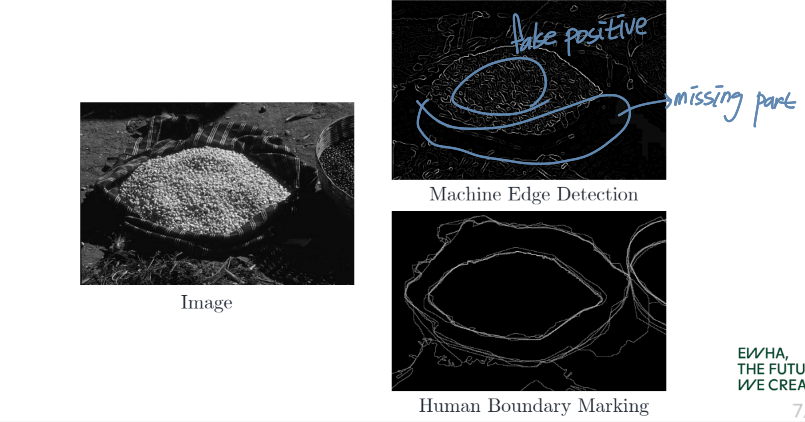
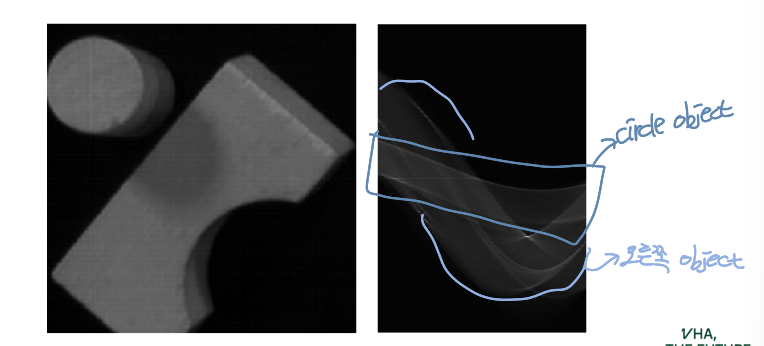
Boundaries of Objects
Boundaries of Objects
Human annotated boundaries

원래 안 보이는 부분까지 boundary를 그리는데 여기서는 그리지 않음
Edge detection
boundary를 잘 찾지 못함

- 코끼리 간의 색이 비슷하여 두 개체 각각의 boundary를 detect하지 못함
- 오른쪽 코끼리 발 옆은 doundary로 detect되면 안 되는데 됨
FP
Multi-scale edge detection
를 많이 사용하고 합쳐서 FP를 줄임

그러나 아직 부족한 부분 많음
Another example
Hough Transform for Line Detection
Hough Transform
structure를 탐지하는 것에 elegant method
- edge는 connected될 필요X
- complete strucre need not be visible
- Key Idea: Edges VOTE for the possible models
투표를 많이 받은 곳이 물체의 위치로 선정
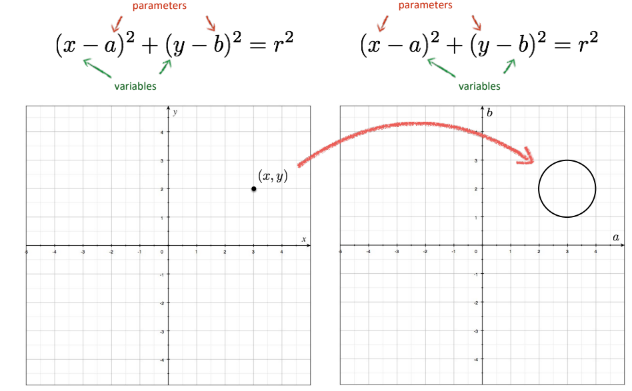
Image and Parameter Space
물체가 line인 경우,
물체에 대한 식을 로 표현할 수 있음
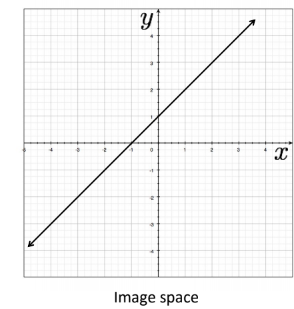
- variables :
