전이학습(Transfer Learning)
: 어떤 목적을 이루기 위해 학습된 모델을 다른 작업에 이용하는 것
- 이미 학습된 pre-trained 모델을 가져오고 마지막 레이어만 새로 학습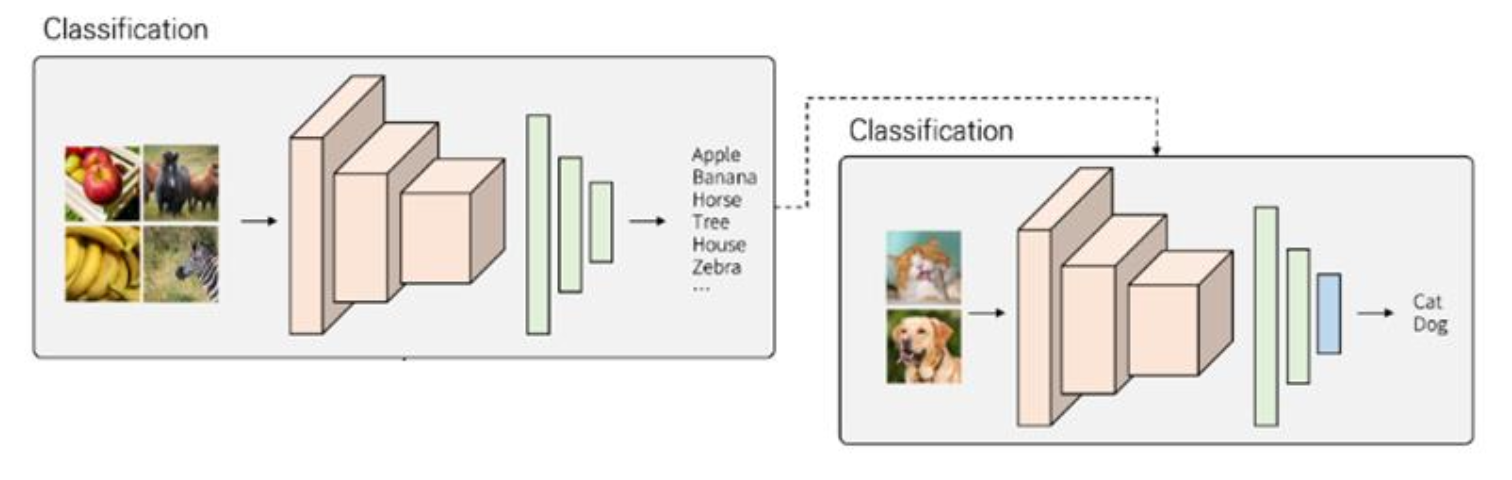 - ImageNet, ResNet, ...
- ImageNet, ResNet, ...
- 학습이 빠르게 수행된다
- overfitting을 예방할 수 있다
이러한 전이학습 시나리오의 중요한 2가지는 다음과 같다:
- Condition
- pretrained 데이터와 새로운 데이터가 비슷한 형태를 가지는 경우
- 새로운 데이터보다 pretrained 데이터의 양이 더 많은 경우
- fine-tuning
- transfer learning에서 사용되는 기법 중 하나
- 사전 학습된 모델을 새로운 문제에 적용하기 위해 일부 가중치를 조절 하는 학습 과정
# License: BSD
# Author: Sasank Chilamkurthy
from __future__ import print_function, division
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.optim import lr_scheduler
import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
import numpy as np
import torchvision
from torchvision import datasets, models, transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import time
import os
import copy
cudnn.benchmark = True
plt.ion() # 대화형 모드Load Data
# 학습을 위해 데이터 증가(augmentation) 및 일반화(normalization)
# 검증을 위한 일반화
data_transforms = {
'train': transforms.Compose([
transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
]),
'val': transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(256),
transforms.CenterCrop(224),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
]),
}
data_dir = 'data/hymenoptera_data'
image_datasets = {x: datasets.ImageFolder(os.path.join(data_dir, x),
data_transforms[x])
for x in ['train', 'val']}
dataloaders = {x: torch.utils.data.DataLoader(image_datasets[x], batch_size=4,
shuffle=True, num_workers=4)
for x in ['train', 'val']}
dataset_sizes = {x: len(image_datasets[x]) for x in ['train', 'val']}
class_names = image_datasets['train'].classes
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
- data augmentation과 normalization을 위한 전처리 과정
- datasets.ImageFolder – 학 습과 검증용 데이터셋 불러오 기
- torch.utils.data.DataLoader – 데이터를 학습에 활용할 수 있도록 batch로 나눔
일부 이미지 시각화하기
def imshow(inp, title=None):
"""tensor를 입력받아 일반적인 이미지로 보여줍니다."""
inp = inp.numpy().transpose((1, 2, 0))
mean = np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406])
std = np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
inp = std * inp + mean
inp = np.clip(inp, 0, 1)
plt.imshow(inp)
if title is not None:
plt.title(title)
plt.pause(0.001) # 갱신이 될 때까지 잠시 기다립니다.
