4 Major Characteristics of OOP
- Encapsulation (캡슐화)
- Inheritance (상속)
- Polymorphism (다형성)
- Abstraction (추상화)
For a deeper introduction into the basic concepts:
What is OOP?(Youtube) + Intro to OOP
Benefits of OOP
Encapsulation

- Groups data and function into one single unit
- Hiding: hides implementation and exposes methods(behavior)
- Good for loose coupling: implementation is always revisable
Encapsulation can be implemented in different ways and refer to a range of practices depending on the language. In practice (in javascript), it primarily means controlling access to attributes and defining specific means of those attributes through methods.
In JS, there are several ways encapsulation can be achieved: 1. via functional scope, 2. closures, 3. private variables (with classes, introduced in ES6.) This link contains detailed examples.
Inheritance
Derived classes can have characteristics of its own that do not exist in the parent class, and also methods with the same name can be overrided to trigger different behavior than the parent class.
Polymorphism
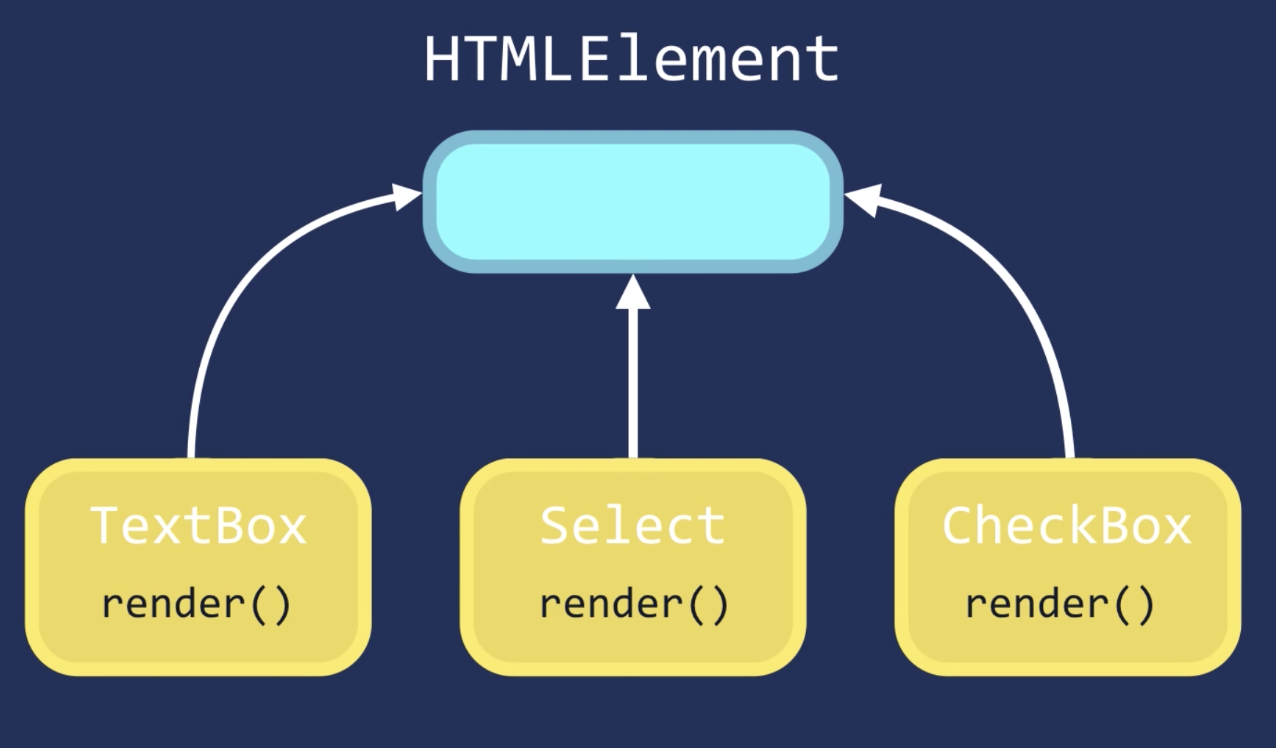
Basically one method name can take on different forms and behavior depending on the type of object.
