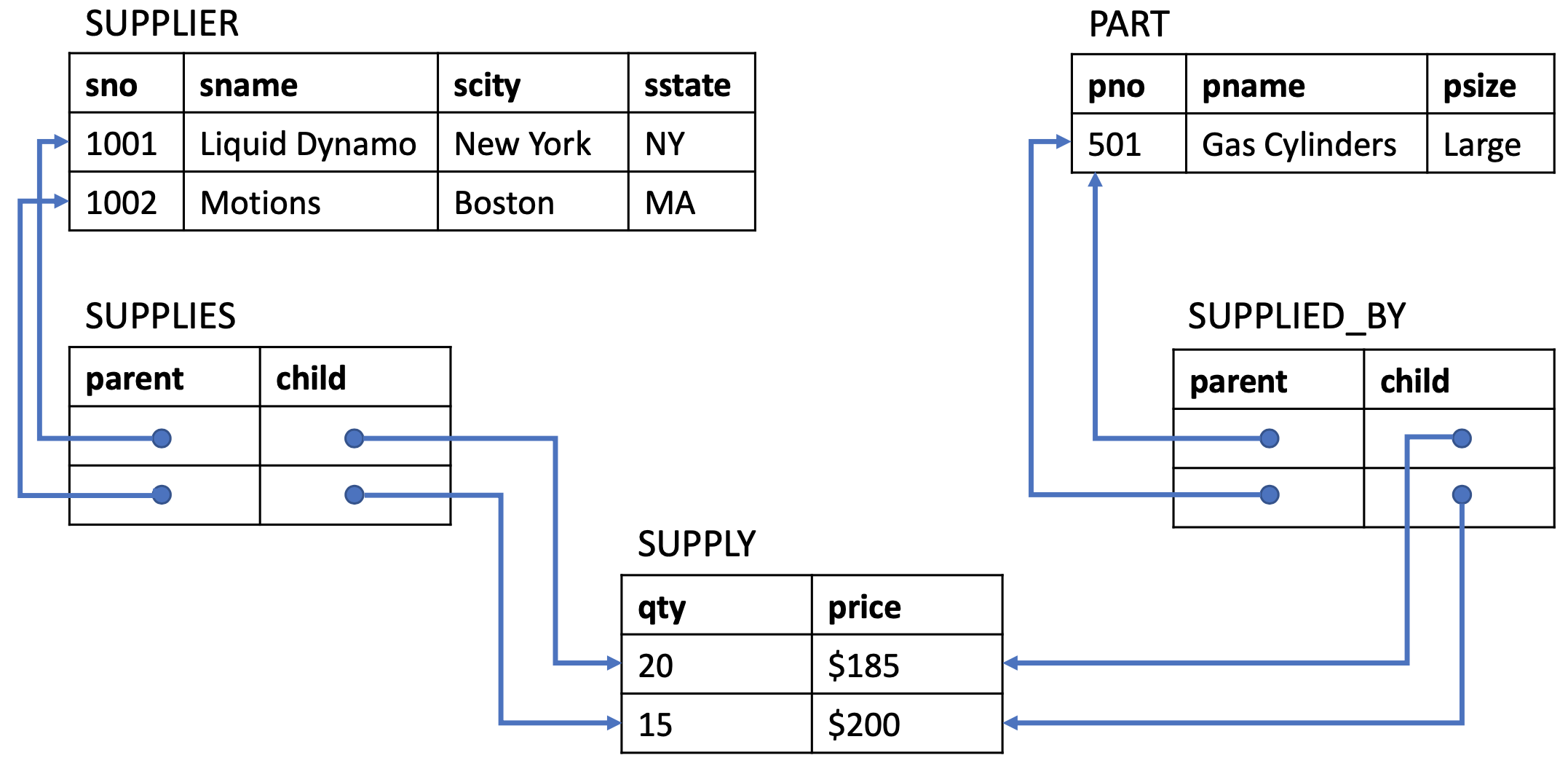
Hierarchical Data Model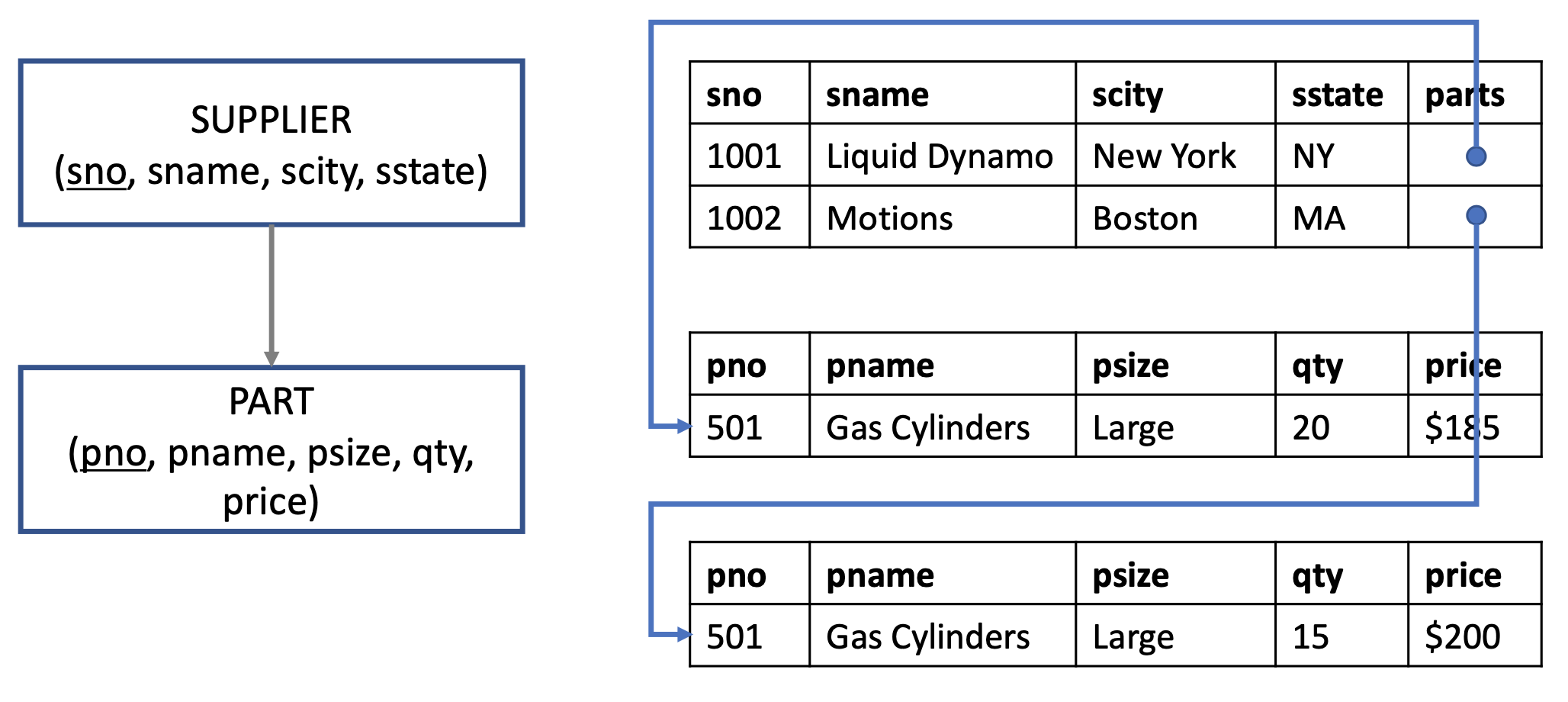
➡️ lost the data independences
➡️ duplicate data
Object-Oriented Data Model
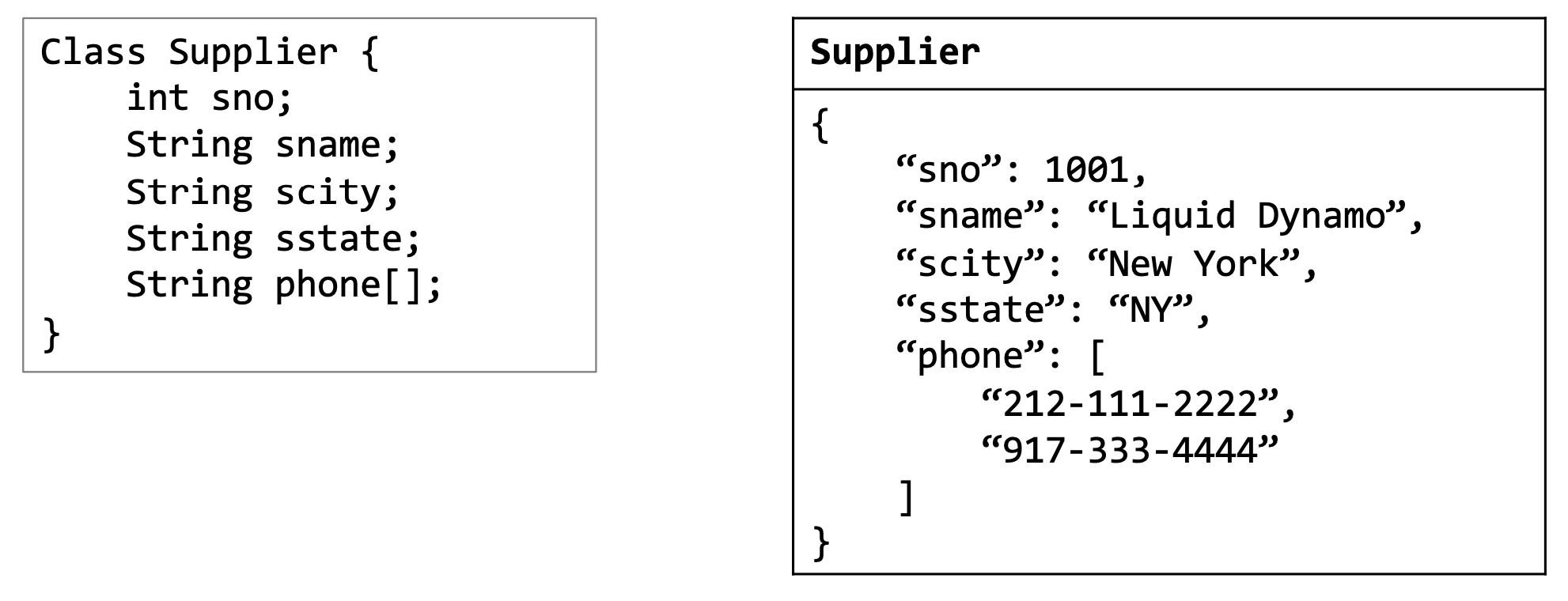
➡️ Indefinite number of data instances ( various cnt of phone number )
➡️ There are still, but not common ( JOSN )
Relational Data Model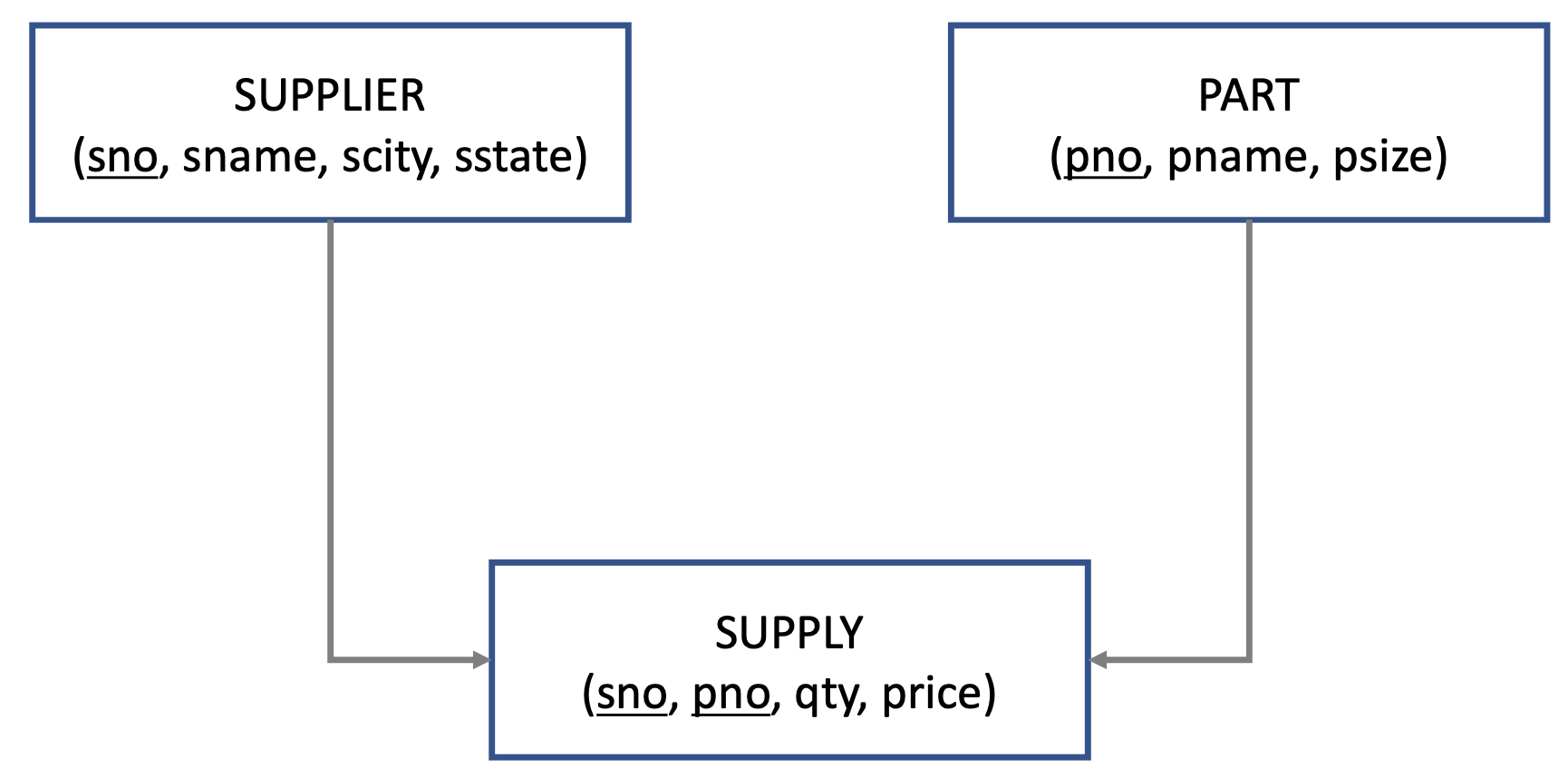
➡️ Effective data model
➡️ generalized method of operation ➡️ SQL
- Relational data model: A data model describes data in terms of relations (관계 측면에서)
- Relation
- An unordered set that contains the relationship of attributes that represent entities ➡️ order does not matter