# 학습 데이터의 배치를 얻습니다.
inputs, classes = next(iter(dataloaders['train']))
# 배치로부터 격자 형태의 이미지를 만듭니다.
out = torchvision.utils.make_grid(inputs)
imshow(out, title=[class_names[x] for x in classes])
데이터 증가를 이해하기 위해 일부 학습용 이미지를 시각화
Training model
def train_model(model, criterion, optimizer, scheduler, num_epochs=25):
since = time.time()
best_model_wts = copy.deepcopy(model.state_dict())
best_acc = 0.0
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
print(f'Epoch {epoch}/{num_epochs - 1}')
print('-' * 10)
# 각 에폭(epoch)은 학습 단계와 검증 단계를 갖습니다.
for phase in ['train', 'val']:
if phase == 'train':
model.train() # 모델을 학습 모드로 설정
else:
model.eval() # 모델을 평가 모드로 설정
running_loss = 0.0
running_corrects = 0
# 데이터를 반복
for inputs, labels in dataloaders[phase]:
inputs = inputs.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
# 매개변수 경사도를 0으로 설정
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 순전파
# 학습 시에만 연산 기록을 추적
with torch.set_grad_enabled(phase == 'train'):
outputs = model(inputs)
_, preds = torch.max(outputs, 1)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
# 학습 단계인 경우 역전파 + 최적화
if phase == 'train':
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 통계
running_loss += loss.item() * inputs.size(0)
running_corrects += torch.sum(preds == labels.data)
if phase == 'train':
scheduler.step()
epoch_loss = running_loss / dataset_sizes[phase]
epoch_acc = running_corrects.double() / dataset_sizes[phase]
print(f'{phase} Loss: {epoch_loss:.4f} Acc: {epoch_acc:.4f}')
# 모델을 깊은 복사(deep copy)함
if phase == 'val' and epoch_acc > best_acc:
best_acc = epoch_acc
best_model_wts = copy.deepcopy(model.state_dict())
print()
time_elapsed = time.time() - since
print(f'Training complete in {time_elapsed // 60:.0f}m {time_elapsed % 60:.0f}s')
print(f'Best val Acc: {best_acc:4f}')
# 가장 나은 모델 가중치를 불러옴
model.load_state_dict(best_model_wts)
return model
- scheduling the learning rate
- saving the best model
- train_model 함수는 딥러닝 model의 학습과 검증을 수행하는 함수
scheduler 매개변수는 torch.optim.lr_scheduler 의 LR 스케쥴러 객체(Object)이다.
모델 예측값 시각화하기
def visualize_model(model, num_images=6):
was_training = model.training
model.eval()
images_so_far = 0
fig = plt.figure()
with torch.no_grad():
for i, (inputs, labels) in enumerate(dataloaders['val']):
inputs = inputs.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
outputs = model(inputs)
_, preds = torch.max(outputs, 1)
for j in range(inputs.size()[0]):
images_so_far += 1
ax = plt.subplot(num_images//2, 2, images_so_far)
ax.axis('off')
ax.set_title(f'predicted: {class_names[preds[j]]}')
imshow(inputs.cpu().data[j])
if images_so_far == num_images:
model.train(mode=was_training)
return
model.train(mode=was_training)일부 이미지에 대한 예측값을 보여주는 일반화된 함수
합성곱 신경망 미세조정 ( Finetuning )
- learning rate scheduler는 학습 도중 학습률을 동적으로 조정하여 학 습 과정을 최적화 하는 기법 중 하나
- 초기에는 높은 학습률로 시작하여 빠르게 수렴하게 하고, 학습이 진 행됨에 따라 학습률을 조금씩 낮추어 더 정교하게 최적점을 찾도록 하는 방식
- 학습이 진행될수록 학습률이 감소하여 더 세밀하게 최적화
model_ft = models.resnet18(weights='IMAGENET1K_V1')
