들어가기 전에
만약 데이터베이스에서 어떤 데이터를 읽어와서 인스턴스를 생성해야 할 때 또는 네트워크를 거쳐서 HTTP 요청을 보내서 가져온 데이터를 기반으로 인스턴스를 만들어야 할 때, 매번 이런 방식으로 데이터베이스나 네트워크를 다녀오게 되면 해당 인스턴스를 만들 때마다 시간이 오래 걸리고, 리소스도 많이 사용하게 될 것이다.
이런 문제를 해결할 수 있는 방법이 있을까?
프로토타입 패턴
프로토타입 패턴이란?
프로토타입 패턴(prototype pattern)은 소프트웨어 디자인 패턴 용어로, 생성할 객체들의 타입이 프로토타입인 인스턴스로부터 결정되도록 하며, 인스턴스는 새 객체를 만들기 위해 자신을 복제(clone)하게 된다.
이처럼 프로토타입 패턴이란 기존 인스턴스를 복제하여 새로운 인스턴스를 만드는 방법을 말한다. 기존 객체를 응용해서 새로운 인스턴스를 만들 때 유용하게 사용할 수 있다.
즉, 매번 데이터베이스나 네트워크를 다녀오면서 객체를 생성하는 대신에 기존에 이미 데이터베이스나 네트워크를 호출을 해서 만들어진 객체를 가지고 그 안에 있는 모든 데이터를 복제해서 새로운 인스턴스를 만들고, 만들어진 새로운 인스턴스에서 원하는 값만 일부 변경해서 더 효율적으로 사용할 수 있게 하는 것이다.
프로토타입 패턴 구조
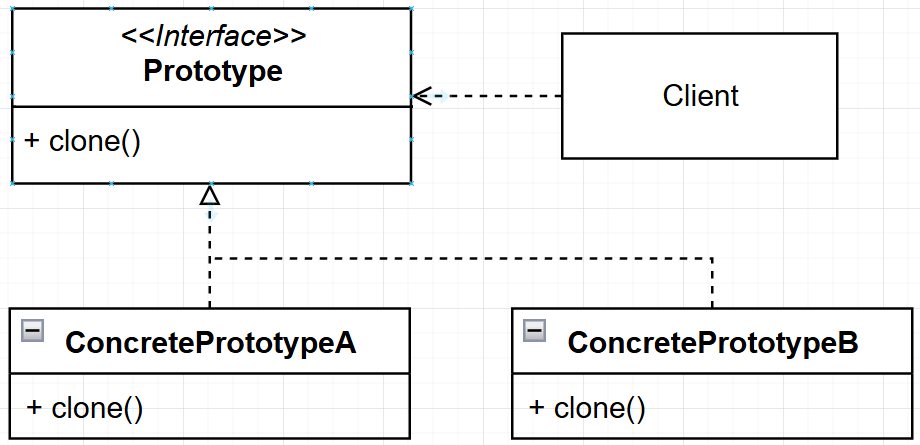
프로토타입 인터페이스에서 제공하는 clone()이라는 추상 메서드를 복제 기능을 제공할 클래스들이 해당 인스턴스를 구현하도록 만들어 주는 것이다.
ConcretePrototypeA 라는 타입의 인스턴스를 어떤 식으로 복제할 지 clone() 추상 메서드를 구현해서 정의하고, 클라이언트가 사용할 때 clone() 이라는 메서드만 사용하면 복제를 받을 수 있게끔 해주는 패턴인 것이다.
결론은 클라이언트가
clone()메서드 사용 시 복제를 받을 수 있게 해주는 것
프로토타입 패턴 장단점
장점
- 복잡한 객체를 만드는 과정을 숨길 수 있다.
- 클라이언트는 구체적인 형식을 몰라도 객체를 생성할 수 있다.
- 상황에 따라서 기존 객체를 복제하는 과정이 새 인스턴스를 만드는 것보다 비용(시간 또는 메모리)적인 면에서 효율적일 수도 있다.
- 추상적인 타입을 리턴할 수 있다.
단점
- 복제한 객체를 만드는 과정 자체가 복잡할 수 있다.
- 특히 순환 참조가 있는 경우
- A -> B -> C -> A
- 특히 순환 참조가 있는 경우
프로토타입 패턴 예제
프로토타입 적용 전
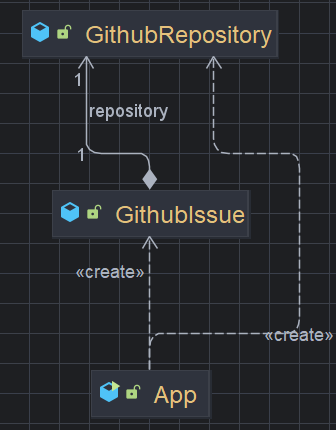
GithubIssue 클래스
public class GithubIssue {
private int id;
private String title;
private GithubRepository repository;
public GithubIssue(GithubRepository repository) {
this.repository = repository;
}
// getter & setter
public String getUrl() {
return "https://github.com/"
+ repository.getUser() + "/" + repository.getName() + "/issues/" + id;
}
}GithubRepository 클래스
public class GithubRepository {
private String user;
private String name;
// getter & setter
}App 실행 클래스 및 실행 결과
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GithubRepository githubRepository = new GithubRepository();
githubRepository.setUser("John");
githubRepository.setName("live-study");
GithubIssue githubIssue = new GithubIssue(githubRepository);
githubIssue.setId(1);
githubIssue.setTitle("1주차 과제: JVM은 무엇이며 자바 코드는 어떻게 실행될까?");
String url = githubIssue.getUrl();
System.out.println(url);
// 만약 새로운 githubIssue를 추가하려면?
