Summary

-
연구배경:
- Quantization은 메모리, inferecne속도 효율적 감소.
-
기존연구 한계:
- 기존 모델들은 accuracy와 hardware efficiency가 tradeoff관계임.
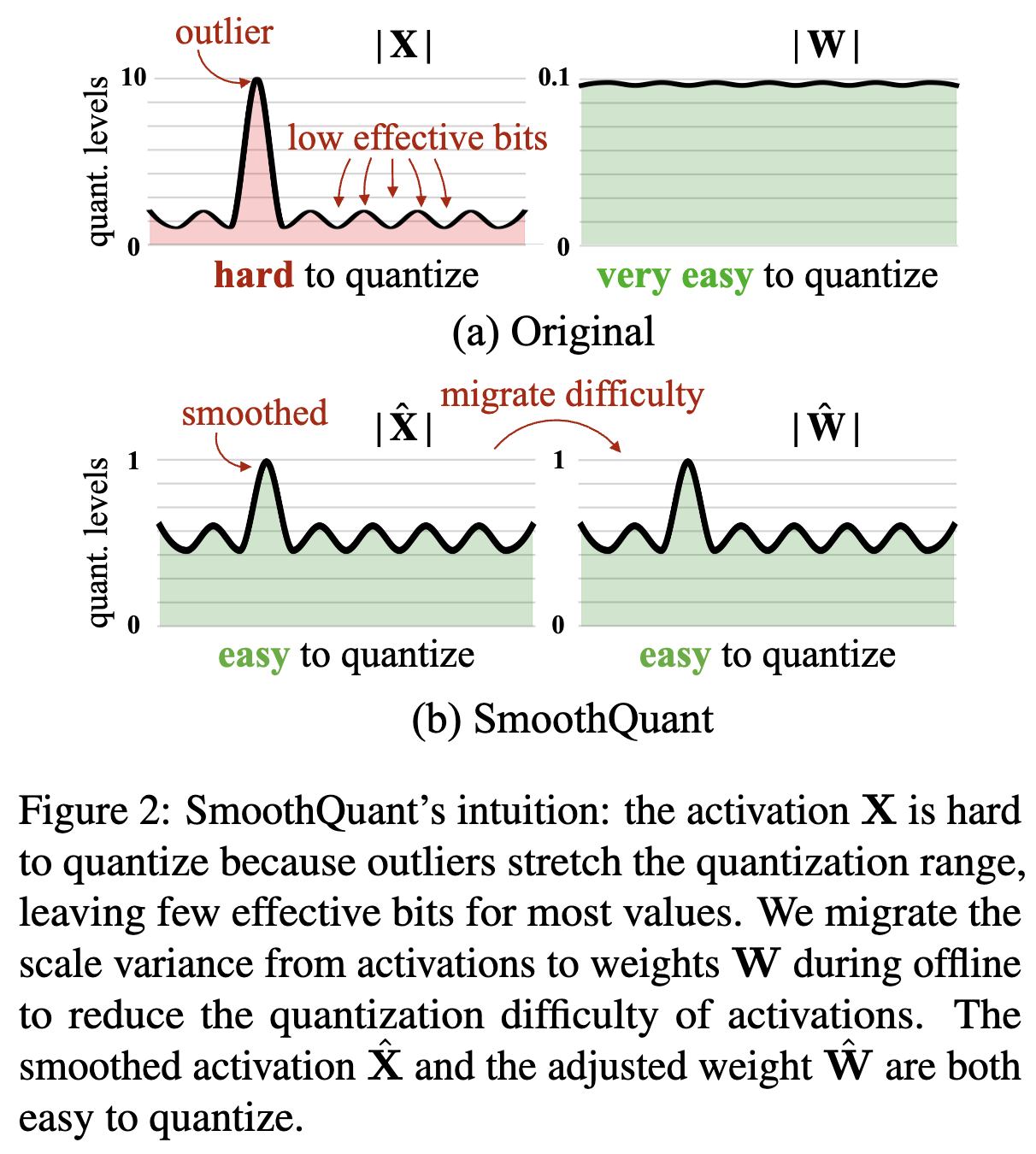
- Quantization할 때 activation (=활성화 함수 출력) 은 outlier로 인해 양자화 힘듦.
-
제안: SmoothQuant
- Activation outliers를 smoothed 하여 양자화 쉽게,
- weights를 migrate difficulty 전가해서 좀더 어렵게
- 대신 수학적으로는 계산하면 결과적으로는 original과 동일한 값
-
장점: 범용 PTQ(훈련 후 양자화) 솔루션
- a training-free
- accuracy-preserving
- LLM에 대한 8비트 가중치, 8비트 활성화(W8A8) 양자화 가능
-
실험 결과
- up to 1.56X speed up
- 2X memory reduction for LLMs with negligible loss in accuracy
- 530B LLM을 single node로 serving 가능
Research Background
Large Language models (LLMs)
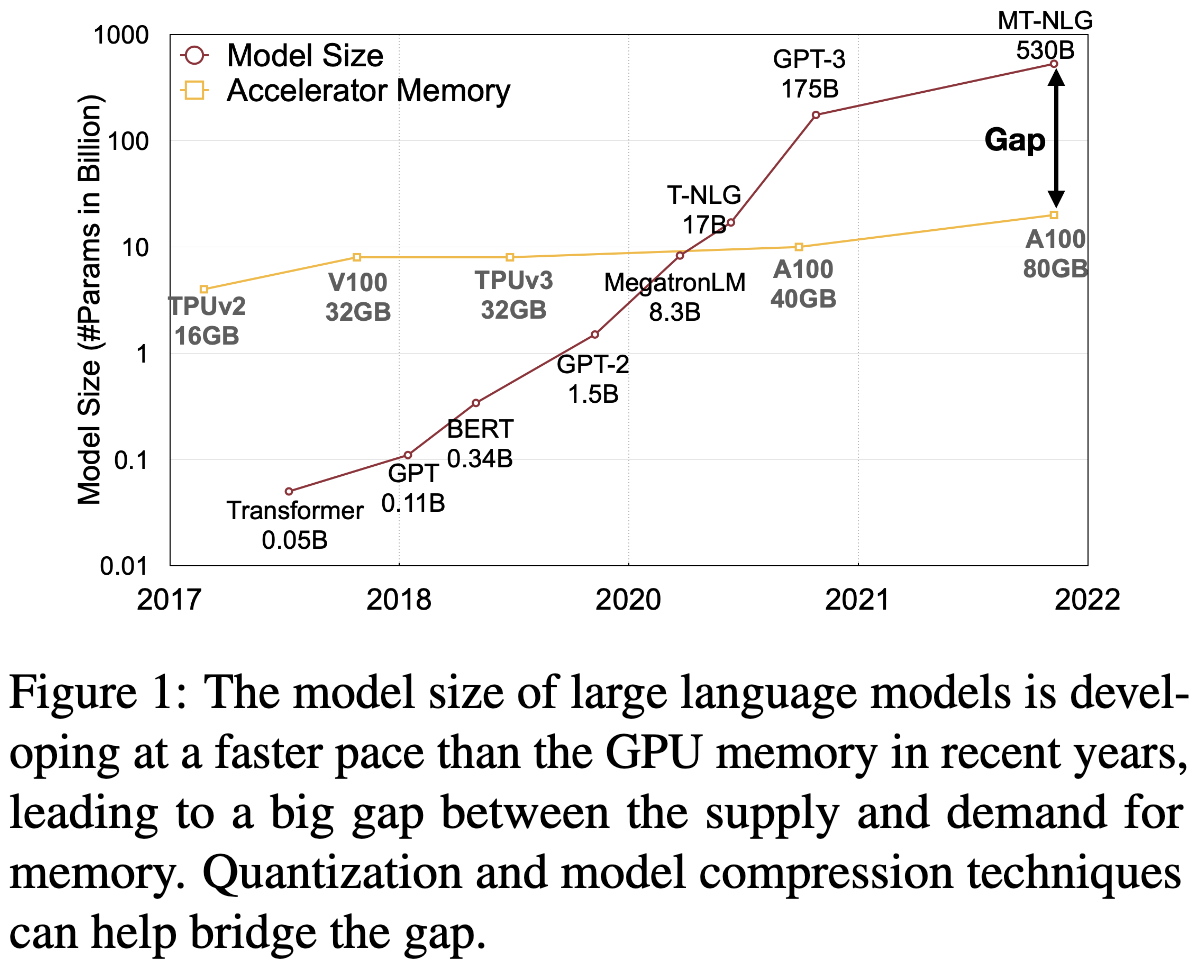
- LLM을 serving 하려면 많은 예산과 envergy가 필요함.
- 하지만 커지는 모델 규모에 비해, GPU 메모리 개발이 속도를 못따라 감.
Model Quantization
- 양자화 기술로 인해, Figure1번에서 볼 수 있는 모델 크기와, GPU 메모리 간의 Gap을 줄일 수 있음.
- BERT같은 애들은 FP32 사용했고, LLM으로 오면서 FP16사용
- 이후에 INT8, INT4까지 양자화하려는 시도들 다수
- 양자화(Quantization)란?
모델 실행 성능과 효율성 향상을 위해 신경망의 가중치(weight)와 활성화 함수(activation function) 출력을 더 작은 비트 수로 표현하도록 변환하는 기술- 신경망 모델 크기 ⬇︎
- 계산 속도 ⬆︎
- 메모리 사용량 ⬇︎
- 효율적 모델 배포와 실행 가능
Quantization of LLMs
- Qlora: Efficient Finetuning of Quantized LLMs (NeurIPS 24')
- GPTQ: weight만 경량화
- zeroquant & nuQmm: per-token and group-wise quantization, customized CUDA kernels
- LLM.int8(): mixed INT8/FP16 to adress activation outliers
- OutlierSuppression: non-scaling layerNorm, token-wise clipping
- only succeeds on small LM (BERT, BART) and fails to maintain the accuracy for LLM.
=> Activation을 잘 다뤄야 양자화 잘한다!!!가 주장
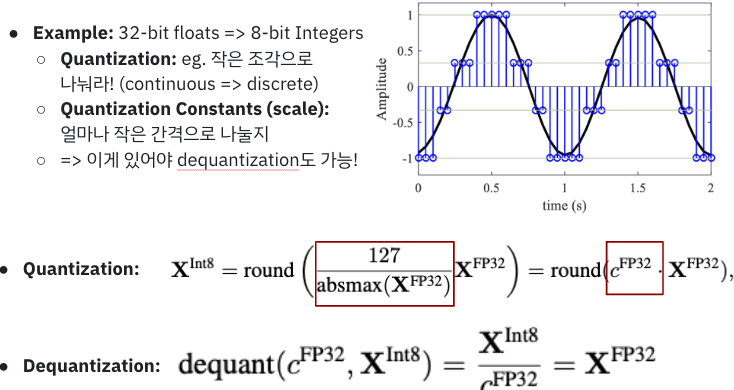
Quantization
How to?
