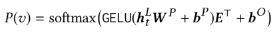📄DialogueRNN: An Attentive RNN for Emotion Detection in Conversations
written by Navonil Majumder, Soujanya Poria, Devamanyu Hazarika, Rada Mihalcea, Alexander Gelbukh, Erik Cambria
Introduction
research community에서 대화에서의 emotion detection은 갈수록 주목 받고 있는 분야임
최근 시스템에서 state-of-art인 모델은 different parties in a conversation을 의미있게 구별하지 못함
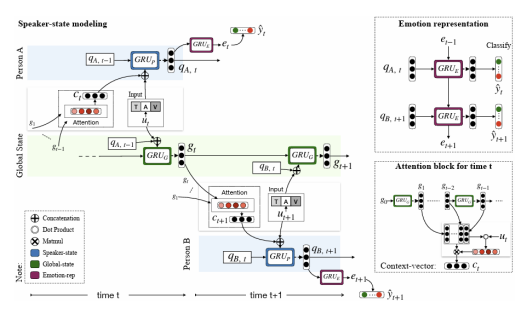
본 논문에서 제안하는 DialogueRNN은 3개의 GRU(Gated Recurrent Unit)를 사용함으로써 이러한 한계를 극복함
GRU
LSTM의 구조는 단순화시키면서 성능은 유지시킨 모델
순차 데이터를 처리하는 데 사용
Reset gate와 update gate로 구성
- Reset gate: 현재 상태에서 얼마나 이전 상태의 정보를 유지할지 결정
- Update gate: 이전 상태의 정보와 새로운 정보 사이의 균형 결정
DialogueRNN
CMN(Conversational Memory Networks)에서 사용된 특징 추출 과정과 동일한 방법 사용하여 특징 추출
- 텍스트 특징 추출
CMN 사용, 각 발화 n-gram 특징으로 변환하여 추출 - 청각적 특징 추출
3D-CNN 사용 - 시각적 특징 추출
openSMILE 사용
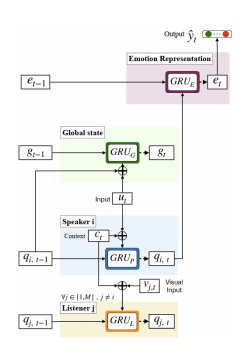
assume the emotion of an utterance in a conversation depends on three major factors
- the speaker
- the context given by the preceding utterances
- the emotion behind the preceding utterances
각 party는 party state를 사용하며 modeled
각 state를 업데이트하고 representation하기 위하여 GRU cells 사용
three GRUs
- Global GRU
대화의 전반적 문맥 파악 후 업데이트 - Party GRU
대화의 개별 화자 상태 모델링 후 업데이트 - Speaker GRU
발화의 감정 표현 디코딩 후 감정 분류에 사용
DialogueRNN Variants
-
DialogueRNN + Listener State Update
발화자의 상태 qs(ut) 기반 청취자 상태 업데이트청취자 상태 업데이트는 DialogueRNN보다 성능이 좋지 않지만 happy label에서는 우수한 성능
-
Bidirectional DialogueRNN
양방향 학습을 통해 대화의 과거, 미래 정보가 포함되어 감정 분류를 위해 더 좋은 문맥 제공미래 발화에서 문맥 파악통해 DialogueRNN보다 성능 향상
-
DialogueRNN + attention
각 et에 대해 attention 적용하여 과거와 미래의 발화에 관련성 제공 -
Bidirectional DialogueRNN + Emotional attention
대화의 모든 감정 표현 통해 대화의 다른 발화에서 문맥 파악다른 모든 방법보다 우수한 성능 보임
Conclusion
CMN과 달리 발화자의 특성을 고려하여 세밀한 문맥파악을 할 수 있었음
DialogueRNN outpuerforms the current state-of-the-art on two distinct datasets in both textual and multimodal settings