- parameters :
이거를 parameter space로 바꾸면
식은 가 되고, line은 point가 됨
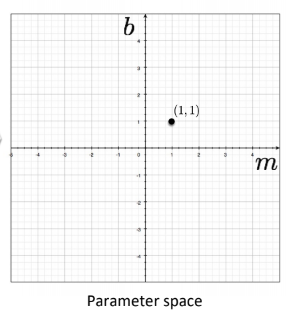
- variables :
- parameters :
Image space에서의 point는 Parameter space에서의 line이 됨
특정 한 점을 지나가는 1차함수는 다양하기 때문에
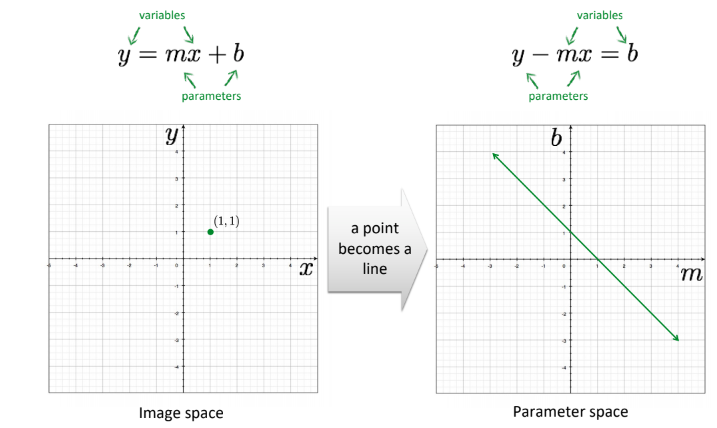
image space에서 두 점이 주어진 경우
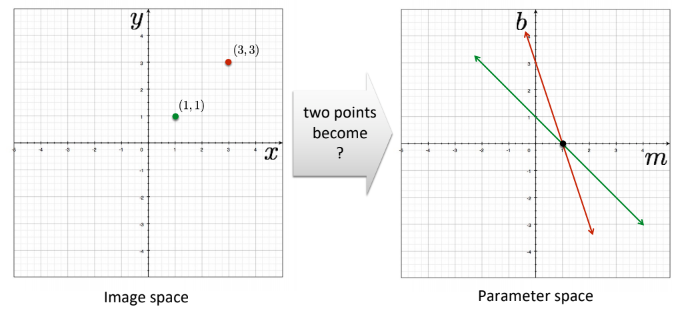
parameter space에서 crossing point가 적절 parameter 값
여러 개의 점이 주어진 경우 적절한 파라미터는 voting을 통해 선택할 수 있음
가장 많은 그래프가 교차하는 지점
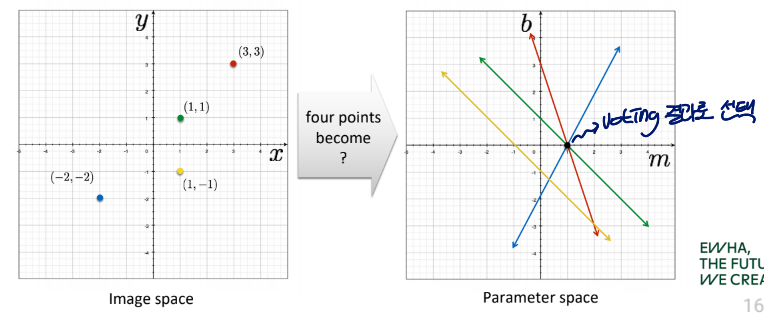
Line Detection by Hough Transform
Algorithm
- quantize parameter space (m,c)
크기에 trade-off 존재
quantize가 클수록 노이즈에 강함 - create accumulator array A(m,c)
- A(m,c)=0으로 설정
- 각 이미지의 edge 에 따라
그냥 line이 지나가는 칸들에 1씩 더하면 된다는 뜻 - A(m,c)의 local maxima 찾기
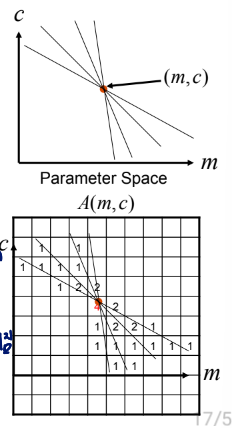
bin을 크게 설정하면 격자가 더 넓어짐
