따수워진 3월인데 이번 프로젝트에서 동시성이 중요하다 생각해서 그에 관련된 내용입니다.
주로 자바에 맞춰진 내용이지만 재밌게 읽어주시어요.
1. 멀티 스레드
a. 멀티 스레드의 정의 및 필요성
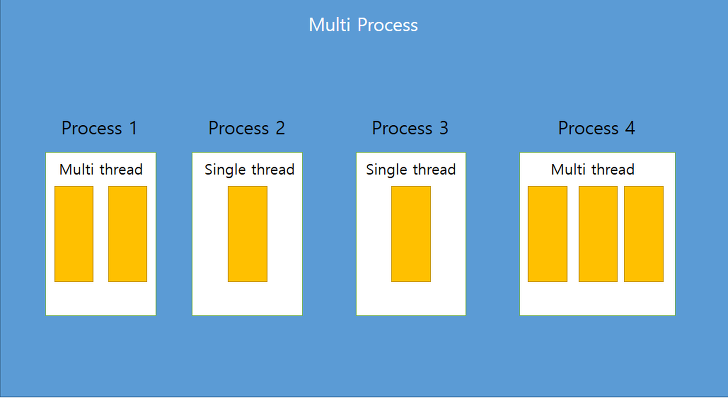
멀티 스레드 : Application 내부에서의 멀티 태스킹
멀티 프로세스: Application 단위의 멀티 태스킹
- 멀티 프로세스
- OS에서 할당받은 메모리로 실행 ⇒ 서로 독립적
- 독립적이기 때문에 하나의 프로세스에 오류가 발생해도 다른 프로세스에 영향 X
- 멀티 스레드
- 프로세스 내부에 생성 ⇒ 서로 영향을 미칠 수 있음
- 하나의 스레드 예외 발생 시 프로세스 자체가 종료될 수 있기 때문에 영향을 미침
- 왜 필요함? 독립적인 든든한 멀티 프로세스 쓰면 되지?
- 리소스 효율성
- 동일 프로세스 내에서 작업 ⇒ 같은 메모리 공간 공유 ⇒ 메모리 효율 굿
- Context Switching
- 멀티 프로세스는 context switching에 오버 헤드 유발 (독립적)
- 멀티 스레드는 같은 메모리 공간 공유로 context switching에 유리함
- I/O 작업 병렬 처리
- CPU 연산보다 I/O 연산 많은 경우 유리 ⇒ CPU가 I/O 작업 기다리는 동안 다른 스레드가 CPU 자원 사용할 수 있기 때문에 응답성 향상
- 리소스 효율성
➡️ 멀티 스레드의 장점 : 반응성, 자원 공유 가능, 경제성, 확장성 (병렬성)
➡️ 프로세스 : 공장 / 스레드 : 공장 직원 / 공장 크기 (프로세스 메모리 한계)에 따라 직원 수(스레드 수) 결정
2. Java의 멀티 스레드
a. 구현 방법
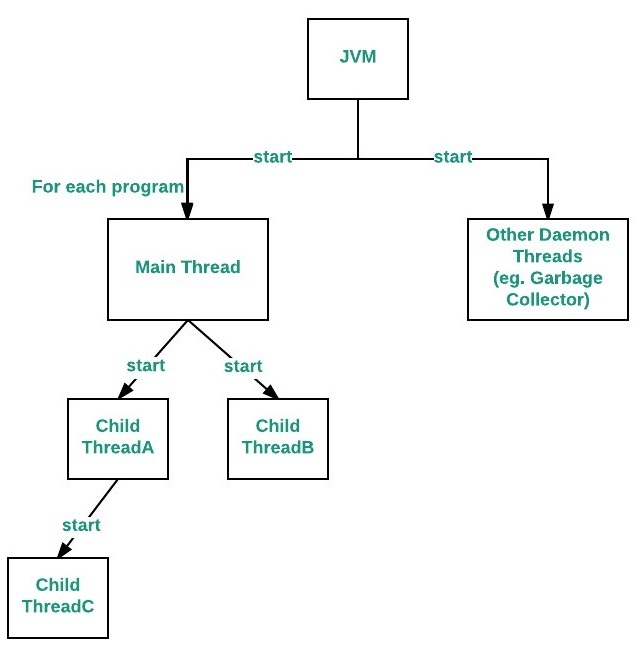
💡 Java ⇒ Main 스레드 : main() 메서드 + (작업 스레드 : Thread, Runnable 구현)
- JVM 이 먼저 Main 스레드를 자동 생성
main()메서드 실행
- 별도의 스레드 (작업 스레드) 없으면 단일 스레드로
main()만 실행됨 main()내부에 또 다른 스레드를 생성 및 실행하는 코드가 있다면 그 스레드 동시 실행
메인 스레드는 JVM이 만들어주면 작업 스레드는 누가 만드나요? ⇒ 바로바로 개발자 여러분
a-1) Thread (Class) java.lang.Thread
- Thread 하위 클래스로 생성하는 방법
-
실행 작업을 Runnable 로 만들지 않고, Thread의 하위 클래스로 작업 스레드 정의
public class WorkerThread extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { // 스레드가 실행할 코드 } } Thread thread = new WorkerThread(); -
익명 객체 구현 시 더 간단
Thread thread = new Thread() { public void run() { // 스레드가 실행할 코드. } } -
Thread 클래스에서 매개변수로 받은 Runnable 구현체가 아닌 Thread 자체 메서드를 사용 가능
