서론
글을 쓰게 된 계기
- 개발 중에 종종 Querydsl의 추상화 기능에 의존해 실제 데이터베이스 쿼리의 형태를 면밀히 검토하지 않는 경우가 많은 것 같다. → 저의 이야기 입니다…
- 특히, 단일 쿼리에서 필요한 모든 정보를 얻기 위해 엔티티를 직접 select 문에 포함시키는 실수를 범하기 쉽다. 아래 코드가 바로 그 코드이다.
queryFactory .select(Projections.fields(Person.class, person.name, person.age, Person.Orders, // Person의 Orders객체를 직접 참조, 1(Person) : N(Orders) Person.Projects // Person의 Projects객체를 직접 참조, 1(Person) : N(Projects) )) .from(person) .where(person.age.gt(18)) .fetch();- 위와 같은 쿼리는 다음과 같은 장점이 있습니다.
- 이런 방식으로 쿼리를 작성하면
Person와Orders,Person와Projects간의 관계가 명확하게 드러난다. 이는 코드의 가독성을 높이고, 엔티티 간 관계를 이해하기 쉽게 만들어 줍니다. - 관련 엔티티를 직접 참조함으로써, 별도의 조인 문법이나 복잡한 표현 없이도 관련 데이터를 쉽게 조회할 수 있다.
- 엔티티 간의 관계가 코드 상에서 직접적으로 표현되므로, 나중에 이 관계가 변경되거나 업데이트되어야 할 때, 관련 코드를 찾고 수정하기가 더 쉽다.
- 이런 방식으로 쿼리를 작성하면
- 위와 같은 쿼리는 다음과 같은 장점이 있습니다.
- 하지만 위와같은 장점도 있지만 아래와 같은 단점들도 존재합니다.
Personentity에서Orders와Projects같은 1:N 관계 데이터를 직접 참조하면, 대량의 데이터를 불러와야 해서 메모리 사용, 처리 시간, 네트워크 부하가 증가할 수 있다.- 한 엔티티의 인스턴스와 관련된 모든 데이터를 함께 불러오는 경우, 데이터가 최신 상태가 아니거나 다른 트랜잭션에 의해 변경되었을 가능성이 있어 데이터 불일치가 발생할 수 있다.
- 관련 데이터를 모두 불러오려고 하면 쿼리가 복잡해지고, 이로 인해 쿼리의 작성 및 유지 관리가 어려워진다.
- 모든 관련 데이터를 불러오는 것은 필요한 데이터만을 캡슐화하는 객체 지향 설계 원칙에 어긋나며, 이로 인해 객체의 크기가 커지고 관리가 어려워질 수 있다.
- 그래서 이러한 단점들이 있기에 밑에서 수정후 메모리 성능 및 시간을 측정해 어느정도의 효율을 뽑아냈는지 확인해보겠다!
본론
기본 세팅
- Entity들의 연관관계
@Entity @Table(name = "categorys") public class Category { @Id @GeneratedValue private Long id; private String name; private String description1; private String description2; private String description3; @OneToMany(mappedBy = "category", fetch = FetchType.LAZY, cascade = CascadeType.ALL, orphanRemoval = true) private List<Product> products = new ArrayList<>(); } @Entity @Table(name = "products") public class Product { @Id @GeneratedValue private Long id; private String name; private Double price; @ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY) @JoinColumn(name = "category_id") private Category category; }- Category와 Product : 일대다(1:N) 관계. 한
Category는 여러Product를 가질 수 있습니다.
- Category와 Product : 일대다(1:N) 관계. 한
테스트 진행하기 1 → 객체로 Select 해오기
- QueryDsl로 Select 진행시 Field에 JPA Entity를 추가하기
@NoArgsConstructor public class ProductDetails1 { private Long id; private String name; private Double price; private Category category; // Category 객체 전체 다 포함 }@Test @DisplayName("Product 안에 category 데이터 다 가져오기") public void test1() { em.flush(); em.clear(); System.out.println("------------ 영속성 컨텍스트 비우기 -----------\n"); JPAQueryFactory queryFactory = new JPAQueryFactory(em); queryFactory .select(Projections.fields(ProductDetails1.class, product.id.as("productId"), product.name.as("productName"), product.price.as("productPrice"), product.category.as("category"))) .from(product) .where(product.price.gt(0)) .orderBy(product.name.asc()) .fetch(); }- Hibernate를 확인해보면 다음과 같다.
