주로 코랩에서 확인을 할 것 같지만
윈도우 파이썬 설치하기
파이썬 공식 홈페이지의 다운로드 페이지
1) 다운로드할 버젼 다운로드
2) 인스톨러 실행
3) 설치 완료 후
을 실행해도 되고 cmd에서 python을 선택해도 된다
JupyterLab
1) pip를 이용해 주피터랩 설치
pip install jupyterlab
2) 설치가 정상적으로 완료되었다면
jupyter lab
위 명령어 실행시 주피터 랩 서버가 실행된다. 종료하려면 랩이 실행중인 브라우저를 닫고, 실행중인 콘솔에서 Ctrl+c를 누른다.
math 사용해서 그래프 그려보기
import math
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 0부터 2파이까지 100개 숫자
x = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 100)
# x값을 sin으로
y = np.sin(x)
# x값을 cos으로
z = np.cos(x)
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.plot(x,z)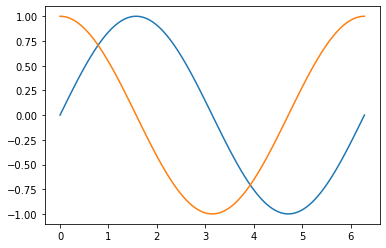
문자열 공백 제거 : strip()
a = " good "
a.strip() #good
a.rstrip() # good
a.lstrip() #good 리스트 vs 튜플
초기값을 변경할 수 없는 것이 튜플
문제 풀기
코딩도장(연습문제)
1)
a = list(range(5, -10, -2))
print(a)
> 결과
[5, 3, 1, -1, -3, -5, -7, -9]
2)
year = [2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018]
population = [10249679, 10195318, 10143645, 10103233, 10022181, 9930616, 9857426, 9838892]
print(year[5:])
print(population[5:])
# 문제가 최근 3년 = 끝에서 부터 값 3개이니
print(year[-3:])
print(population[-3:])
> 결과
[2016, 2017, 2018]
[9930616, 9857426, 9838892]
[2016, 2017, 2018]
[9930616, 9857426, 9838892]
3)
n = -32, 75, 97, -10, 9, 32, 4, -15, 0, 76, 14, 2
print(n[1::2])
> 결과
(75, -10, 32, -15, 76, 2)
4)
camille = {
'health': 575.6,
'health_regen': 1.7,
'mana': 338.8,
'mana_regen': 1.63,
'melee': 125,
'attack_damage': 60,
'attack_speed': 0.625,
'armor': 26,
'magic_resistance': 32.1,
'movement_speed': 340
}
print(camille['health'])
print(camille['movement_speed'])
> 결과
575.6
340
5)
written_test = 75
coding_test = True
if written_test >= 80 and coding_test == True :
print('합격')
else :
print('불합격')
> 결과
불합격
6)
x = int(input())
if 11 <= x <= 20 :
print('11~20')
elif 21 <= x <= 30 :
print('21~30')
else :
print('아무것도 해당하지 않음')
> 결과
5
아무것도 해당하지 않음
7)
# Unit. 16
for i in range(10):
print(i , "Hello world")
# 시부레 숫자와 문자는 +로 연결할 수 없는걸 왜 까먹었냐고
# 몇 번 돌렸는지 알고 싶으면 위처럼 , 로 구분해주란말이야 멍ㄹ청아
> 결과
0 Hello world
1 Hello world
2 Hello world
3 Hello world
4 Hello world
5 Hello world
6 Hello world
7 Hello world
8 Hello world
9 Hello world
8)
# 2 ~ 6 까지
for i in range(2, 6) :
print(i)
# 2 ~ 10 까지인데 2씩 증가
for i in range(2, 10, 2):
print(i)
> 결과
2
4
6
8
9)
cnt = int(input('반복할 횟수? : '))
for i in range(cnt) :
print(i+1, "번 반복중")
> 결과
반복할 횟수? : 5
1 번 반복중
2 번 반복중
3 번 반복중
4 번 반복중
5 번 반복중
10)