- (1) 출력값 고정 (보통 max값) (=> outlier가 문제 일으키는 부분)
- (2) 양자화 레벨로 나누기 (=> INT8은 0~255)
- (3) N: bit 사이즈/ ∆: Quantization step size
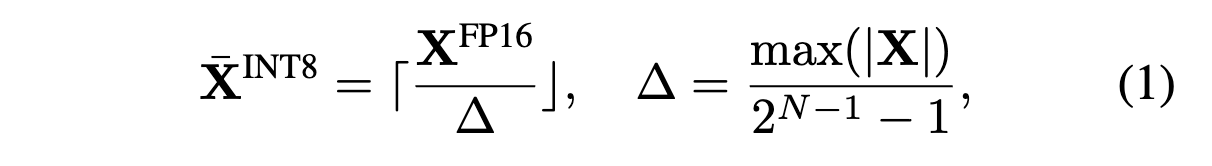
👉 (예시코드) Activation Quantization
- 활성화 함수 출력 8비트 정수로 양자화:
출력값 범위 0-2로 고정 후 255개의양자화 레벨로 나누기 (8bit 0~255)
원래는 출력값을 보통 max값으로함. => 이게 outlier 방지하기 위함.import numpy as np # Example activation output (floating-point) activation_output = np.array([0.1, 0.5, 0.9, 1.2, 1.5], dtype=np.float32) # Quantization parameters (for 8-bit quantization) quantization_levels = 255 # 8-bit has 256 levels (0 to 255) activation_min = 0.0 activation_max = 2.0 # Quantization step scale = quantization_levels / (activation_max - activation_min) quantized_output = np.round(activation_output * scale).astype(np.int32) print("Original activation output:", activation_output) print("Quantized activation output:", quantized_output)
Quantization 기법들
- Static Quantization: 미리 가중치와 활성화 값 사전에 양자화
- Dynamic Quantization: Inference 시 활성화 값 양자화
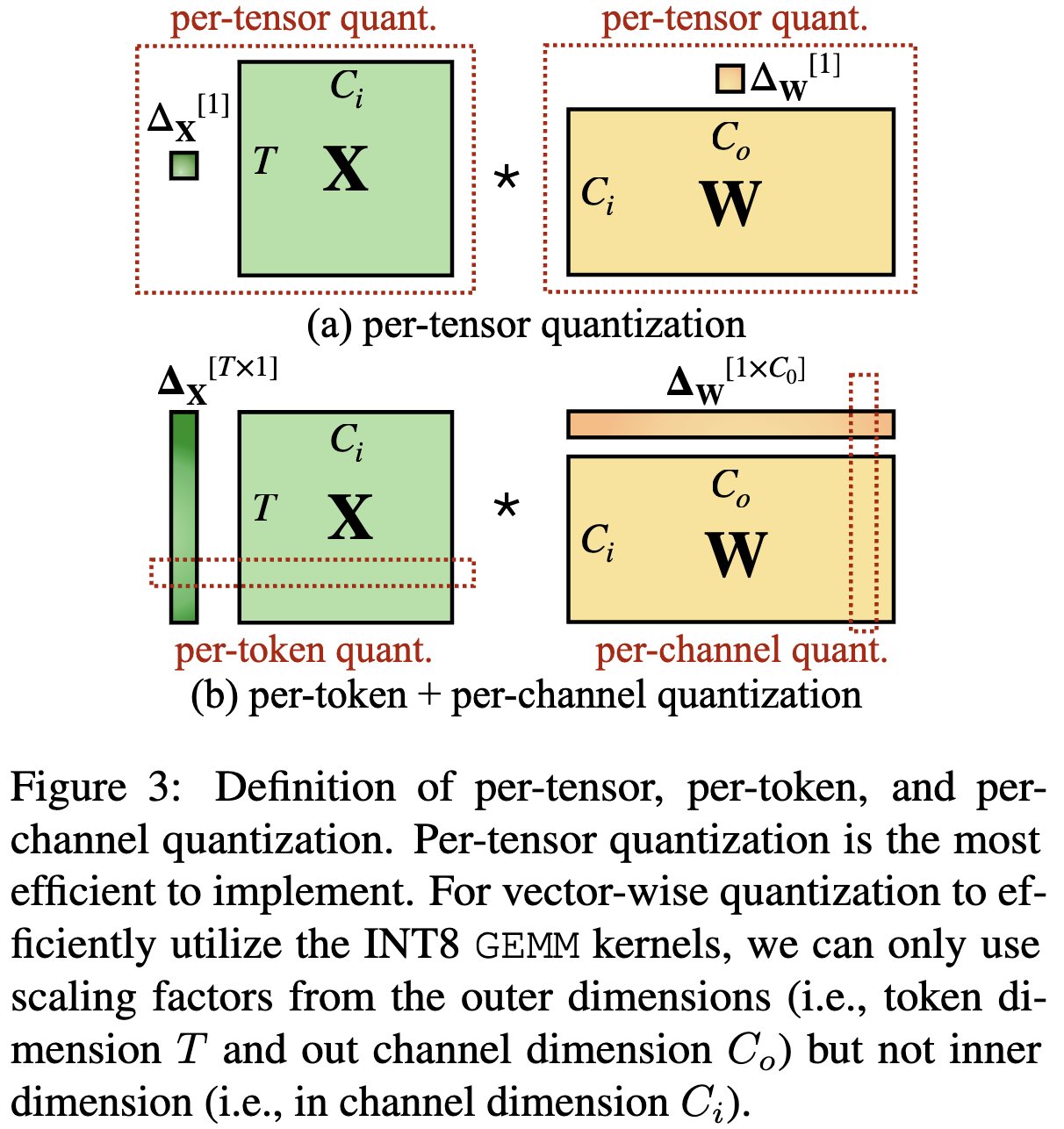
- Per-Tensor Quantization: 텐서 전체에 동일한 스케일과 제로포인트를 사용.
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.quantize_per_tensor.html
- Per-Channel Quantization: 각 채널마다 개별 스케일과 제로포인트를 사용.
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.quantize_per_channel.html
- Per-Token Quantization: NLP에서 각 토큰 임베딩을 개별적으로 양자화.
- Group-wize qunatization: channel마다 서로다른 quantization 적용
- Per-Tensor Quantization: 텐서 전체에 동일한 스케일과 제로포인트를 사용.
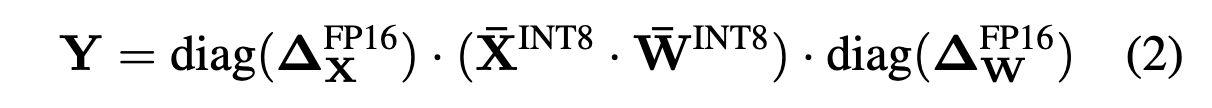
https://www.tensorflow.org/lite/performance/post_training_quantization?hl=ko
Review of Quantization Difficulty
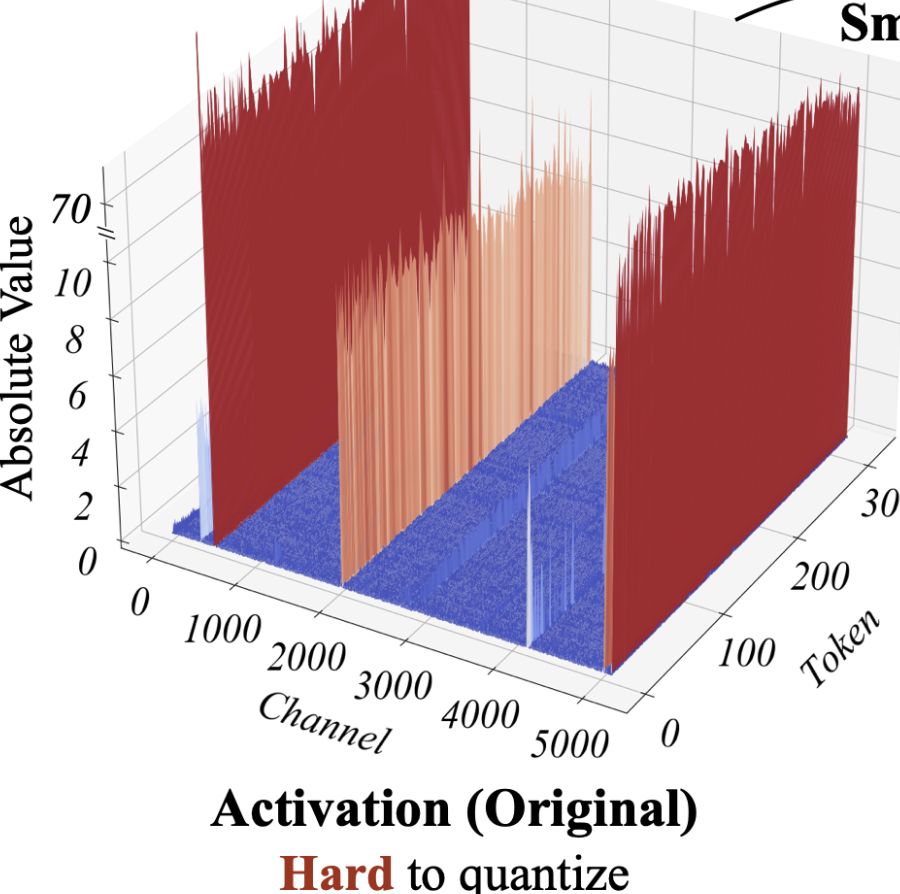
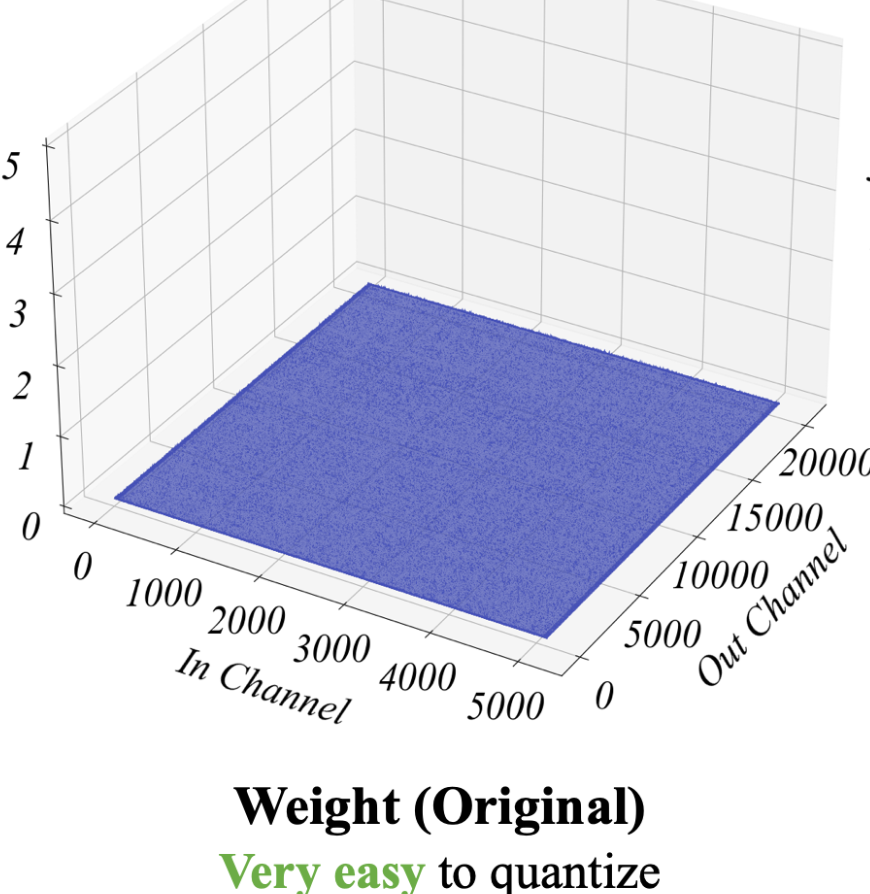
1. Activations are harder to qunatize than weights
- 기존 연구에 따르면, weights를 INT8, INT4까지 양자화했을 때 성능 하락 없었음.