num_ftrs = model_ft.fc.in_features
# 여기서 각 출력 샘플의 크기는 2로 설정합니다.
# 또는, ``nn.Linear(num_ftrs, len (class_names))`` 로 일반화할 수 있습니다.
model_ft.fc = nn.Linear(num_ftrs, 2)
model_ft = model_ft.to(device)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 모든 매개변수들이 최적화되었는지 관찰
optimizer_ft = optim.SGD(model_ft.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.9)
# 7 에폭마다 0.1씩 학습률 감소
exp_lr_scheduler = lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer_ft, step_size=7, gamma=0.1)
미리 학습한 모델을 불러온 후 마지막의 완전히 연결된 계층을 초기화
학습 및 평가하기
CPU에서는 15-25분 가량, GPU에서는 1분도 이내의 시간이 걸린다.
model_ft = train_model(model_ft, criterion, optimizer_ft, exp_lr_scheduler,
num_epochs=25)
visualize_model(model_ft)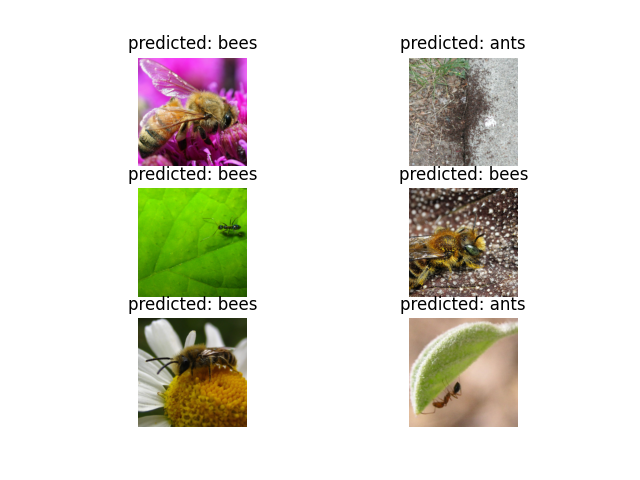
고정된 특징 추출기로써의 합성곱 신경망
pretrained 데이터들의 매개변수 고정, 가중치 그대로 사용
model_conv = torchvision.models.resnet18(weights='IMAGENET1K_V1')
for param in model_conv.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
# 새로 생성된 모듈의 매개변수는 기본값이 requires_grad=True 임
num_ftrs = model_conv.fc.in_features
model_conv.fc = nn.Linear(num_ftrs, 2)
model_conv = model_conv.to(device)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 이전과는 다르게 마지막 계층의 매개변수들만 최적화되는지 관찰
optimizer_conv = optim.SGD(model_conv.fc.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.9)
# 7 에폭마다 0.1씩 학습률 감소
exp_lr_scheduler = lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer_conv, step_size=7, gamma=0.1)학습 및 평가하기
CPU에서 실행하는 경우 이전과 비교했을 때 약 절반 가량의 시간만이 소요될 것이다.
이는 대부분의 신경망에서 경사도를 계산할 필요가 없기 때문이다.
하지만, 순전파는 계산이 필요합니다.
model_conv = train_model(model_conv, criterion, optimizer_conv,
exp_lr_scheduler, num_epochs=25)
visualize_model(model_conv)
plt.ioff()
plt.show()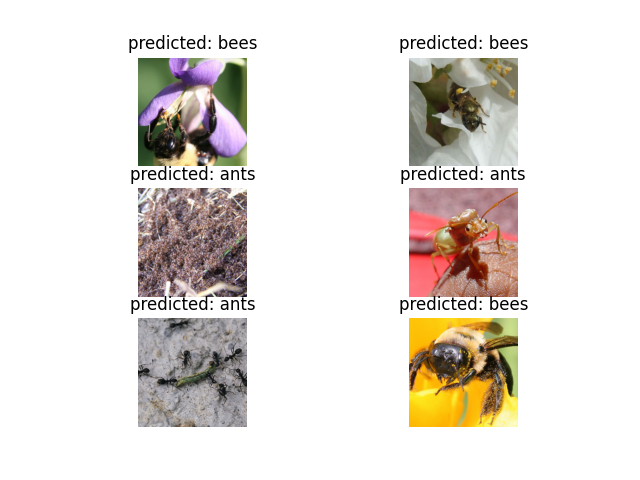
출처 : PyTorch Tutorials https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/transfer_learning_tutorial.html