-
a-2) Runnable (Interface)
- Thread 클래스 직접 객체화해서 생성하는 방법
public class ThreadTest { Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { // 스레드가 실행할 코드 } }); }- Runnable 인터페이스라
run()메서드 구현된 target이 필요run(): 작업 스레드가 실행할 코드 작성- ! ! ! !실제 스레드 아님! ! ! ! ⇒ 어떤 작업할지에 대한 코드이지 절대 스레드 아님
- Runnable 구현체를 매개값으로 Thread 생성자 호출해야 작업 스레드 생성
- 작업 스레드 생성되면 바로 실행되는 것이 아닌
thread.start()호출해야 실행됨
- Runnable 인터페이스라
[간단 정리]
| 기준 | Runnable 구현 방식 | Thread 상속 방식 |
|---|---|---|
| 유연성 | 다른 클래스도 상속 가능, 더 유연한 구조 | 다중 상속 불가, 상속 구조의 제한 |
| 재사용성 | Runnable 구현체는 여러 스레드에서 재사용 가능 | 각 스레드가 고유한 작업 로직을 가짐 |
| 객체 지향 설계 원칙 | 구성(Composition) 원칙 | 상속 (Ingeritance) 사용 |
| 코드 복잡성 | 다소 복잡, Thread 와 Runnable 분리 | 간결하고 직관적 |
| 스레드 동작 변경 | Thread 의 동작을 직접 수정하기 어려움 | Thread 클래스의 동작을 직접 변경 가능 |
| 작업과 스레드 결합 | 작업 로직과 스레드 분리 가능 | 작업 로직과 스레드 강하게 결합 |
➡️ extends Thread
단점 : 방식은 하나만 상속 가능함 / 장점 : run() 외에 다른 메서드를 Override 해야한다면 사용
➡️ implements Runnable
run() 만 사용해도 되는 경우 Runnable 사용 / Thread를 상속받을 클래스가 다른 클래스도 상속 받아야 한다면 Runnable 사용
b. 생명 주기
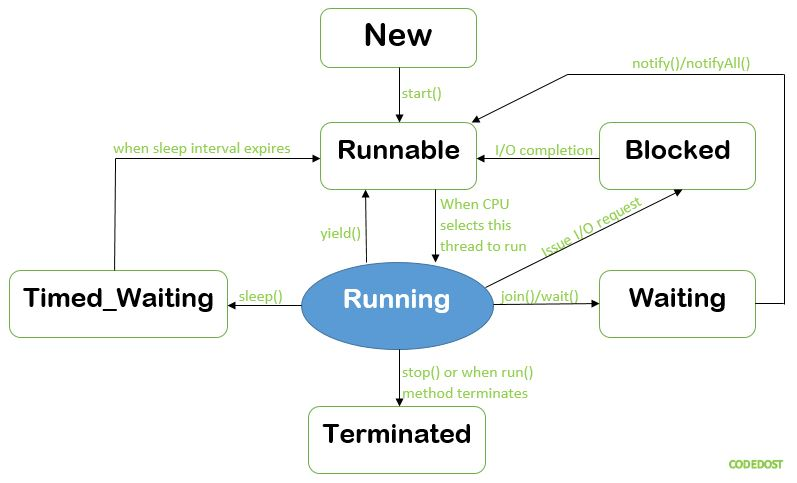
b-1) 스레드의 상태
- New : 스레드 생성 후 아직
start()호출 안된 상태 - Runnable : 실행 중 혹은 실행 가능한 상태
- Blocked : 동기화 블록에 의해 일시정지된 상태 (Lock이 풀릴 때 까지 기다림)
- Waiting, Timed_waiting : 스레드의 작업이 종료된 상태는 아니지만 실행 불가능 (UnRunnable) 일시정지 상태, Timed가 붙으면 정지 시간이 지정된 경우
- Terminated : 스레드의 작업이 종료된 상태
// Thread 상태 확인 방법
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Thread thread = new Thread();
System.out.println(thread.getState()); // 출력 : NEW
}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Thread thread = new Thread();