Better Parameterization
Note:
- accumulator가 너무 큼
- 메모리와 계산량이 많이 요구됨
Improvement
finite accumulator size 설정
-
Line equation:
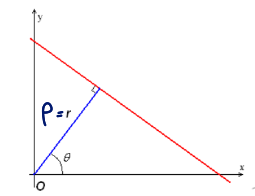
- : line과 origin의 수직 거리
: 이미지의 대각선 길이
- : line과 origin의 수직 거리
Image and Parameter Space
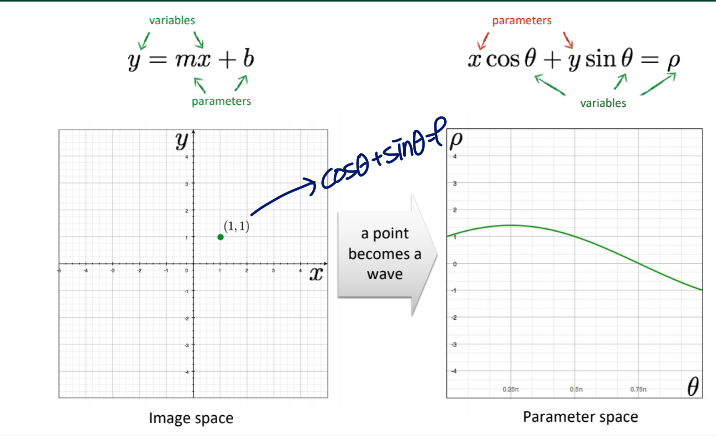
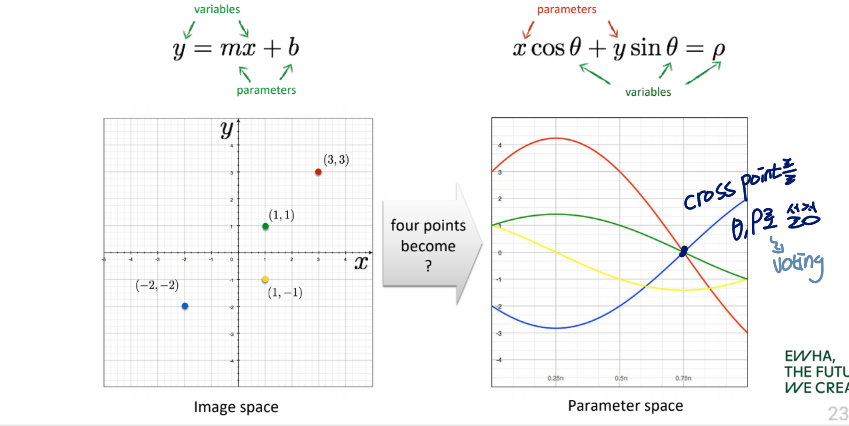
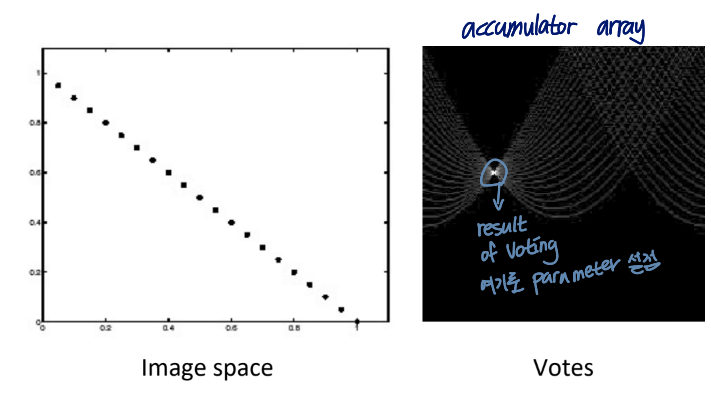
Image Space and Vote
Basic Shapes
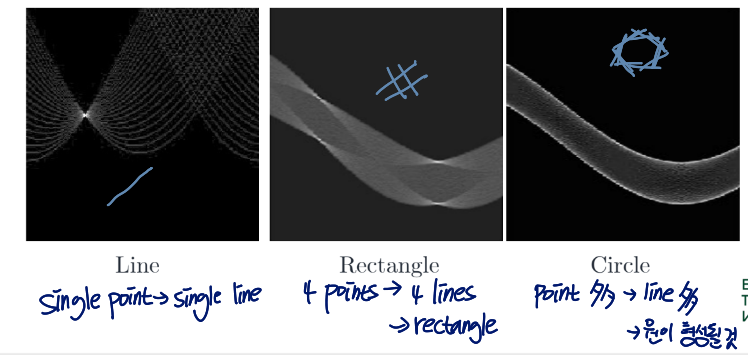
뒤의 두 경우는 이미지에 선이 많은 경우
간단히 생각하면 local maxima의 개수가 line의 개수를 나타내고, 이에 따라 모양이 형성될 것
Real-World Example
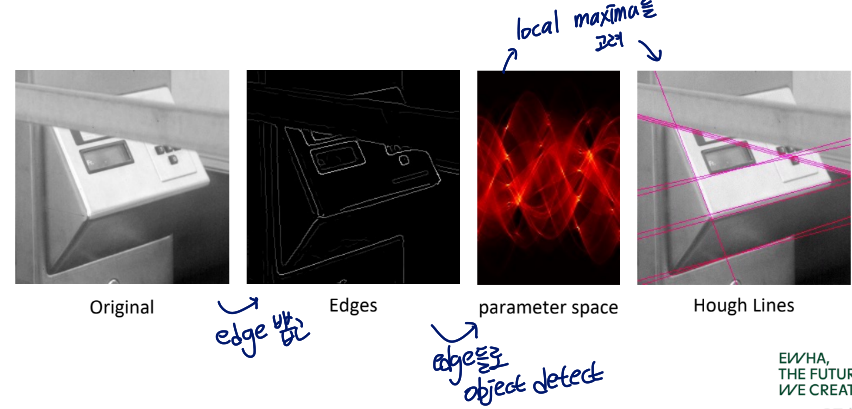
- original image에서 edge detection
- detect한 edge point들을 parameter space로 표현
- maxima들 뽑아서 그 값들을 사용해 boundary 형성
Mechanics of the Hough Transform
How many lines?
- count the peaks in the Hough array
