Introduction
-
computer vision task에서 transformer의 attention mechanism과 MLP-mixer model이 좋은 performance를 보여줌
-
network의 모델들은 input image를 다른 방법으로 처리함
-CNN은 window를 sliding하여 처리하며, ViT or MLP는 sequential patches를 처리 -
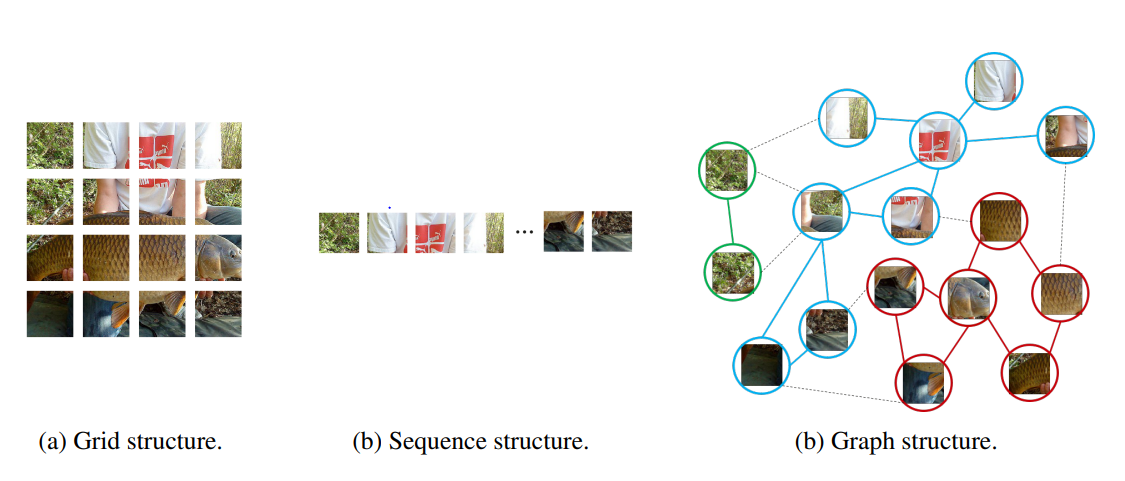
vision GNN 저자들은 regular grid or sequence representation과 달리 유연성있게 image를 process 할 수 있는 graph structure 방법론인 ViG model을 제시
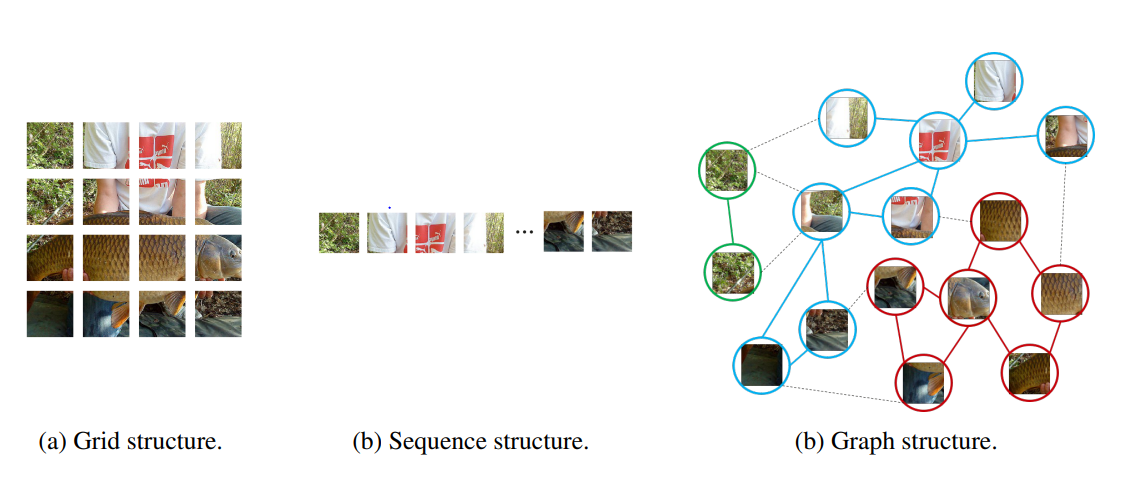
-ViG model은 Grapher and FFN modules로 구성
- Grapher module : node의 information processing을 위한 graph convolution 연산 수행
- FFN : over-smoothing을 완화하고 node의 feature transform과 diversity를 위해 사용
ViG
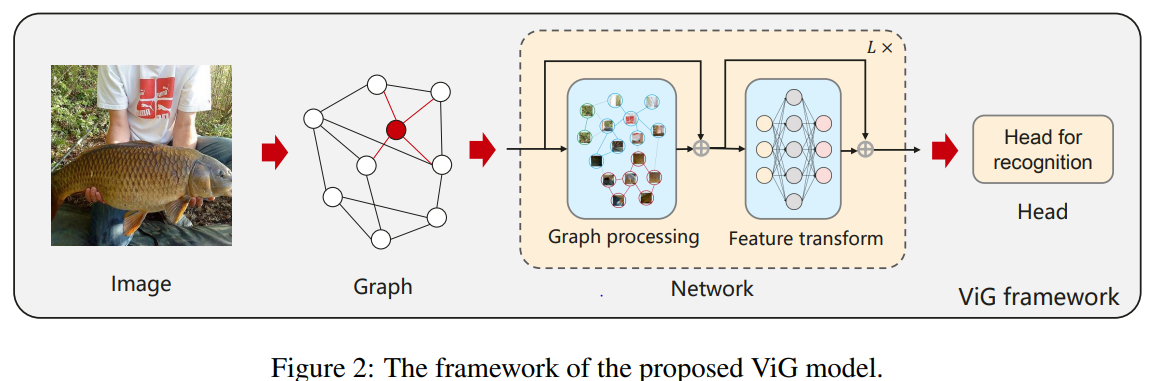
1. ViG Block
Graph Structure of Image
-(1) H×W×3 Image를 N-patches로 나눠 feature vector로 transform
- featrue vector: ∈
- X = [, ,···, ]
-(2) feature vector를 node로 표현
- = {, ,···, }
-(3) 각각의 node 에 K개의 이웃 node를 찾아 edge를 추가한다.
- () : K nearest neighbors
- 만약 ∈ ()이라면 에서 에 를 추가
(1), (2), (3) 과정을 진행하여 = 를 얻고 이후 GNN을 이용하여 representation을 추출