System.out.println(thread.getState()); // 출력 : RUNNABLE
}b-2) 각 상태 간 전이와 메서드 정리
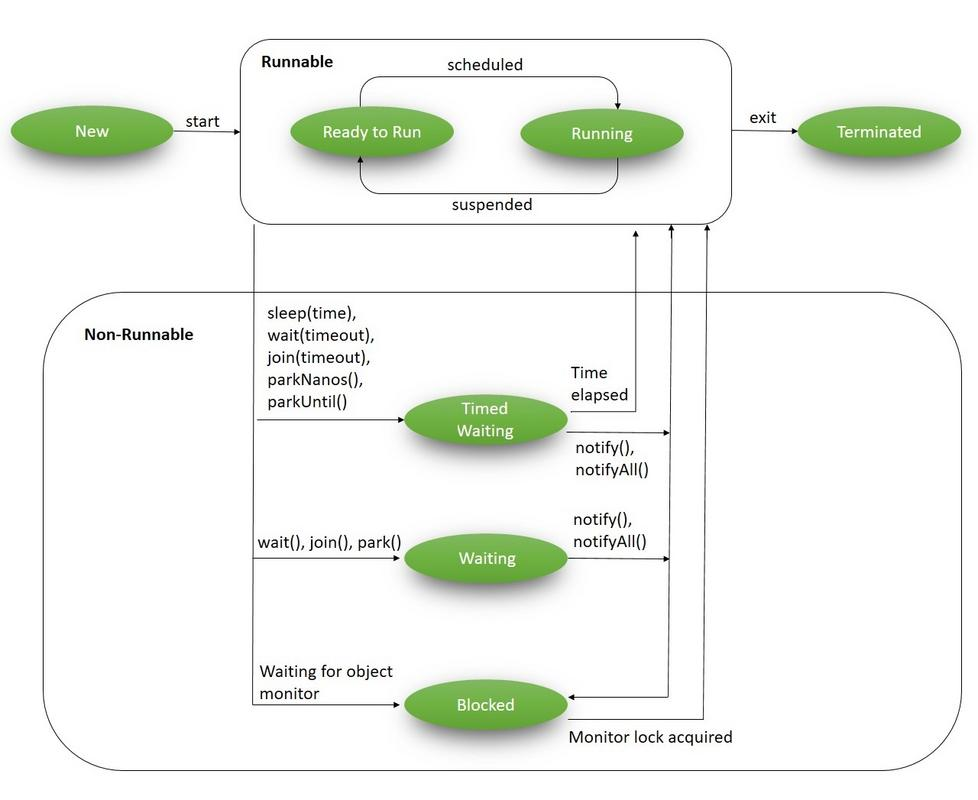
| 전이 상태 | 조건 및 메서드 |
|---|---|
| New → Runnable | 조건 : start() 메서드 호출start() : 메서드 호출 시 스레드가 Runnable 상태로 변함 |
| Runnable → Blocked | 다른 스레드가 해당 모니터 락 점유 시 동기화된 메서드 또는 블록에 진입 시 자동 발생 |
| Runnable → Waiting | 조건 : 스레드가 무기한 대기해야 할 때 Object.wait() : 스레드가 특정 객체 모니터 락을 해제하고 다른 스레드의 신호 대기 Thread.join() : 특정 스레드가 종료될 때 까지 대기LockSupport.park() : 스레드가 외부의 신호를 받을 때 까지 대기 |
| Runnable → Timed_waiting | 조건 : 스레드가 일정 시간 동안 대기해야 할 때Thread.sleep(long millis) : 지정된 시간 동안 일시 중단Object.wait(long timeout) : 특정 객체의 모니터 락 해제 후 주어진 시간 동안 대기Thread.join(long millis) : 주어진 시간 동안 다른 스레드가 종료될 때 까지 대기LockSupport.parkNanos(long nanos) / parkUntil(long deadline) : 주어진 시간 또는 시간 한계까지 스레드 중단 |
| Blocked → Runnable | 조건 : 스레드가 기다리던 모니터 락 흭득 시 락 점유 스레드 해제 시 자동으로 해당 모니터 락 흭득 |
| Waiting → Runnable | 조건 : 스레드가 기다리던 조건이 충족되거나 신호를 받으면Object.notify /notifyAll() : 대기 중인 스레드에 신호 보낸 후 다시 실행 가능하게LockSupport.unpark() : 대기 중인 스레드를 다시 실행 가능한 상태로 |
| Timed_waiting → Runnable | 조건 : 대기 시간 끝나면 자동으로 다시 실행 가능 상태로Thread.sleep() / wait() 에서 지정된 시간 끝나면 자동 전이 |
| Runnable → Terminated | 조건 : run() 메서드가 정상적으로 종료되거나 예외 발생으로 스레드가 실행 안될 때run() 종료 혹은 예외 발생 시 자동으로 Terminated 상태 |
c. 동작 원리
c-1) JVM에서의 멀티스레드 동작 원리
💡1 자바 애플리케이션 = 1 JVM = 여러 개의 스레드 실행 가능
즉, JVM이 프로세스의 단위라 할 수 있음
JVM 띄우는 데 필요한 메모리에 비해 스레드 사용이 훨씬 유리 ⇒ 스레드 사용
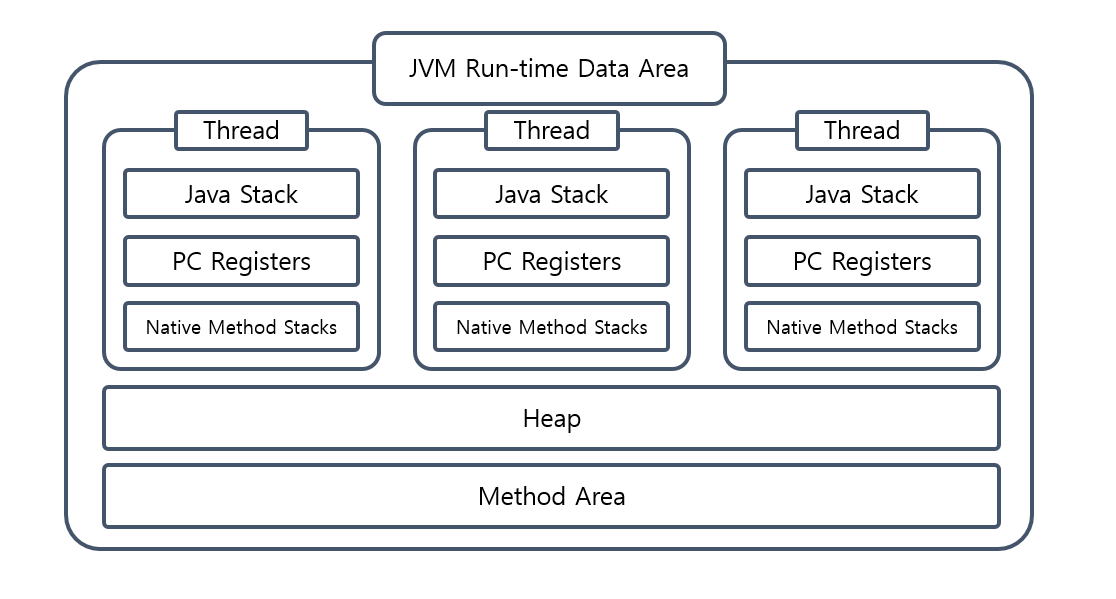
- 공통 영역 : 이 곳이 꼬이면 문제가 발생하기 때문에 동기화가 매우 중요!!