- 인접한 peak를 single peak로 취급
Which points belong to each line?
- line에 가까운 점 찾기
Quantization error
- cells가 얼마나 커야 되는지
크기에 따라 trade-off가 존재- Too big : 다른 line을 합치게 될 수 있음
- Too small : line을 찾기 어려워짐
large vote를 받은 bucket이 없어서 voting이 어려움
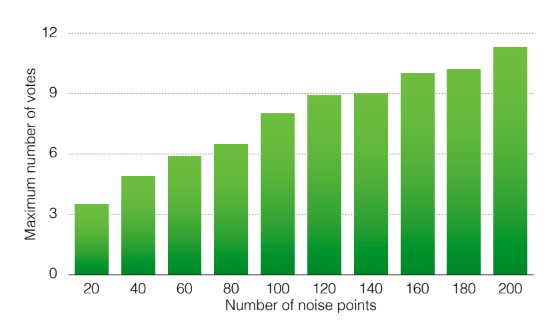
Difficulties of noise
measurements는 noisy함
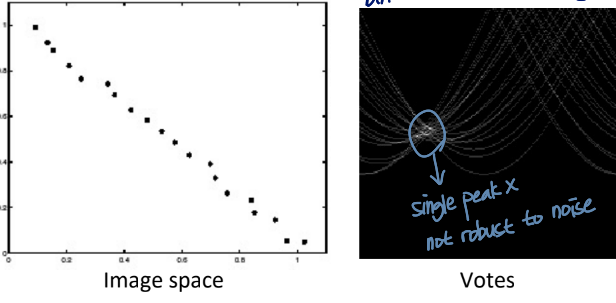
noise로 인해 single peak를 찾기 어려워질 수 있음
not robust to noise
bin의 크기를 키움으로써 해결할 수 있긴 한데,.. 노이즈가 너무 크면 이것도 잘 안 될 수 있음
noise가 증가할수록 fewer votes land in a single bin
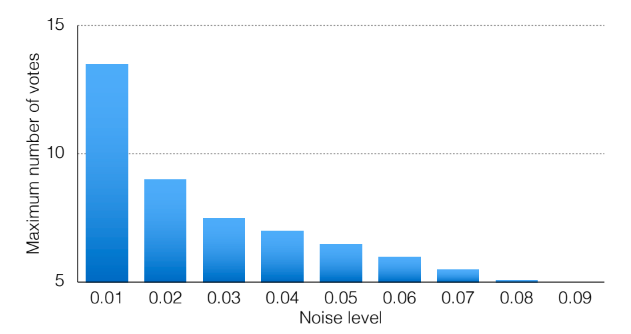
noise가 증가할수록 false peaks가 증가함
Hough Transform for Circle Detection
Finding Circles by Hough Transform
원형 물체에 대해 식을 표현하면
- For Image space
- variables :
- parameters :
- For Parameter space
- variables :
