아이디어를 준 동료에게 감사 인사를 드립니다.
overview
DFL 코드를 보다가.. kernel (1,1) 짜리를 보게 되고, 예전 fastvit 에 기억으로 각 channel 간의 축소, 혹은 확대로 새로운 출력을 생성하는 것을 기억해냈다. 그런데..
class DFL(nn.Module):
"""
Integral module of Distribution Focal Loss (DFL).
Proposed in Generalized Focal Loss https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9792391
"""
def __init__(self, c1=16):
"""Initialize a convolutional layer with a given number of input channels."""
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(c1, 1, 1, bias=False).requires_grad_(False)
x = torch.arange(c1, dtype=torch.float)
self.conv.weight.data[:] = nn.Parameter(x.view(1, c1, 1, 1))
self.c1 = c1-
key code
nn.Conv2d(c1, 1, 1, bias=False).requires_grad_(False) -
kernel 로 이 이 되었을 때, channel reduction 시에
weighted sum이 되는가? -
질문은 어디서
sum이 되고, 어디서clip이 되는거야? 의 질문이 시작이 되었다.
이번 post 는 sum 이 어디서 어떻게 이루어 지는지 확인해보자.
where does the weighted sum occur?
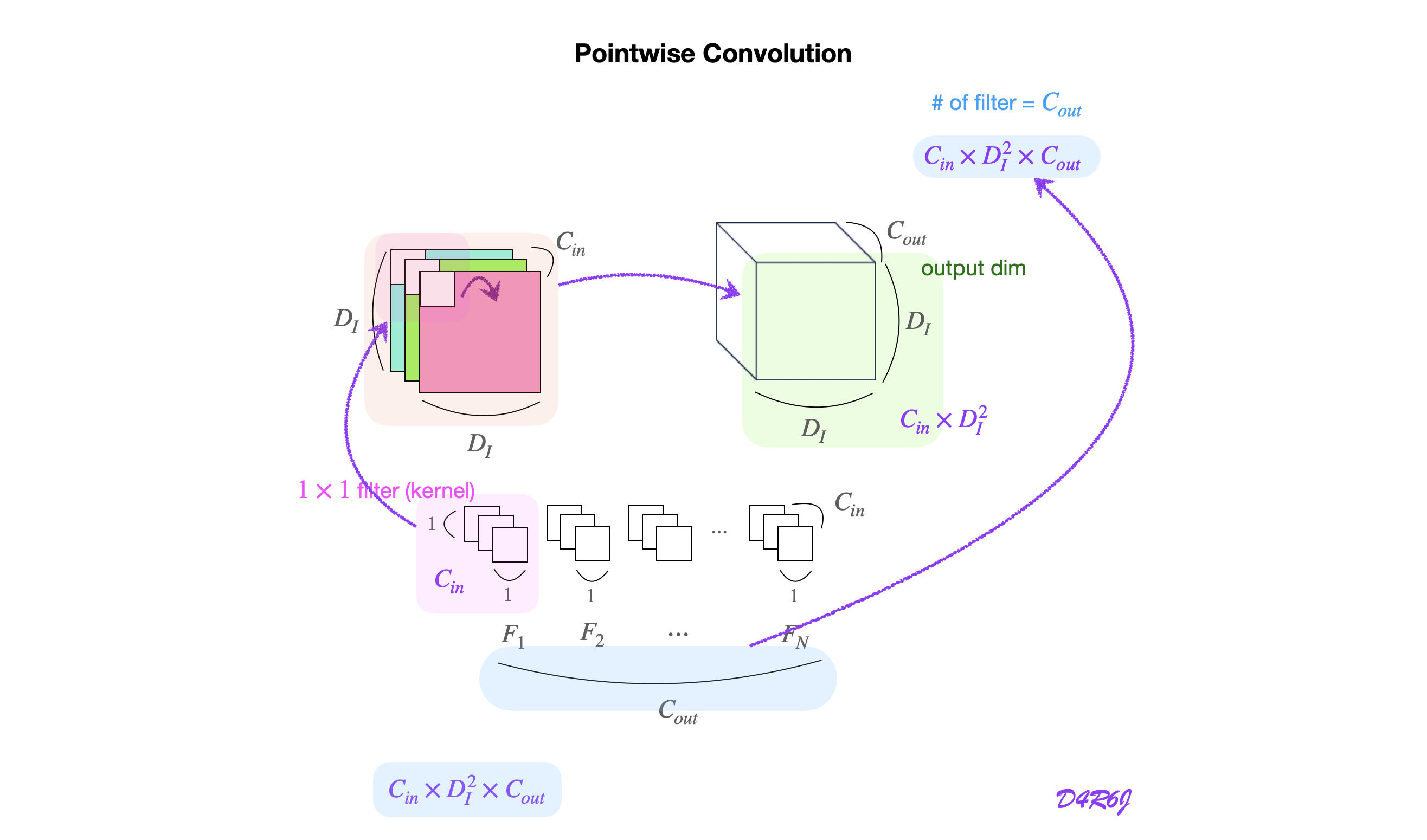
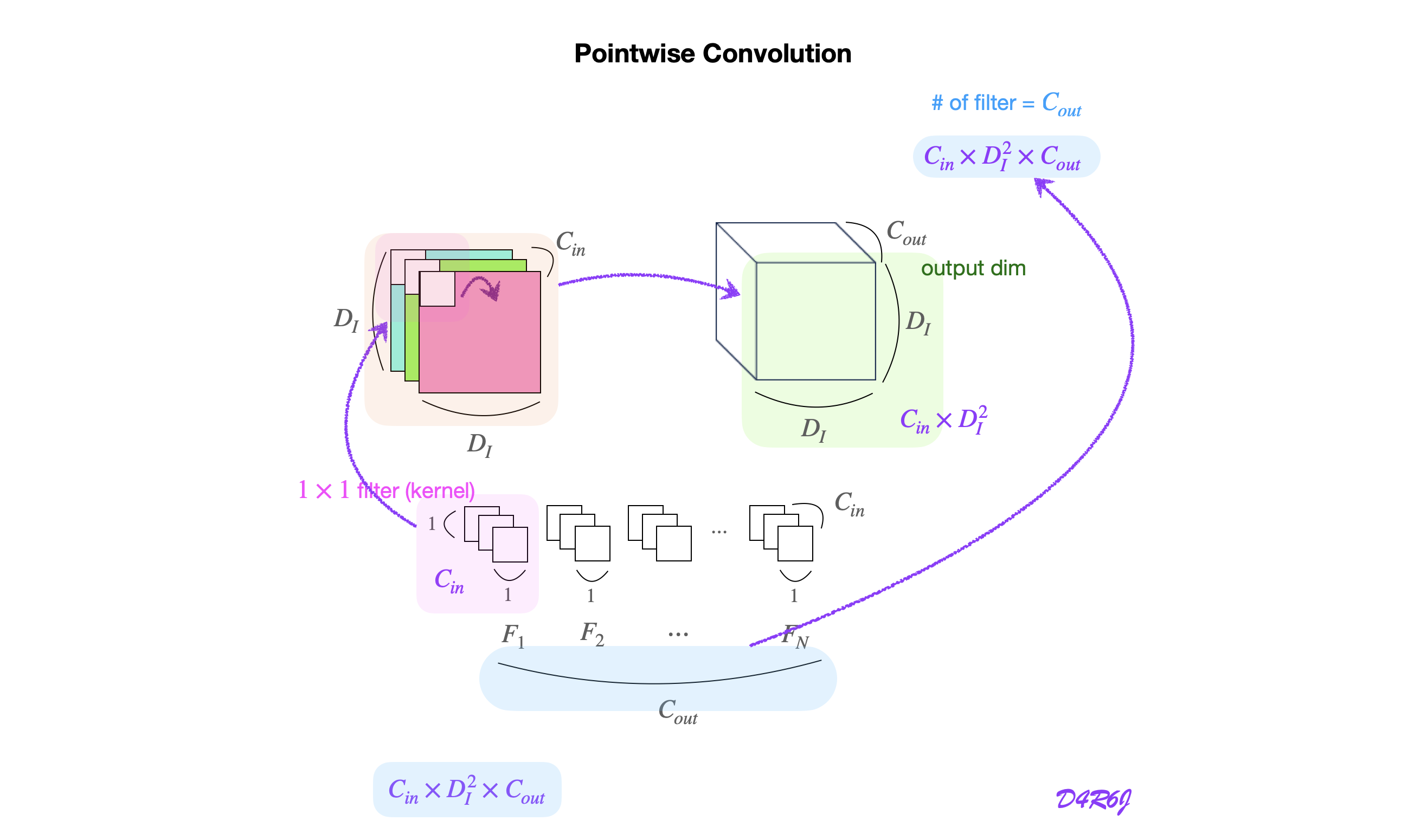
kernel (1,1) 인 합성곱 연산을 의미를 되짚어보자.
