#INTRO
한달 전 직접 빚은 도자기 그릇 완성 !
#최종 프로젝트 진행
이탈 확률 예측 모델링 데이터셋 준비
-
기본 데이터 셋 :
Transactions 테이블 + Customers 테이블
= 2년 동안 구매한 이력이 있는 고객 中 ‘club_member_status’ 가 LEFT_CLUB인 고객 제외 (현재 데이터 기준 135만개 행) -
이탈여부 컬럼 부여 : 4번 군집 + RFM 세그먼트 ('동면 고객', '이탈 고객') =
1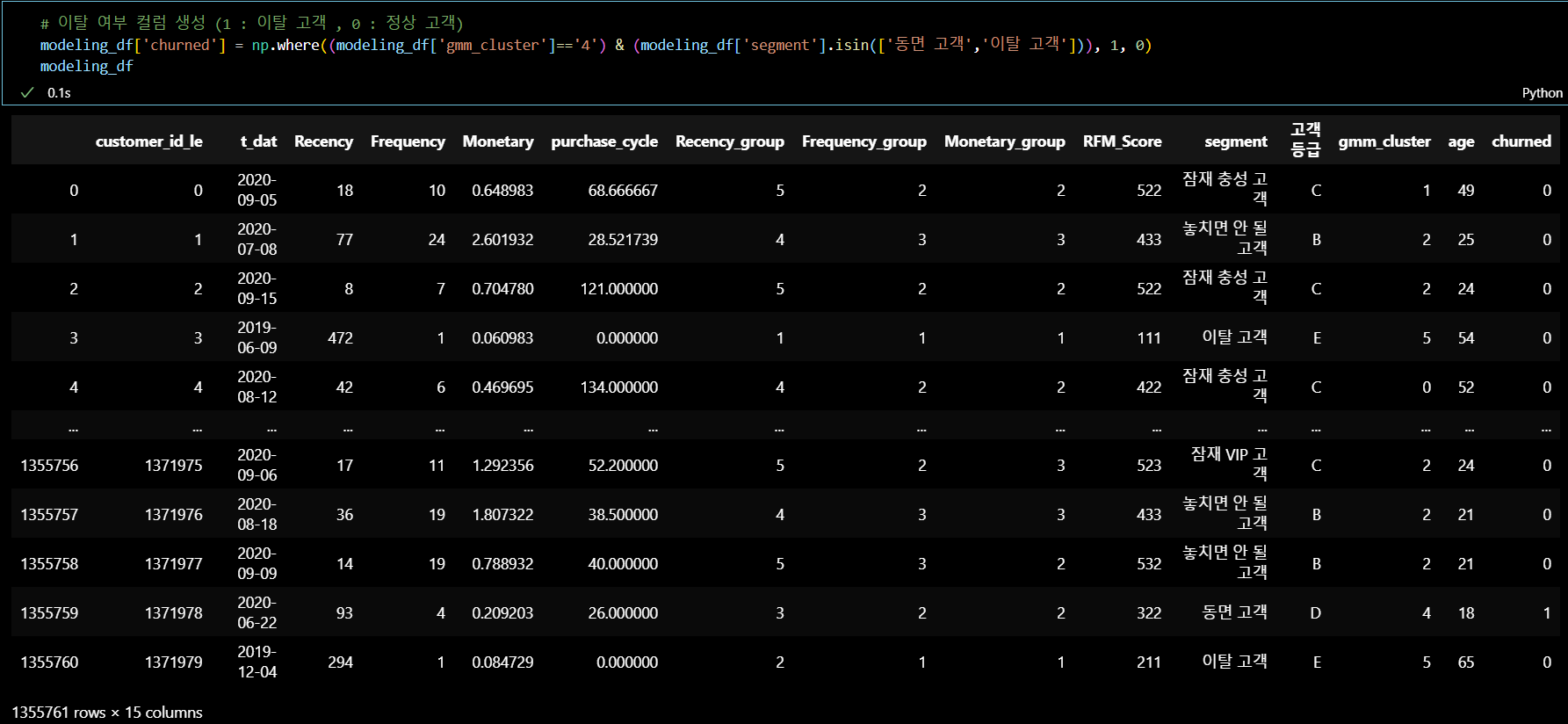
-
모델에 활용할 데이터 셋 준비
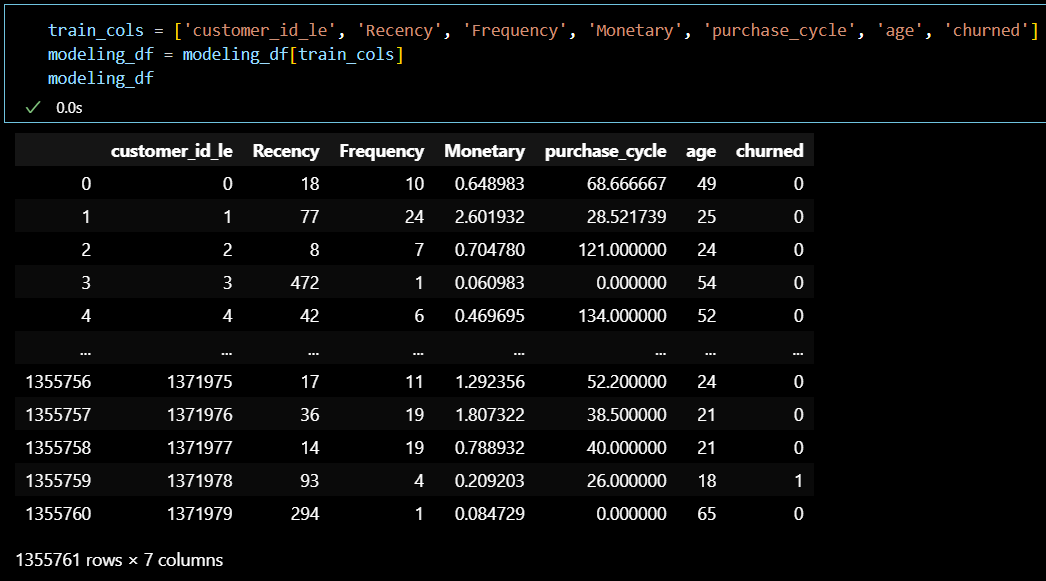
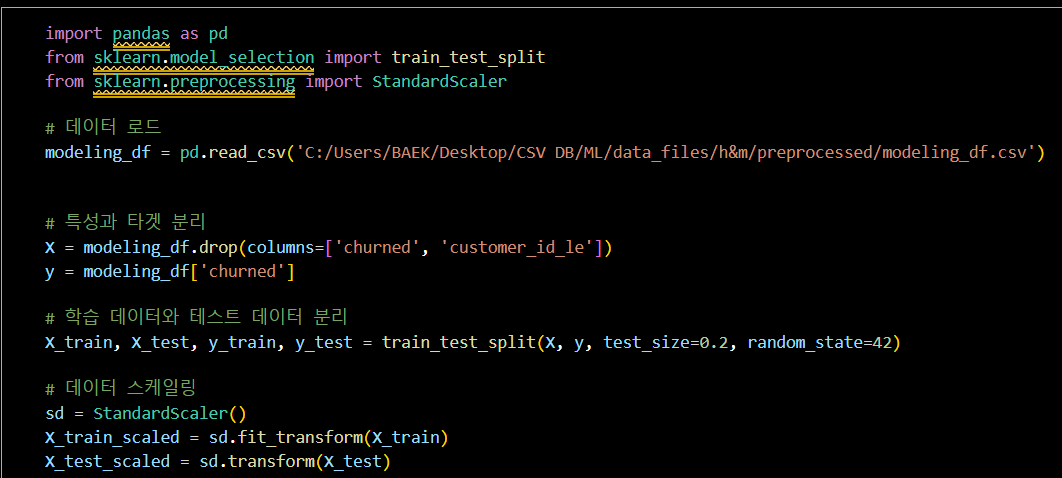
모델링 기본 세팅 (데이터 분리)
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
# 데이터 로드
modeling_df = pd.read_csv('C:/Users/BAEK/Desktop/CSV DB/ML/data_files/h&m/preprocessed/modeling_df.csv')
# 특성과 타겟 분리
X = modeling_df.drop(columns=['churned', 'customer_id_le'])
y = modeling_df['churned']
# 학습 데이터와 테스트 데이터 분리
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 데이터 스케일링
sd = StandardScaler()