Hibernate: select product0_.id as col_0_0_, product0_.name as col_1_0_, product0_.price as col_2_0_, product0_.category_id as col_3_0_, category1_.id as id1_1_, category1_.description1 as descript2_1_, category1_.description2 as descript3_1_, category1_.description3 as descript4_1_, category1_.name as name5_1_ from products product0_ inner join categorys category1_ on product0_.category_id=category1_.id where product0_.price>? order by product0_.name asc - 보는것과 같이 Category 전체 데이터를 로드하고 있다. → 사실 많은 컬럼이 들어가 있지는 않지만 이건 너무나도 간단하게 만든 Entity라 그렇고, 실제로는 더 많은 컬럼들이 있을 것이다.
- 물론 비즈니스 로직상 전체 데이터를 봐야한다면 인정하겠지만, 그렇지 않다면 데이터가 중간에 변경될 경우도 있을테고 메모리 사용량도 증가할테고 속도도 느려질 것이다.
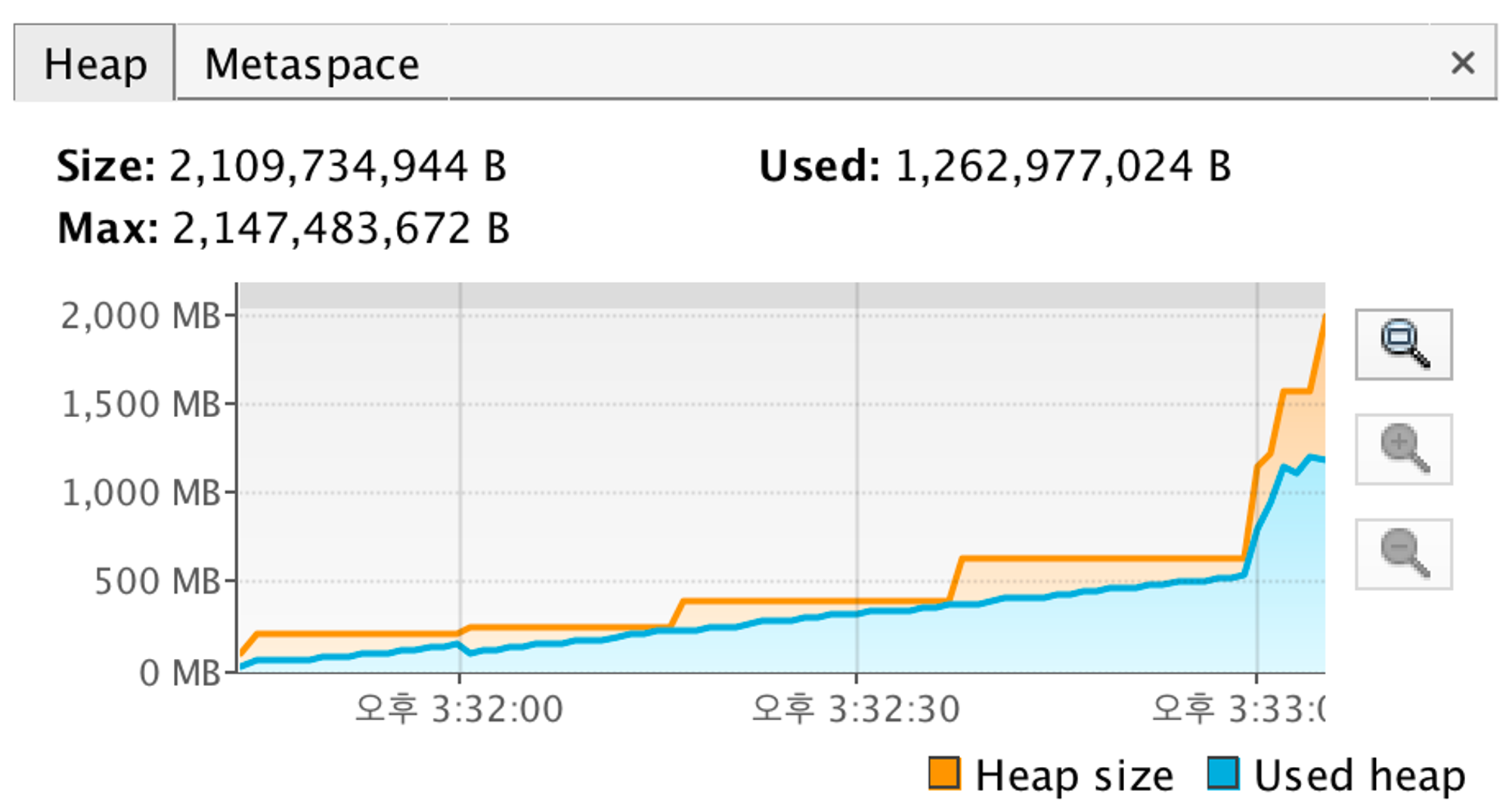
- 위 사진(JVM Heap)을 보면 알수 있듯이, 총 2,500,000 Row를 가져오는데 1.25GB 메모리를 사용한 것으로 파악이 된다. 그리고 시간도 30초가 걸린 것으로 파악이 된다.
- 이러한 문제가 있기에 전체 데이터를 가져오는 것이 아닌 딱 필요한 데이터를 가져오는 방식을 채택하게 되었다. 아래는 그 방법을 토대로 짠 코드이다.
- Hibernate를 확인해보면 다음과 같다.
테스트 진행하기 2 → Id로 Select 해오기
- QueryDsl로 Select 진행시 Field에 JPA Entity의 Id만 추가하기
@NoArgsConstructor public class ProductDetails2 { private Long productId; private String productName; private Double productPrice; private Long categoryId; // Category 객체의 ID만 포함 }@Test @DisplayName("Product 안에 category Id 만 가져오기") public void test2() { em.flush(); em.clear(); System.out.println("------------ 영속성 컨텍스트 비우기 -----------\n"); JPAQueryFactory queryFactory = new JPAQueryFactory(em); QProduct product = QProduct.product; QCategory category = QCategory.category; queryFactory .select(Projections.fields(ProductDetails2.class, product.id.as("productId"), product.name.as("productName"), product.price.as("productPrice"), product.category.id.as("categoryId"))) .from(product) .where(product.price.gt(0)) .orderBy(product.name.asc()) .fetch(); }- Hibernate를 확인해보면 다음과 같다.
Hibernate: select product0_.category_id as col_0_0_, product0_.name as col_1_0_, product0_.price as col_2_0_ from products product0_ where product0_.price>? order by product0_.name asc - Category 전체 데이터를 가져오는 것이 아니라 Id만 가져왔다.