- Method 영역 : 클래스 정보, 정적 변수 등 JVM 프로세스가 시작될 때 데이터 할당
- Heap 영역 : 동적으로 데이터 할당, 레퍼런스 타입 객체 생성 시 실제 객체 올라가는 영역
- 독자적인 영역
- Stack Area
- 메서드 호출 시 호출된 메서드를 위한 frame 생성
- 메서드 scope 내에서 발생하는 지역변수, 매개변수, 리턴값 등을 frame에 저장
- 메서드 scope 종료 시 (return 시) frame에 할당된 변수 및 frame 반환
- 메서드 내에서 메서드 호출 시 호출된 메서드 frame이 바로 위에 생기며 실행 흐름이 해당 메서드로 넘어감
- PC Registers
- 해당 스레드에서의 명령 흐름 추적 및 관리
- 현재 수행중인 JVM 명령의 주소 저장
- 연산을 위해 필요한 피연산자를 임시 저장
- Native Method Stack
- 자바가 아닌 다른 언어를 JNI 를 통해 실행하기 위한 코드 공간
- Stack Area
c-2) 스레드의 스케줄링 및 운영체제와의 상호작용
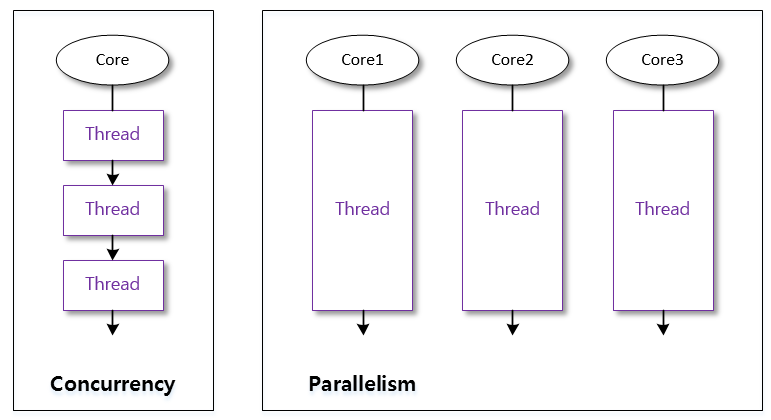
💡멀티스레드 = 동시성 or 병렬성으로 실행
- 동시성 : 멀티 태스킹을 위해 하나의 코어에서 멀티 스레드를 바꿔가며 실행하는 성질
- 병렬성 : 멀티 태스킹을 위해 멀티 코어에서 개별 스레드를 동시에 실행하는 성질
- 싱글 코어 CPU를 이용한 멀티 스레드 작업은 병렬 실행되는 것 같지만, 번갈아 실행되는 동시성 작업 ⇒ 빠르게 진행되기 때문에 병렬성으로 보임
- 우선순위, RR (Round-Robin) 등등…
- 우선순위 : 개발자가 코드로 제어 가능
- Round Robin : 개발자가 코드로 제어 불가능
- 시간 할당량을 정해서 하나의 스레드를 정해진 시간만큼 실행, 다시 다른 스레드 실행 ⇒ OS가 설정하기 때문에 개발자는 아무것도 못함
- 자바에서 생성된 Thread는 모두 5의 우선순위를 가짐
- main 함수 또한 우선순위가 5임
- 스레드의 우선순위 = 상속받는 스레드로부터 받음 (main이 기본이라 5)
- Thread에 할당할 수 있는 우선순위는 1~10으로 분류, 숫자가 작을수록 우선순위 낮음
getPriority(), setPriority(int p)메서드 이용해 우선순위 설정- !!!!!! 우선순위는 절대적으로 지켜지지 않음 !!!!!!! 그저 우선순위가 높은 스레드에게 상대적으로 많은 양의 실행시간이 주어짐
⇒ 왜? OS한테 힌트를 주는 것이기 때문에 모든 결정은 OS가 해줌
c-3) 스레드 풀과 JVM의 스레드 관리
💡JVM 생성보다는 스레드 생성이 가볍지만 스레드 생성이 과연 모든 요청마다 생성할 만큼 가벼운가? ⇒ 아님
그럼 어떻게 관리? ⇒ 스레드 풀 Thread Pool
- 웹 환경에서 고객의 요청이 들어올 때 마다 스레드를 생성하면 응답 속도 매우 낮아짐
- 스레드들이 Context Switching 할 때도 오버 헤드 발생
- Thread Pool : 스레드를 효과적으로 관리하고 재사용하는데 도움을 주는 객체
- 스레드 생성, 소멸 비용 감소
- 여러 작업 동시 실행 지원
- 스레드를 특정 개수 만들어 놓고 기존 스레드 재사용하는 방식
- WAS의 주요 튜닝 포인트 = 최대 스레드 수(max thread)
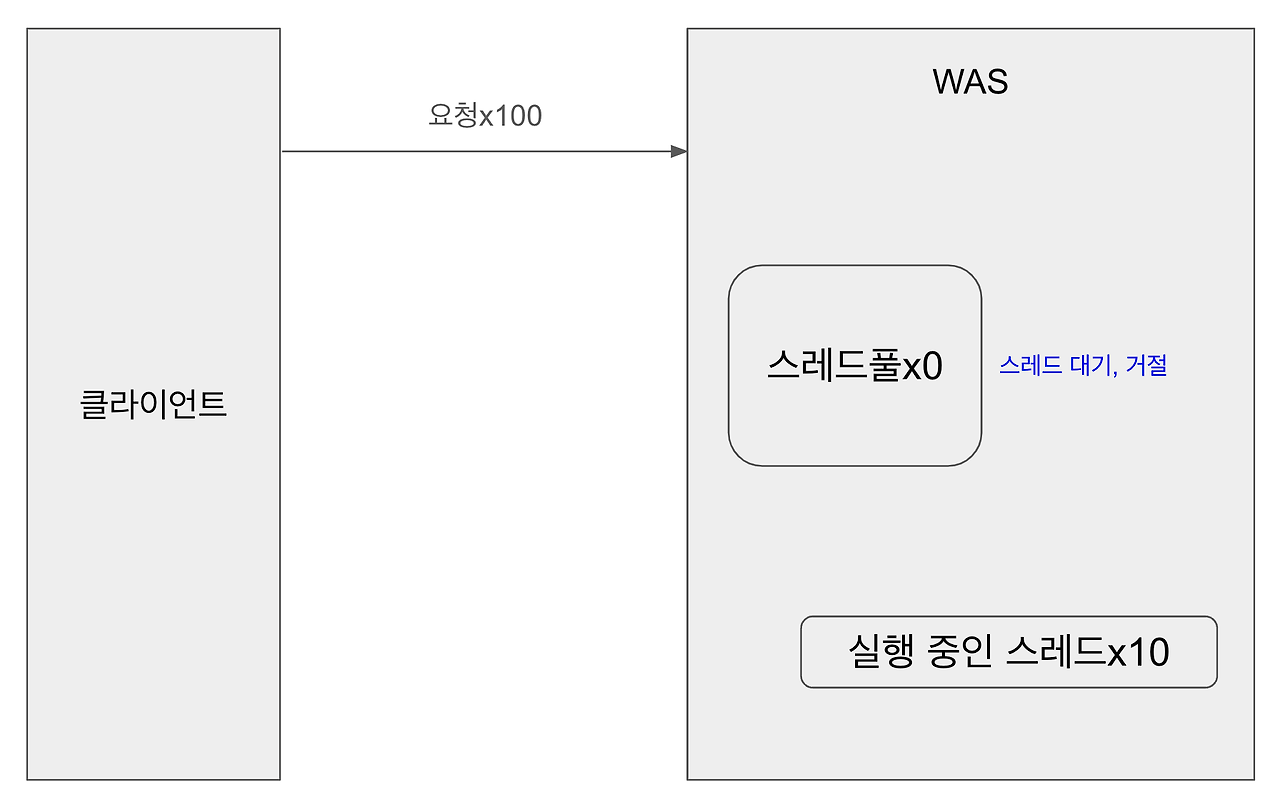
- 낮을 경우 : 동시 요청이 많은 경우 서버 리소스 여유, 클라이언트 응답 지연
- 높을 경우 : 동시 요청이 많은 경우 서버 리소스 임계점 초과로 서버 다운
- 장애 발생 : 클라우드 서버? 서버를 늘린 후 튜닝하기
- 기준이 정말 애매함. 그냥 적당한 값 (= CPU, 로직 복잡도, I/O 리소스 상황, 운영 중인 하드웨어 제원 등등 요인이 굉장히 많음)
- 구현 코드
Executors클래스 사용 : 스레드 개수 5로 제한
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
executor.submit(() -> {
// 실행할 작업
});
executor.shutdown();
c-4) 데몬 스레드와 비데몬 스레드
- 비데몬 스레드 (사용자 스레드)
- 주요 작업을 수행하는 스레드 (일반 스레드란 의미)
- JVM이 종료되기 전에 모든 비데몬 스레드는 종료되어야 함
- 데몬 스레드 (백그라운드 작업)
-
JVM 종료 시 자동으로 종료
-
보조 작업에 사용됨
-
사용법
setDaemon(boolean tf)Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() { //구현 } thread.setDaemon(true); // 데몬 스레드 설정
-
3. 동기화
a. 동기화의 필요성 및 문제점
- 특정 메모리 공간을 공유하기 때문에 메모리에 올라간 객체, 변수 등등 변화 발생 시 갱신을 알려줘야함
- 스레드 A가 객체 Obj 변경 ⇒ 스레드 B에서 Obj 변경 동기화 없이 사용 시 에러 발생
💡 이런 문제점을 어떻게 해결할까?
