
대용량의 LLM 들은 big-tech 에서 너무나도 잘 뽑아내고 있다.
OpenSource 로 Qwen3, Gemma3 만 보더라도 거의 대부분 문제될 것이 없다.
현재 산업은 LLM/MLLM 위에 올라가 있으며, 어떻게 사용할 것인가에 대한 내용이 중요하다.
Gemma : https://huggingface.co/google
Qwen : https://huggingface.co/Qwen
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model_name = "Qwen/Qwen3-8B"
# load the tokenizer and the model
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype="auto",
device_map="auto"
)
# prepare the model input
prompt = "Give me a short introduction to large language model."
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True,
enable_thinking=True # Switches between thinking and non-thinking modes. Default is True.
)에서 보면, enable_thinking 이 true 로 하게 되면 추론 시에 사용자의 말의 의미 분석을 진행한다. 그리고 모델 자체가 내 의도 파악을 하고 생각을 한번 집고 넘어간다. ~이런 위험이 생기지 않을까 걱정하고 있는 듯 합니다. ~안정성을 테스트 하는 것이 중요합니다. 와 같이 답을 내기 전 기, 승, 전, 결 을 내고 시작을 하게 된다.
그래서 PEFT 와 Reasoning 모델을 좀 생각해보고 넘어가려 한다. 빠르게 구조만 파악하고, 이후에 MCP 계열을 개발해 볼 계정이다.
PEFT
사실 Transformer 계열 이기에 가능한 형태로 볼 수 있다.
- RoLA 를 잠시 살펴보자.
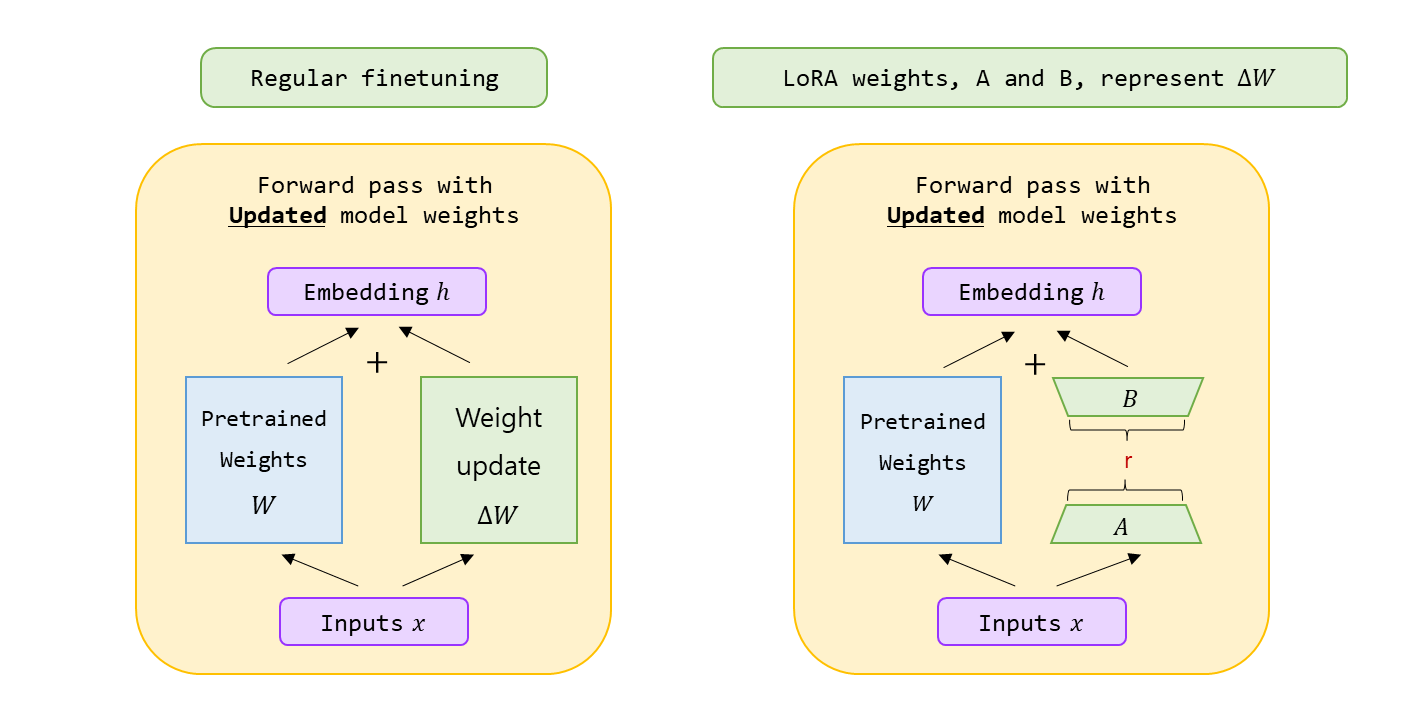
실제 식을 보면 가 기본이 된다.