# 리스트의 요소에 10을 곱해서 출력하기
x = [49, -17, 25, 102, 8, 62, 21]
for i in range(len(x)):
print(x[i] * 10)
# 정답
for i in x:
print(i * 10, end=' ') #출력 후 다음줄로 넘어가지 않고 옆으로 연달아 나오게끔 함
> 결과
490
-170
250
1020
80
620
210
490 -170 250 1020 80 620 210
11)
# Unit 17
# 입력값을 받아 그 수 만큼 반복하는 방법은 두가지
# 1. 입력받은 수 만큼 i를 +1 시켜주기
cnt = int(input('반복할 횟수 입력 : '))
i = 0
while i < cnt :
print(i, end=" ")
i+= 1
print()
# 2. 입력받은 수를 0이 될때까지 감소시키기
cnt = int(input('반복할 횟 수 입력'))
while cnt > 0 :
print(cnt, end = " ")
cnt -= 1
> 결과
반복할 횟수 입력 : 5
0 1 2 3 4
반복할 횟 수 입력5
5 4 3 2 1
12)
# 연습문제 : 3으로 끝나는 숫자만 출력하기
i = 0
while True :
if i%10 != 3:
i += 1
continue
if i > 73 :
break
print(i, end=' ')
i += 1
> 결과
3 13 23 33 43 53 63 73
13)
# 연습문제 : 역삼각형 모양으로 별 출력하기
for i in range(5) :
for j in range(5) :
if j >= i :
print("*", end = " ")
print()
> 결과
* * * * *
* * * *
* * *
* *
*
14)
# 연습문제 : 산 모양으로 출력하기
for i in range(10) :
for j in reversed(range(10)) :
if j < i :
print(i, end=" ")
elif j > i :
print(" ", end="")
print()
> 결과
1
2 2
3 3 3
4 4 4 4
5 5 5 5 5
6 6 6 6 6 6
7 7 7 7 7 7 7
8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8
9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9
15)
# FizzBuzz 문제
# 1) 1 - 100 까지 출력
# i = 0
# while i <= 100 :
# print(i)
# i += 1
# 2) 3의 배수는 Fizz 출력
# i = 1
# while i <= 100 :
# if i % 3 == 0 :
# print("Fizz")
# else :
# print(i)
# i += 1
# 3) 5의 배수는 Buzz 출력
# i = 1
# while i <= 100 :
# if i % 3 == 0 :
# print("Fizz")
# elif i % 5 == 0:
# print("Buzz")
# else :
# print(i)
# i += 1
# 4) 3과 5의 배수는 FizzBuzz출력
# i = 1
# while i <= 100 :
# if i%3 == 0 and i%5 == 0:
# print("FizzBuzz")
# elif i % 3 == 0 :
# print("Fizz")
# elif i % 5 == 0:
# print("Buzz")
# else :
# print(i)
# i += 1
# 5) 코드 단축하기
for i in range(1, 101) :
print('Fizz' * (i%3 == 0) + 'Buzz' * (i%5 == 0))
16)
# 연습문제 : 2와 11의 배수, 공배수 처리하기
for i in range(1, 101) :
if i%2 == 0 and i%11 == 0 :
print("FizzBuzz")
elif i%2 == 0 :
print("Fizz")
elif i%11 == 0 :
print("Buzz")
else :
print(i)로또 번호 출력하기
import random
# 로또 번호 출력하기
cnt = int(input("몇 장 구매하시나요?"))
while cnt > 0 :
sNum = ""
i = 1
while i < 7 :
a = random.randint(1, 45)
if i < 6 :
sNum += str(a) + ", "
i += 1
else :
sNum += str(a)
i += 1
print(sNum)
cnt -= 1
> 결과
몇 장 구매하시나요?3
45, 16, 20, 11, 45, 14
44, 16, 37, 44, 20, 9
3, 40, 5, 23, 45, 17백준
1)
# 백준 3003 : 킹 퀸 룩 비숍 나이트 폰
x = [1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 8]