2. Outliers make activation quantization difficult
- quantization level 구할 때 value를 maximize 하는 데, outlier가 있으면 이게 다른 애들에 비해 100배 이상 뛰어버릴 때도 있음.
- 만약 channel i의 max값이 m_i고 전체 메트릭스의 max값이 m이면, i채널의 효율적인 양자화 level은 (2^8 X m_i) / m임. 그럼 non-outlier channel에서는 양자화레벨이 매우매우 작게 설정될 수 있음.
3. Outliers persist in fixed channels.
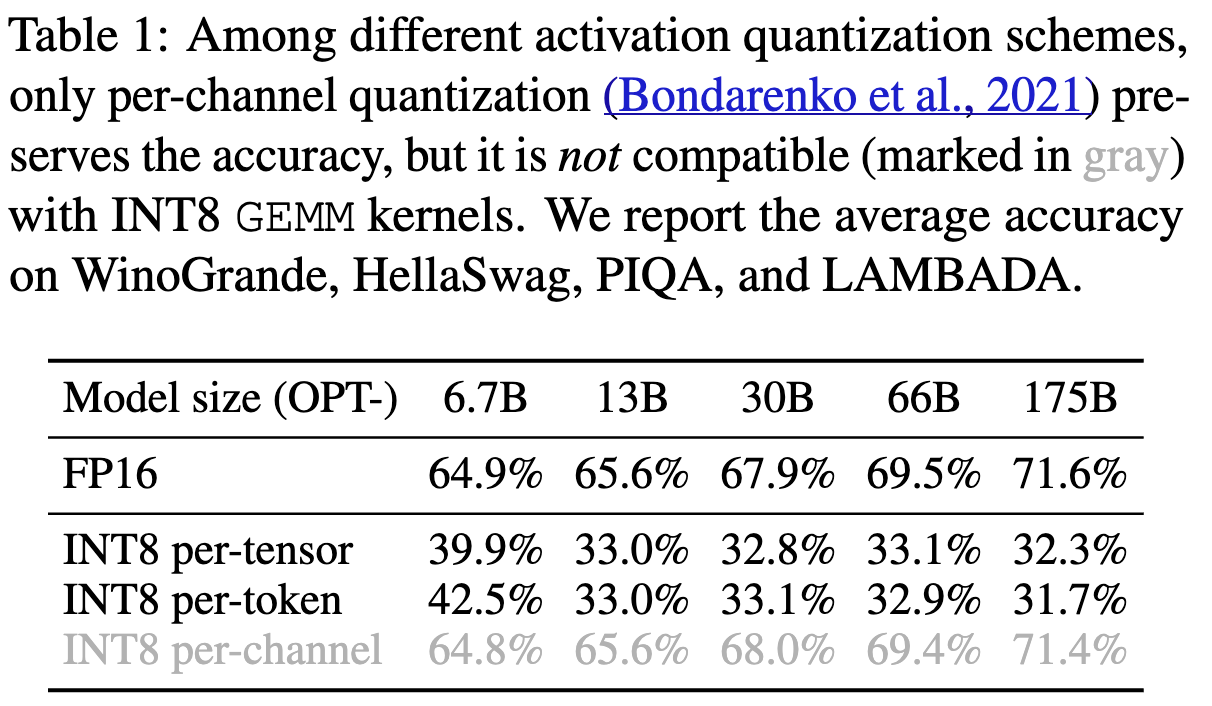
- per-channel 방식이 성능 유지하면서, outlier 최소화해서 효과 좋음
- But, GMMs 같이 효과적으로 연산하기 어려움. 왜냐면 채널별로 양자화 해야하니까, 행렬연산하기 어려움
per token, per channel의 기존에 정해진 embedding, channel 사이즈를 기반으로 scaling factors를 계산해야함. 그래서 tensor-wise 가 제일 효율 적임.
# Example token embeddings embeddings = torch.tensor([[0.1, 0.2, 0.3], [0.4, 0.5, 0.6]], dtype=torch.float32) # Quantization parameters per token scales = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.2]) zero_points = torch.tensor([0, 0]) # Quantize each token embedding individually quantized_embeddings = > torch.stack([torch.quantize_per_tensor(embeddings[i], scales[i], zero_points[i], dtype=torch.quint8) for i in range(embeddings.size(0))]) print("Quantized embeddings (per-token):", quantized_embeddings)
SmoothQuant
https://github.com/mit-han-lab/smoothquant/blob/main/smoothquant/fake_quant.py
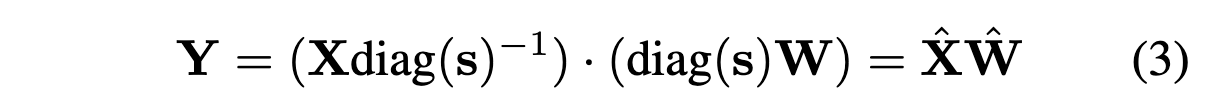
Migrate the quantization difficulty from activations to weights
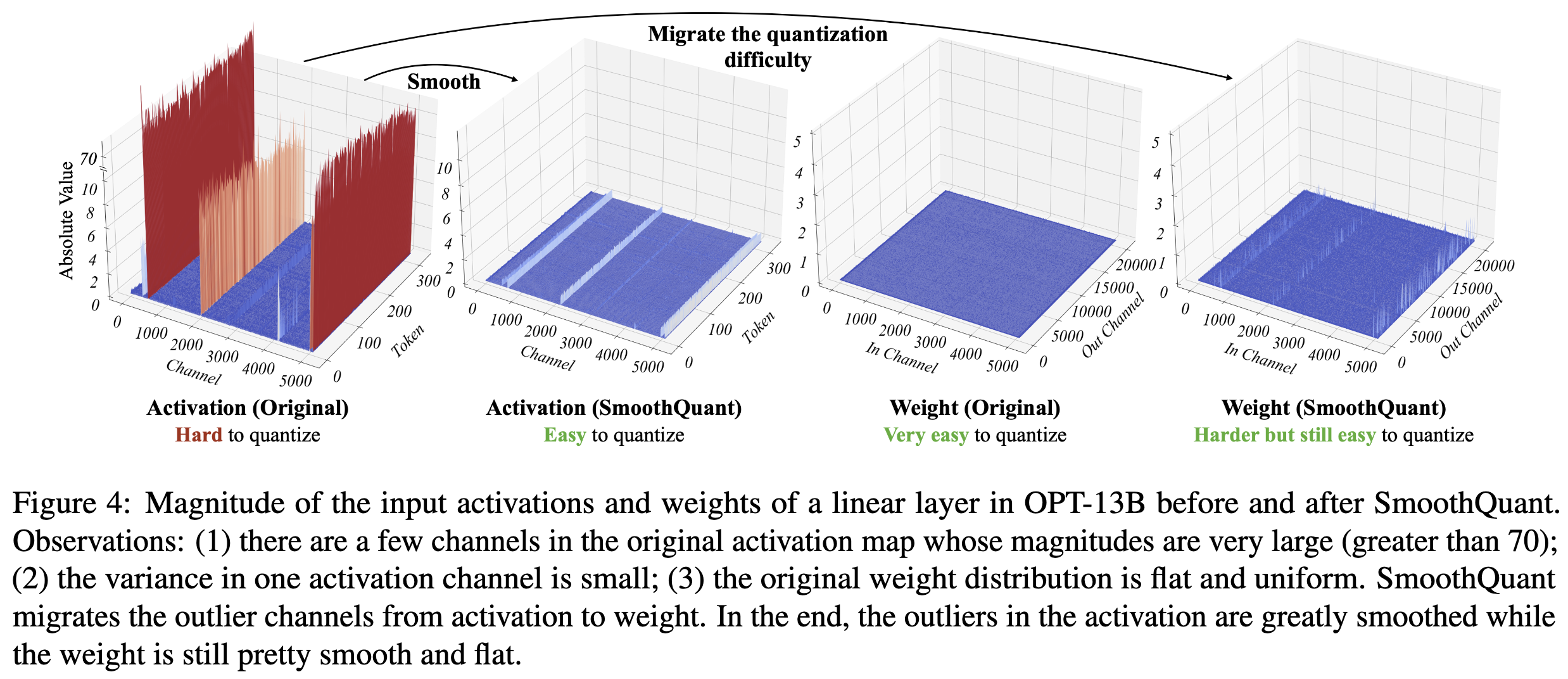
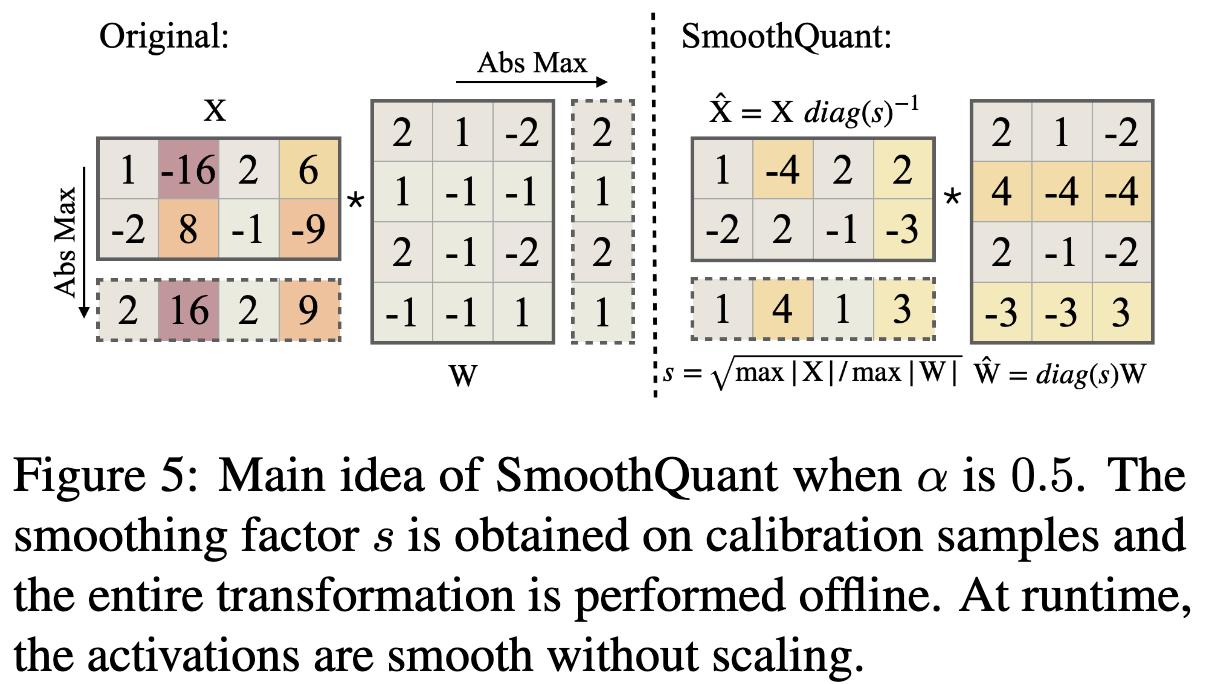
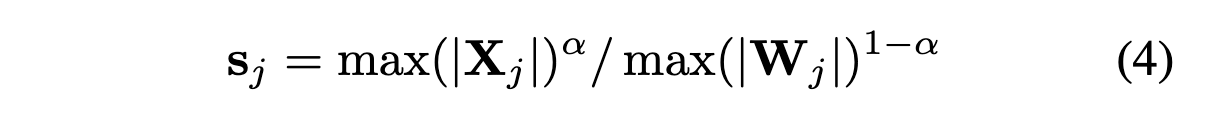
- smoothing factor alpha
실험적으로 0.5가 양자화 difficulty하기 위해서 split할 때 제일 balanced되는 포인트였다고 함. / per-tensor나 static일 때 특히 same qunatizer쓸 때 좋았다고 함. - 둘다 비슷한 maximum value를 가지니까, 똑같이 quantization difficulty를 겪는다.