Abstraction
Unlike javascript, Typescript has interface that does not expose the implementation details at all - it only includes properties and methods.
How JS implements OOP patterns
Prototypal OOP
In more "sane" object-oriented languages, you create a class, you spawn objects off of them, and you're done with it. If you need to make a global change you do it at the class level, and all instantiated objects pick up that change automatically. But JavaScript is NOT a "sane" object-oriented language.
..
Instead, JavaScript uses what's called prototypal OOP. For the best possible explanation of how this stacks up to classical OOP, I recommend reading The Good Parts, by Douglas Crockford. ~Steve Kwan
Closure module pattern (encapsulation)
function makeCounter() {
let value = 0;
return {
increase: function() {
value++;
},
decrease: function() {
value--;
},
getValue: function() {
return value;
}
}
}
let counter1 = makeCounter()
counter1.increase()
counter1.getValue() // 1
let counter2 = makeCounter()
counter2.decrease()
counter2.decrease()
counter2.getValue() // -2Inheritance (prototype inheritance model)
Prototypal Inheritance
Adds new properties and methods to existing objects by setting its prototype object (e.gobject.__proto__)Pseudoclassical Inheritance
Has become unnecessary with ES6. The idea is to create an “inherited” function that assists in associating the child class to the parent classFunctional Inheritance
Inheriting properties by applying an augmenting function to an object instance. The defined augmenting function employs dynamic object extension to add additional properties and methods to an object instance.
For detailed examples of all three types of inheritance, check out this link and this link
Polymorphism
Sub-type
... involves creating derivative objects from a parent object. It’s can be called Inclusion Polymorphism, Subclassing, or Inheritance. Derivatives objects can then override a method from the parent and it’ll still work. ~link
class Human {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name
}
sayHi() {
console.log(`Hi! My name is ${name}`)
}
}
class Developer extends Human {/* ... */}
class Designer extends Human {/* ... */}
class Developer extends Human () {
sayHi() {
console.log(`Hi! My name is ${name}. I am a developer.`)