X_train_scaled = sd.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_scaled = sd.transform(X_test)로지스틱 회귀 모델
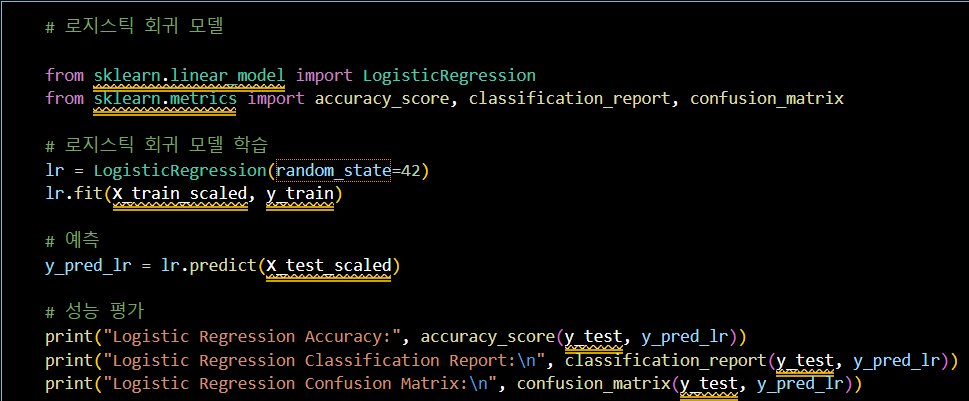
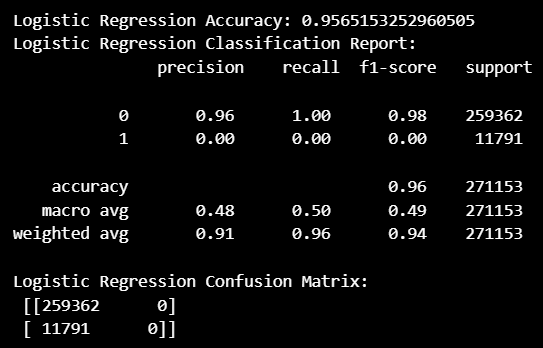
# 로지스틱 회귀 모델
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, classification_report, confusion_matrix
# 로지스틱 회귀 모델 학습
lr = LogisticRegression(random_state=42)
lr.fit(X_train_scaled, y_train)
# 예측
y_pred_lr = lr.predict(X_test_scaled)
# 성능 평가
print("Logistic Regression Accuracy:", accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred_lr))
print("Logistic Regression Classification Report:\n", classification_report(y_test, y_pred_lr))
print("Logistic Regression Confusion Matrix:\n", confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred_lr))- 모델 성능 확인 (정확도 0.95)
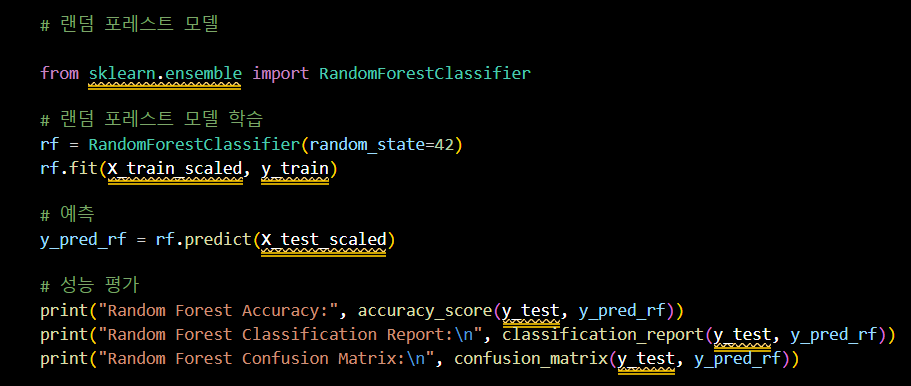
