라이브러리 설명
웹의 특정 컴포넌트를 canvas 형태로 변경하고 싶을 때 사용하는 라이브러리
공식 문서
사용 방법
설치
npm install --save html2canvas
yarn add html2canvas사용
html2canvas(element).then(function(canvas) {
document.body.appendChild(canvas);
});html2canvas의 파라미터로 canvas형식으로 변환을 원하는 노드 객체를 넣어주면 된다.
const captureResult = () => {
html2canvas(document.getElementById("capture"), {
backgroundColor: "#000000",
}).then(function (canvas) {
const downloadLink = document.createElement("a");
downloadLink.download = "filename.png";
downloadLink.href = canvas.toDataURL();
downloadLink.click();
});
};내가 작성한 코드의 경우, 버튼 클릭시 캔버스를 이미지 형식으로 다운 받을 수 있도록 작성한 코드로 promise의 결과값으로 canvas를 받아 png 형식으로 다운로드 받을 수 있도록 해주었다.
원리
처음 캔버스로 바꿀 노드를 받아오게 되면, 해당 노드를 캔버스 내에 그리기 위해 클론하는 과정을 거친다.
// html2canvas/src/index.ts
const renderElement = async (element: HTMLElement, opts: Partial<Options>): Promise<HTMLCanvasElement> => {
if (!element || typeof element !== 'object') {
return Promise.reject('Invalid element provided as first argument');
}
// ... 생략
const cloneOptions: CloneConfigurations = {
allowTaint: opts.allowTaint ?? false,
onclone: opts.onclone,
ignoreElements: opts.ignoreElements,
inlineImages: foreignObjectRendering,
copyStyles: foreignObjectRendering
};
const documentCloner = new DocumentCloner(context, element, cloneOptions);
const clonedElement = documentCloner.clonedReferenceElement;
if (!clonedElement) {
return Promise.reject(`Unable to find element in cloned iframe`);
}노드를 클론하는 DocumentCloner는 재귀 형식으로 노드를 타고 내려가면서 clone을 생성한다.
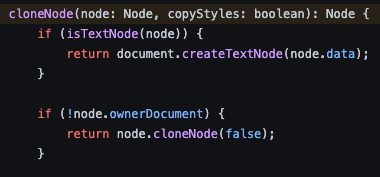
클론이 끝나고 나면, 원하던 컴포넌트의 높이와 넓이에 맞는 캔버스 객체를 하나 생성해준다.
// html2canvas/src/render/canvas/canvas-renderer.js
constructor(context: Context, options: RenderConfigurations) {
super(context, options);
this.canvas = options.canvas ? options.canvas : document.createElement('canvas');
this.ctx = this.canvas.getContext('2d') as CanvasRenderingContext2D;
if (!options.canvas) {
this.canvas.width = Math.floor(options.width * options.scale);
this.canvas.height = Math.floor(options.height * options.scale);
this.canvas.style.width = `${options.width}px`;
this.canvas.style.height = `${options.height}px`;
}
this.fontMetrics = new FontMetrics(document);
this.ctx.scale(this.options.scale, this.options.scale);
this.ctx.translate(-options.x, -options.y);
this.ctx.textBaseline = 'bottom';
this._activeEffects = [];
this.context.logger.debug(
`Canvas renderer initialized (${options.width}x${options.height}) with scale ${options.scale}`
);
}앞서 클론한 노드들을 바탕으로 해당 노드의 타입을 구분에 이에 맞춰 만들어진 캔버스안에 그려내는 방식으로 동작한다.
async renderNodeContent(paint: ElementPaint): Promise<void> {
this.applyEffects(paint.getEffects(EffectTarget.CONTENT));
const container = paint.container;
const curves = paint.curves;
const styles = container.styles;
for (const child of container.textNodes) {
await this.renderTextNode(child, styles);
}
if (container instanceof ImageElementContainer) {
try {
const image = await this.context.cache.match(container.src);
this.renderReplacedElement(container, curves, image);
} catch (e) {
this.context.logger.error(`Error loading image ${container.src}`);
}
}
if (container instanceof CanvasElementContainer) {
this.renderReplacedElement(container, curves, container.canvas);
}
if (container instanceof SVGElementContainer) {
try {
const image = await this.context.cache.match(container.svg);
this.renderReplacedElement(container, curves, image);
} catch (e) {
this.context.logger.error(`Error loading svg ${container.svg.substring(0, 255)}`);
}
}
...
...

재..재밌다!!