지난 포스팅에서 자주 사용되는 Array, ArrayList, LinkedList에 대해 알아봤다. 선형 자료구조에서 규칙을 정한게 스택과 큐다.
4️⃣ 스택(Stack) | 탐색: O(n) 삽입,삭제: O(1)
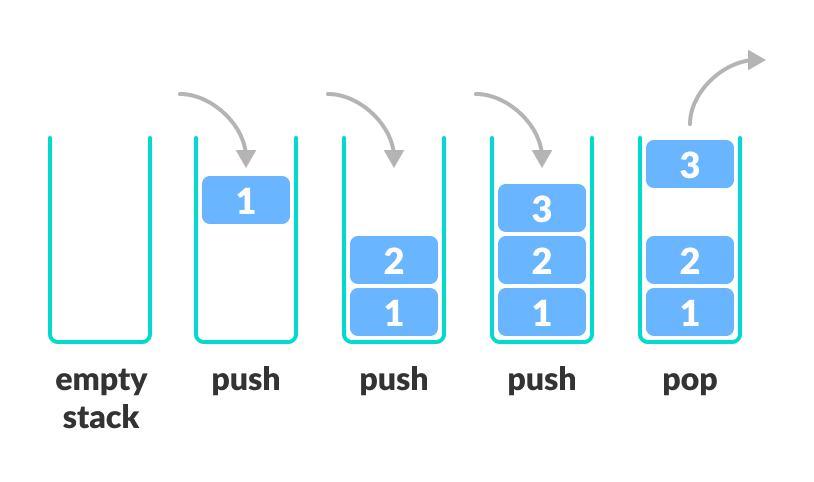
- 한쪽 끝에서만 자료를 넣고 빼는게 가능한
후입선출(LIFO)성질을 가진 자료구조 - 재귀, DFS, 웹 페이지 뒤로 가기 등에 사용
- 주로
Array로 구현 (LinkedList도 가능) - 시간 복잡도
- 탐색: 특정 요소를 찾기 위해 앞에서부터 하나씩 확인해야하고 최악의 경우 완전탐색이 이루어져야 하므로
O(n) - 삽입, 제거: 맨위부터 삽입,제거 되므로
O(1)
- 탐색: 특정 요소를 찾기 위해 앞에서부터 하나씩 확인해야하고 최악의 경우 완전탐색이 이루어져야 하므로
class Stack {
private int[] arr;
private int top;
private int capacity; // 스택의 최대 크기
public Stack(int size) {
arr = new int[size];
capacity = size;
top = -1; // 초기 top은 -1 (스택이 비어있음)
}
public void push(int item) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("스택이 가득 찼습니다!");
return;
}
arr[++top] = item;
System.out.println(item + "를 스택에 추가했습니다.");
}
public int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("스택이 비어있습니다!");
return -1;
}
System.out.println(arr[top] + "를 스택에서 제거했습니다.");
return arr[top--];
}
// 스택의 맨 위 데이터 확인 (Peek)
public int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("스택이 비어있습니다!");
return -1;
}
return arr[top];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return top == capacity - 1;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack stack = new Stack(5);
stack.push(10);
stack.push(20);
stack.push(30);
stack.push(40);
stack.push(50);
// 스택이 가득 찬 상태에서 다시 push 시도
stack.push(60); // "스택이 가득 찼습니다!" 출력됨
// 데이터 확인
System.out.println("스택의 맨 위 값: " + stack.peek()); // 50
// 데이터 제거
stack.pop();
stack.pop();
System.out.println("스택의 맨 위 값: " + stack.peek()); // 30
}
}- 이처럼 스택은 맨 위(top)에만 접근할 수 있다.
- 새로운 요소를 추가할 때는 먼저 스택이 가득 찼는지(isFull) 확인한 뒤, top을 증가시켜 요소를 추가한다.
- 삭제할 때도 스택이 비었는지(isEmpty)를 확인한 후, 맨 위(top)에서 요소를 제거한다.