알파 크게 할 수록 weight가 양자화하기 어렵게 만드는 거임.
Applying SmoothQuant to Transformer blocks
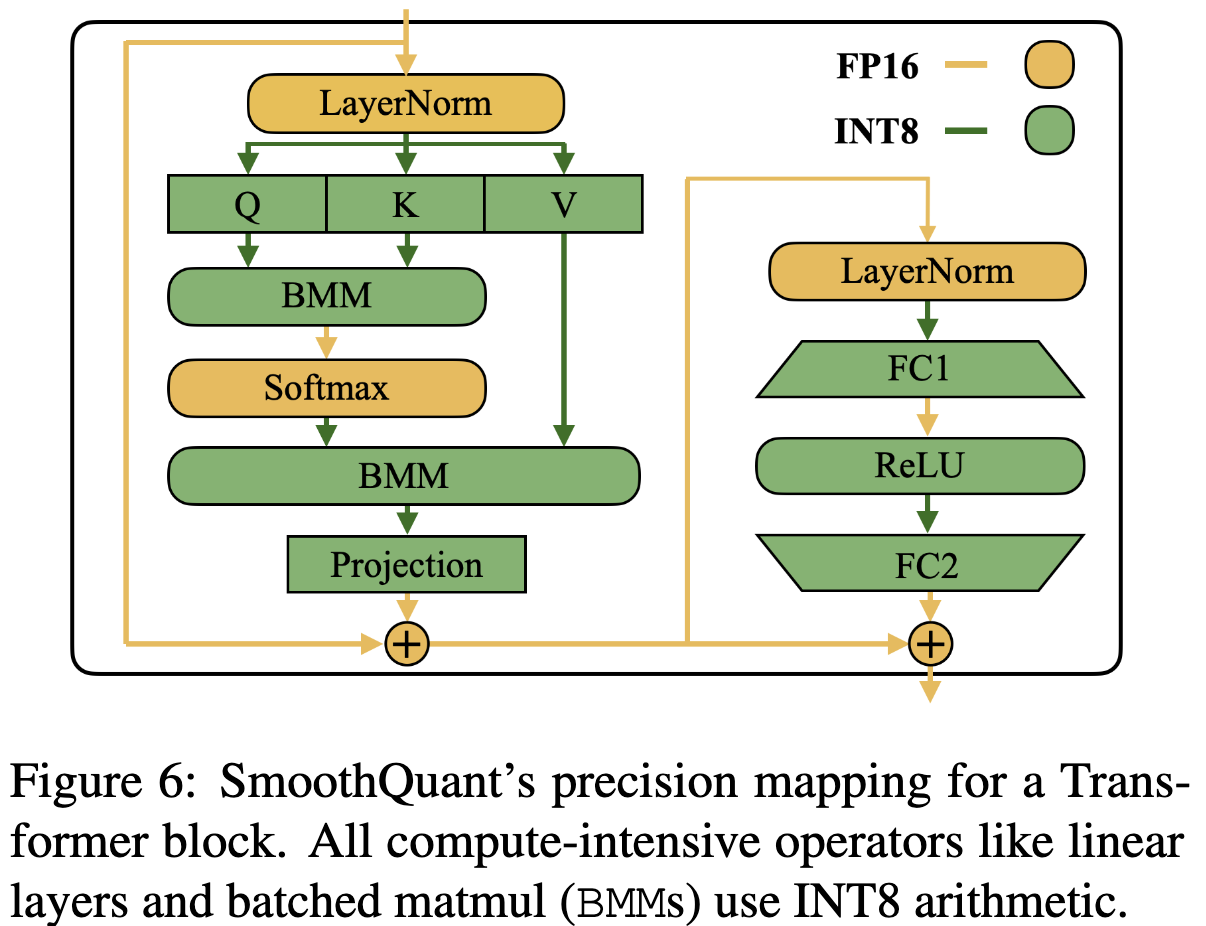
Experiments
Experimental Setups
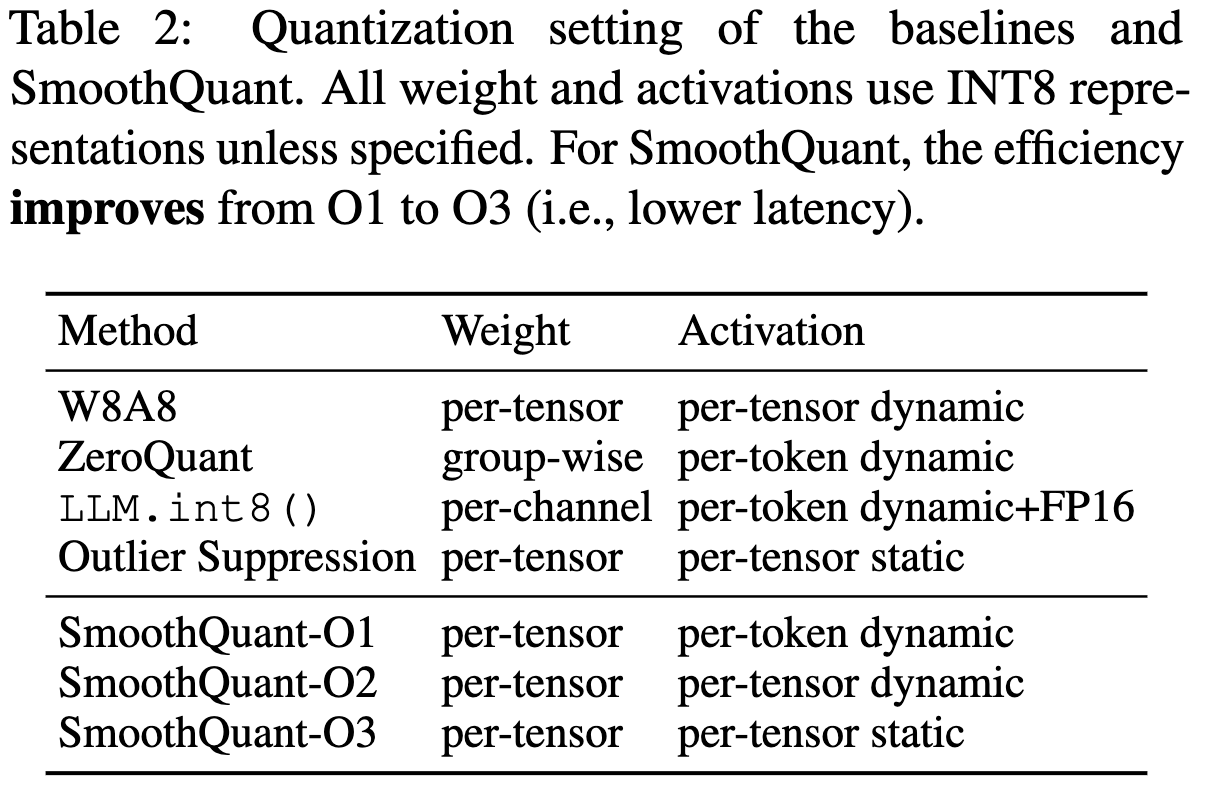
- Baselines
- O1~O3로 갈수록 the efficiency improve
- O3가 static이니까, 사전에 정의되기 때문에 inference때 계산 추가 필요없어서 메모리 덜 잡아먹음
- Models and Datasets
- OPT : meta꺼
- Bloom: 무료 소스코드
- GLM-130B: 칭화대
- Activation smoothing
- 모델별로 다르게, 뒤에 실험 있음. 수동으로 조정해가면서 해야함.
- Implementation
- 두 개의 백앤드에서 비교 실험
- (1) Pytorch Huggingface
- (2) FasterTransformer
- INT8 linear model, Batched matrix multiplication (BMM) 적용
- 단순하게 FP16 모델을 INT8 kernels로 바꿈
- 두 개의 백앤드에서 비교 실험
Accurate Quantization
-
Accuracy of zero-shot tasks with OPT models
- 베이스라인 FP16과 비등한 결과.