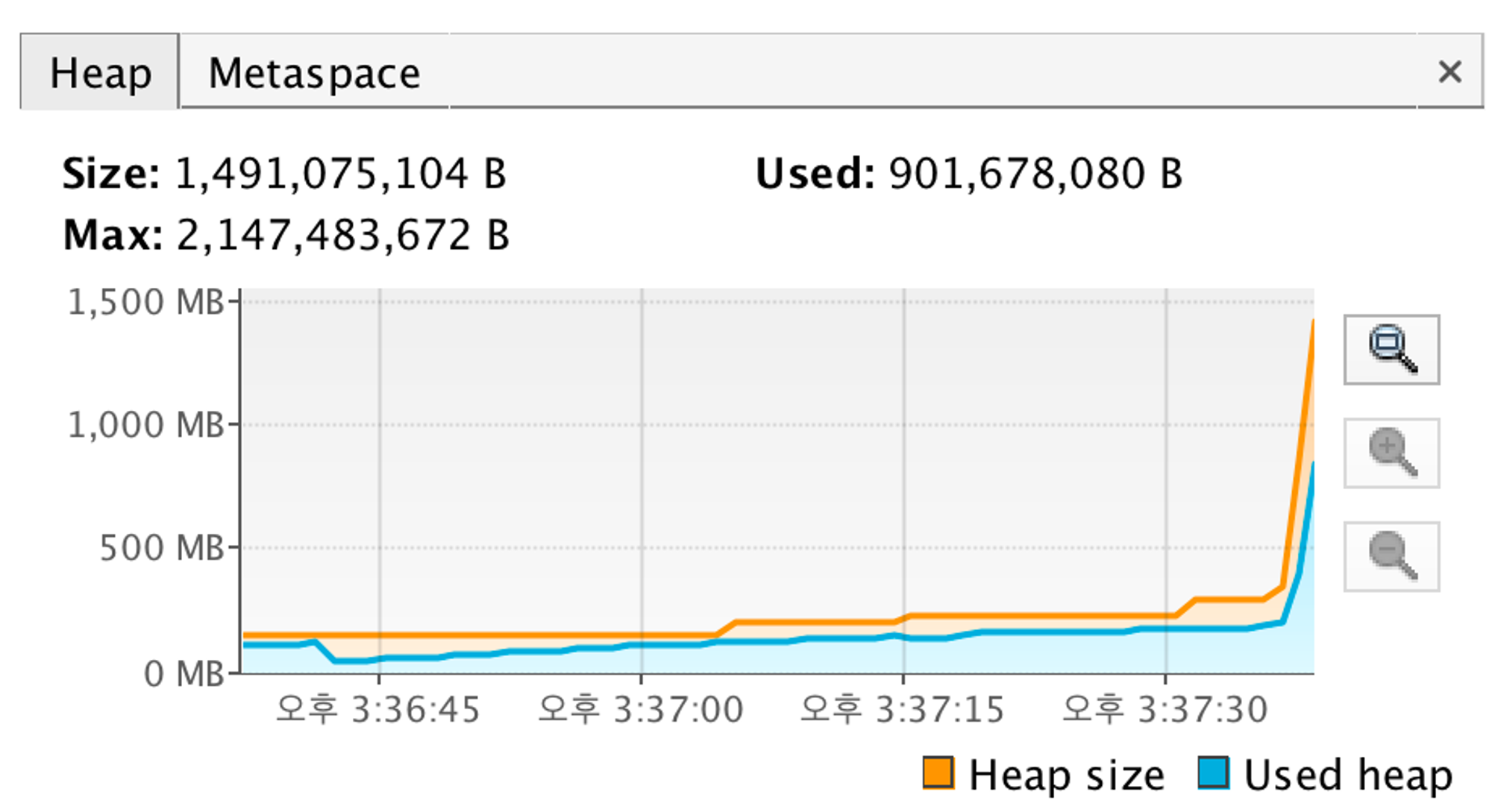
- 위 사진(JVM Heap)에서 볼수 있듯이 메모리 사용량이 0.9GB로 줄은 것으로 보인다. 원래 전체 컬럼을 가져오는 것 대비 1.39배의 효율을 보였다.
- 또한, 속도도 5초 정도 걸린 것으로 파악이 된다. 그 전 30초에 걸린 것이 비해 6배의 효율을 보였다.
- Hibernate를 확인해보면 다음과 같다.
테스트 진행하기 3 → Id로 Select 해오기 with Pagination
- QueryDsl로 Select 진행시 Field에 JPA Entity의 Id만 추가하고 pagination으로 가져온다.
@Test @DisplayName("Product 안에 category Id 만 가져오기 with Pagination") public void test5() { em.flush(); em.clear(); System.out.println("------------ 영속성 컨텍스트 비우기 -----------\n"); JPAQueryFactory queryFactory = new JPAQueryFactory(em); QProduct product = QProduct.product; int pageNumber = 1; int pageSize = 20; long offset = (pageNumber - 1) * pageSize; List<ProductDetails2> results = queryFactory .select(Projections.fields(ProductDetails2.class, product.id.as("productId"), product.name.as("productName"), product.price.as("productPrice"), product.category.id.as("categoryId"))) .from(product) .where(product.price.gt(0)) .orderBy(product.name.asc()) .offset(offset) .limit(pageSize) .fetch(); }pageNumber→ 페이지 번호이다.pageSize→ 페이지 당 항목 수이다.offset→ 페이지 시작 위치 계산이다.- 또한, queryFactory를 보면 offset, limit 메소드가 추가된 것을 볼수 있다.