}
}https://github.com/ship/live-study/issues/1프로토타입 패턴 적용 후
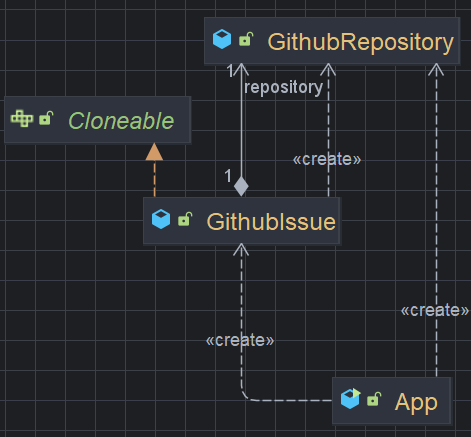
clone()은 Object 클래스 내부에 있다. 하지만 해당 메서드는 equals()처럼 그냥 사용하진 못한다. 그 이유는 Object 클래스 내부를 보면 알 수 있다.
@IntrinsicCandidate
protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;Object 내부를 보면 clone() 메서드가 protected로 되어있는 것을 볼 수 있다. 따라서 해당 메서드를 사용하기 위해선 복제하려는 클래스가 Clonable 인터페이스를 구현해야 한다. 만약 복제하려는 객체의 클래스가 Clonable 인터페이스를 구현하고 있지 않을 경우 CloneNotSupportException이 발생한다.
또한 clone() 메서드는 기본적으로 얕은 복사를 지원하지만 재정의를 통해 깊은 복사를 할 수도 있다.
얕은 복사와 깊은 복사
얕은 복사는
Stack에 참조하고 있는 단순 주소값을 복제하는 것이다.
깊은 복사는 새로운 객체에Heap데이터를 복제하는 것이다.
GithubIssue 클래스
public class GithubIssue implements Cloneable {
private int id;
private String title;
private GithubRepository repository;
public GithubIssue(GithubRepository repository) {
this.repository = repository;
}
// getter & setter
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object object) {
if (this == object) return true;
if (object == null || getClass() != object.getClass()) return false;
GithubIssue that = (GithubIssue) object;
return getId() == that.getId()
&& Objects.equals(getTitle(), that.getTitle())
&& Objects.equals(repository, that.repository);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(getId(), getTitle(), repository);
}
public String getUrl() {
return "https://github.com/"
+ repository.getUser() + "/" + repository.getName() + "/issues/" + id;
}
}위처럼 Clonable을 구현해야만 clone() 메서드를 사용할 수 있으며 super.clone()을 리턴하는 경우 얕은 복사를 수행한다. 하지만 clone() 메서드를 아래와 같이 구현한다면 깊은 복사를 수행하게 만들 수도 있다.
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
GithubRepository githubRepository = new GithubRepository();
githubRepository.setUser(this.repository.getUser());
githubRepository.setName(this.repository.getName());
GithubIssue githubIssue = new GithubIssue(githubRepository);
githubIssue.setId(this.id);
githubIssue.setTitle(this.title);
return githubIssue;
}이 두 방식에 대한 자세한 결과는 실행 결과 부분에서 다시 언급하겠다.
GithubRepository
public class GithubRepository {
private String user;
private String name;
// getter & setter
}App 실행 클래스 및 실행 결과
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
GithubRepository githubRepository = new GithubRepository();
githubRepository.setUser("John");
githubRepository.setName("live-study");
GithubIssue githubIssue = new GithubIssue(githubRepository);
githubIssue.setId(1);
githubIssue.setTitle("1주차 과제: JVM은 무엇이며 자바 코드는 어떻게 실행될까?");
String url = githubIssue.getUrl();
System.out.println("githubIssue.getUrl(): " + url);
GithubIssue clone = (GithubIssue) githubIssue.clone();
System.out.println("clone.getUrl(): " + clone.getUrl());
System.out.println("clone != githubIssue: " + (clone != githubIssue));
System.out.println("clone.equals(githubIssue): " + clone.equals(githubIssue));
System.out.println("clone.getClass() == githubIssue.getClass(): " + (clone.getClass() == githubIssue.getClass()));
System.out.println("clone.getRepository() == githubIssue.getRepository(): " + (clone.getRepository() == githubIssue.getRepository()));
}
}githubIssue.getUrl(): https://github.com/ship/live-study/issues/1
clone.getUrl(): https://github.com/ship/live-study/issues/1
clone != githubIssue: true
clone.equals(githubIssue): true
clone.getClass() == githubIssue.getClass(): true
clone.getRepository() == githubIssue.getRepository(): true얕은 복사를 수행했을 땐 전부 true가 나온 것을 확인할 수 있다. 이제 clone()을 구현해서 깊은 복사를 수행했을 때의 결과를 봐보자.
githubIssue.getUrl(): https://github.com/ship/live-study/issues/1
clone.getUrl(): https://github.com/ship/live-study/issues/1
clone != githubIssue: true
clone.equals(githubIssue): false
clone.getClass() == githubIssue.getClass(): true
clone.getRepository() == githubIssue.getRepository(): false깊은 복사를 했을 땐 GithubRepository의 객체가 새로 생성되기 때문에 결과가 바뀐 것을 볼 수 있다.