멀티 스레드 프로그램에서 단 하나의 스레드만 실행할 수 있는 코드영역
임계영역(critical section) + 잠금(lock)
➡️ 임계영역 : 공유 데이터 사용하는 코드 영역
➡️ 잠금(락, lock) : 공유 데이터(객체)가 가지고 있는 성질 (lcok을 흭득한 단 하나의 스레드만 코드 수행 가능)
➡️ 이 모든 과정 : 스레드의 동기화 Synchronized
b. 자바의 동기화 메커니즘
b-1) Synchronized
public synchronized void cal() {
// 연산 처리
...
}
synchronized(객체 참조변수) {
//...
}메서드에 synchronized 키워드 사용 시 메서드 전체가 임계 영역으로 설정됨
특정 코드만 임계 영역 설정 시 synchronized(객체 참조변수) 활용
⇒ synchronized 블록으로 이 영역에 들어가면 지정된 객체의 lock을 얻고 벗어나면 lock 반납하는 시스템
[뱅킹 시스템 예제]
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable r = new RunnableEx();
new Thread(r).start();
new Thread(r).start();
new Thread(r).start();
}
}
class Account {
private int balance = 1000;
public int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void withdraw(int money) {
if (balance >= money) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
balance -= money;
}
}
}
class RunnableEx implements Runnable {
Account acc = new Account();
public void run() {
while (acc.getBalance() > 0) {
// 100, 200, 300 중 임의의 한 값으로 출금(withdraw)
int money = (int) (Math.random() * 3 + 1) * 100;
acc.withdraw(money);
System.out.println("balance : " + acc.getBalance());
System.out.println("출금되었습니다.");
}
}
}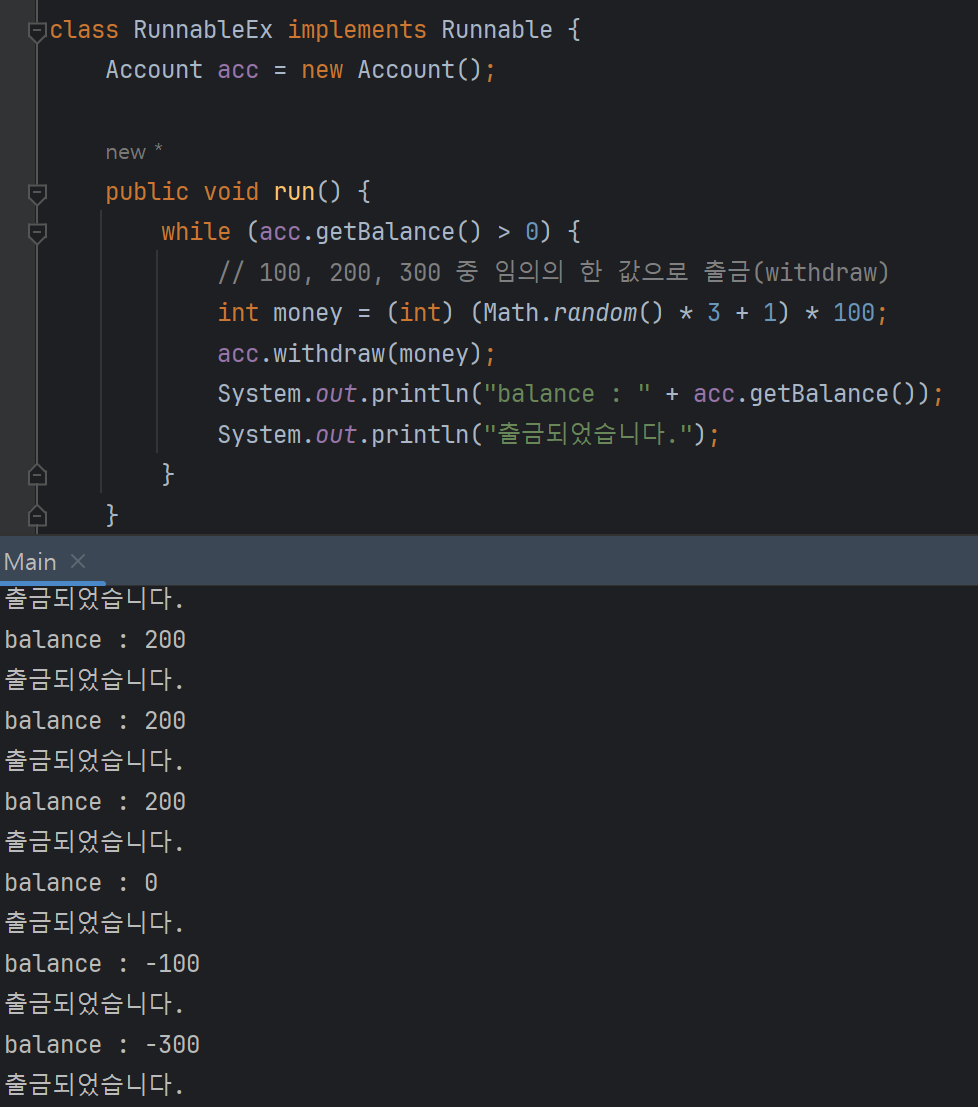
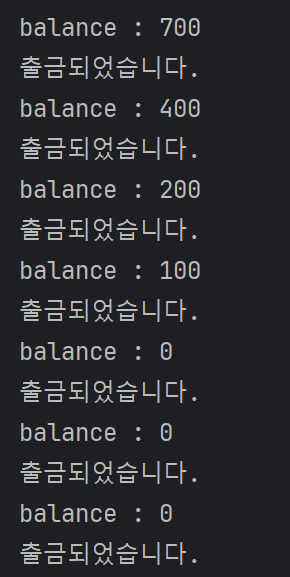
- 잔고 음수면 출금이 안되게 했는데 출금이 된다 ⇒ 은행 파산
- if문 돌면서 다른 스레드가 나타나서 출금함 ⇒ 싱크가 안맞음
class Account {
private int balance = 1000;
public int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public synchronized void withdraw(int money) {
if (balance >= money) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
balance -= money;
}
}
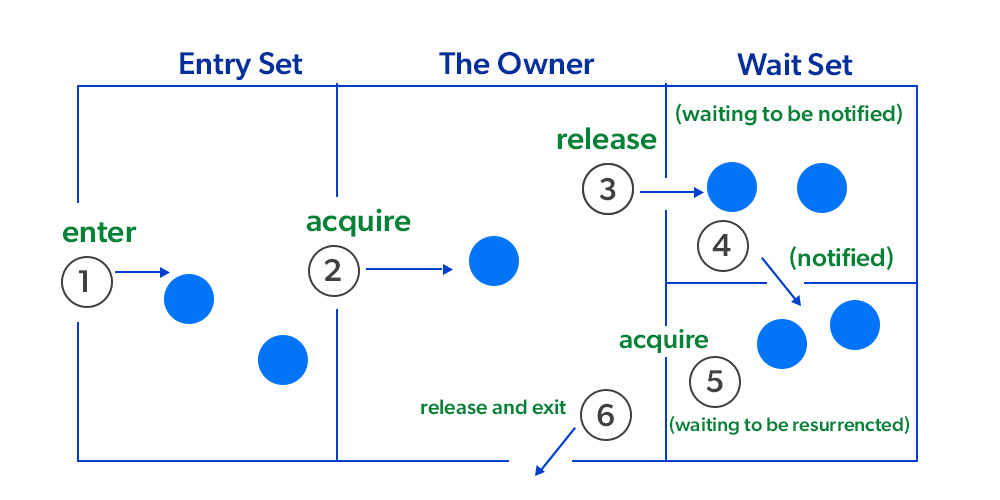
b-2) 객체 락과 모니터링 - wait(), notify()
Object객체에 구현되어 있는wait(),notify()wait(): Runnable 상태에서 Waiting 상태로 (lock 소유 ⇒ lock release)notify(): Waiting 상태에서 Runnable 상태로 ⇒ 스레드 중 임의로 선택(구현에 따라 다름)- wati() 와 notify() 흐름 예제 (Consumer-Producer)
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class ProducerConsumer {
// Shared queue used by both producer and consumer
private static final Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// Maximum capacity of the queue