- Hibernate를 확인해보면 다음과 같다.
Hibernate: select product0_.id as col_0_0_, product0_.name as col_1_0_, product0_.price as col_2_0_, product0_.category_id as col_3_0_ from products product0_ where product0_.price>? order by product0_.name asc limit ? - 원래 기존 Hibernate와 동일하지만 다른 한가지가 있다면, limit 부분이 추가가 되었다.
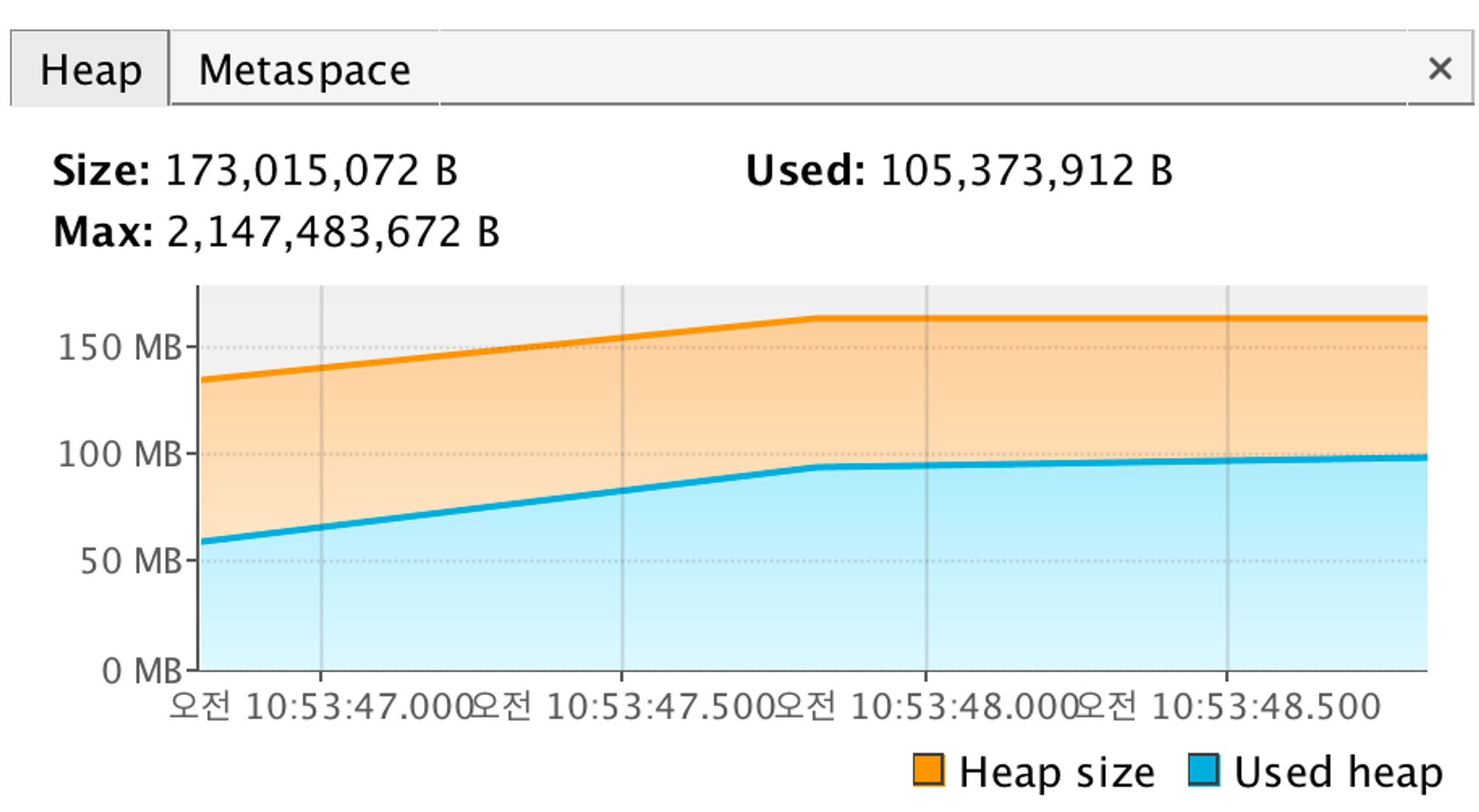
- 위 사진(JVM Heap)에서 볼수 있듯이 메모리 사용량이 0.1GB로 줄은 것으로 보인다.
