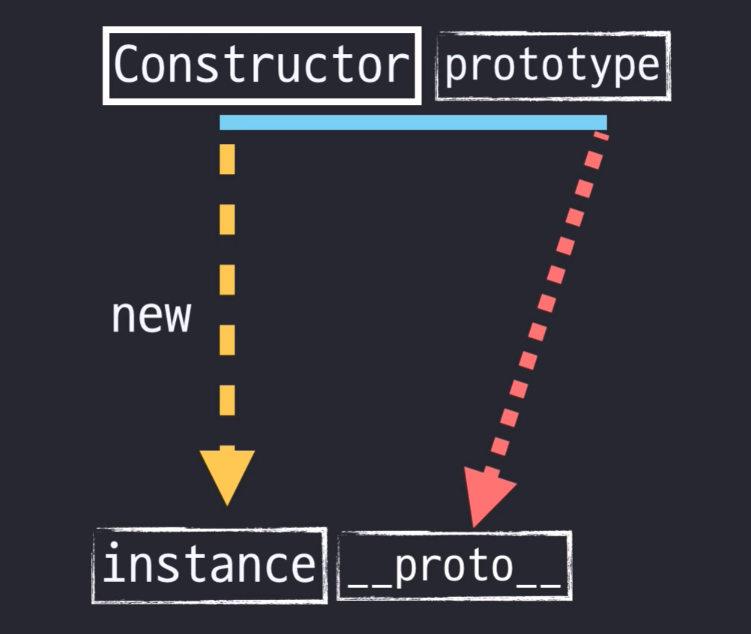
[Constructor]
class 내에서 객체를 생성하고 초기화하기 위한 특별한 메서드
- 객체를 만들고 객체의 초기세팅을 한다.
class Polygon {
constructor() {
this.name = 'Polygon';
}
}
const poly1 = new Polygon();
console.log(poly1.name);
// expected output: "Polygon"- 함수에 new를 붙이면 객체를 생성하는 생성자가 된다.
[Prototype]
Object.prototype 속성은 Object 프로토타입(원형) 객체를 나타낸다
function Person (name, first, second){
this.name = name;
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
Person.prototype.sum = function (){
return `prototype : ` + (this.first + this.second);
}
let kim = new Person('kim', 10, 20);
console.log(kim.sum()); //30[Class]
함수이다. class 표현식과 class 선언 두 가지 방법을 제공
class Person{
construtor(name, first, second){
this.name = name;
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
sum(){
return this.first + this.second;
}
}
let kim = new Person('kim', 10, 20);
console.log(kim.sum()); //30[inheritance(상속)]
- extends에 class명을 쓰면 class를 확장한다는 의미이다.
class Person{
construtor(name, first, second){
this.name = name;
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
sum(){
return this.first + this.second;
}
}
class PersonPlus extends Person {
avg(){
return (this.first + this.second)/2;
}
}
let kim = new PersonPlus('kim', 10, 20);
console.log(kim.avg()); //15[Super]
상속받는 부모class와 자식class의 중복된 부분을 나타낸다
-
super() : 부모class의 생성자(constructor)
-
super.메소드 : 부모class의 메소드가 호출
class Person{
construtor(name, first, second){
this.name = name;
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
sum(){
return this.first + this.second;
}
}
class PersonPlus extends Person {
constructor(name, first, second, third){
super(name, first, second);
this.third = third;
}
sum(){
return super.sum() + this.third;
}
avg(){
return (this.first + this.second + this.third)/3;
}
}
let kim = new PersonPlus('kim', 10, 20, 30);
console.log(kim.sum()); //20[ _ _ proto _ _ ]
- 객체가 생성될 때 조상이었던 함수의 Prototype Object를 가리킨다.
let superObj = {superVal:"super"}
let subObj = {subVal:"sub"}
subObj.__proto__ = superObj;
console.log(subObj.subVal); // "sub"
console.log(subObj.superVal); // "super"
subObj.superVal = "sub";
console.log(subObj.superVal); // "sub"
console.log(superObj.superVal); // "super"[Object.create()]
- proto 의 기능을 대체할 수 있다.
let superObj = {superVal:"super"}
let subObj = Object.create(superObj);
subObj.subVal = "sub";
console.log(subObj.subVal); // "sub"
console.log(subObj.superVal); // "super"
subObj.superVal = "sub";
console.log(subObj.superVal); // "sub"
console.log(superObj.superVal); // "super"