private static final int CAPACITY = 10;
// Producer task
private static final Runnable producer = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (queue) {
// Wait if the queue is full
while (queue.size() == CAPACITY) {
try {
System.out.println("Queue is at max capacity");
queue.wait(); // Release the lock and wait
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// Add item to the queue
queue.add(10);
System.out.println("Added 10 to the queue");
queue.notifyAll(); // Notify all waiting consumers
try {
Thread.sleep(2000); // Simulate some delay in production
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
};
// Consumer task
private static final Runnable consumer = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (queue) {
// Wait if the queue is empty
while (queue.isEmpty()) {
try {
System.out.println("Queue is empty, waiting");
queue.wait(); // Release the lock and wait
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// Remove item from the queue
System.out.println("Removed " + queue.remove() + " from the queue");
queue.notifyAll(); // Notify all waiting producers
try {
Thread.sleep(2000); // Simulate some delay in consumption
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
};
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Main thread started");
// Create and start the producer thread
Thread producerThread = new Thread(producer, "Producer");
// Create and start the consumer thread
Thread consumerThread = new Thread(consumer, "Consumer");
producerThread.start();
consumerThread.start();
System.out.println("Main thread exiting");
}
}- 문제점
- Consumer가 계속 wait를 해도 notify 대상이 Consumer만 나오면 Producer는 lock을 흭득하지 못함
- Starvation (기아 현상)
- 어떻게 해결하나요? ⇒ notifyAll() : 모두를 깨워버리자!
- 여러 쓰레드가 lock을 얻으려고 노력
- Race Condition (경쟁 상태)
➡️ [java.util.concurrent 패키지를 사용해 문제점 해결]
c. Volatile vs Synchronized vs Atomic
- Synchronized : 특정 메서드 또는 객체 동시성 해결 키워드
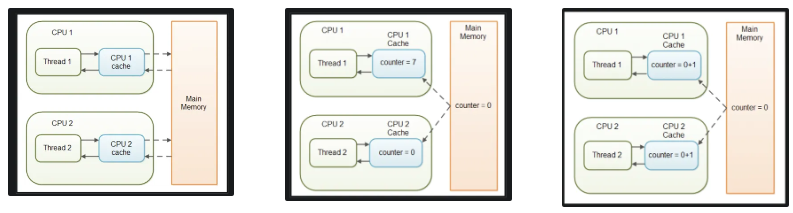
- volatile : 변수의 가시성 문제를 해결하기 위한 키워드
- Java 변수를 Caching 하지 않을 것이다.