The advantages of graph representation of the image
- complex object를 모델링하는데 grid, sequence보다 유연하다.
- object는 parts의 composition으로 볼 수 있으며 graph structure는 parts간의 연결을 구성할 수 있다.
(사람은 머리, 팔, 다리,...로 나눌 수 있음)
Graph-level processing
-image feature로 만든 graph를 graph convolution layer에 통과시켜 target node의 이웃 노드들로부터 imformation을 aggregate
[graph convolution operation]
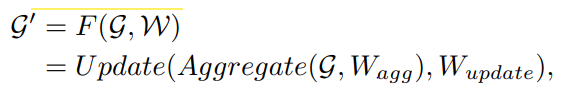
and are the learnable weights of the aggregation and update operations
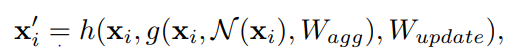
aggregation operation: 이웃 노드들로부터 features 정보를 받아 집계
update operation: 집계된 정보를 기존 노드와 결합하여 새로운 노드 representation 생성
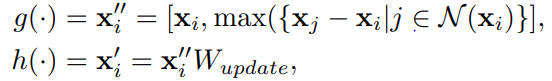
max-relative aggregation 사용
즉, 해당 노드와 주변 노드의 표현 간의 차이중 최댓값을 찾아 이웃 노드들의 표현과 현재 노드의 표현 간의 차이를 최대화함으로써 그래프 내에서 xi의 중요성을 강조하고, 주변 노드들의 정보를 고려하여 xj의 표현을 업데이트합니다.
[multi-head update operation]
- aggregated feature 를 h-heads로 split
- 각각의 head는 다른 update weight를 갖고 동시에 update되며 concat하여 final values를 얻는다.
- 즉, multi-head update operation은 다양한 특성을 학습할 수 있어 성능을 향상시킨다.
