1. 세그먼트 트리란?
정의 및 시간 복잡도
-
특정 구간합을 빠르게 구하기 위해 만들어진 자료구조이다.
-
어떤 숫자 배열에 대해,
1.특정구간의 합 구하기연산과2.특정 위치의 값 바꾸기연산이 있을 때 이를 배열로 구현하는 것과 세그먼트 트리로 구하는 방식의 시간 복잡도는 다음과 같다. -
배열 세그먼트 트리 1. 특정구간의 합 구하기 O(N) O(logN) 2. 특정 인덱스의 값 바꾸기 O(1) O(logN) -
위의 특징처럼 세그먼트 트리는
특정 구간의 특성을 빠르게 구하기위한 자료구조이다.
구현 방식
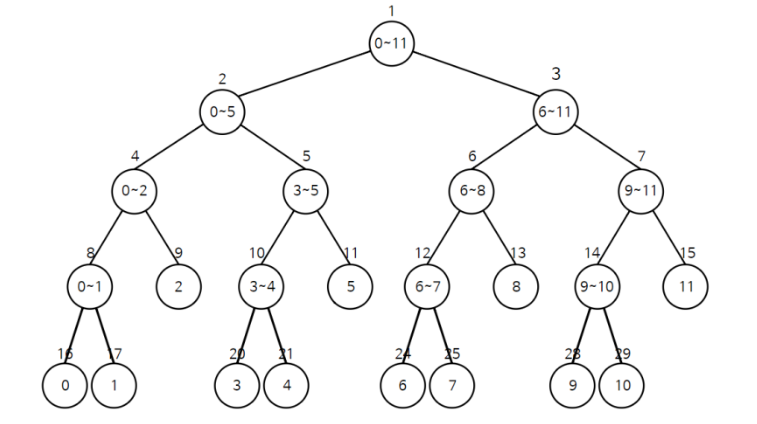
- 세그먼트 트리는 원래 데이터의 범위를 반씩 분할하여 그 구간의 특성들을 저장해 나아간다.
- 우선, 아래 그림에서 루트 노드는 1번 인덱스부터 시작하는데 그 이유는 인덱스에서 2를 곱했을 때 왼쪽 자식 노드가 나오기 때문에 계산에 용이함 때문이다.
- 인덱스가 0~11 범위의 배열을 세그먼트 트리로 구성한다면 아래와 같이 구성할 수 있다.
2. 구현
자바를 이용한 구현은 아래와 같다.
public static class SegmentTree{
private long[] tree;
// 생성자에서 세그먼트 트리의 전체노드 수 계산하여 메모리 할당
SegmentTree(int n) {
double height = Math.ceil(Math.log(n)/Math.log(2)) + 1;
long nodeCnt = Math.round(Math.pow(2, height));
tree = new long[Math.toIntExact(nodeCnt)];
}
//세그먼트 트리의 노드 값 초기화
long init(long[] arr, int node, int start, int end) {
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
//트리의 리프노드인 경우
if (start == end) return tree[node] = arr[start];
// 리프노드가 아닌 경우에는 자식노드 값을 더해서 노드의값 초기화
else {
return tree[node] = init(arr, node*2, start, mid)
+ init(arr, node*2+1, mid+1, end);
}
}
// 배열의 특정 구간 합을 세그먼트 트리로 구하기
long sum(int node, int start, int end, int left, int right) {
// 노드가 가지는 값의 구간이 구하려고 하는 합의 구간에 속하지 않는 경우 0리턴
if (end < left || right < start) return 0;
// 노드가 가지는 값이 구간이 구하려고 하는 합이랑 일치하는 경우 노드값 리턴
else if (left <= start && right >= end) return tree[node];
// 다음 2가지 경우 자식노드를 탐색해서 값을 리턴
// 1. 노드가 가지는 값의 구간이 구하려고 하는 합의 구간에 일부는 속하고 일부는 안속할때
// 2. 노드가 가지는 값의 구간이 구하려고 하는 합의 구간을 모두 포함하는 경우
else return sum(node*2, start, (start+end)/2, left, right)
+ sum(node*2+1, (start+end)/2+1, end, left, right);
}
//배열의 특정 인덱스 값이 변경될 경우 세그먼트 트리의 노드 값 변경
long update(int node, int start, int end, int index, long changeValue) {
//노드가 가지는 값의 구간에 배열의 변경될 인덱스가 포함안될 경우
if (index < start || end < index) return tree[node];
//노드가 가지는 값의 구간과 배열의 변경될 인덱스값이 같은 경우
else if (start == index && end == index) return tree[node] = changeValue;
//노드가 가지는 값의 구간에 배열의 변경될 인덱스값이 포함되는 경우 자식 노드를 탐색후 리턴
else return tree[node] = update(node*2, start, (start+end)/2, index, changeValue)
+ update(node*2+1, (start+end)/2+1, end, index, changeValue);
}
}