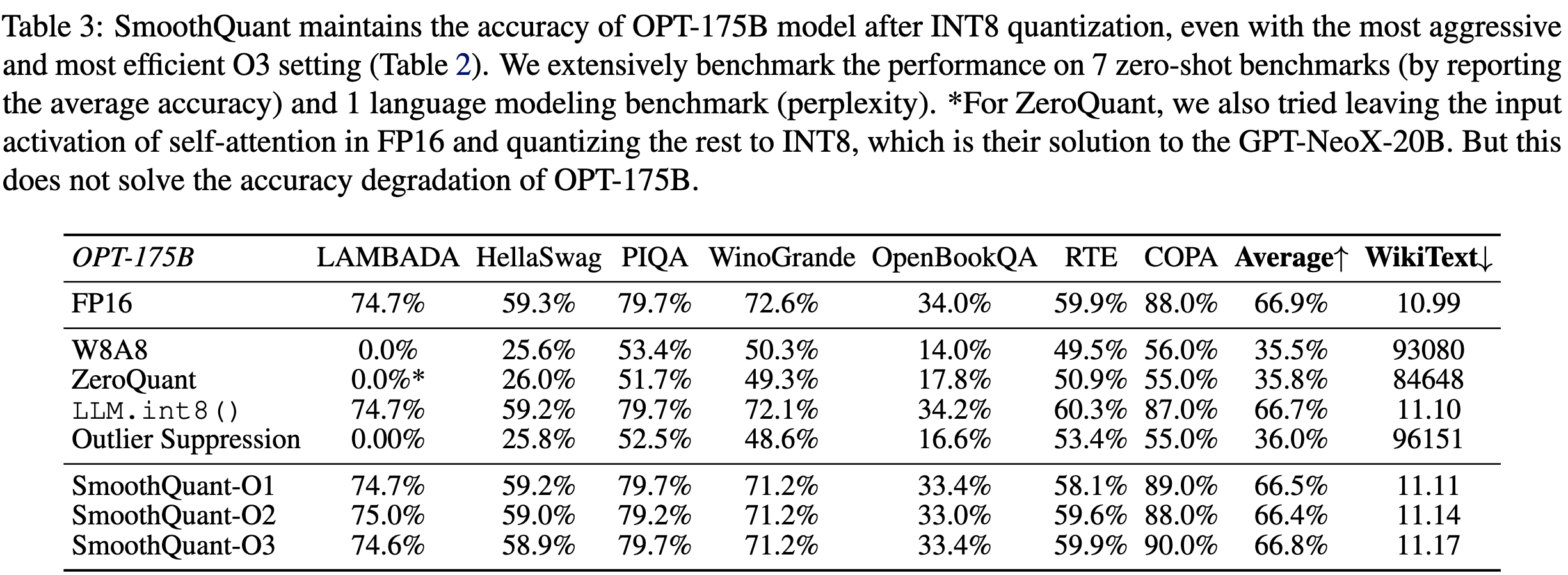
- 베이스라인 FP16과 비등한 결과.
-
Results of different LLMs
- 다양한 LLM 모델에서도 잘 작동함
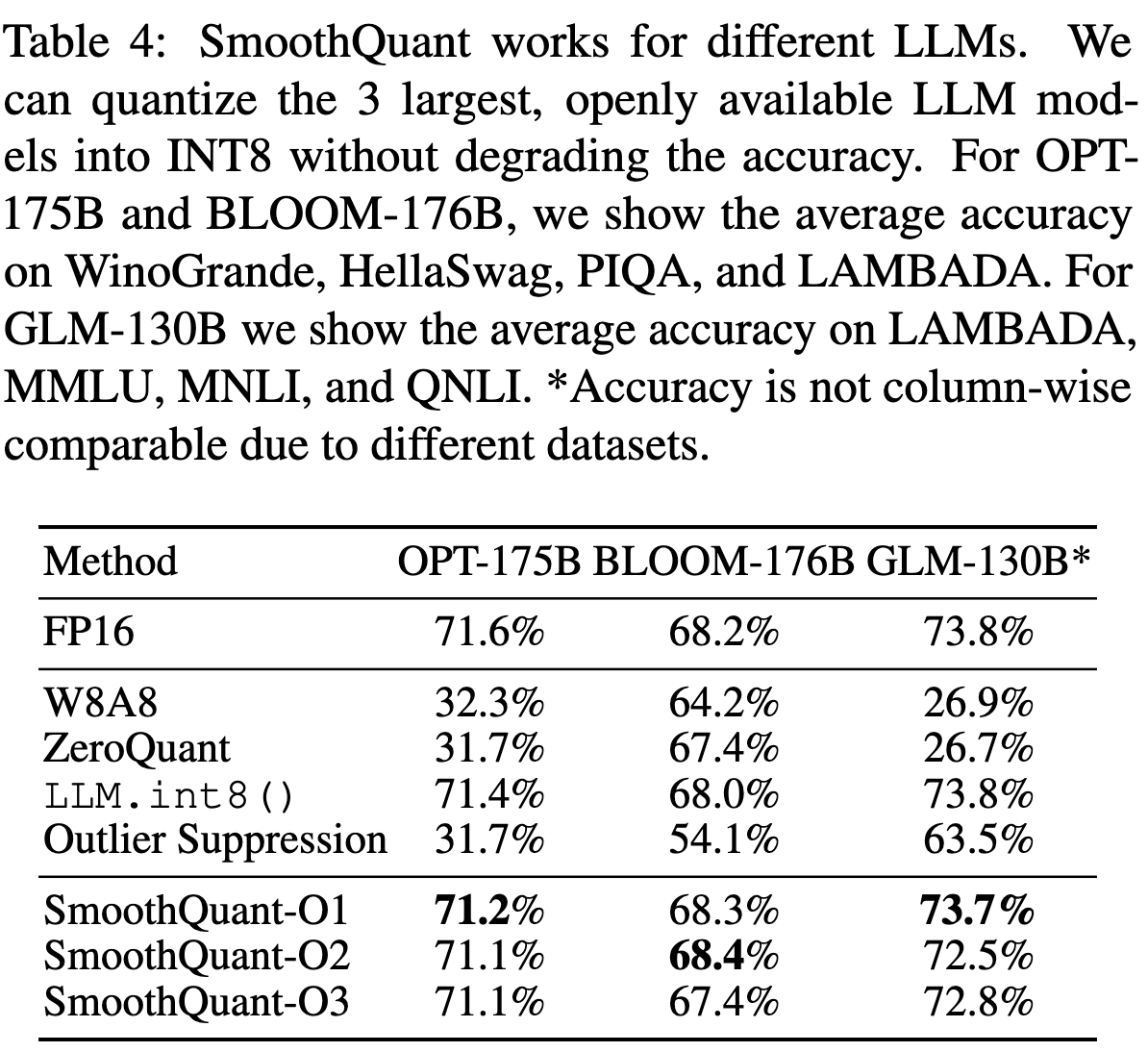
- 다양한 LLM 모델에서도 잘 작동함
-
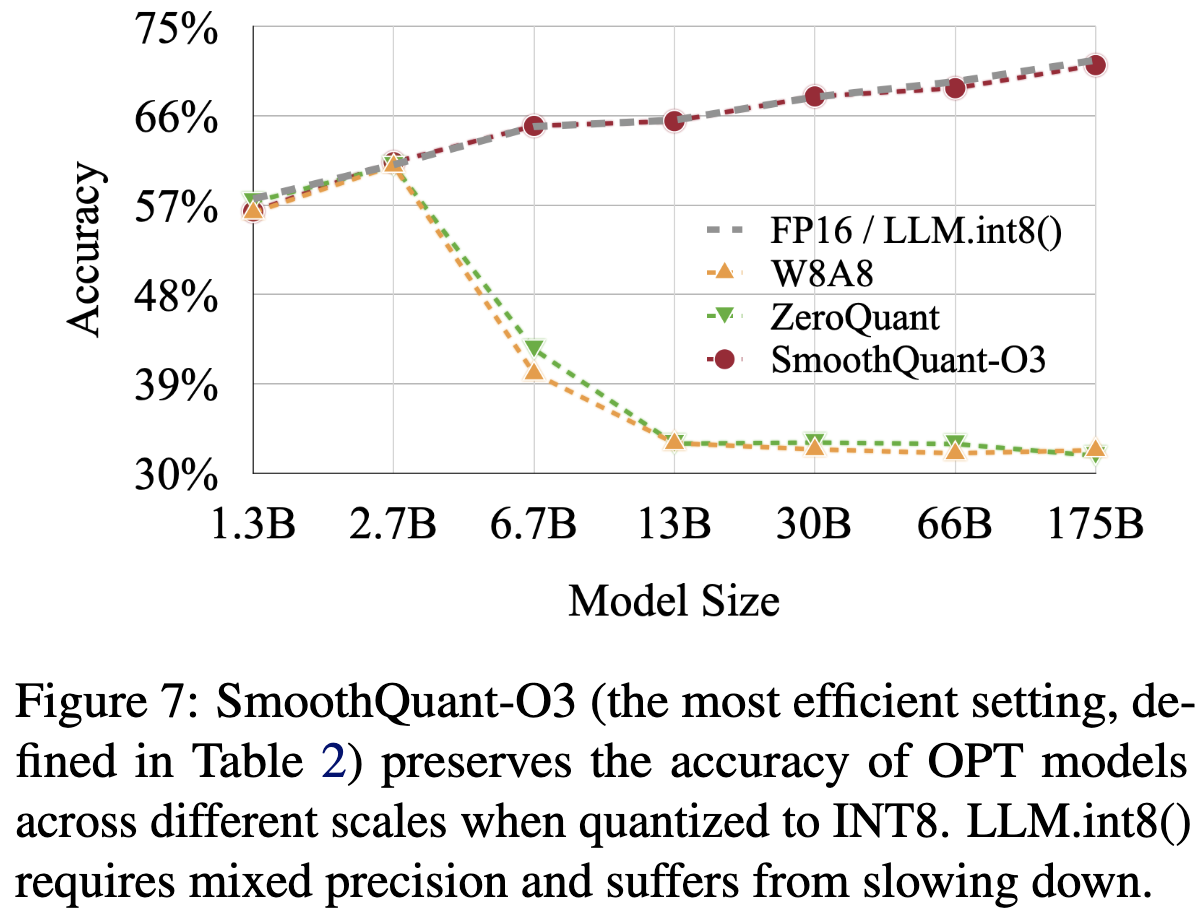
Results on LLMs of different sizes
- 모델 사이즈가 작아져도 성능을 유지한다
- FP16/LLM.int8()은 느려짐
-
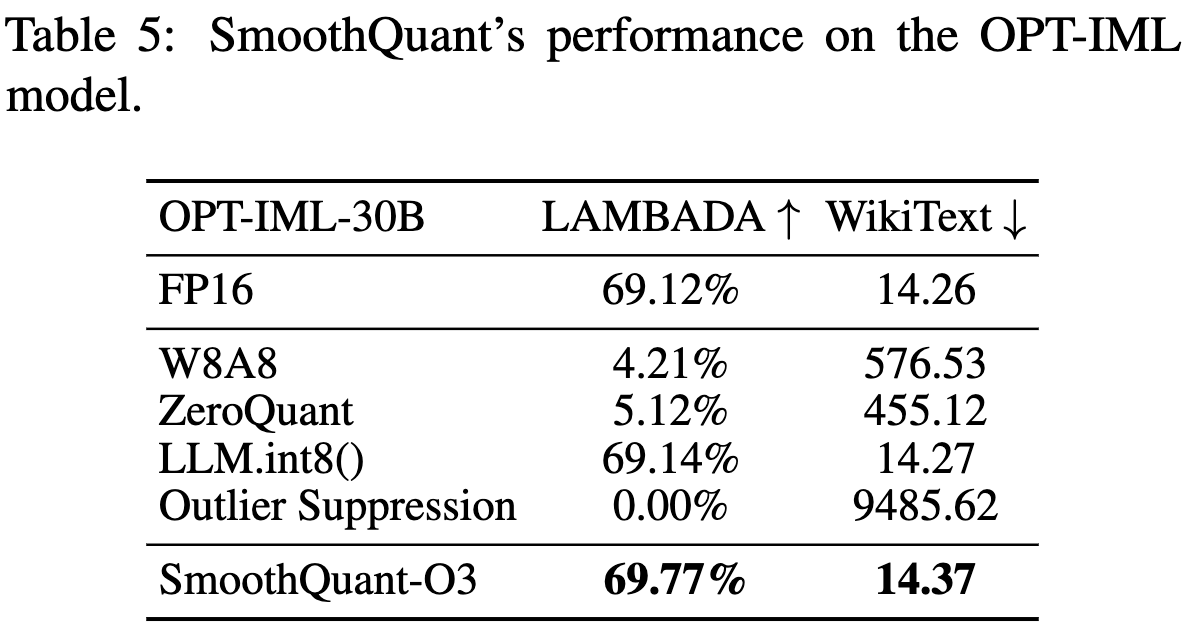
Results on Instruction-Tuned LLM
- vanilla LLM으로 실험하기 힘드니까, instructed-LLM으로 비교 실험.
