드림코딩 엘리 Array.api 문제
1번(join)
// Q1. make a string out of an array
{
const fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange'];
}
내코딩
join이라는 메소드 아예 몰랐음
엘리코딩
{
const fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange'];
const result = fruits.join();
console.log(result);
}Join : A string used to separate one element of an array from the next in the resulting String. If omitted, the array elements are separated with a comma.
2번(split)
// Q2. make an array out of a string
{
const fruits = '🍎, 🥝, 🍌, 🍒';
}
내코딩
split을 생각했지만 seperator를 생각하지 못해 ["🍎, 🥝, 🍌, 🍒"] 전체가 묶어서 나옴
엘리코딩
{
const fruits = '🍎, 🥝, 🍌, 🍒';
const result = fruits.split(',');
console.log(result);
}3번(reverse)
// Q3. make this array look like this: [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
{
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
}
내코딩
{const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const NewArray=[];
for(i=array.length-1; i>=0; i--) {
NewArray.push(array[i]);
}
console.log(NewArray);
}reverse 라는 메소드 몰라 for문으로 작성 -> reverse로 효율적으로 작성 가능
엘리코딩
{
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const result = array.reverse();
console.log(result);
}
4번 (slice)
// Q4. make new array without the first two elements
{
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
}
내코딩
{
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const newArray = array.slice(2);
console.log(newArray);
}여기서 포인트는 새로운 배열을 만들어야 되므로 splice를 쓰지 못함
class Student {
constructor(name, age, enrolled, score) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.enrolled = enrolled;
this.score = score;
}
}
const students = [
new Student('A', 29, true, 45),
new Student('B', 28, false, 80),
new Student('C', 30, true, 90),
new Student('D', 40, false, 66),
new Student('E', 18, true, 88),
];
5번(find)
// Q5. find a student with the score 90
{
}
엘리코딩
const result = students.find(function(student,index){
console.log(student,index);
}) //
Student {name: "A", age: 29, enrolled: true, score: 45} 0
Student {name: "B", age: 28, enrolled: false, score: 80} 1
Student {name: "C", age: 30, enrolled: true, score: 90} 2
Student {name: "D", age: 40, enrolled: false, score: 66} 3
Student {name: "E", age: 18, enrolled: true, score: 88} 4
{
const result = students.find(function(student){
return student.score === 90;
})
console.log(result);
}arrow function
{
const result = students.find((student) => student.score === 90);
console.log(result);
}find<S extends T>(predicate: (this: void, value: T, index: number, obj: T[]) => value is S, thisArg?: any): S | undefined; * Returns the value of the first element in the array where predicate is true, and undefined콜백함수에서 찾은 것중 첫번 째로 트루인 것을 리턴해줌
6번 (filter)
// Q6. make an array of enrolled students
{
{
const result = students.filter((student) => student.enrolled)
console.log(result);
}
}7번 (map)
// Q7. make an array containing only the students' scores
// result should be: [45, 80, 90, 66, 88]
{
{
const result = students.map((studnet)=>studnet.score);
console.log(result);
}
}8번 (some)
// Q8. check if there is a student with the score lower than 50
내코딩
{
const result = students.filter((student) => student.score < 50);
console.log(result);
}위와 같이 filter를 쓰면 위 조건에 해당되는 array을 단순히 가져다 줌
엘리코딩
some(callbackfn: (value: T, index: number, array: T[]) => unknown, thisArg?: any): boolean;
- Determines whether the specified callback function returns true for any element of an array.
{
const result = students.some((student) => student.score < 50);
console.log(result);
}
ref)
every(callbackfn: (value: T, index: number, array: T[]) => unknown, thisArg?: any): boolean;
9번 (reduce)
// Q9. compute students' average score
{
}
reduce는 우리가 원하는 시작점부터 모든 배열을 돌면서 어떤 값을 누적할 때 쓰는 것
reduceRight은 꺼꾸로 호출됨
{
const result = students.reduce((prev,curr) => {
console.log('----------');
console.log(prev);
console.log(curr);
});
}
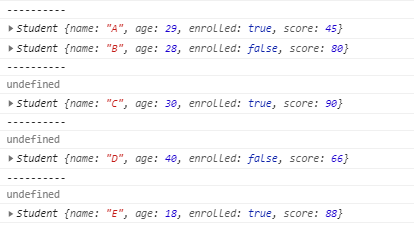
curr은 배열 하나하나 순차적으로 전달되지만 prev값은 return한 값이 그 다음 호출 될 떄 prev 값으로 들어간다
{
const result = students.reduce((prev,curr) => {
console.log('----------');
console.log(prev);
console.log(curr);
return prev + curr.score;
},0);
console.log(result/students.length);
}arrow function
{
const result = students.reduce((prev,curr) => prev + curr.score,0);
console.log(result/students.length);
}10번 (map, join)
// Q10. make a string containing all the scores
// result should be: '45, 80, 90, 66, 88'
{
{
const result = students.map((studnet)=>studnet.score).join();
console.log(result);
}}
11번 (sort)
// Bonus! do Q10 sorted in ascending order
// result should be: '45, 66, 80, 88, 90'
{
{
const result = students
.map( (student) => student.score)
.sort( (a, b) => a-b)
.join();
console.log(result);
}
}
ref
.sort( (a, b) => b-a) 인 경우 큰 순으로 앞으로 정렬