# 예제 입력에는 , 이 없었는데 확인할때 자꾸 , 을 넣어버려서 그것도 걸려버렸다..
# y = list(map(int, input().replace(',', " ").split()))
y = list(map(int, input().split()))
for i in range(6):
print(x[i]-y[i], end=" ")
> 입력
2 1 3 0 4 2
> 출력
-1 0 -1 2 -2 6
2)
# 백준 25083 : 새싹
print(" ,r'\"7")
print("r`-_ ,' ,/")
print(" \\. \". L_r'")
print(" `~\\/")
print(" |")
print(" |")
> 출력
,r'"7
r`-_ ,' ,/
\. ". L_r'
`~\/
|
|
3)
# 백준 2525 : 오븐 시계
H, M = map(int, input().split())
t = int(input())
time_h = t // 60
time_M = t % 60
# print(time_h)
# print(time_M)
H += time_h
M += time_M
if M >= 60:
H += 1
M -= 60
if H >= 24:
H -= 24
print(str(H) + " " + str(M))
> 입력
17 40
80
> 출력
19 0
4)
# 백준 2480 : 주사위 세개
# 제출
a, b, c = map(int, input().split())
pay = 0
if a == b == c :
pay = 10000 + (a*1000)
elif a == b or a == c :
pay = 1000 + (a*100)
elif b == c :
pay = 1000 + (b*100)
elif a > b :
if a > c :
pay = a * 100
else :
pay = c * 100
elif a < b :
if c < b :
pay = b * 100
else :
pay = c * 100
else :
pay = c * 100
print(pay)
> 입력
6 2 5
> 출력
600
(위 코드를 간추려보자면)
# 간추리기
a, b, c = map(int, input().split())
if a == b == c:
print(10000+a*1000)
elif a == b:
print(1000+a*100)
elif a == c:
print(1000+a*100)
elif b == c:
print(1000+b*100)
else:
print(100 * max(a,b,c))
5)
# 백준 8393번 : 합
a = int(input())
sum = 0
for i in range(a+1) :
sum = sum + i
print(sum)
> 입력
3
> 출력
6
6)
# 백준 25304번 : 영수증
# 영수증에 적힌 총 금액 x
x = int(input().strip())
# 영수증에 적힌 구매한 물건의 종류 수
y = int(input().strip())
# 물건 총합 변수 초기화
total = 0
# 물건개수대로 입력 받아야
for i in range(y) :
# 리스트로 저장? - 하고 있을 필요가 없구나..!
# a : 금액 b : 갯수
a, b = map(int, input().split())
#print("a = " + str(a), "b = " + str( b))
total += a * b
# 처음에 적어준 가격과 total값이 일치하는가?
if total == x :
print("Yes")
else :
print("No")
> 입력
250000
4
20000 5
30000 2
10000 6
5000 8
> 출력
No
7)
# 백준 15552번 : 빠른 A+B
# Python 에서 input대신 sys.stdin.readline을 사용하면 조금 더 빠른 입력을 받을 수 있다.
# 단, 가장 끝의 개행문자까지 같이 입력받기 때문에 문자열을 저장하고 싶을 경우
# .rstrip()을 추가로 해주는 것이 좋다.
# 코랩에서 sys.stdin.readline 사용 안됨
# 추후 다시 해보기
8)
# 백준 11021번 : A+B - 7
# 테스트 케이스 개수 T
T = int(input())
for i in range(T) :
A, B = map(int, input().split())
print("Case #"+str(i+1)+":", A+B)
> 입력
1
2 3
> 출력
Case #1: 5
9)
# 백준 10871번 : X보다 작은 수
# 첫째줄에 수열 N과 기준 수 X가 주어진다
A, X = map(int, input().split())
N = list(map(int, input().split()))
z = ""
for i in range(A) :
if N[i] < X :
z += str(N[i]) + " "
print(z)
> 입력
10 5
1 10 4 9 2 3 8 5 7 6
> 출력
1 4 2 3
10)
# 백준 1110번 : 더하기 사이클
# 기준수 입력받기
N = int(input())
endNum = N
i = 0
#while True :
while i < 5 :
# 앞A 뒤B 자리 나누기
# // : 소수점 아래는 버리고 값만 먹기
A = N//10
B = N%10
# A와 B를 더하고 10으로 일의 자리를 C에 넣기
C = (A+B)%10
# 새로운 N은 BC
N = (B*10) + C
i += 1
if endNum == N :
break
print(i)
> 입력
26
> 출력
4