- 결과적으로 smoothquant가 instruction-tuned LLM에 잘 적용할 수 있음.
-
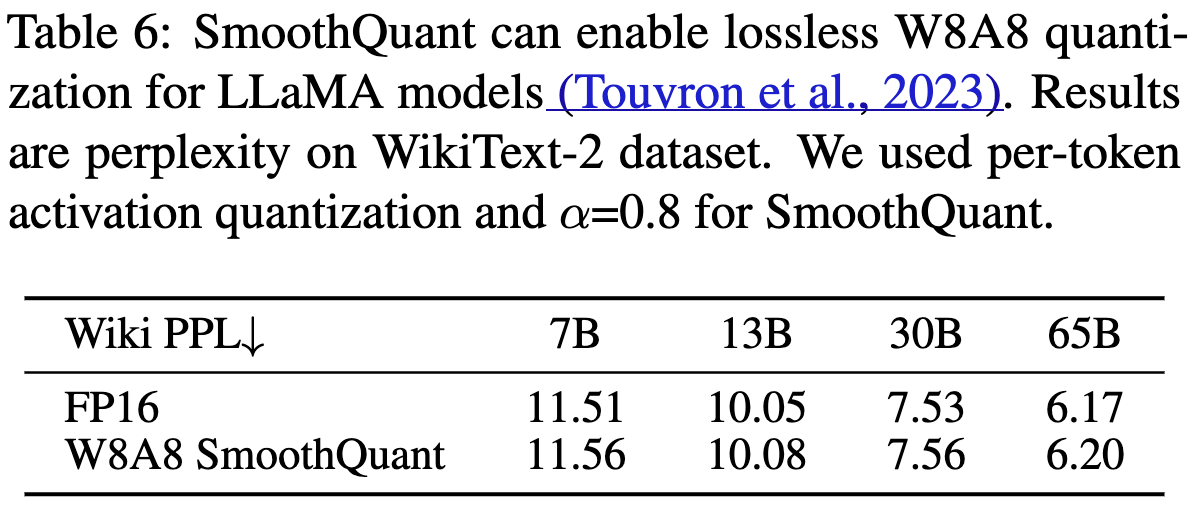
Results on LLaMA models
- 상대적으로 LLaMA 계열은 activation outlier issues가 다른 OPT나 BLOOM에 비해 심하지 않았음.
- 그럼에도 불구하고 LLaMA 모델에서도 성능 하락이 없었음
Speedup and Memory Saving: Memory Consumption in GPU and latency
-
Setting
- peak GPU memory 사용량 비교
- LLM.int8()만 accuracy 보존하면서 quantization하는 애여서 얘랑만 비교함
- NVIDIA A100 80GB
-
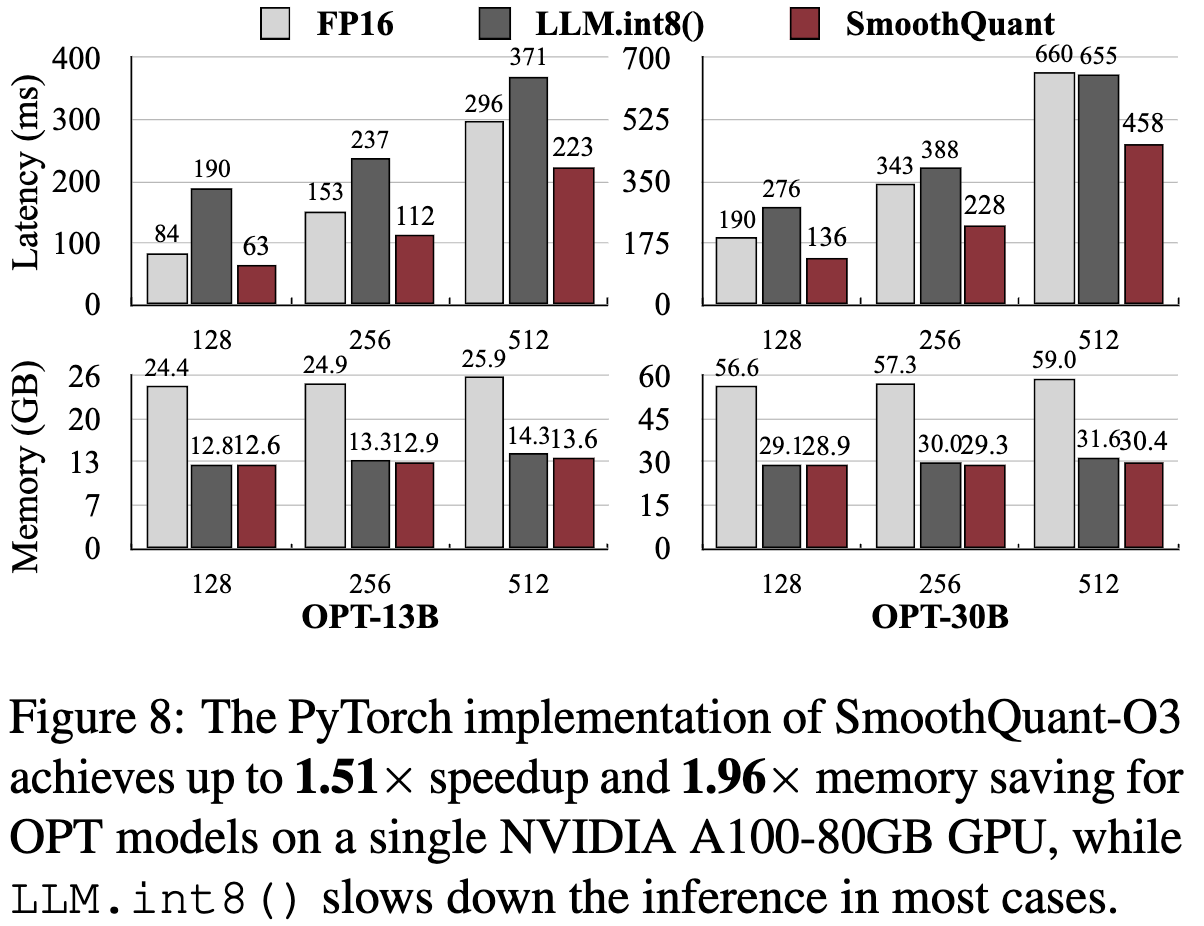
Context-stage: Pytorch Implementation
-
LLM.int8()보다 smoothquant가 메모리에서는 비슷하지만 속도는 빠름
- (1) Smoothquant는 int8 GEMMs 사용해서 계산 효율적으로 가능
- (2) LLM.int8()은 mixed-precision activation representation을 사용하기 때문에 large overhead가 있어서 속도가 느린 것 같다고 말함 (LLM.int8()은 int8/FP16 번갈아서 사용함)
- (성능 측면에서 LLM.int8()과 계속 비등비등함. 그래서 속도로 우리가 빠르다!를 계속 강조하고 있음. 결과적으로는 smoothquant가 inference할 때 속도
-
-
Context-stage: FasterTransformer Implementation
- Smoothquant 빠름
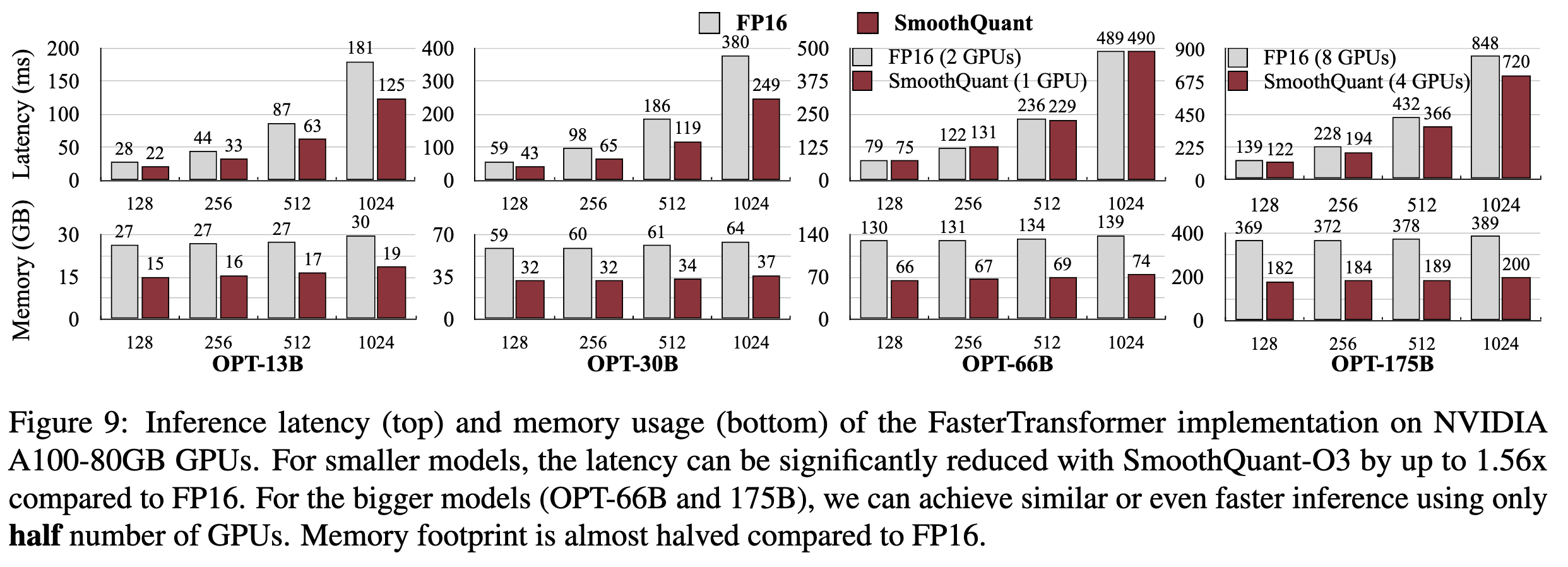
- Smoothquant 빠름
-
Decoding-stage
- 빠름!