- 또한, 전체 컬럼을 가져온 결과(1.25GB) → Id값 하나만 가져온 결과(0.9GB) → Pagination(0.1GB)으로 처리한 결과를 보니 점점 더 메모리 사용량이 줄어든 것으로 확인이 된다.
- 물론 전체 limit된 사이즈가 20으로 작은 사이즈이지만, 가져올 때 한번에 다 가져오는 경우는 극히 드물지 않을까라는 나만의 생각이 있다.
테스트 진행하기 4 → Id로 Select 해오기 with Streaming
- QueryDsl로 Select 진행시 Field에 JPA Entity의 Id만 추가하고 streaming으로 가져온다.
@Test @DisplayName("Product 안에 category Id 만 가져오기 with Streaming") public void test4() { em.flush(); em.clear(); System.out.println("------------ 영속성 컨텍스트 비우기 -----------\n"); JPAQueryFactory queryFactory = new JPAQueryFactory(em); QProduct product = QProduct.product; try (Stream<ProductDetails2> stream = queryFactory .select(Projections.fields(ProductDetails2.class, product.id.as("productId"), product.name.as("productName"), product.price.as("productPrice"), product.category.id.as("categoryId"))) .from(product) .where(product.price.gt(0)) .orderBy(product.name.asc()) .stream()) { stream.forEach(productDetails2 -> { // 각 Product 객체에 대한 처리 System.out.println(productDetails2.getProductName()); }); } }queryFactory.stream()메소드를 사용하여 데이터베이스 결과를Stream<ProductDetails2>로 변환한다.- 이 스트리밍 방식은 대량의 데이터를 처리할 때 유용하며, 전체 데이터를 메모리에 한 번에 로드하지 않아도 된다.
- 이는 메모리 사용량을 줄여주고, 대규모 데이터셋에 대한 처리 가능성을 높여준다.
- 스트림은 자원을 사용하므로 적절한 자원 관리가 필요합니다.
try-with-resources구문을 사용하여 스트림을 자동으로 닫아주므로, 메모리 누수를 방지할 수 있습니다.
- 스트림에서는
forEach메소드를 사용하여 각 요소에 대한 처리를 할 수 있습니다. 이 예제에서는 각ProductDetails2객체의productName을 출력합니다. - 스트리밍은 데이터를 순차적으로 처리하기 때문에 대규모 데이터셋에서는 성능 저하가 발생할 수 있습니다.
- 데이터 처리에 복잡한 연산이 포함되어 있다면, 성능에 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다.
- 그러나 스트리밍은 메모리 효율성이 높아 대용량 데이터 처리에 적합합니다.
- Hibernate를 확인해보면 다음과 같다.
Hibernate: select product0_.id as col_0_0_, product0_.name as col_1_0_, product0_.price as col_2_0_, product0_.category_id as col_3_0_ from products product0_ where product0_.price>? order by product0_.name asc - Hibernate는 기존에 사용했던 쿼리와 동일하다.