- feature map 의 각 위치에서 모든 channel 에 kernel 을 적용하여 새로운 출력을 생성하는 방법.
-
채널 결합
- Pointwise Conv 는 입력 데이터의 각 channel 을 독립적으로 처리
- channel 간의 결합을 통해 새로운 출력을 생성.
-
dimension reduction and expension
- 입력 데이터의 채널 수를 줄이거나 늘리는데 사용한다.
- input channel 256, kernel
(1,1)을 사용, output channel 64 개를 생성하면 reduction.
-
연산의 효율성
- 공간적인 정보는 변경하지 않고, 채널 간의 결합만을 수행하므로, 연산량이 적고 효율적.
full code
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
SEED_NUM = 3355
torch.manual_seed(SEED_NUM)
class SimplePointwiseCNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(SimplePointwiseCNN, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(
in_channels=3,
out_channels=1,
kernel_size=1,
bias=False
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
return x
# input data : batch size, # of channel, height, weidth
input_data = torch.ones(1, 3, 32, 64)
# create model
model = SimplePointwiseCNN()
# dimension of input data
print(input_data.shape)
# use model
output_data = model(input_data)
# dimension of output data
print(output_data.shape)SimplePointwiseCNN
Conv2d를 이용, in_channel3out_channel1- bias 는 일단
False로 설정하여 noise 를 없애고 테스트에 들어간다.
torch.ones
- 원하는 shape 으로 1 을 채운 tensor 를 구성한다.
- 테스트를 위해서, 값을 잘 판단하기 위해서 1 로 모두 초기화 한다.
explain functions
-
_conv_forwardfunctionclass Conv2d(_ConvNd): ... def _conv_forward(self, input: Tensor, weight: Tensor, bias: Optional[Tensor]): if self.padding_mode != 'zeros': return F.conv2d( F.pad(input, self._reversed_padding_repeated_twice, mode=self.padding_mode), weight, bias, self.stride, _pair(0), self.dilation, self.groups ) return F.conv2d(input, weight, bias, self.stride, self.padding, self.dilation, self.groups) def forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor: return self._conv_forward(input, self.weight, self.bias)conv2d 를 콜하는데..
-
SEED 를 고정해야
uniform_의 값의 randomness 제어.SEED_NUM = 3355 torch.manual_seed(SEED_NUM) tensor = torch.empty(3, 3) tensor.uniform_(0, 1) print(tensor)randomness 제어 확인..
