무엇을 했나?
Object Detection 전처리
- CNN Layer의 모델링을 한 차례 경험했으니, 4일차 부터는 Object Detection을 진행하였다.
- 그 중 4일차는 yolo 모델을 위한 데이터 전처리를 수행하였다.
- yolo 모델의 요구사항에 맞도록 데이터 구조를 맞추었다.
- json으로 작성된 annotation을 txt 파일로 변환하였다.
- 실무에서 데이터 전처리는 전체 딥러닝 과정의 80~95%를 차지하는 매우 중요한 과정으로, 모델에에 따라 적절하게 데이터를 나누고, lable을 생성하는 연습을 진행하였다.
데이터 분리
- 학습용 데이터와 검증용 데이터를 이미지, 레이블끼리 분류하는 과정이다.
클래스별로 분류된 이미지, 레이블 샘플링
- 가장 먼저 yolo 모델에 맞춘 디렉토리 구조를 생성하였다.
# 구조에 맞는 디렉토리 생성
!mkdir /content/Dataset/images;
!mkdir /content/Dataset/images/train; mkdir /content/Dataset/images/val
!mkdir /content/Dataset/labels;
!mkdir /content/Dataset/labels/train; mkdir /content/Dataset/labels/val
- 루트 디렉토리에서 image, label이 구분되고, 각각 학습용, 검증용 데이터가 들어가는 구조이다.
- 이미지 및 레이블 데이터가 클래스별로 다른 디렉토리에 들어있으므로, 각 디렉토리를 리스트에 담아 for loop을 이용하여 처리하였다.
- jpg와 json 파일을 구분하기 위해 glob 모듈을 사용하였다.
# Dataset metadata 입력
won_list = [디렉토리 리스트]
# 파일 담아오기
image_files = dict()
for won in won_list:
image_files[won] = glob.glob(data_path+won+'/*.jpg')
json_files = dict()
for won in won_list:
json_files[won] = glob.glob(data_path+won+'/*.json')학습 데이터, 검증 데이터 분류
- 8:2로 데이터를 나눌 것이므로, random 모듈을 이용해서 추출할 파일 인덱스를 샘플링하였다.
- 클래스 별로 데이터 개수가 다르기 때문에 딕셔너리와 for loop을 이용해서 클래스별 파일 개수에 맞추어 샘플링하였다.
# 랜덤 샘플링 (난수고정)
random.seed(23)
random_num = dict()
for won in won_list:
test_num = round(len(image_files[won]) * 0.2)
random_num[won] = random.sample((range(len(image_files[won]))), test_num)- 먼저 샘플링된 검증용 데이터를 구조에 맞게 나눈 디렉토리로 이동시켰다.
# 파일 이동
for won in won_list:
for i in random_num[won]:
shutil.move(image_files[won][i], data_path+'images/val/')
shutil.move(json_files[won][i], data_path+'labels/val/')- 남아있는 파일을 모두 학습용 데이터이므로 학습용 디렉토리로 이동시켰다.
# 남아있는 파일 다시 담아오기 (train data)
image_files = dict()
for won in won_list:
image_files[won] = glob.glob(data_path+won+'/*.jpg')
json_files = dict()
for won in won_list:
json_files[won] = glob.glob(data_path+won+'/*.json')
# 남아있는 파일을 전부 train으로 복사
for won in won_list:
for image in image_files[won]:
shutil.copy2(image, data_path+'images/train/')
for json in json_files[won]:
shutil.copy2(json, data_path+'labels/train/')데이터 전처리
이미지 크롭
- 이미지 데이터를 살펴보았을 때, 이미지의 비율(가로 크기, 세로크기)이 일정하지 않았다.
또한 대부분의 경우 object 하나가 이미지 중앙에 위치하는 형태였으므로, 1:1의 비율을 갖도록 크롭하는 과정을 진행하였다. - 성능 개선을 노린 것도 있지만, 이미지 데이터를 처리하는 연습을 하고 싶었다.