W_0: PriorBA: New DATA 의 영향을 인코딩한 작은 변화량(W_0 + BA): Posterior
로 생각해 볼 수 있다.
다만, matrix 가 변형, 왜곡 으로 인한 분포가 변하는 것에 대한 문제가 존재한다.
- New DATA 를 지나치게 오랬동안 학습 후
BA는 새로운 작업에 과적응 ( Over-adaptation ) 을 하여 모델을 편향 시킨다.
- Prior 통제에 새로운 데이터가 압도적으로 강하면 Posterior 행동에서 Prior 를 누른다.
- LLM 과 같이 Robust 한 모델이 아닌, Light 한 모델 일 경우 더욱 흔들리기 좋다.
쉽게 말해서, 극단적인 예시로 보자면
으로 아주 살짝만 New data 를 더해서 지장이 없게 해야 하는데, 위와 같은 이유로 문제가 발생할 수 있다.
- Fine tuning 은 미묘한 작업이다.
- Over-training 에 대한
A,B의 weight 들이 과도하게 커진다. r이라는 rank 로 인한 자유도 제한의 문제도 있다.- 는 의 모든 가능한 변화를 표현할 수 없다.
r만큼의 rank 를 가진 변화만 가능하여 의존하게 된다.
- 어떤
layer를 건드릴 지에 따라서 흔들릴 가능성이 높다.
class LoRALayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_dim, out_dim, rank, alpha):
super().__init__()
std_dev = 1 / torch.sqrt(torch.tensor(rank).float())
self.A = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(in_dim, rank) * std_dev)
self.B = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(rank, out_dim))
self.alpha = alpha
def forward(self, x):
x = self.alpha * (x @ self.A @ self.B)
return xin_dim : LoRA 를 사용하여 수정하기를 원하는 layer 의 input 차원.
out_dim : 해당 layer 의 output 차원
class LinearWithLoRA(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, linear, rank, alpha):
super().__init__()
self.linear = linear
self.lora = LoRALayer(
linear.in_features, linear.out_features, rank, alpha
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.linear(x) + self.lora(x)기존에 개발한 Linear layer 와 합쳐서 LoRA 를 사용한다.
Reasoning model
위와 같은 이유로 더 나은 발전 방향으로 나온 모델 방법이다.
- 이러한 finetuning 의 미묘하고 까다로운 작업 대신,
- reward 를 통한 모델의 prior distribution 을 덜 손상시키는 기반의 방법으로 태어났다.
추론 모델 (Reasoning Model) 과 강화 학습 (RL) 이 연결 되어 모델과 티키타카, 즉 "상호작용" 하면서 시행착오를 하면서 어떤 행동에 대한 응답이 더 좋은 보상을 받는지 학습을 하게 된다.
- 위에서 봤듯이 finetuning 은 에 의해서 가 변형되거나 억제될 가능의 여기가 있다면
- 보상을 가지고 "Aha!" 를 위한 시행 착오를 겪어 유연하게 답을 찾아가므로 손상이 덜된다.
대신 Reward 설계가 빡새다.
1 + 1 = 2와 같은 문제의 reward 는 설계가 쉬우나,LLM 의 추론을 평가하는 reward model 구축은 매우 어렵다.- 따라서 소위 잘하는 LLM 을 두고 평가하는 방식으로 가져가는 방식을 취한다.
여기서 집고 넘어갈 부분이 있다. 현재 LLM 의 성능은 Language 뿐만 아니라 전 영역에서 너무 잘하고 있다. 이미지 분석, 번역, 영상 해석, 그리고 초기 random 성을 prompt 로 성격을 잡아서 여러 형태로 만들어 낼 수 있다. 다수의 LLM 으로 평가하고 말과 추론을 더 잘하며 hallucination 이 적은 방향으로 계속 진화 하고 있다.
- DeepSeek-R1-Zero 의 전용 Template.