tensor([[0.4735, 0.7487, 0.4722], [0.2841, 0.0332, 0.3359], [0.1788, 0.6278, 0.2463]])uniform_의 값을 보는 이유는 다음과 같다. -
reset_parametersfunction
Conv2d는_ConvNd를 상속 받고, 부모의__init__에서register_parameters를 사용,def reset_parameters(self) -> None: init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight, a=math.sqrt(5)) if self.bias is not None: fan_in, _ = init._calculate_fan_in_and_fan_out(self.weight) if fan_in != 0: bound = 1 / math.sqrt(fan_in) init.uniform_(self.bias, -bound, bound)-
self.weight이kaiming_uniform_을 사용하여 초기화를 한다. -
sqrt(5)를 사용하는 이유는 기존의uniform함수 초기화에서 kaiming 으로 변경했지만, 이전 버전을 보존하기 위해서 사용. -
이 tensor 는 로
uniform_을 사용. 여기서,
-
-
F.conv2dfunctionreturn F.conv2d(input, weight, bias, self.stride, self.padding, self.dilation, self.groups)-
input tensor

-
weight tensor
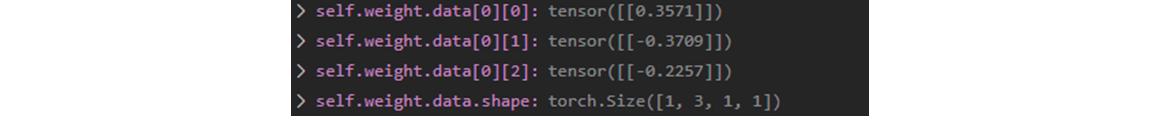
-
output tensor

소수점 을 round 쳤으면..수치가 대략 맞으면, 일단
weighted-sum이 맞다.
-
F.conv2d
-
pytorch/aten/src/ATen/functorch/BatchRulesDecompositions.cppm.impl("conv2d", native::conv2d_symint); -
pytorch/include/ATen/ops/convolution.h// aten::convolution(Tensor input, Tensor weight, Tensor? bias, SymInt[] stride, SymInt[] padding, SymInt[] dilation, bool transposed, SymInt[] output_padding, SymInt groups) -> Tensor inline at::Tensor convolution_symint(const at::Tensor & input, const at::Tensor & weight, const c10::optional<at::Tensor> & bias, c10::SymIntArrayRef stride, c10::SymIntArrayRef padding, c10::SymIntArrayRef dilation, bool transposed, c10::SymIntArrayRef output_padding, c10::SymInt groups) { return at::_ops::convolution::call(input, weight, bias, stride, padding, dilation, transposed, output_padding, groups); }역시
input,weight을 const reference 로 받네.. 바뀌지 않아야 하니.. -
pytorch/include/ATen/ops/convolution_ops.hstruct TORCH_API convolution { using schema = at::Tensor (const at::Tensor &, const at::Tensor &, const c10::optional<at::Tensor> &, c10::SymIntArrayRef, c10::SymIntArrayRef, c10::SymIntArrayRef, bool, c10::SymIntArrayRef, c10::SymInt); using ptr_schema = schema*; // See Note [static constexpr char* members for windows NVCC] STATIC_CONSTEXPR_STR_INL_EXCEPT_WIN_CUDA(name, "aten::convolution") STATIC_CONSTEXPR_STR_INL_EXCEPT_WIN_CUDA(overload_name, "") STATIC_CONSTEXPR_STR_INL_EXCEPT_WIN_CUDA(schema_str, "convolution(Tensor input, Tensor weight, Tensor? bias, SymInt[] stride, SymInt[] padding, SymInt[] dilation, bool transposed, SymInt[] output_padding, SymInt groups) -> Tensor") static at::Tensor call(const at::Tensor & input, const at::Tensor & weight, const c10::optional<at::Tensor> & bias, c10::SymIntArrayRef stride, c10::SymIntArrayRef padding, c10::SymIntArrayRef dilation, bool transposed, c10::SymIntArrayRef output_padding, c10::SymInt groups); static at::Tensor redispatch(c10::DispatchKeySet dispatchKeySet, const at::Tensor & input, const at::Tensor & weight, const c10::optional<at::Tensor> & bias, c10::SymIntArrayRef stride, c10::SymIntArrayRef padding, c10::SymIntArrayRef dilation, bool transposed, c10::SymIntArrayRef output_padding, c10::SymInt groups); }; -