- parameters :
Let's assume radius known
- For Image space
- variables :
- parameters :
- For Parameter space
- variables :
- parameters :
Image and Parameter Space
이 경우, image space에서의 point는 parameter space에서 원이 됨
점이 여러 개 주어진 경우
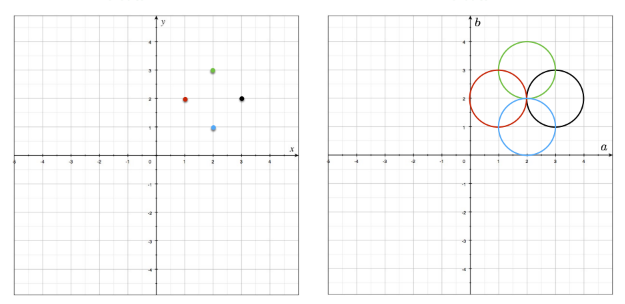
그리고 가장 많은 원이 교차하는 점이 파라미터로 채택됨
Finding Circles by Hough Transform
What if radius is unknown?
- 역원뿔 모양을 형성하게 됨
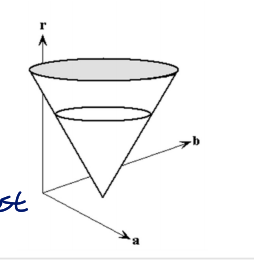
- 3차원 배열 사용 : A(A,b,r)
- parameter 수에 따라 size of accumulator와 computation이 exponential하게 증가하게 됨
→ need high computational cost
Using Gradient Information
Gradient information은 많은 양의 계산을 save할 수 있음
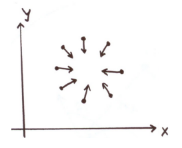
- Edge Location:
- Edge Direction:
radius에 대해 이미 알고 있다고 가정하면,
→ need to increment only one point in accumulator
compact해짐!