- Main Memory에서만 가져다 쓰겠다
- 여러 스레드에서 동시에 접근 가능해서 멀티 스레드에선… (원자성 보장 X)
- Atomic : volatile의 원자성 보장 X 문제 해결
- 동기화 / 락 안함 ⇒ CAS(Compare-And-Swap) 알고리즘 채택
- 스레드가 공유 변수값 read
- 가져온 값을 새로운 값으로 연산
- 공유 변수의 현재 값이 이전에 읽은 값과 같은지 비교
- 현재 값이 이전 읽었던 값과 같으면 새로운 값, 아니면 다시 받아서 연산
- 완벽한 동시성 해결일까?
- 절대 아님.
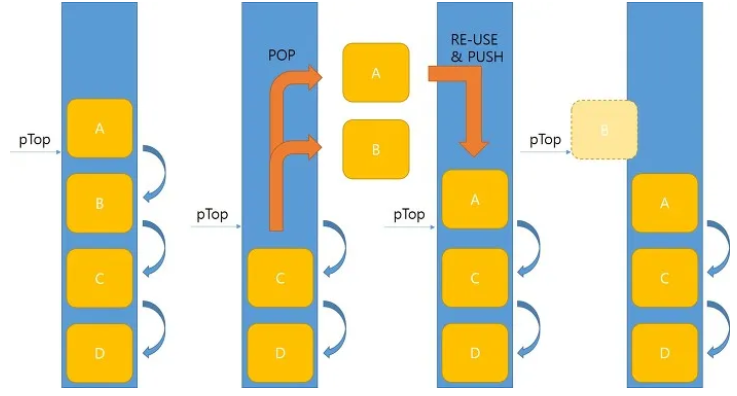
- ex) 스레드 1에서 Atomic 변수 값을 읽은 상태
1. 스레드 2가 같은 변수의 값을 변경 후 원래 값으로 되돌림
2. 스레드 1이 변수 값을 다시 읽음 (같다고 판단)
3. 중간에 값이 변경됐다가 다시 돌아온 것이라 다름
3-1. ABA 문제 : 스택이나 큐에서 pop() 연산 등에서 발생
4. 데이터 무결성, ABA로 인한 데드락 등의 문제가 있음-
AtomicStampedReference,AtomicMarkableReference등 사용 가능하지만 ABA 문제만 해결 가능 (참조 주소값 + 연산 횟수 확인으로 중간에 값이 변경됐는지까지 확인)CAS(&s->top, top, new_top) && CAS(&->pop_count, pop_count, pop_count+1)➡️ 어떤 자료구조를 사용해야 이런 일이 없을지까지 고려해야한다.
-
d. Deadlock, Livelock
- DeadLock : 둘 이상 작업이 서로 작업이 끝나기를 기다리고 있어서 아무것도 못하는 상태
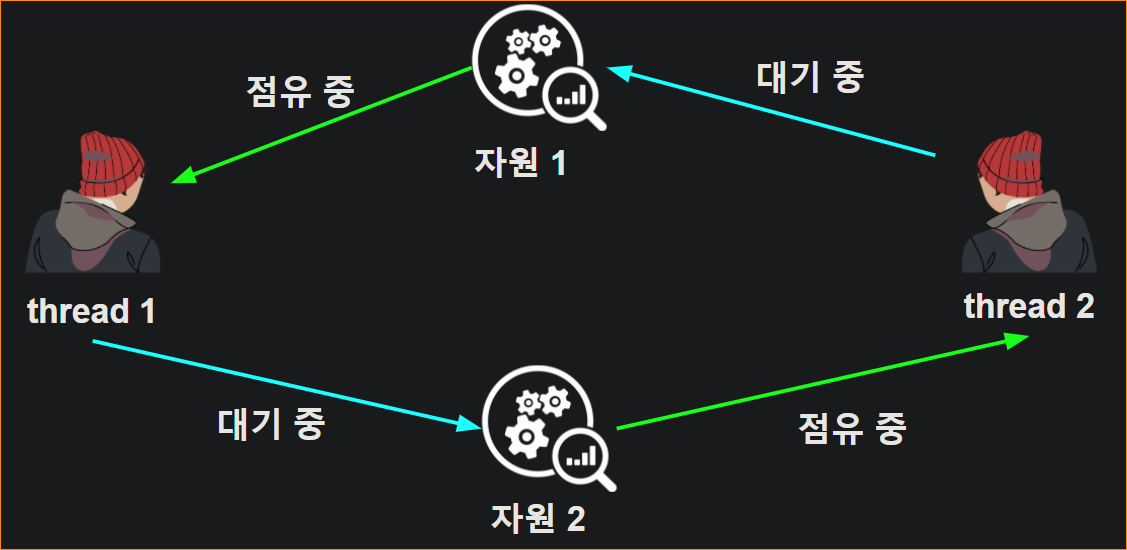

- 위 4가지 조건 모두 만족해야 데드락 상태, 예방 방법도 넷 중 하나만 해결해서 해결
- 회피 : 자원 요청 방식에 추가 정보 제공 → circular wait 발생 회피
- 자원 할당 그래프 알고리즘
- 은행원 알고리즘
- 회피 : 자원 요청 방식에 추가 정보 제공 → circular wait 발생 회피
- 무시 : 별로 상관 없으면 그냥 무시하는 것도 방법!