Relation (Table)
- Attribute (column) = feature = variable
- Attribute values are required to be atomic (indivisible data type)
- Atomic data type : int, float, string ... ↔️ cf. class, structure - The set of allowed values for each attribute is called the domain (possible value range) of the attribute
- NULL is a member of every domain, indicating that the value is “unknown” ➡️ misssing or N/A
- Attribute values are required to be atomic (indivisible data type)
- Tuple (row) = record = data instance(point)
- A tuple is a set of attribute values (also known as its domain) in the relation
- Each tuple has one value for each attribute of the relation
- Values are (normally) atomic/scalar
 ➡️ Schema ( Header ) : Structure of table, List of attributes and their types
➡️ Schema ( Header ) : Structure of table, List of attributes and their types
Notation
- Using a table
- Using a set notation
- Structure: instructor(ID, name, dept_name, salary)
- Tuples: (76766, Crick, Biology, 72000.00),
(83821, Brandt, Comp. Sci., 92000.00),
(45565, Katz, Comp. Sci., 75000.00) - Ordered sets ➡️ attributes in a tuple : order does matter
Ex_ (76766, Crick, Biology, 72000.00) != (72000.00, Biology, Crick, 76766)
Keys
- Key : Identifier for records within a relation
- One type of constraints (unique)
- One or more attributes form a key