- pillow 라이브러리를 이용하여 이미지를 처리하였다.
# 더 최신 버전이 있지만 오류가 발생할 가능성이 있어 9.0.0 버전 사용
!pip install Pillow==9.0.0
import os
from PIL import Image- 이미지를 크롭하는 함수를 설정하였다.
- 간단히 가로길이, 세로길이 중 더 긴 것을 찾아 짧은 쪽과 맞추는 함수이다. 이미지가 치우치는 것을 막기 위해 양옆을 동일한 비율로 잘라주었다.
# crop 함수 설정
"""
이미지를 1:1 비율이 되도록 자르는 함수입니다.
"""
def crop(file):
img = Image.open(file)
w, h = img.size
crop_len = abs(w - h) // 2
if w == h:
img_cropped = img
elif w > h:
img_cropped = img.crop((crop_len, 0, w-crop_len, h))
else:
img_cropped = img.crop((0, crop_len, w, h-crop_len))
return img_cropped- 파일을 불러와 for loop을 이용하여 이미지를 처리하였다.
# 파일 불러오기
train_path = '/content/Dataset/images/train/*'
test_path = '/content/Dataset/images/val/*'
train_files = glob.glob(train_path)
test_files = glob.glob(test_path)
# 이미지 처리 (기존 이미지 덮어씌움)
for file in train_files:
img_cropped = crop(file)
img_cropped.save(file)
for file in test_files:
img_cropped = crop(file)
img_cropped.save(file)
- crop이 잘 이루어졌음을 확인할 수 있다.
json에서 정보 추출
- json에 저장된 사진 정보 및 bounding box 정보를 yolo 모델에 맞는 text 파일로 바꾸어주어야 한다.
- yolo에서 요구하는 양식은 각 바운딩 박스가
class x_center y_center width, height순서로 저장되어야 한다. 또한 0~1의 범위로 normalization이 이루어져 있어야 한다.

yolo document에서 제공하는 가이드
- 해당 양식에 맞게 데이터를 전처리하는 함수를 만들었다.
- 원래 클래스는 16개로 앞면과 뒷면을 구분하였지만 앞뒷면 구분을 없애고 8개 클래스로 만들어주었다.
- 이미지는 1:1로 crop하였으나 annotation은 그대로이므로, crop한 이미지에 맞추어서 정규화하는 작업이 다소 번거로웠다.
- 최종적으로 yolo annotation 형식에 맞는 문자열을 반환한다.
def json_to_txt(file, classes):
result = dict()
with open(file, mode='r') as f:
data = json.load(f)
# 이미지 처리를 위한 변수 설정
points = data['shapes'][0]['points']
x1, y1 = points[0]
x2, y2 = points[1]
width, height = data['imageWidth'], data['imageHeight']
# 라벨 획득 (앞면, 뒷면 구분 제거)
text = data['shapes'][0]['label']
idx = text.rfind('_')
label = text[:idx]
# crop 반영
crop_len = abs(width-height) // 2
if width > height:
width = height
x1 = max(x1-crop_len, 0)
x2 = min(x2-crop_len, width)
elif width < height:
height = width
y1 = max(y1-crop_len, 0)
y2 = min(y2-crop_len, height)
# 정규화 (0 ~ 1 min-max)
x1 = x1 / width
x2 = x2 / width
y1 = y1 / height
y2 = y2 / height
# x, y, w, h 계산
x = (x1 + x2) / 2
y = (y1 + y2) / 2
w = (x2 - x1)
h = (y2 - y1)
# 정해진 형식의 문자열로 반환
return f'{classes[label]} {x} {y} {w} {h}'- 이제 처리된 문자열을 텍스트 파일로 만들어 저장하였다.