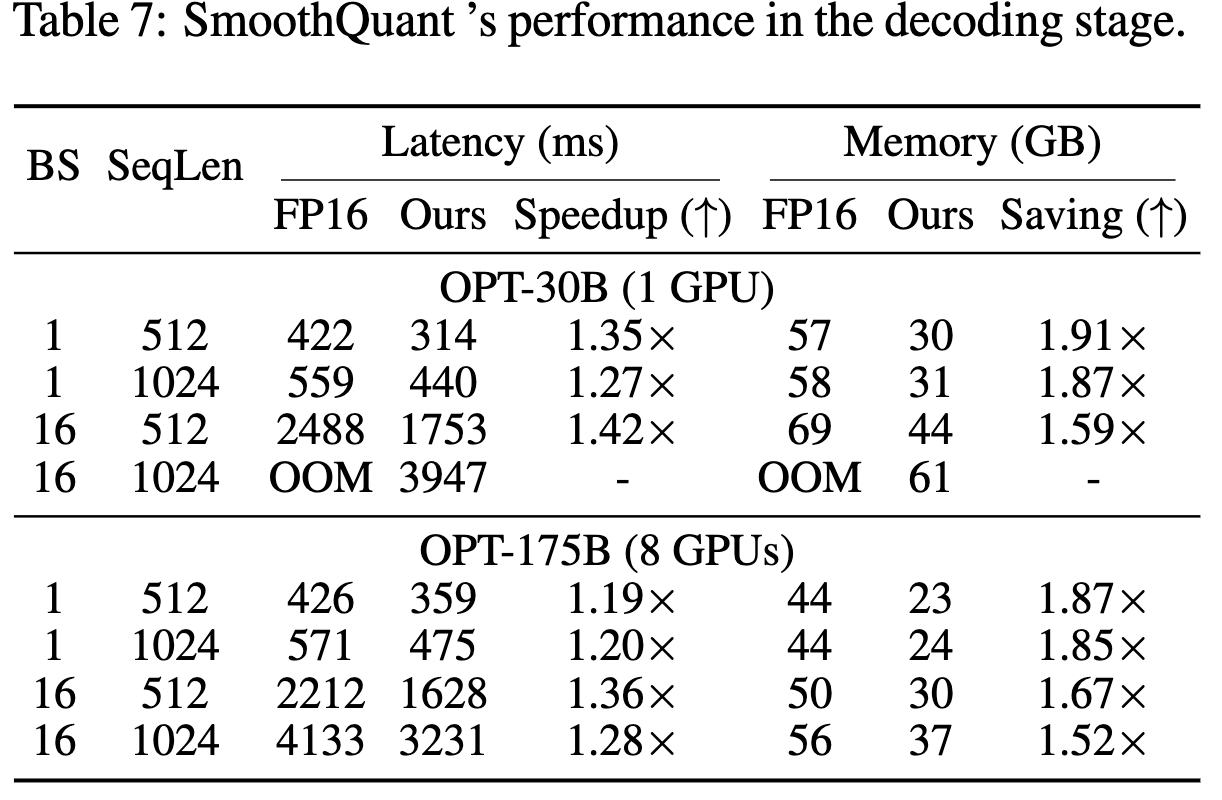
- 빠름!
Scaling Up: 530B Model Within a Single Node
엄청 큰 모델에서도 Single node 효율적으로 양자화 잘함.
a single node: 1대의 컴퓨터-node에 있는 GPU사용한다는 뜻
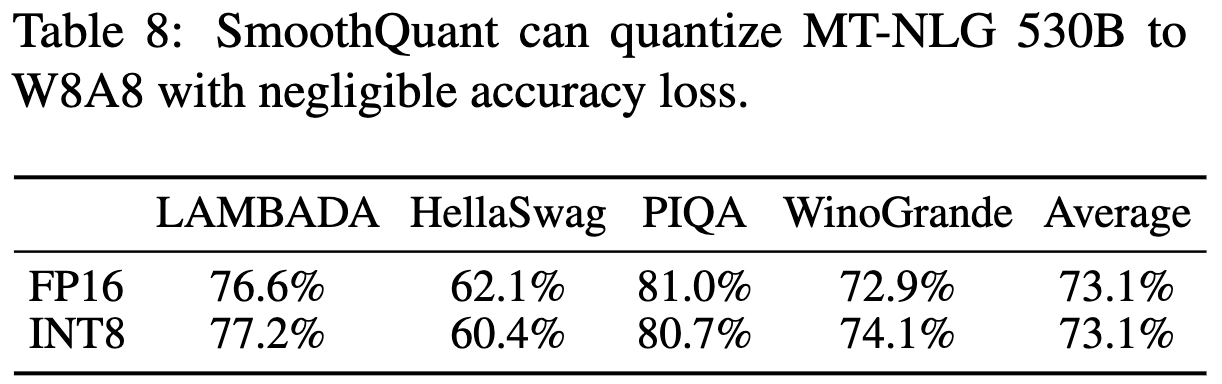
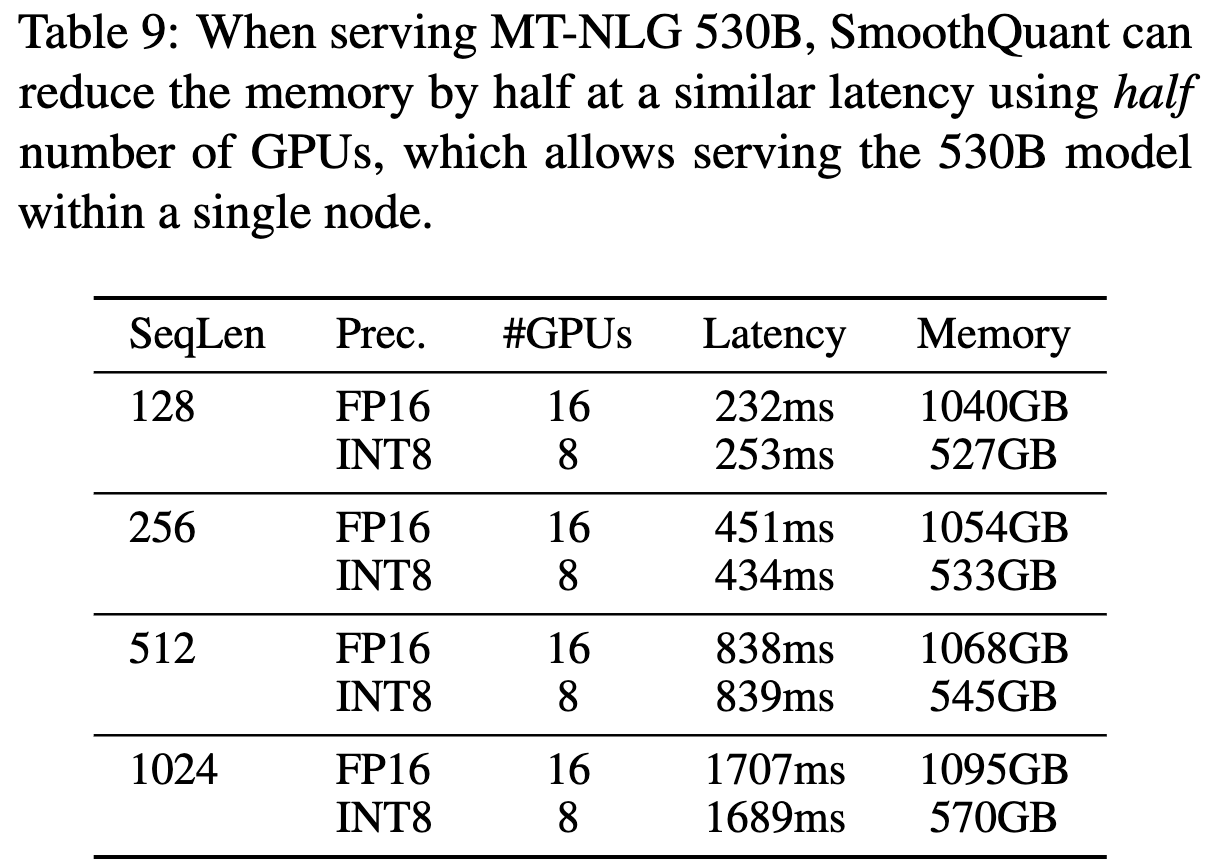
Ablation Study
-
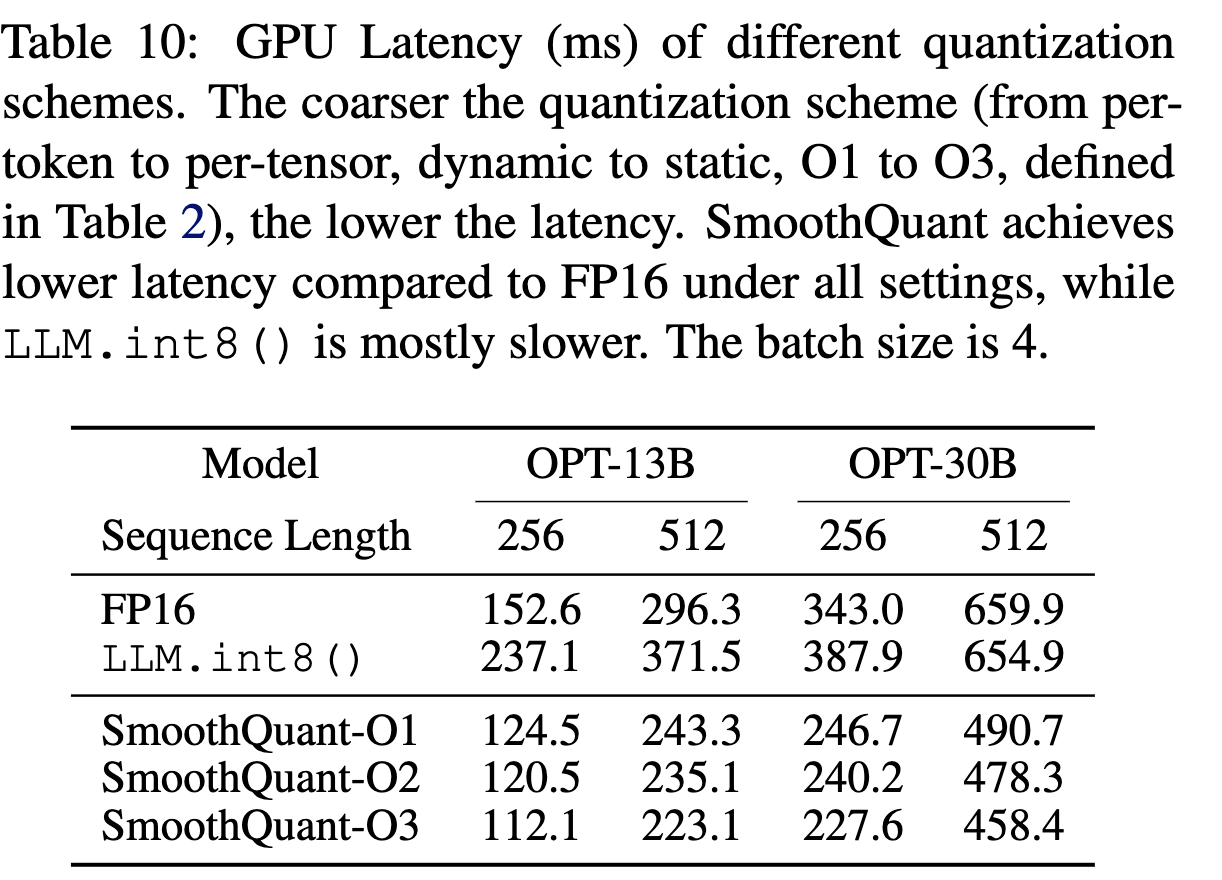
Quantization schemes
- O3이 efficiency 제일 좋음.