5️⃣ 큐(Queue) | 탐색: O(n) 삽입, 삭제 : O(1)
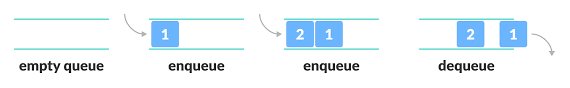
- 양쪽 끝에서 데이터의 삽입, 삭제가 가능한
선입선출(FIFO)성질을 가진 자료구조 - CPU 작업이나 네트워크 접속을 기다리는 행렬, BFS 등에 사용
- 주로
LinkedList로 구현 (Array도 가능) - 시간 복잡도
- 탐색: 앞에서부터 하나씩 확인해야하므로
O(n) - 삽입, 제거: 맨 뒤에 추가하여 삽입하거나 맨 앞부터 제거하므로
O(1)
- 탐색: 앞에서부터 하나씩 확인해야하므로
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
class Queue {
private LinkedList<Integer> queue;
public Queue() {
queue = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void enqueue(int item) {
queue.addLast(item);
System.out.println(item + "를 큐에 삽입했습니다.");
}
public int dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("큐가 비어있습니다!");
}
int removedItem = queue.removeFirst();
System.out.println(removedItem + "를 큐에서 제거했습니다.");
return removedItem;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return queue.isEmpty();
}
public int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("큐가 비어있습니다!");
}
return queue.getFirst();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue queue = new Queue();
queue.enqueue(10);
queue.enqueue(20);
queue.enqueue(30);
queue.enqueue(40);
System.out.println("큐의 첫 번째 값: " + queue.peek()); // 10
queue.dequeue(); // 10 제거
queue.dequeue(); // 20 제거
// 다시 데이터 확인 (Peek)
System.out.println("큐의 첫 번째 값: " + queue.peek()); // 30
System.out.println("큐가 비었나요? " + queue.isEmpty()); // false
}
}- 큐는 앞(front)과 뒤(rear) 양쪽 끝에서 삽입과 삭제가 이루어진다.
- 새로운 요소를 추가할 때는 큐의 뒤쪽에 추가되며, 삭제는 앞쪽에서 이루어진다.
- 먼저, 큐가 비어있는지(isEmpty)를 확인한 후에 삭제하고, 요소가 정상적으로 삭제되면 다음 요소를 처리한다.
그런데 만약, 들어온 순서에 의한 처리가 아니라 더 중요한 작업부터 처리해야 하는 경우라면? 예를 들어, 긴급 보안 점검이나 시스템 요청 같은 경우 스택이나 큐로 처리할 경우 해당 요청이 지연되는 문제가 발생할 수 있다. 이러한 상황에는 우선순위 큐를 사용해서 빠르게 처리할 수 있다.
🤫 우선순위 큐(Priority Queue) | 탐색:O(1) 삽입, 삭제: O(log n)
- 각 요소에 우선순위를 매겨 우선순위가 높은 요소부터 우선적으로 처리하는
비선형 자료구조 - 주로 Heap을 사용하여 구현
- 시간복잡도
- 탐색: 우선순위가 가장 높은 요소를 확인하므로
O(1) - 삽입, 제거: Heap에 요소를 삽입, 제거하는것과 동일하므로
O(log n)
- 탐색: 우선순위가 가장 높은 요소를 확인하므로
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
class PriorityQueueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
priorityQueue.add(30);
priorityQueue.add(10);
priorityQueue.add(20);
System.out.println("가장 높은 우선순위 요소: " + priorityQueue.peek()); // 10
priorityQueue.poll(); // 10 제거
System.out.println("다음 우선순위 요소: " + priorityQueue.peek()); // 20
}
}- PriorityQueue는 기본적으로 Min-Heap을 사용하여 우선순위가 가장 낮은 값이 먼저 처리된다.
- add()로 요소를 추가하고, peek()으로 최우선 요소를 확인한다.
- poll()로 최우선 요소를 제거한다.
💅🏻💅🏻💅🏻 정리
| Stack | Queue | Priority Queue | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 특징 | LIFO | FIFO | 우선순위에 따라 처리 |
| 구현 형태 | Array, LinkedList | LinkedList, Array | Heap (Min-Heap, Max-Heap) |
| 사용 영역 | 뒤로가기, 메모리 영역 | CPU 스케줄링, Ready Queue, 프린터 큐 | 작업 스케줄링, 네트워크 관리 |
| 시간 복잡도 | 삽입/삭제: O(1) 탐색: O(n) | 삽입/삭제: O(1) 탐색: O(n) | 삽입/삭제: O(log n) 탐색: O(1) |