SYSTEM_PROMPT = (
"A conversation between User and Assistant. The user asks a question, and the Assistant solves it. The assistant "
"first thinks about the reasoning process in the mind and then provides the user with the answer. The reasoning "
"process and answer are enclosed within <think> </think> and <answer> </answer> tags, respectively, i.e., "
"<think> reasoning process here </think><answer> answer here </answer>"
)
# Format into conversation
def make_conversation(example):
return {
"prompt": [
{"role": "system", "content": SYSTEM_PROMPT},
{"role": "user", "content": example["problem"]},
],
}
dataset = dataset.map(make_conversation)-
DeepSeek-R1-Zero 의 Accuracy rewards
accuracy reward model 은 응답이 알맞는지, 올바른지 평가를 한다.-
예를 들어서, deterministic 한 결과가 포함된 수학 문제의 경우, 모델은 지정된 형식 ( 예 : box 안에 ) 으로 최종 답을 제공해야 하므로, 믿을 수 있는 정확성의 rule-based 검증이 요구된다.
-
마찬가지로 LeetCode 문제의 경우, compiler 는 사전 정의된 테스트 사례를 기반으로 피드백을 생성하기 위해 사용할 수 있다.
-
def accuracy_reward(completions, solution, **kwargs):
"""Reward function that checks if the completion is the same as the ground truth."""
contents = [completion[0]["content"] for completion in completions]
rewards = []
for content, sol in zip(contents, solution):
gold_parsed = parse(sol,
extraction_mode="first_match",
extraction_config=[LatexExtractionConfig()]
)
if len(gold_parsed) != 0:
# We require the answer to be provided in correct latex (no malformed operators)
answer_parsed = parse(
content,
extraction_config=[
LatexExtractionConfig(
normalization_config=NormalizationConfig(
nits=False,
malformed_operators=False,
basic_latex=True,
equations=True,
boxed=True,
units=True,
),
# Ensures that boxed is tried first
boxed_match_priority=0,
try_extract_without_anchor=False,
)
],
extraction_mode="first_match",
)
# Reward 1 if the content is the same as the ground truth, 0 otherwise
reward = float(verify(answer_parsed, gold_parsed))
else:
# If the gold solution is not parseable, we reward 1 to skip this example
reward = 1.0
print("Failed to parse gold solution: ", sol)
rewards.append(reward)
return rewards- DeepSeek-R1-Zero 의 Format rewards
<think>와</think>tag 사이에 thinking process 를 배치하도록 모델에 강제하는 format reward model 을 사용.
def format_reward(completions, **kwargs):
"""Reward function that checks if the completion has a specific format."""
pattern = r"^<think>.*?</think><answer>.*?</answer>$"
completion_contents = [completion[0]["content"] for completion in completions]
matches = [re.match(pattern, content) for content in completion_contents]
return [1.0 if match else 0.0 for match in matches]-
일반적은 RL (강화학습) 에서는 actor-critic 방식이 많다. critic 은 value function 을 학습하여 actor 의 policy 의 개선을 돕는데 사용한다.
-
human feedback을 통해 학습된 reward model 이 복잡한 환경에서의 critic 역할을 대신하여 학습 과정을 단순화 한다.
-
reward model 없이 직접적으로 Rule-based 로 계산된 reward function 들이다. 따라서 리소스가 절약 되게 된다.
-
LLM + Rule-based function 이 lightweight critic model 을 대신한다.
Cold start problem
모델 초기에 어떤 행동이 보상을 받을지 전혀 알지 못하므로
- 아기가 처음 해매듯이 매우 비효율적으로 해매고, 수렴하는 데
- 엄청난 시간과 자원이 소모된다.
RL 의 Imitation Learning 이 생각나게 된다.
- 정답 label 이 있는 데이터로 학습하게 되는데 supervised learning 방식으로 훈련한다.
- expert demonstrations, 양질의 행동 데이터를 통해서 모방하도록 supervised learning 방식으로 훈련한다.
대신, 100 Billion 의 모델 크기라면,
- 그 크기의 모델 학습을 돌릴 resource 를 가지고 있어야 하고,
- 그 크기에 초기 데이터로 학습할 만한 고품질 pair 대규모의 데이터를 가지고 있어야 한다.
- 따라서
W_0가 준비되어 있고, Efficient Fine-Tuning 으로 한다. - 다만 위에서 말한 것처럼
EFT방식은 예민한 작업이므로, 조금 더 생각해서 Finetuning 후 작업을 진행하는 것이 좋다.
Conclusion
이와 같이 LLM 분야 와 더불어 Multi-Modal Large Language Model (MLLM) 도 계속 발전하고 있다. 점점 더 parameter 수는 작아지고 있고, gemma 3n 을 봐도 점점 더 edge device 의 활용도가 가속화 되고, 방향성이 확고화 되고 있음을 볼 수 있다.