- LLM.int8()은 느림
-
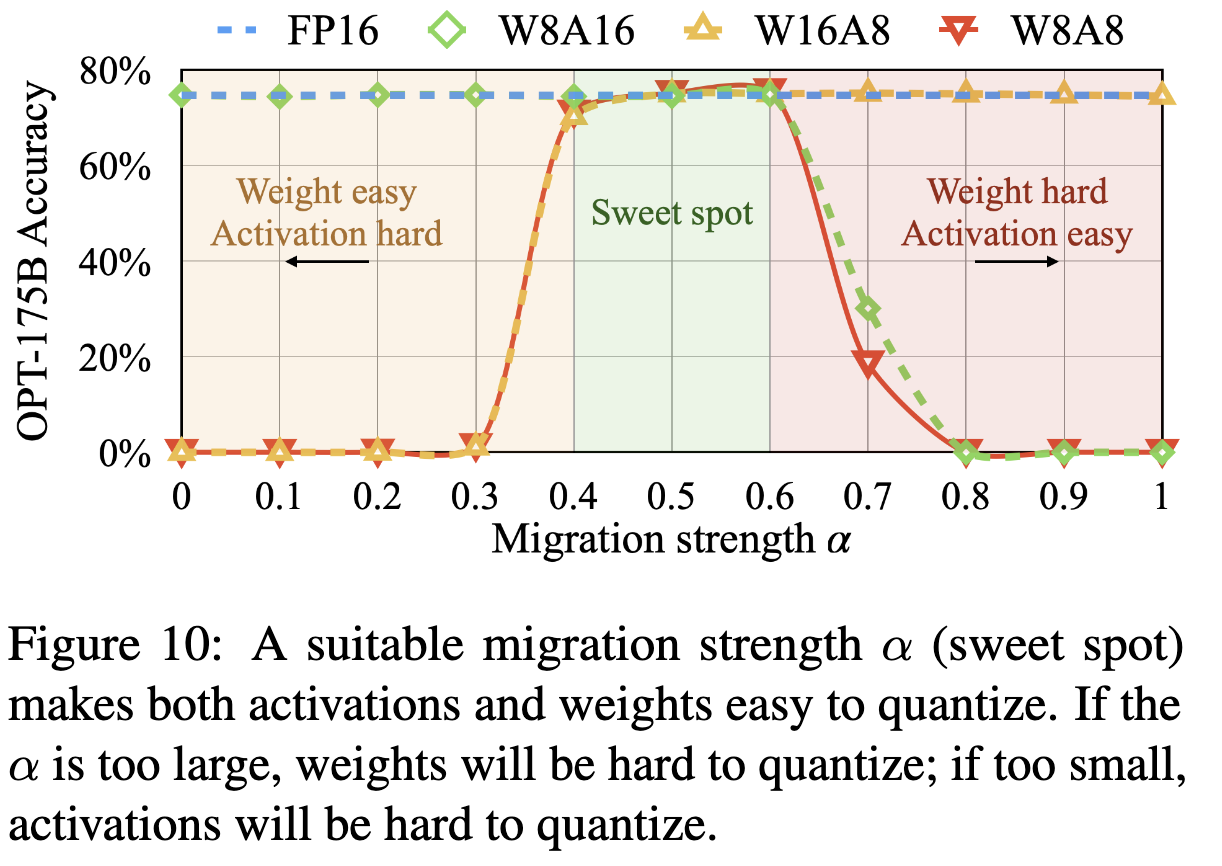
Migration strength
-
activation이랑 weights의 양자화를 얼마나 어렵게(difficulty)할지 quantization level 조절할 수 있도록 alpha 비율 조절 필요함.
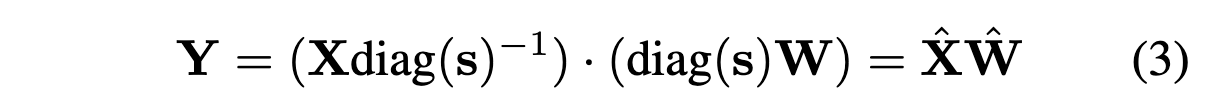
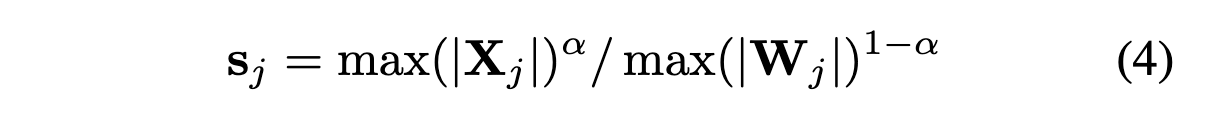
-
Conclusion
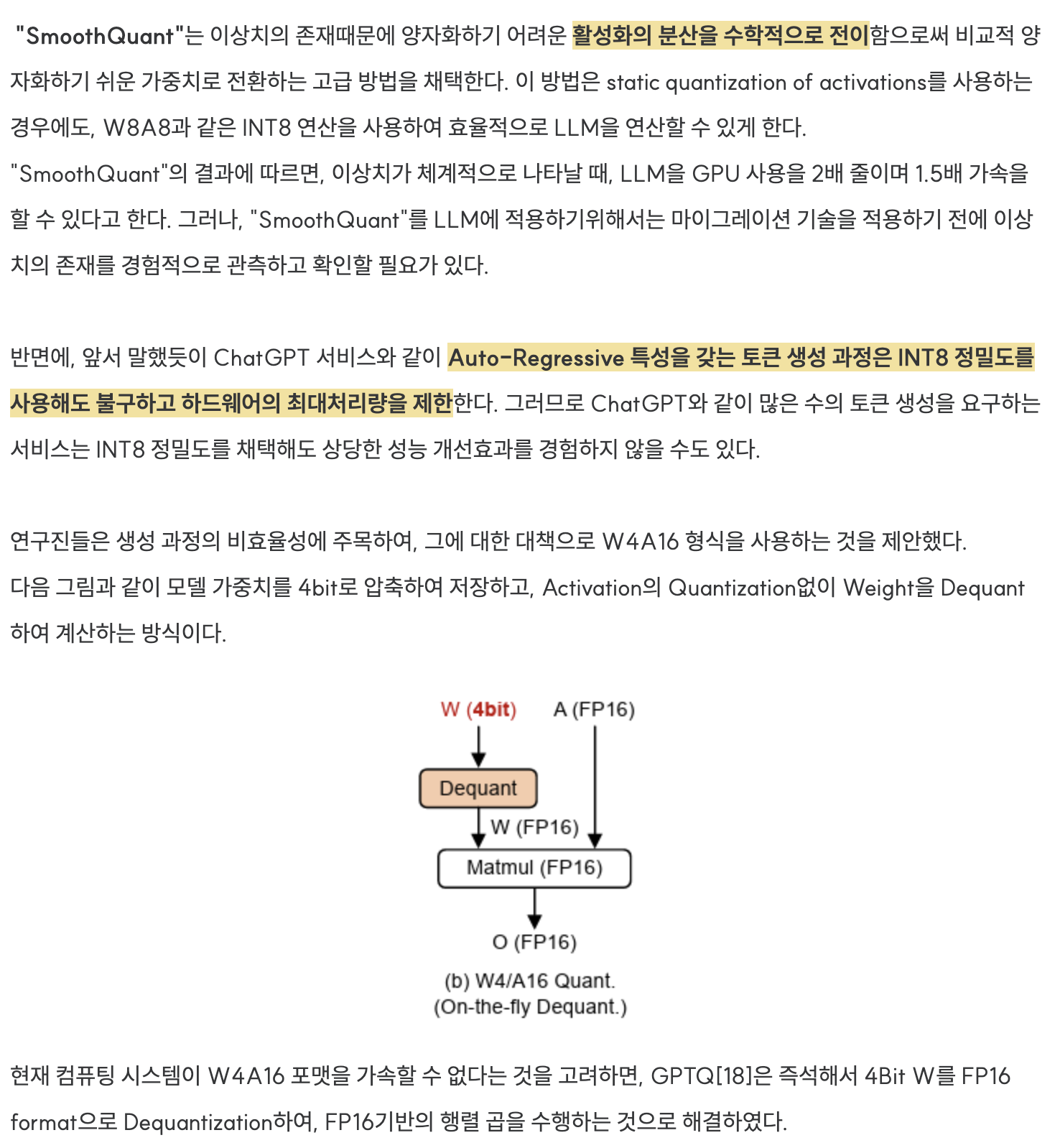
Discussion on Weight-Only Quantization
- weights-only quantization이랑은 비교 안하고, weights-activation quantization애들이랑 비교한 이유 설명
TensorRT-LLM
https://github.com/NVIDIA/TensorRT-LLM
: To maximize performance and reduce memory footprint, TensorRT-LLM allows the models to be executed using different quantization modes (refer to support matrix). TensorRT-LLM supports INT4 or INT8 weights (and FP16 activations; a.k.a. INT4/INT8 weight-only) as well as a complete implementation of the SmoothQuant technique.

activation, weight quantization에 대해서 잘 설명해주셔서 좋았습니다~!!