[Oracle이 준 Deadlock 예제]
public class Deadlock {
static class Friend {
private final String name;
public Friend(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public synchronized void bow(Friend bower) {
System.out.format("%s: %s"
+ " has bowed to me!%n",
this.name, bower.getName());
bower.bowBack(this);
}
public synchronized void bowBack(Friend bower) {
System.out.format("%s: %s"
+ " has bowed back to me!%n",
this.name, bower.getName());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Friend alphonse =
new Friend("Alphonse");
final Friend gaston =
new Friend("Gaston");
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() { alphonse.bow(gaston); }
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() { gaston.bow(alphonse); }
}).start();
}
}- LiveLock : 두 스레드가 서로 양보하려다가 작업이 안되는 상황
- 각 스레드가 실패한 작업 동시 재시도할 시 발생 (양보 상황)
- 각 스레드가 실패한 행동 재시도하는 시간을 무작위로하면 회피 가능
- 흔하지 않지만 멀티 스레드 설계에 있어 아주 어려움
➡️ 어떻게 해결하나요? ⇒ 스레드 풀 Thread Pool 사용
e. Appendix: java.util.concurrent
💡 멀티 스레드 동시성 해결을 위해 유용하게 사용되는 패키지
- Locks : 상호 배제를 사용할 수 있는 클래스 제공
- Atomic : 동기화가 되어 있는 변수 제공
- Executors : 스레드 풀 생성, 스레드 생명 주기 관리, Task 등록 및 실행 처리
- Synchronizers : 특수 목적의 동기화를 처리하는 5개 클래스
| 이름 | 기능 | Class |
|---|---|---|
| Locks | Synchronized를 더 정교하고 명시적으로 사용하기 위함, fairness 제공 | ReentrantLock, ReadWriteLock |
| Aotmic | Atomic을 위해 제공. CAS 알고리즘 사용 | AtomicInteger, AtomicReference |
| Executors | 스레드 풀 사용을 위한 클래스 | Executor 인터페이스 |
| Synchronizers | 스레드 간의 협력을 쉽게 구현하기 위한 도구 | CountDownLatch: 스레드가 조건 만족할 떄까지 기다리거나 특정 수의 작업이 완료될 때까지 기다림 CyclicBarrier:일정 수의 스레드가 모두 모일 때까지 기다렸다가 모이면 동시에 실행Semaphore :일정 수의 스레드만 임계 구역 진입 가능 |
4. 스레드 로컬 ThreadLocal
a. ThreadLocal 클래스의 개념
💡자바에서 지원하는 Thread Safe한 기술로 각각의 스레드 별로 별도의 저장공간을 제공하는 컨테이너
- ThreadLocal이 활용되는 환경은 해당 컨테이너를 가진 서비스가 싱글톤 객체로 공유되는 객체
- 즉, 모든 스레드는 동일한 ThreadLocal에 접근함
- 필요한 이유
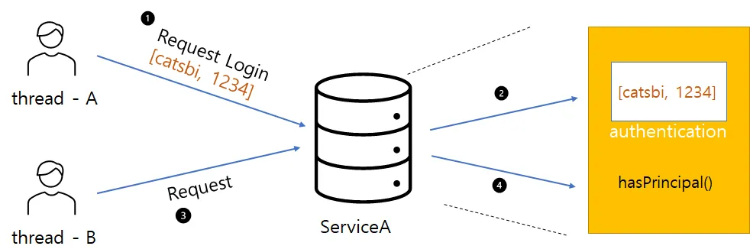
public class ServiceA {
//사용자 인증 정보
private Authentication authentication;
private UserRepository userRepository;
private final ServiceA instance = new ServiceA();
public static ServiceA getInstance(){
return instance;
}
public boolean login(LoginForm form) {
User user = userRepository.findById(form.getId()).orElseThrow(NoSuchException::new);
if(PasswordEncoder.matches(user.getPassword(), form.getPassword())){
authentication = Authentication.of(form.getId(), form.getPassword, ...);
}
}
public boolean hasPrincipal(){
return !authentication == null;
}
}- 스레드 A에서 로그인 요청하며 로그인 정보 전달
- 서비스 A는 로그인 정보 비교 후 인증 정보 저장
- 스레드 B에서 자원 접근 요청
- 서비스 A는 hasPrincipal() 메서드를 통해 인증 정보 존재 확인
- 스레드 A를 통해 저장된 인증정보가 있어 스레드 B의 요청인 자원 접근 허가
- 싱글톤 객체이기 때문에 내부 자원들도 모두 공유됨 ⇒ 모든 스레드 공유 가능
- 심지어 정보 변경도 가능(접근 가능하니)하기 때문에 ThreadLocal 필요
b. 스레드별 데이터 격리
- 그럼 어떻게 작동하나요 ⇒ Thread + ThreadLocal
[Thread]
public class Thread implements Runnable {
//...logics
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
}[ThreadLocal]
public class ThreadLocal<T> {
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}
static class ThreadLocalMap {
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
}
}Thread에서 객체를threadLocals라는 인스턴스 변수를 가지고 있음ThreadLocal에서ThreadLocalMap클래스를 이용해 key/value 로 보관- get, set을 현재 수행중인
Thread를currentThread()를 통해 리턴 ⇒ 현재 사용 중인 스레드만 사용 가능을 보장
c. 어디에 사용?
- Spring Security
package org.springframework.security.core.context;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
final class ThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy implements SecurityContextHolderStrategy {
private static final ThreadLocal<SecurityContext> contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<>();
@Override
public void clearContext() {
contextHolder.remove();
}
@Override
public SecurityContext getContext() {
SecurityContext ctx = contextHolder.get();
if (ctx == null) {
ctx = createEmptyContext();
contextHolder.set(ctx);
}
return ctx;
}
@Override
public void setContext(SecurityContext context) {
Assert.notNull(context, "Only non-null SecurityContext instances are permitted");
contextHolder.set(context);
}
@Override
public SecurityContext createEmptyContext() {
return new SecurityContextImpl();
}
}- SecurityContextHolder의 SecurityContext 안에 Authentication 보관
- 기본 전략 : MODE_THREADLOCAL = 스레드 로컬 사용해서 보관
- 기본 전략 : MODE_THREADLOCAL = 스레드 로컬 사용해서 보관
RequestContextHolder- HttpServletRequest 를 조회할 수 있는 RequestContextHolder에서도 요청 정보를 ThreadLocal을 이용해 관리
public abstract class RequestContextHolder {
...
private static final ThreadLocal<RequestAttributes> requestAttributesHolder = new NamedThreadLocal("Request attributes");
private static final ThreadLocal<RequestAttributes> inheritableRequestAttributesHolder = new NamedInheritableThreadLocal("Request context");
...
public static void resetRequestAttributes() {
requestAttributesHolder.remove();
inheritableRequestAttributesHolder.remove();
}
}마무리

대략 정신이 멍해지는 내용인데 끝까지 읽어주셔서 감사합니다 👍
다음 주 부터는 새로운 프로젝트와 관련된 글과 함께 돌아올게요
Reference
volatile, synchronized, atomic
Concurrent
Atomic, CAS
DeadLock, LiveLock
전반적인 지식
전반적인 지식2
스레드풀