}
}
class Designer extends Human () {
sayHi() {
console.log(`Hi! My name is ${name}. I am a designer.`)
}
}
const zell = new Human('Zell')
const vincy = new Developer('Vincy')
const tim = new Designer('Tim')
zell.sayHi() // Hi! My name is Zell.
vincy.sayHi() // Hi! My name is Vincy. I am a developer.
tim.sayHi() // Hi! My name is Tim. I am a designer.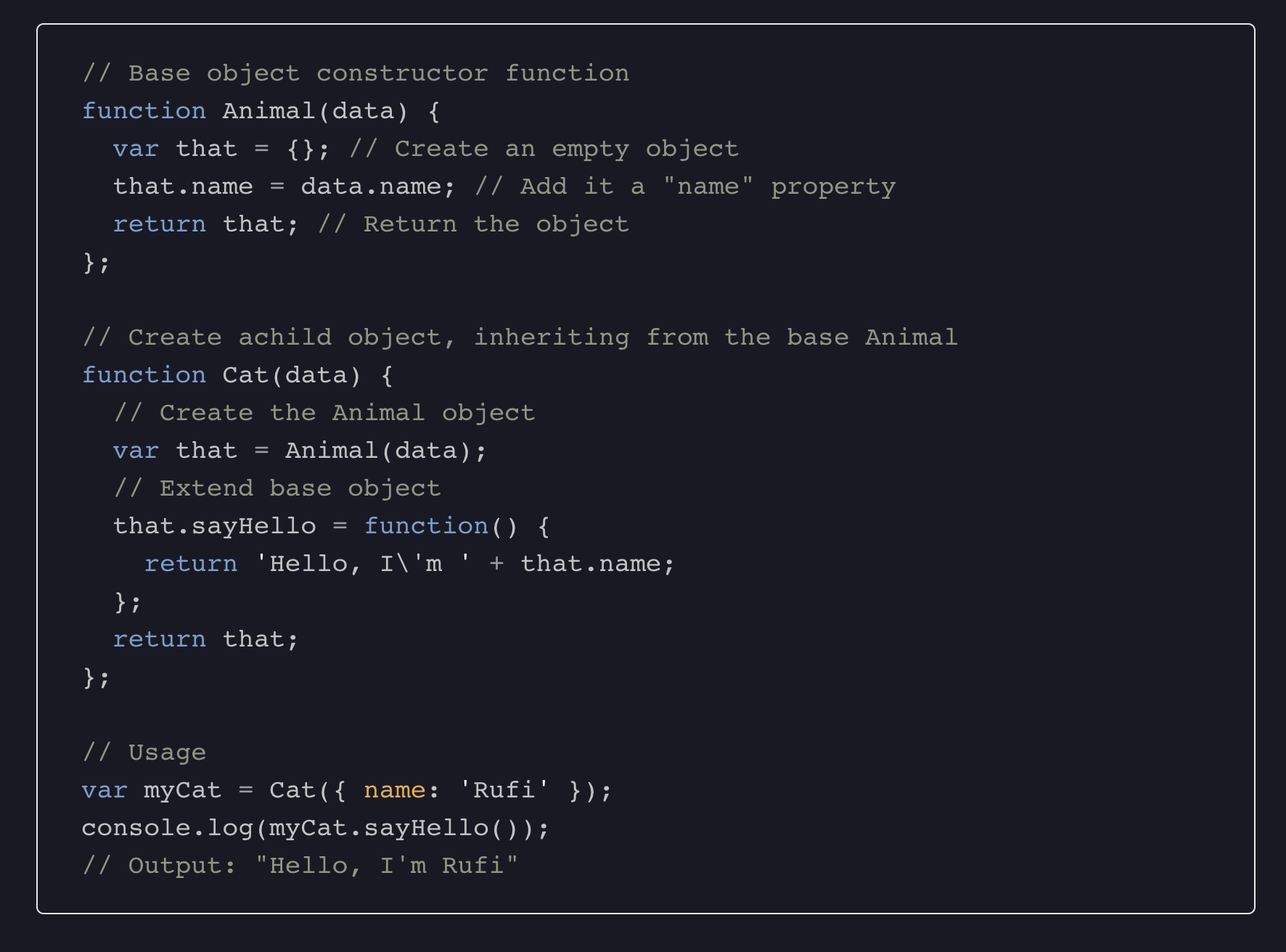
Adhoc
...used to describe creation of something without previous planning. In other words, Adhoc Polymorphism means to change something from one form to another on the spot.~link
-
Forms of adhoc polymorphism include: 1. operator overloading, 2. function overloading, and 3. coercion polymorphism.
-
Operator overloading:
// Adding numbers
1 + 1 // Results in 2
// Adding Strings
'Hello' + ' ' + 'World' // Results in 'Hello World'
// Adding Numbers to Strings
1 + 'up' // Results in '1up'Function overloading:
functions do something different depending on the argument passed onto it
//c++
// Volume of a Cube.
int Volume(int s) {
return s * s * s;
}
// Volume of a Cuboid.
long Volume(long l, int b, int h) {
return l * b * h;
}function volumeCuboid (length, breadth, height) {
return length * breadth * height
}
function volumeCube (length) {
return volumeCuboid(length, length, length)
}
// Overloading happens here
function calculateVolume (...args) {
if (args.length === 3) return volumeCuboid(...args)
return volumeCube(args[0])
}function createShape (size, shape) {
if (shape === 'triangle') return new Triangle(/* ... */)
if (shape === 'rectangle') return new Rectangle(/* ... */)
if (shape === 'square') return new Square(/* ... */)
}Coercion overloading:
..refers to type coercion, which converts the value from one type to another when evaluating them
Parametric
- polymorphism that relates to 'parameters'
does not care what goes in and out - Data that can contain many types of data (arrays, objects)
- Functions that can work with many types of data (e.g.
map,Object.assign)
Takes in an object or array and spits out an object or array, and it doesn't matter what that object or array contains
References
Types of Inheritance in Javascript
Polymorphism in Javascript - this link describes pseudoclassical inheritance in confusing terms, use other resources for inheritance types