- A key for a relation ➡️ do NOT allow duplicates of the same values of the key attributes
Primary Keys
- A relation’s primary key uniquely identifies a single tuple
- instructor(ID, name, dept_name, salary)
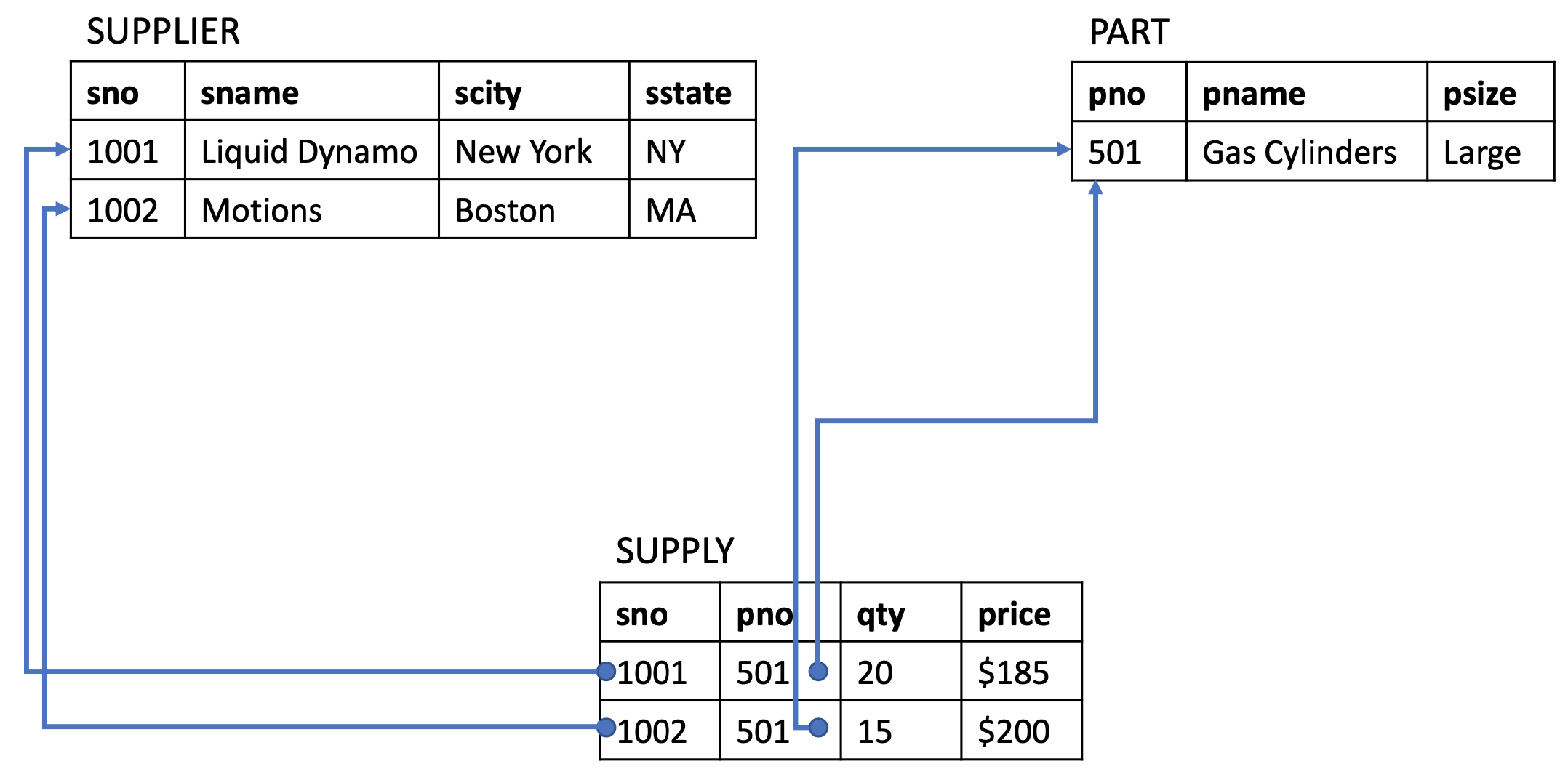
Foreign Keys
- A foreign key specifies that an attribute from one relation has to map to a tuple in another relation
- Value in one relation must appear in another relation
- Referencing relation ➡️ Referenced relation
- Value in one relation must appear in another relation
Data Language
- Data definition language (DDL)
- How to represent relations and information in a database
- Defines database schemas
- How to represent relations and information in a database
- Data manipulation language (DML)
- How to store and retrieve information from a database
- Procedural
- The query specifies the (high-level) strategy the DBMS should use to find the desired results
- Based on relational algebra
Database Schema
- Database: a collection of relations (tables)
- Database schema: the logical structure of the database
- Database instance: a snapshot of the data in the database at a given instant in time
- Relation instance: a snapshot of a relation (attributes and tuples) at a given instant in time
HGU 전산전자공학부 홍참길 교수님의 23-1 Database System 수업을 듣고 작성한 포스트이며, 첨부한 모든 사진은 교수님 수업 PPT의 사진 원본에 필기를 한 수정본입니다.