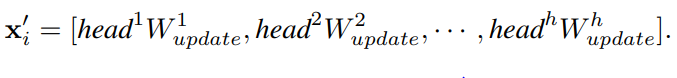
ViG block
저자들은 GNN의 over-smoothing 문제를 완화시키기 위한 Grapher module 제시
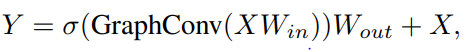
∈
, : weights of fully-connected layers
: non-linear activation function(ReLU, GeLU)
또한 feature transformation capacity와 over-smoothing 문제를 위해 FFN module 제시
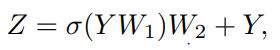
∈
, : weights of fully-connected layers
2. Network Architecture
computer vision에서 architecture는 흔히 isotropic architecture와 pyramid architecture를 사용
저자들은 두 개의 architecture를 각각 ViG에 적용
- isotropic architecture
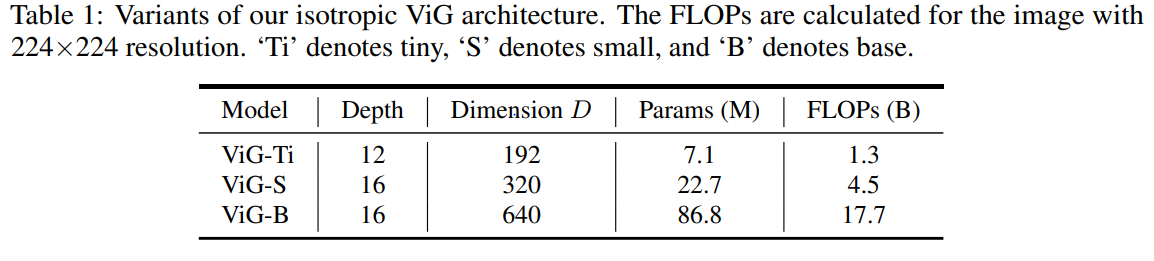
N(patch size) : 196, K(num of neighbor ) : 9~18 h(num of heads) : 4
- pyramid architecture
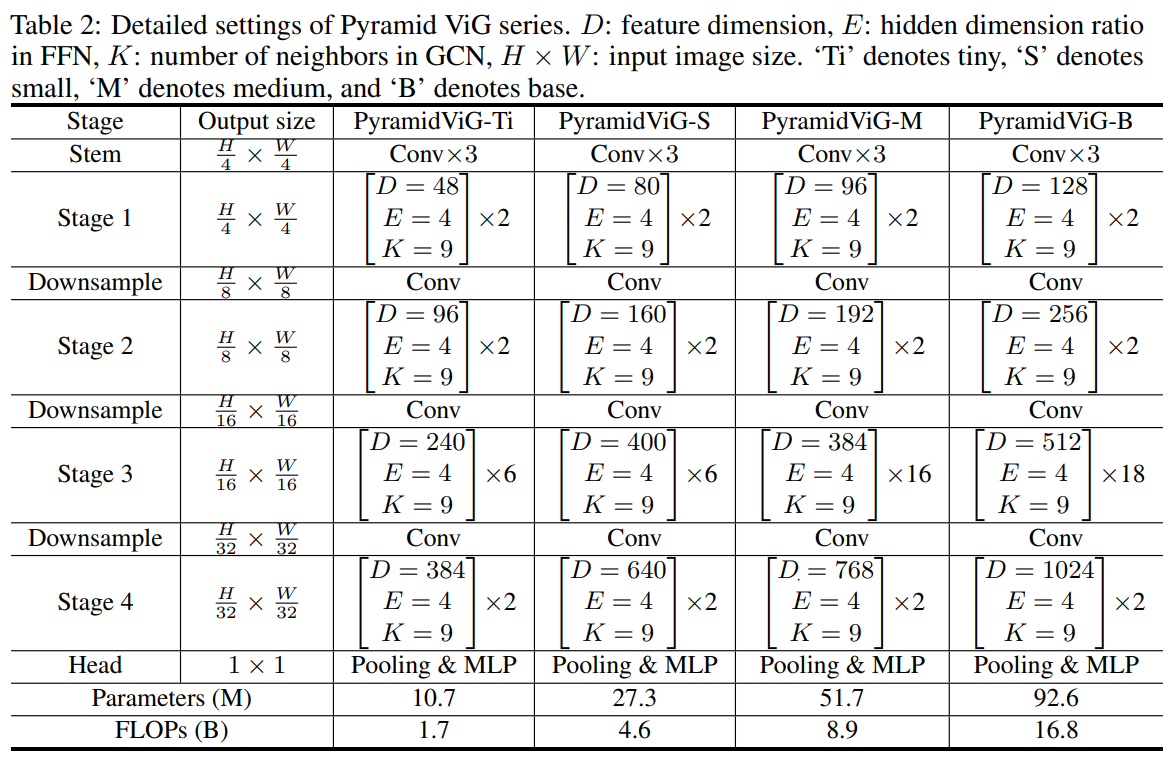