pytorch/aten/src/ATen/native/Convolution.cppat::Tensor convolution( const Tensor& input, const Tensor& weight, const std::optional<Tensor>& bias_opt, IntArrayRef stride, IntArrayRef padding, IntArrayRef dilation, bool transposed, IntArrayRef output_padding, int64_t groups) { // See [Note: hacky wrapper removal for optional tensor] c10::MaybeOwned<Tensor> bias_maybe_owned = at::borrow_from_optional_tensor(bias_opt); const Tensor& bias = *bias_maybe_owned; auto& ctx = at::globalContext(); // See Note [Enabling Deterministic Operations] bool deterministic = ctx.deterministicCuDNN() || ctx.deterministicAlgorithms(); return at::_convolution(input, weight, bias, stride, padding, dilation, transposed, output_padding, groups, ctx.benchmarkCuDNN(), deterministic, ctx.userEnabledCuDNN(), ctx.allowTF32CuDNN()); } -
pytorch/aten/src/ATen/native/cudnn/ConvShared.cppTensor cudnn_convolution( const Tensor& input_t, const Tensor& weight_t, IntArrayRef padding, IntArrayRef stride, IntArrayRef dilation, int64_t groups, bool benchmark, bool deterministic, bool allow_tf32) { TensorArg input{input_t, "input", 1}, weight{weight_t, "weight", 2}; CheckedFrom c = "cudnn_convolution"; auto memory_format = cudnn_conv_suggest_memory_format(input_t, weight_t); Tensor output_t = at::detail::empty_cuda( conv_output_size( input_t.sizes(), weight_t.sizes(), padding, stride, dilation), input->options().memory_format(memory_format)); // ...여기서
output을 cuda memory 로 만들어서 받네. cudnn 까지 봐야 할듯 ㅋ -
pytorch/aten/src/ATen/native/cudnn/Conv_v7.cppvoid raw_cudnn_convolution_forward_out_32bit( const Tensor& output, const Tensor& input, const Tensor& weight, IntArrayRef padding, IntArrayRef stride, IntArrayRef dilation, int64_t groups, bool benchmark, bool deterministic, bool allow_tf32) { auto dataType = getCudnnDataType(input); ... AlgoIterator<cudnnConvolutionFwdAlgoPerf_t>(args, benchmark) .try_all([&](const cudnnConvolutionFwdAlgoPerf_t& fwdAlgPerf) { Tensor workspace = allocate_workspace(fwdAlgPerf.memory, input); // update convDesc mathType since cudnn 7.4+ now requires both algo + // mathType to figure out whether to use Tensor core kernels or not See // Note [behavior of cudnnFind and cudnnGet] ASSERT_CORRECT_PRECISION(fwdAlgPerf.mathType); AT_CUDNN_CHECK_WITH_SHAPES( cudnnSetConvolutionMathType( args.cdesc.mut_desc(), fwdAlgPerf.mathType), args); Constant one(dataType, 1); Constant zero(dataType, 0); AT_CUDNN_CHECK_WITH_SHAPES( cudnnConvolutionForward( args.handle, &one, args.idesc.desc(), input.const_data_ptr(), args.wdesc.desc(), weight.const_data_ptr(), args.cdesc.desc(), fwdAlgPerf.algo, workspace.data_ptr(), fwdAlgPerf.memory, &zero, args.odesc.desc(), output.data_ptr()), args, "Forward algorithm: ", static_cast<int>(fwdAlgPerf.algo), "\n"); }); -
'cudnnConvolutionForward' in cuDNN doc
cudnnConvolutionForward이 보인다.cudnn여기까지 들어왔네.cudnnStatus_t cudnnConvolutionForward( cudnnHandle_t handle, const void *alpha, const cudnnTensorDescriptor_t xDesc, const void *x, const cudnnFilterDescriptor_t wDesc, const void *w, const cudnnConvolutionDescriptor_t convDesc, cudnnConvolutionFwdAlgo_t algo, void *workSpace, size_t workSpaceSizeInBytes, const void *beta, const cudnnTensorDescriptor_t yDesc, void *y)const void *x:input.const_data_ptr()const void *w:weight.const_data_ptr()void *y:output.data_ptr()