랜덤 포레스트 모델
# 랜덤 포레스트 모델
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
# 랜덤 포레스트 모델 학습
rf = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=42)
rf.fit(X_train_scaled, y_train)
# 예측
y_pred_rf = rf.predict(X_test_scaled)
# 성능 평가
print("Random Forest Accuracy:", accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred_rf))
print("Random Forest Classification Report:\n", classification_report(y_test, y_pred_rf))
print("Random Forest Confusion Matrix:\n", confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred_rf))- 모델 성능 확인 (정확도 0.96)
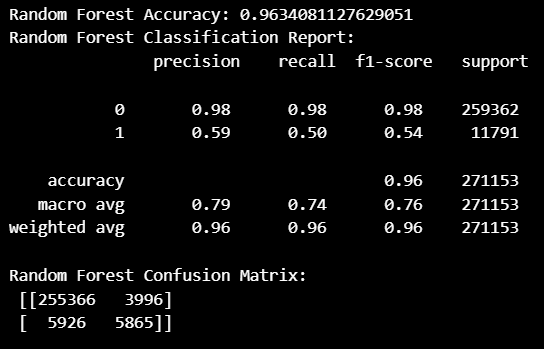
두 모델 모두 1 (이탈 고객) 예측에 대한 성능이 많이 떨어진다.
전체 데이터 (135만 개) 중 이탈 고객1값이 6만 개가 채 되지 않아서
생기는 문제인 것으로 판단.
하이퍼 파라미터 조정 또는 오버 샘플링 (1 값) 을 통한
성능 개선 작업이 필요할 것 같다.
#OUTRO
오늘의 한 줄.
주말은 왜 이렇게 시간이 빨리 가는 건지..ㅋㅋ