Experiments
Datasets
- image classification task: ImageNet
- object detection task: COCO 2017
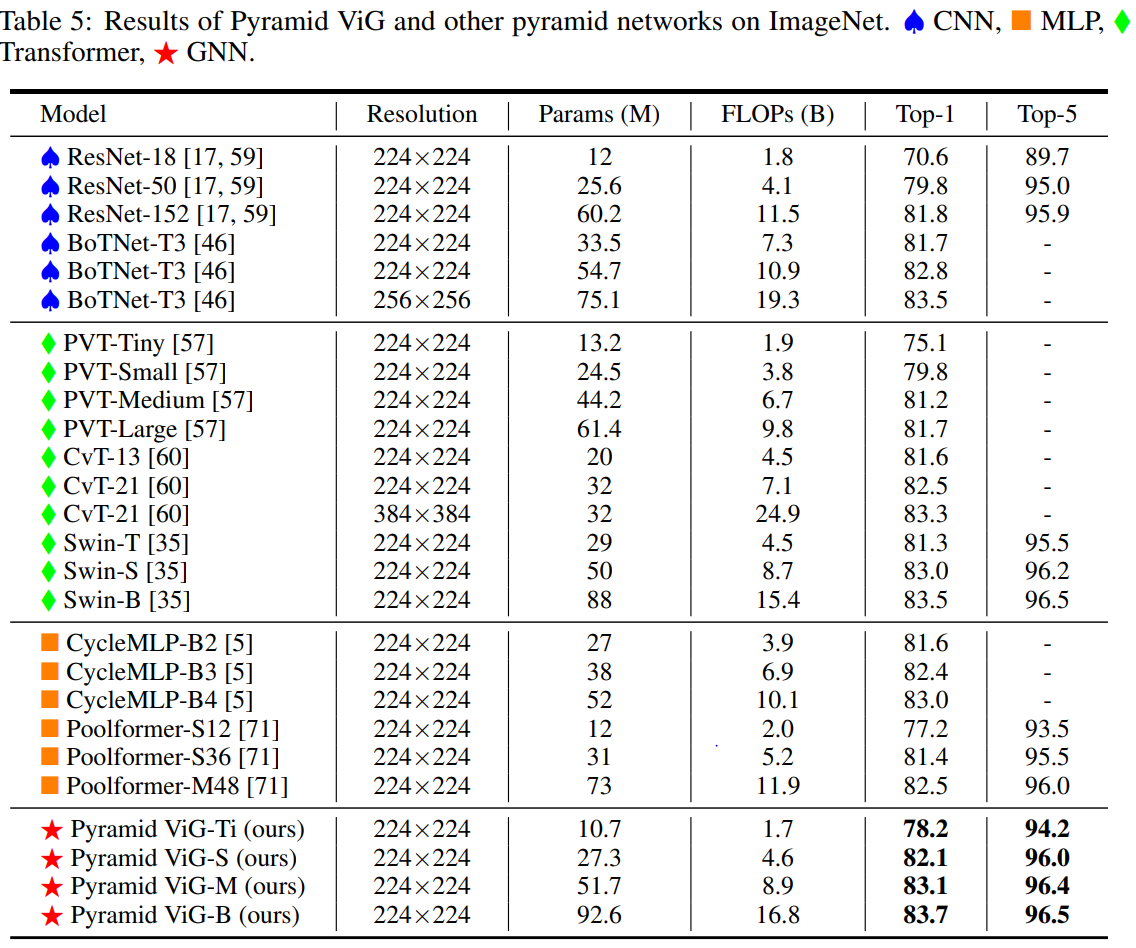
image classification
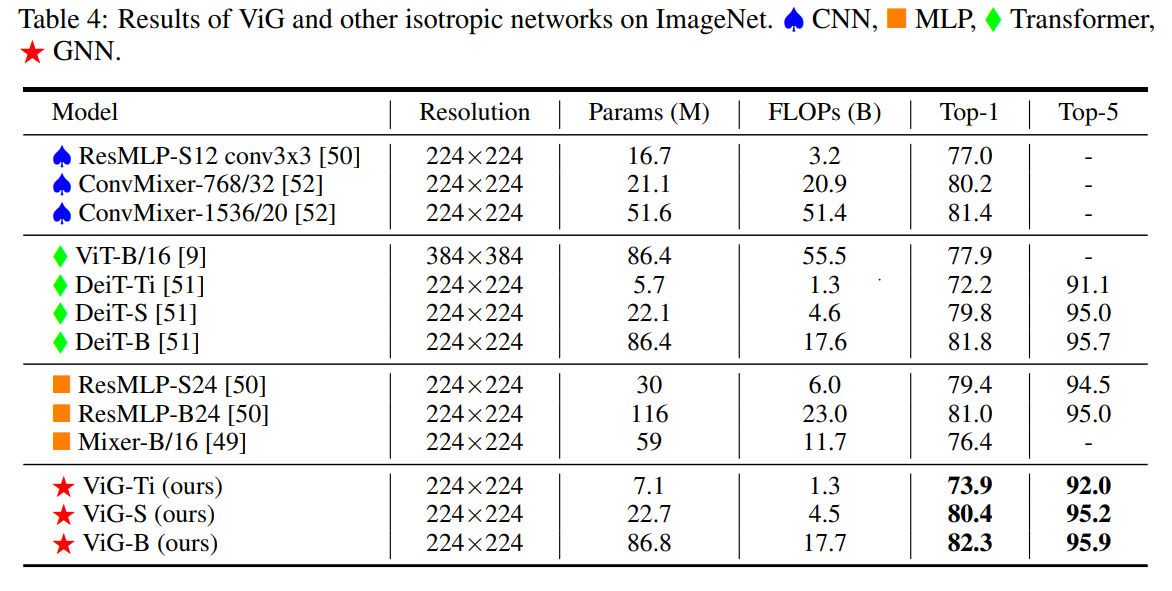
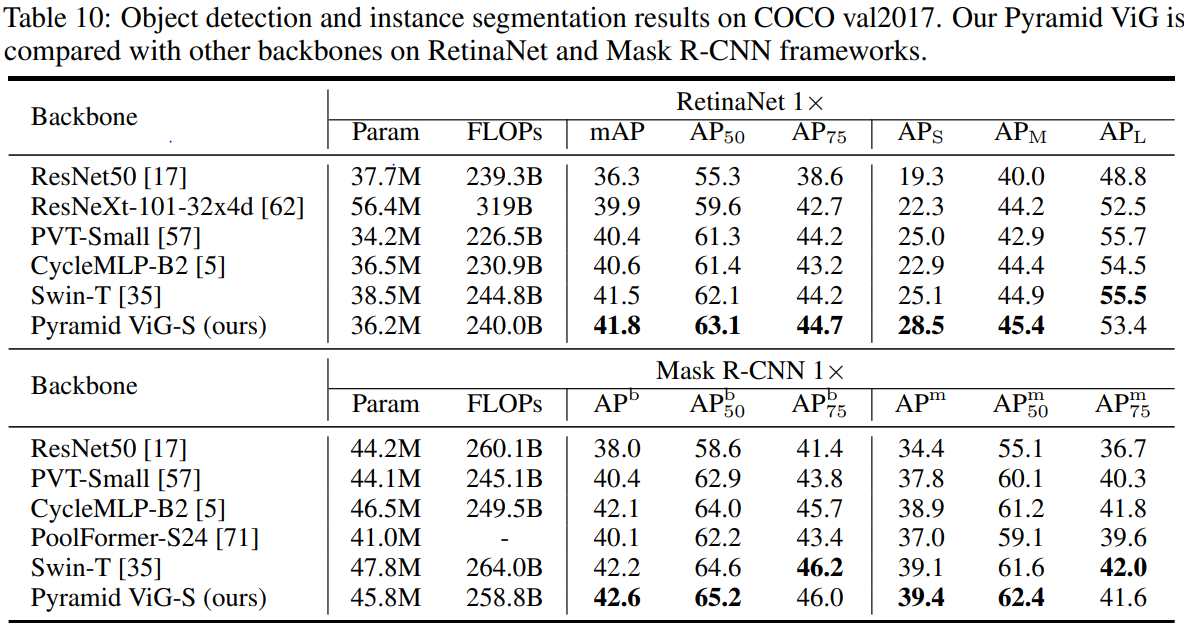
object detection
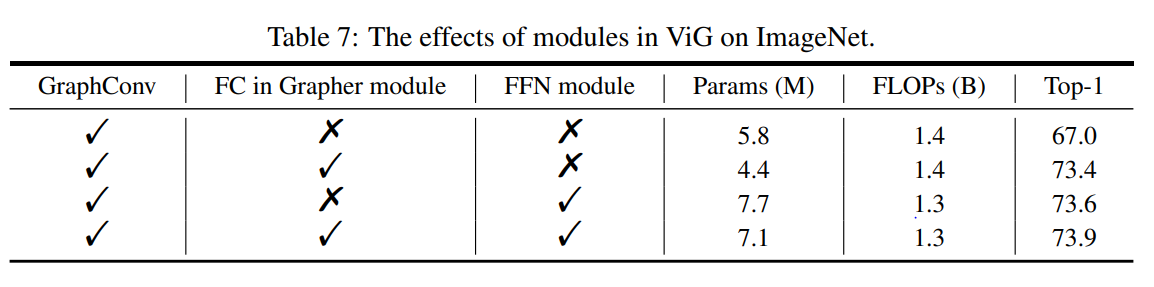
effects of module in ViG
Visualization