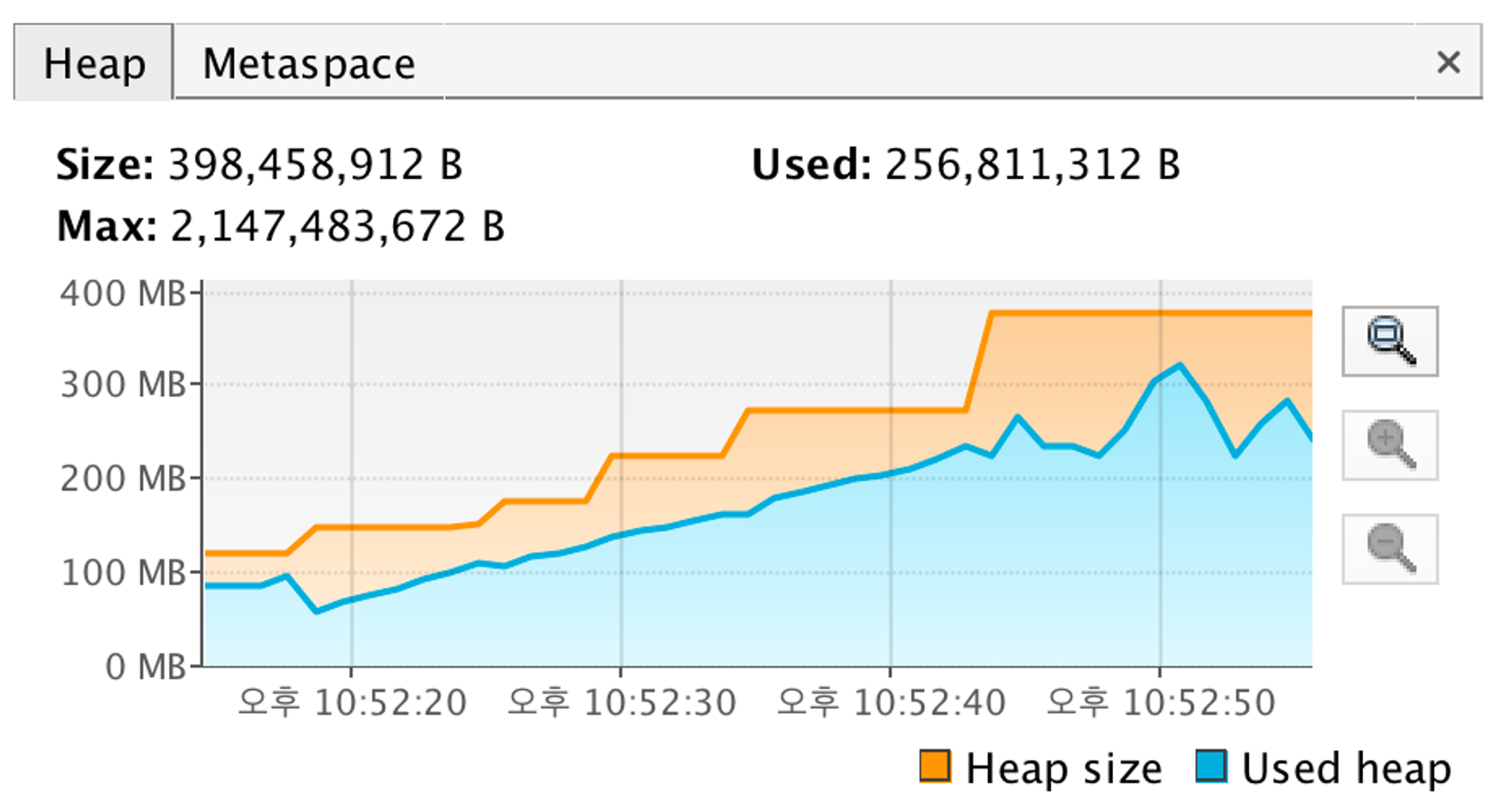
- 자자 이제 JVM Heap을 확인해보자. 위 사진으로 볼수 있듯이 메모리 사용량이 0.25GB로 줄은 것으로 보인다.
- 우리는 전체 컬럼을 가져온 결과(1.25GB) → Id값 하나만 가져온 결과(0.9GB) → streaming(0.25GB)으로 처리한 결과를 보니 점점 더 메모리 사용량이 줄어든 것으로 확인이 된다.
- 나머지 성능 최적화는 다음 블로그에서 포스팅하겠다!
- 아직 Pagination이 좋은 이유만 설명했는데, 데이터가 수백만건이 되면 뒤로 갈수록 문제가 생긴다.
- 그런 부분에 대해서 챕터 2에서 다뤄볼 예정이다!