Finding Coins
동전 두 개의 size가 각각 주어짐
- 27 pixels
- 34.5 pixels
→ two different Hough transform with separate accumulators 하면 됨
- 큰 동전 용
- 작은 동전 용
Edge를 뽑아내고
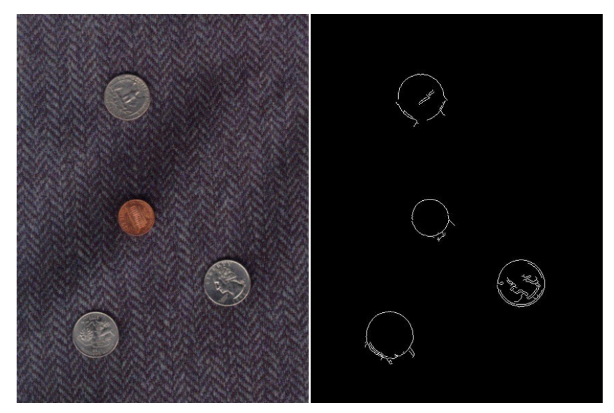

Boundary detect
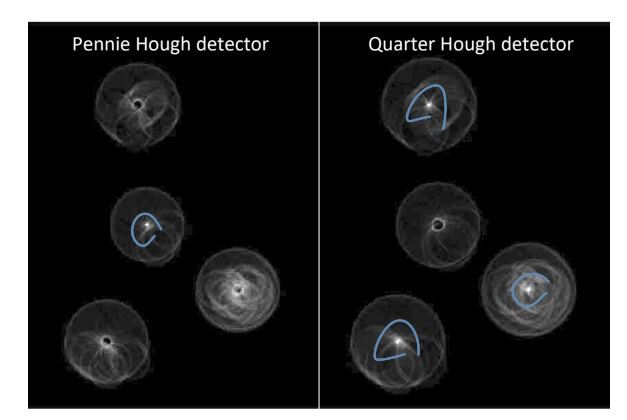
pennie 하나, quarter 3개 탐지
Generalized Hough Transform
Model의 shape가 방정식을 통해 표현이 안 되는 경우가 있음
silhouette only, random shape
Goal
Find the object center
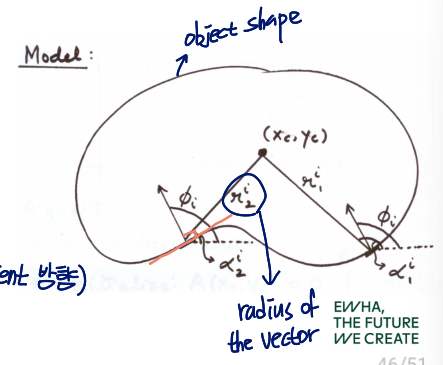
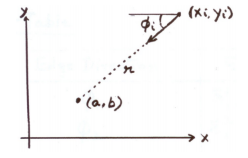
- referent point 선정
- for each point obtain
- : a vector form from boundary point to reference
- : gradient 방향(orientation)
즉,
같은 direction을 가지는 vector들끼리 모은 table 생성
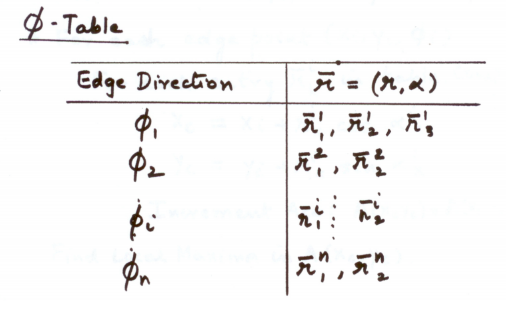
Algorithm
given edges를 통해 object center 를 찾고자 함
1. Accumulator Array A(x_c, y_c) 생성
2. Accumulator Array 초기화
3. For each edge point
- For each entry in table, compute:
- Increment Accumulator:
- 에서 local maxima 찾기
Scale과 각도도 고려해서 4차원 space에서 voting할 수도 있음
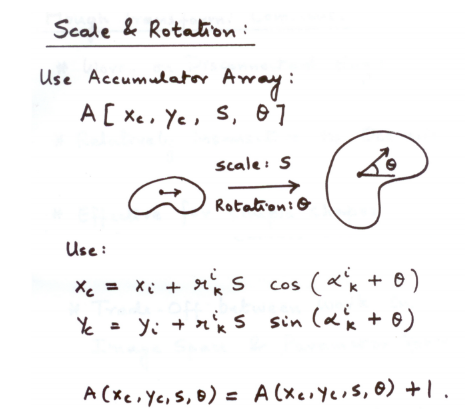
Hough Transform: Comments
사실 Hough Transform은 오래된 method라 요즘 많이 사용하지는 않음
Pros
- deals with occlusion well
- detects multiple instances
- robust to noise
Cons
- bad computational complexity
object가 complex한 경우 - difficult to set parameters