아무래도 channel 1 로 줄어들면서 reduction 이 되는데, input
x와 weightw의 곱의 합으로 값은 되는데, 실제 연산은 cuDNN 의 코드가 없다. cpu 코드로 보면 될 것 같은데.. -
pytorch/aten/src/ATen/native/Convolution.cppat::Tensor _convolution( const Tensor& input_r, const Tensor& weight_r, const std::optional<Tensor>& bias_r_opt, IntArrayRef stride_, IntArrayRef padding_, IntArrayRef dilation_, bool transposed_, IntArrayRef output_padding_, int64_t groups_, bool benchmark, bool deterministic, bool cudnn_enabled, bool allow_tf32) { // ... // Select appropriate backend to use. auto bias_sizes_opt = bias.defined() ? std::optional<IntArrayRef>(bias.sizes()) : c10::nullopt; bool need_backward = GradMode::is_enabled() && (input.requires_grad() || weight.requires_grad() || (bias.defined() && bias.requires_grad())); ConvBackend backend = _select_conv_backend(input, weight, bias, c10::OptionalIntArrayRef(bias_sizes_opt), need_backward, params); at::MemoryFormat backend_memory_format = determine_backend_memory_format(input, weight, backend); // Call the backend. Tensor output; auto kernel_size = weight.sizes().slice(2); switch (backend) { // ... case ConvBackend::Empty: { Tensor weight_view; // Use permute and clone to avoid at::_unsafe_view(weight, -1) failure for non-contiguous cases where // view size is not compatible with input tensor's size and stride. if(weight.is_contiguous()) { weight_view = at::_unsafe_view(weight, -1); } else if (weight.is_contiguous(at::MemoryFormat::ChannelsLast)) { weight_view = at::_unsafe_view(at::permute(weight, {0, 2, 3, 1}), -1); } else if (weight.is_contiguous(at::MemoryFormat::ChannelsLast3d)) { weight_view = at::_unsafe_view(at::permute(weight, {0, 2, 3, 4, 1}), -1); } else { weight_view = at::_unsafe_view(weight.clone(at::MemoryFormat::Contiguous), -1); } output = (input.size(1) == 0) ? (input.view(-1) * weight_view) : (input * weight_view[0]); if (bias.defined()) { output.add_(bias[0]); } output = output.view(calc_output_size(input, weight, params)); break; }output을 보면,input.view와weight_view를 곱하는 것을 알 수 있다. -
torch/include/ATen/native/ConvUtils.htemplate <typename T> static inline std::vector<T> _conv_output_size( ArrayRef<T> input_size, ArrayRef<T> weight_size, ArrayRef<T> padding, ArrayRef<T> stride, ArrayRef<T> dilation = ArrayRef<T>() ) { // ASSERT(input_size.size() > 2) // ASSERT(input_size.size() == weight_size.size()) bool has_dilation = !dilation.empty(); auto dim = input_size.size(); std::vector<T> output_size(dim); output_size[0] = input_size[input_batch_size_dim]; output_size[1] = weight_size[weight_output_channels_dim]; for (const auto d : c10::irange(2, dim)) { auto dilation_ = has_dilation ? dilation[d - 2] : 1; auto kernel = dilation_ * (weight_size[d] - 1) + 1; output_size[d] = (input_size[d] + (2 * padding[d - 2]) - kernel) / stride[d - 2] + 1; } return output_size; }내가 보고자 했던 코드 라인
output_size[d] = (input_size[d] + (2 * padding[d - 2]) - kernel) / stride[d - 2] + 1;많이 봤던 식이다.
- : number of input features
- : number of output features
- : convolution kernel size
- : convolution padding size
- : convolution stride size
