Create / Form
To add a new post, we need a form to fill in.
1. url
path('add_post', AddPostView.as_view(), name="add_post"),2. view
-
CreateView -
fields = '__all__': it's from model field. if you want to specify fields,fields = ('title', 'body',)pick and choose.
Note that without the , at the end of the () is treated as a string and cause error
class AddPostView(CreateView):
model = Post
template_name = 'add_posts.html'
fields = '__all__'3. template
-
Django form
{{ form.as_p }}means each box will be surrounded by p tag. Variations are 'as_ul', 'as_table' -
Button 'Post' goes back to home. but how?
-> at models.py, we addget_absolute_urlmethod to redirect (check below)
<form method="POST">
{% csrf_token %}
{{ form.as_p }}
<button class="btn btn-secondary"> Post </button>
-as_table needs table tags around
<table>
<form method="POST">
{% csrf_token %}
{{ form.as_table }}
</form>
</table>
<button class="btn btn-secondary"> Post </button>? get_absolute_url
4. models.py
to be directed to created post.
from django.urls import reverse
class Post(models.Model):
~
def get_absolute_url(self):
return reverse('article-detail', args=(str(self.id)))
#url name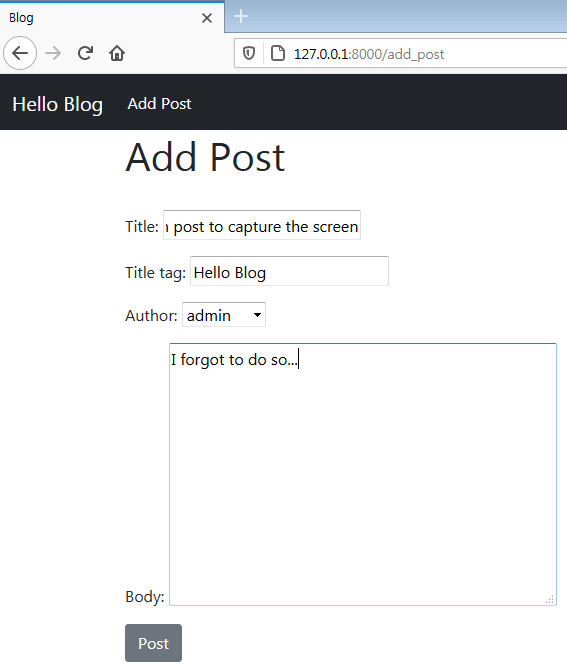
5. styling
0. create forms.py
class PostForm(forms.ModelForm):
inherit forms. ModelForm allows us to create form fields for our Post model.
- add styling: widget dictionary
- we need 'class: form-control' to apply bootstrap on our form.
- each fields: TextInput, Select(dropdown), Textarea etc
from django import forms
from .models import Post
class PostForm(forms.ModelForm):
class Meta:
model = Post
fields = ('title', 'title_tag', 'author', 'body')
#for bootstrap
widgets = {
'title': forms.TextInput(
attrs={'class': 'form-control'}), #css
'title_tag': forms.TextInput(
attrs={'class': 'form-control'}),
'author': forms.Select(
attrs={'class': 'form-control'}), #dropdown
'body': forms.Textarea(
attrs={'class': 'form-control'}),
}1. url
same as above
path('add_post', AddPostView.as_view(), name="add_post"),2. view
Note that when using form_class, we don't need to specify fields as it's already in form_class.
from .forms import PostForm
class AddPostView(CreateView):
model = Post
form_class = PostForm
template_name = 'add_posts.html'
#fields = '__all__' # no need anymore
3. template
- Bootstrap: Wrap tags with
<div class="form-group">and each tag has to have'class=form-control'in order to be bootstrap applied. (in our case, it applied in forms.py and template got {{form}} connected.