- 기존의 json 파일 이름을 이용해 txt 파일을 만들었다.
for file in train_files:
annot = json_to_txt(file, classes)
txt_file = file.replace('.json', '.txt')
with open(txt_file, mode='w') as f:
text = annot
f.write(text)
for file in test_files:
annot = json_to_txt(file, classes)
txt_file = file.replace('.json', '.txt')
with open(txt_file, mode='w') as f:
text = annot
f.write(text)yaml 파일 작성
-
마지막으로 yolo 모델에게 파일 위치와 클래스 종류 등을 전달하는 yaml 파일을 작성하였다.
-
yolo document에서 알려주는 yaml파일의 형식은 다음과 같다.
# Train/val/test sets as 1) dir: path/to/imgs, 2) file: path/to/imgs.txt, or 3) list: [path/to/imgs1, path/to/imgs2, ..]
path: ../datasets/coco128 # dataset root dir
train: images/train2017 # train images (relative to 'path') 128 images
val: images/train2017 # val images (relative to 'path') 128 images
test: # test images (optional)
# Classes (80 COCO classes)
names:
0: person
1: bicycle
2: car
...
77: teddy bear
78: hair drier
79: toothbrush- PyYAML 라이브러리를 이용해, 딕셔너리 형식으로 필요한 양식을 작성하였다.
document = {
'path' : '/content/drive/MyDrive/my_data/220320_mini_project_money/images/',
'train' : 'train',
'val' : 'val',
'nc' : 8,
'names' : won_dict
}
# dump 함수를 이용하여 저장
with open('/content/drive/MyDrive/my_data/220320_mini_project_money/money.yaml', 'w') as f :
yaml.dump(document, f)- 이제 모델 학습 및 평가를 위한 전처리 작업이 끝났다.
- 5일차에는 모델링 및 평가를 수행할 것이다.
소감
좋았던 점
- 단순히 데이터를 분리하고, annotation 파일을 만드는 것 외에 이미지 crop 등 별도의 처리를 하는 과정을 직접 시도해보았다. 많은 연습이 된 것 같다.
아쉬운 점
-
만약 이 모델을 실제로 사용한다면 object가 회전되어 있거나, 여러 각도에서 사진이 찍혔거나, 어느 한쪽으로 치우치고 일부만 보이는 등의 사례가 있을 것이다. 그런데 학습 데이터는 대부분 정중앙에 object 하나만 찍혀있는 형태여서 일반적인 성능이 잘 나올 수 있을지는 의문이다.
-
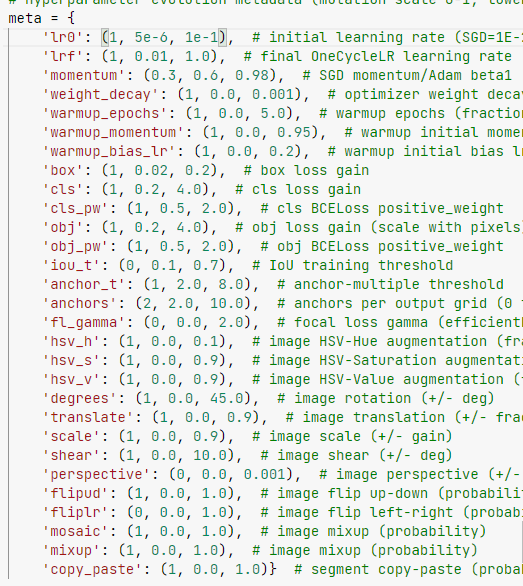
때문에 Data Augmentation을 시도해보고 싶었으나, yolo 모델 자체에 적용하는 generator는 찾을 수 없었다.
별도로 변형된 이미지를 따로 생성하면 가능하겠지만, 이는 시간 부족으로 시도하지 못했다.
train.py 파일을 뜯어보니 yolo 자체에서 augmentation을 적용하는 것을 발견하였다. 이를 적절히 조절하면 원하는 augmentation이 가능할 것으로 보인다.