<div class="form-group">
<form method="POST">
{% csrf_token %}
{{ form.as_table }}
<br/>
<button class="btn btn-secondary"> Post </button>
</form>
</div>4. Bonus
- Pass placeholder text
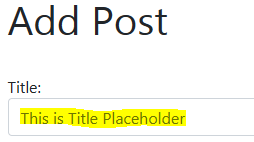
widgets = {'title': forms.TextInput(attrs={
'class': 'form-control',
'placeholder':'This is Title Placeholder'})}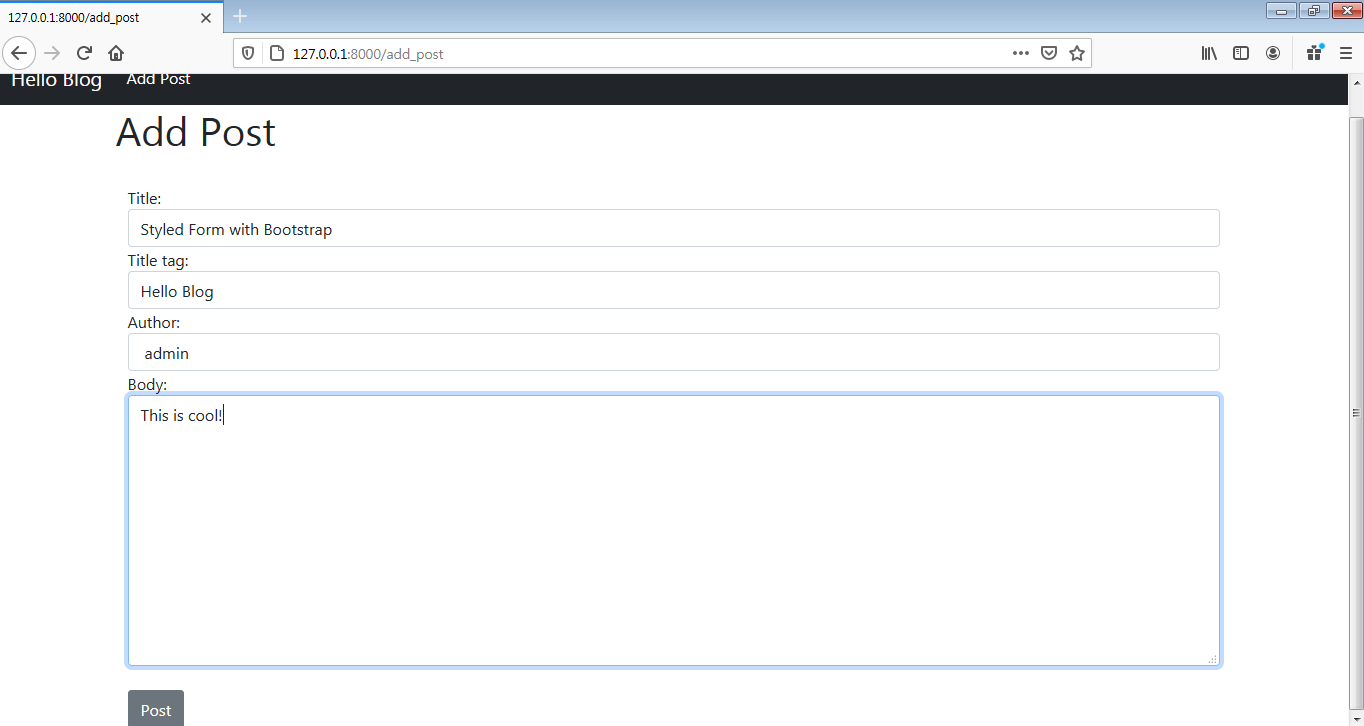
Update(Edit)
1. url
path('article/edit/<int:pk>',
UpdatePostView.as_view(), name="update_post"),2. view
-
UpdateView
Use either form_class or fields. If you use both, It will crash. form_class to use bootstrap. Firelds are default django form. -
pre-populated
class UpdatePostView(UpdateView):
model = Post
template_name = 'update_post.html'
fields = ['title', 'title_tag', 'body']
#form_class = PostForm3. template
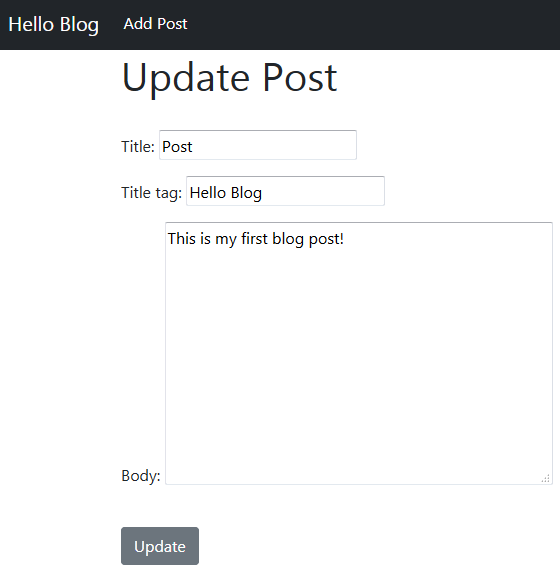
create 'update_post.html'
{% extends 'base.html' %}
{% block title %} Update Post {% endblock %}
{% block content %}
<h1> Update Post </h1>
<br/>
<div class="form-group">
<form method="POST">
{% csrf_token %}
{{ form.as_p }}
<br/>
<button class="btn btn-secondary"> Update </button>
</form>
</div>
{% endblock %}
- add link at home.html
<small><a href="{% url 'update_post' post.pk %}">
Edit </a></small>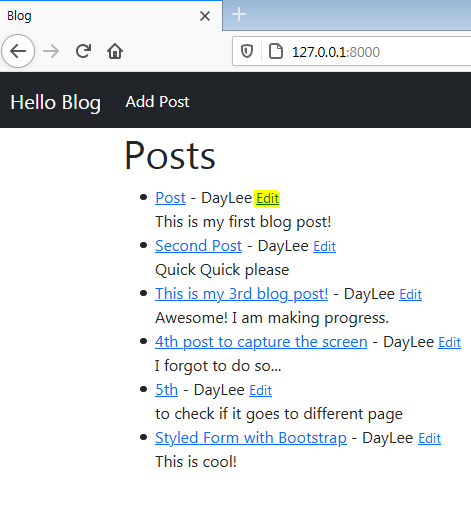
Delete
1. url
path('article/<int:pk>/remove',
DeletePostView.as_view(), name="delete_post"),2. view
Not like create, 'Post' button, where we used get_absolute_url, Delete doesn't work that way.
use success_url = reverse_lazy('home') instead.
reverse_lazy
from django.urls import reverse_lazy
class DeletePostView(DeleteView):
model = Post
template_name = 'delete_post.html'
success_url = reverse_lazy('home')3. template
<form method="POST">: even though we don't need a form here, we need to use 'POST' method. Hence, we need a form tag.
<div class="form-group">
<form method="POST">
{% csrf_token %}
<strong> Are you sure you want to delete this post?
</strong><br/><br/>
<button class="btn btn-secondary"> Delete Post </button>
</div>
4. Bonus: order
Latest one shown on top of the blog list
Put negative id minus'-' for ordering
class HomeView(ListView):
~
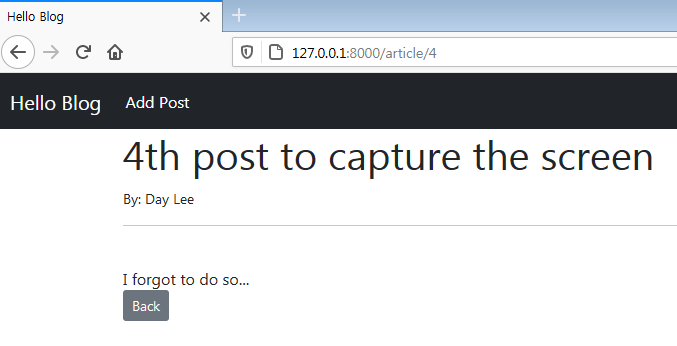
ordering = ['-id']This is kinda hacky way tho, better to use date field. (Photo: 4th one went up! It was on the bottom.)
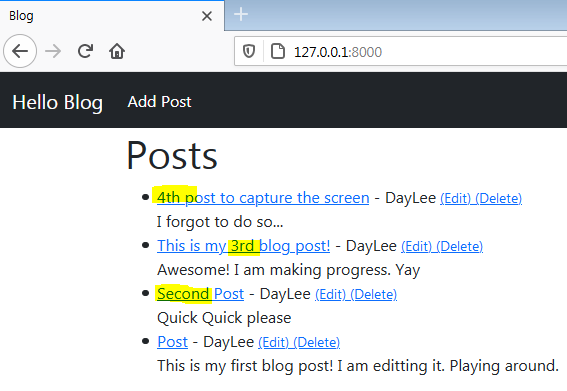
Order Blog Posts
(Add new field into Model)
Problem: we need to modify model to add date.
But we have old post(data) that doesn't have date fields, we need to tweak a bit when makemigrations and migrate 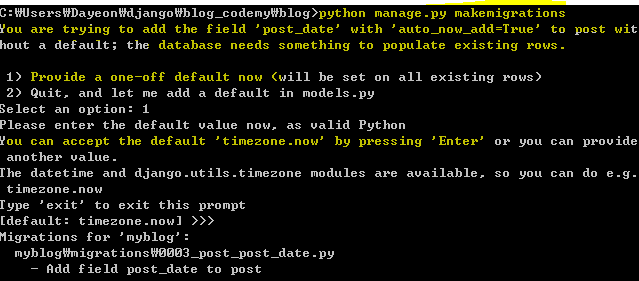
migrate: push the data into DB.
we can check changes in migrations folder.
1. models.py
models.DateField(auto_now_add=True)
automatically assign date
from datetime import datetime, date
class Post(models.Model):
~
post_date = models.DateField(auto_now_add=True)
2. view
ordering done by date by using new field DateField in model.
['-post_date'] by latest
class HomeView(ListView):
model = Post
template_name = 'home.html'
ordering = ['-post_date']3. template
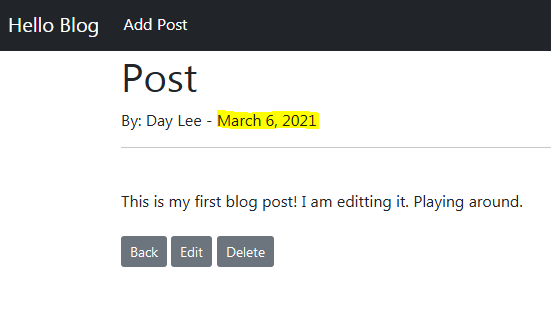
{{ post.post_date}}